Abstract
C20H14F4I2N4O2, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 5.0726(1) Å, b = 10.9432(2) Å, c = 19.8090(3) Å, α = 104.475(2)°, β = 90.427(2)°, γ = 92.908(2)°, V = 1063.10(3) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0329, wRref(F2) = 0.0907, T = 100 K.
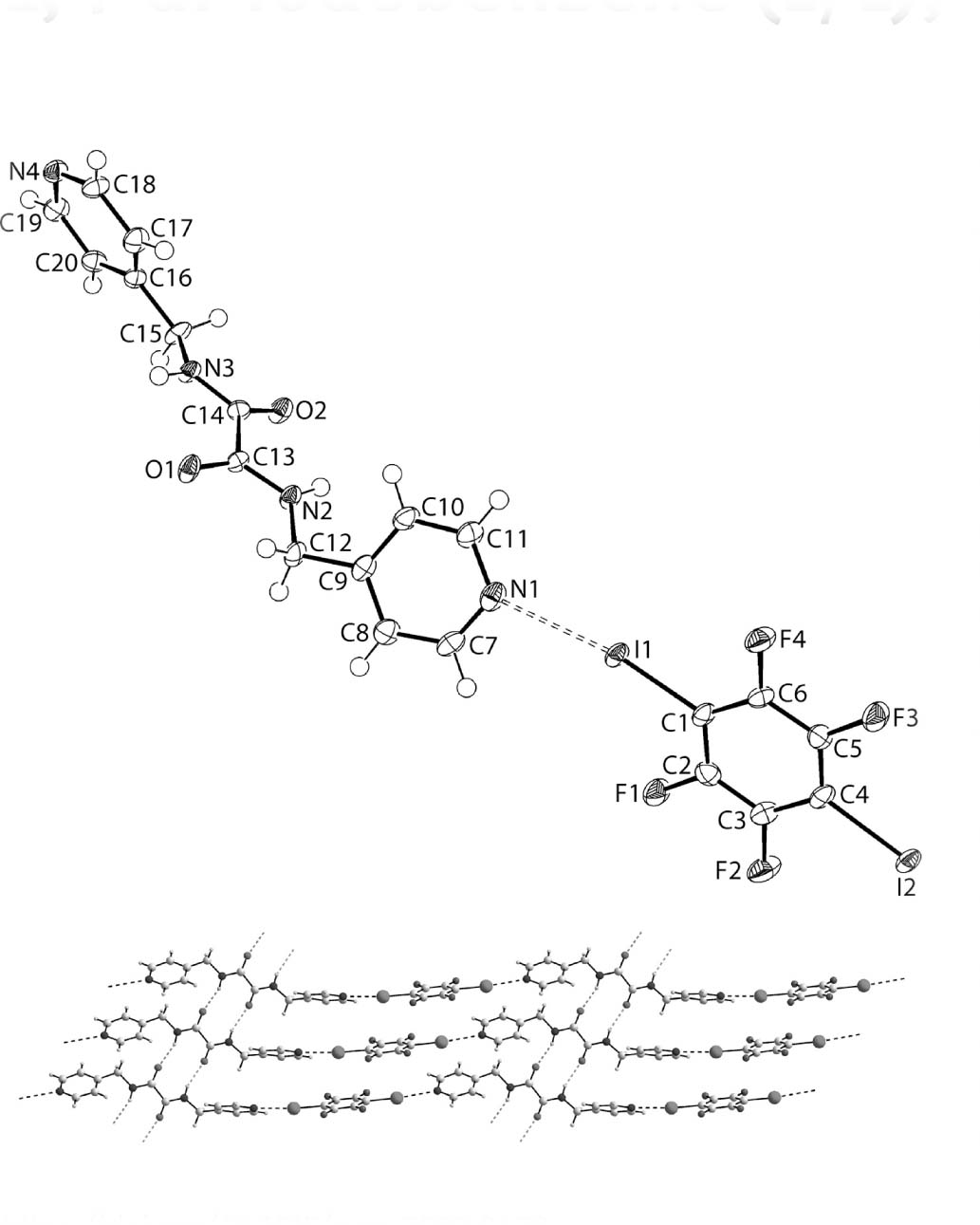
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.18 × 0.09 × 0.07 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 23.8 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 76.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 26223, 4449, 0.054 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4243 |
| N(param)refined: | 295 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | −0.93660(3) | 0.72803(2) | 0.57419(2) | 0.01511(9) |
| I2 | −1.85947(4) | 0.96049(2) | 0.83098(2) | 0.01554(9) |
| F1 | −1.2374(4) | 0.98419(19) | 0.61693(10) | 0.0229(4) |
| F2 | −1.5833(5) | 1.07247(19) | 0.71513(11) | 0.0257(5) |
| F3 | −1.5620(4) | 0.69523(19) | 0.78998(10) | 0.0231(4) |
| F4 | −1.1973(4) | 0.61157(18) | 0.69594(10) | 0.0215(4) |
| C1 | −1.2092(6) | 0.7939(3) | 0.65246(17) | 0.0148(6) |
| C2 | −1.3121(7) | 0.9113(3) | 0.66020(18) | 0.0170(7) |
| C3 | −1.4939(7) | 0.9564(3) | 0.71006(17) | 0.0164(6) |
| C4 | −1.5862(6) | 0.8858(3) | 0.75486(16) | 0.0153(6) |
| C5 | −1.4846(6) | 0.7679(3) | 0.74753(17) | 0.0158(6) |
| C6 | −1.2971(6) | 0.7243(3) | 0.69823(17) | 0.0150(6) |
| O1 | 0.3945(4) | 0.5968(2) | 0.22104(11) | 0.0177(5) |
| O2 | −0.1600(4) | 0.4795(2) | 0.11436(11) | 0.0180(5) |
| N1 | −0.5684(5) | 0.6843(3) | 0.46768(14) | 0.0192(6) |
| N2 | −0.0394(5) | 0.6170(3) | 0.24624(14) | 0.0153(5) |
| H2N | −0.199(3) | 0.593(3) | 0.2295(19) | 0.018* |
| N3 | 0.2693(5) | 0.4341(2) | 0.09621(13) | 0.0141(5) |
| H3N | 0.432(3) | 0.449(4) | 0.1126(19) | 0.017* |
| N4 | 0.7928(5) | 0.1093(3) | −0.07489(14) | 0.0177(5) |
| C7 | −0.4752(6) | 0.7953(3) | 0.45856(17) | 0.0187(6) |
| H7 | −0.540422 | 0.870062 | 0.487435 | 0.022* |
| C8 | −0.2896(6) | 0.8080(3) | 0.40965(16) | 0.0182(6) |
| H8 | −0.227550 | 0.889331 | 0.405787 | 0.022* |
| C9 | −0.1958(6) | 0.6994(3) | 0.36625(16) | 0.0154(6) |
| C10 | −0.2921(6) | 0.5835(3) | 0.37495(17) | 0.0183(6) |
| H10 | −0.233456 | 0.507198 | 0.346043 | 0.022* |
| C11 | −0.4746(7) | 0.5803(3) | 0.42624(17) | 0.0188(7) |
| H11 | −0.536217 | 0.500314 | 0.432276 | 0.023* |
| C12 | 0.0081(6) | 0.7098(3) | 0.31267(16) | 0.0176(6) |
| H12A | 0.009152 | 0.795642 | 0.304760 | 0.021* |
| H12B | 0.184608 | 0.698732 | 0.331218 | 0.021* |
| C13 | 0.1604(6) | 0.5721(3) | 0.20635(15) | 0.0123(6) |
| C14 | 0.0725(6) | 0.4876(3) | 0.13412(15) | 0.0140(6) |
| C15 | 0.2249(6) | 0.3760(3) | 0.02171(15) | 0.0173(6) |
| H15A | 0.224919 | 0.443511 | −0.003513 | 0.021* |
| H15B | 0.048369 | 0.331320 | 0.014776 | 0.021* |
| C16 | 0.4290(6) | 0.2838(3) | −0.00954(16) | 0.0153(6) |
| C17 | 0.5356(6) | 0.2013(3) | 0.02478(16) | 0.0187(6) |
| H17 | 0.487556 | 0.203071 | 0.071259 | 0.022* |
| C18 | 0.7136(7) | 0.1161(3) | −0.00964(17) | 0.0178(6) |
| H18 | 0.783210 | 0.059389 | 0.014351 | 0.021* |
| C19 | 0.6897(7) | 0.1900(3) | −0.10696(16) | 0.0186(6) |
| H19 | 0.743754 | 0.187247 | −0.153117 | 0.022* |
| C20 | 0.5096(6) | 0.2775(3) | −0.07743(16) | 0.0165(6) |
| H20 | 0.441875 | 0.332321 | −0.102916 | 0.020* |
Source of material
N,N′-Bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)oxalamide, 4LH2, was prepared according to the literature procedure [5] (melting point, m.pt: 474–475 K; lit. [5]: 486–487 K). 1,4-Diiodotetrafluorobenzene was purchased from Aldrich (Gillingham, Dorset, United Kingdom) and used as received without purification. The co-crystal was prepared through solvent drop-assisted grinding of 4LH2 (0.154 g, 1 mmol) and 1,4-C6F4I2 (0.402 g, 1 mmol). The mixture was ground for 15 mins in the presence of few drops of methanol that lead to a beige slurry. This was dissolved in dimethylformamide (2 mL) and carefully layered with the same volume of benzene. Colourless crystals were obtained after about three days. M.pt: 451–453 K. IR (ATR; cm−1): 3282(m) ν(N—H), 3058–2938(w) ν(C—H), 1655–1642(s) ν(C=O), 1603–1511(s) ν(C=C), 1417(s) ν(C—F), 1360(m) ν(C—N), 755(s) δ(C=C), 482(s) ν(C—I).
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The N-bound H-atoms were located in a difference Fourier map but were refined with a distance restraint of N—H = 0.88 ± 0.01 Å, and with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Uequiv(N). The maximum and minimum residual electron density peaks of 2.65 and 1.59 e Å−3, respectively, were located 1.00 and 0.80 Å from the I1 atom, respectively.
Comment
As noted in a recent bibliographic review [6], isomeric molecules of the general formula (n-C5H4N)CH2N(H)C(=O)C(=O)N(H)CH2(C5H4N-n), for n = 2, 3 and 4, hereafter abbreviated as nLH2, featured prominently in the early days of “crystal engineering.” The isomeric molecules have potential hydrogen bonding functionality in the two terminal n-pyridyl residues (acceptors) and in the central di-amide group (donors and acceptors). Exploiting this functionality and by systematically co-crystallising nLH2 with bi-functional carboxylic acids, two-dimensional sheets could be generated. An example of this is found in the co-crystal comprising equal amounts of 3LH2 and N,N′-dicarboxymethylurea [7]. The 3LH2 molecules self-assembled into supramolecular tapes via amide-N—H⋯O(amide) hydrogen bonding and 10-membered amide synthons {⋯HNC2O}2. Connections between parallel tapes leading to two-dimensional arrays were mediated by bifunctional carboxylic acids forming hydroxy-O—H⋯N(pyridyl) hydrogen bonds [7]. Using the same principles, two-dimensional sheets were generated whereby the supramolecular tapes of 3LH2 formed by amide-N—H⋯O(amide) hydrogen bonding were linked by N⋯I halogen bonds, such as in the 1:1 co-crystal of 3LH2 and 1,4-di-iodobuta-1,3-diyne, that is, I—C≡C—C≡C—I [8]. However, the formation of supramolecular tapes for nLH2 is not always reliable [6]. Thus, in the 1:1 co-crystal formed between 3LH2 and the prototype bridging halogen-bonding molecule, 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene, supramolecular tapes are formed but, mediated by via amide-N—H⋯N(pyridyl) hydrogen bonds and 18-membered {⋯HNC2NC3N}2 synthons [9]. Halogen bonding is also observed but, of the type O⋯I resulting in the formation of a two-dimensional array. As a part of continuing studies of the formation of multi-component crystals of nLH2 [10], [11], [12], the title 1:1 co-crystal containing the co-formers 4LH2 and 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene was prepared and characterised crystallographically.
The molecular structures of the independent molecules comprising the asymmetric unit, each in a general position, are shown in the figure (70% displacement ellipsoids). The central C2N2O2 residue is approximately planar with the r.m.s. deviation of the fitted atoms being 0.0705 Å, and with the maximum deviation from the plane being 0.0948(15) Å for the O2 atom. This is in fact unusual as the central residue is usually considerably more planar [6]. The deviation from planarity arises from a twist about the central C13—C14 bond as seen in the torsion angle of O1—C13—C14—O2 of −167.6(3)°. While the C13—C14 bond length may be considered long at 1.546(4) Å, the distance falls in the usual range for nLH2 molecules, an observation ascribed to the presence of electronegative substituents at each of the carbon atoms [6]. The appended methylene-carbon atoms lie to the same side of the central plane with deviations of 0.074(5) Å, for the C12 atom, and 0.223(5) Å, for C15. The pyridyl rings also lie to the same side of the molecule so that the conformation approximates syn-periplanar. The dihedral angle between the central plane and the N1- and N4-pyridyl rings are 68.32(10) and 63.82(9)°, respectively. The dihedral angle between the pyridyl rings is 47.90(11)°, consistent with a splayed relationship, and emphasises the conformational flexibility of these molecules [6]. As is always observed in the nLH2 molecules [6], intramolecular amide-N—H⋯O(amide) hydrogen bonds are evident which give rise to S(5) loops [N2—H2n⋯O2: H2n⋯O2 = 2.32(4) Å, N2⋯O2 = 2.717(3) Å with angle at H2n = 107(2)° and N3—H3n⋯O1: H3n⋯O1 = 2.36(4) Å, N3⋯O1 = 2.711(3) Å with angle at H3n = 104(2)°].
As evident from the figure, the independent molecules are connected by N⋯I halogen bonds [N1⋯I1 = 2.795(3) Å and, from symmetry, N4⋯I2i = 2.840(3) Å for symmetry operation (i) 3 + x, −1 + y, −1 + z]. The result is a linear supramolecular chain along [3 −1 −1]. Links between chains leading to a two-dimensional array are of the type amide-N—H⋯O(amide) hydrogen bonding and as these occur on either side of the central di-amide residue, a supramolecular tape is sustained by these interactions [N2—H2n⋯O1ii: H2n⋯O1ii = 2.071(16) Å, N2⋯O1ii = 2.899(3) Å with angle at H2n = 158(3)°; N3—H3n⋯O2iii: H3n⋯O2iii = 2.078(17) Å, N3⋯O2iii = 2.917(3) Å with angle at H3n = 160(3)° for (ii) −1 + x, y, z and (iii) 1 + x, y, z]. The aforementioned layers are connected into double-layers via methylene-C—H⋯O(amide) interactions [C15—H15a⋯O2iv: H15a⋯O2iv = 2.57 Å, C15⋯O2iv = 3.471(4) Å with angle at H15a = 152° for (iv) −x, 1−y, −z]. The double layers inter-digitate so that fluoro atoms lie in voids defined by the 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene molecules but, directional interactions are not apparent. Accordingly, in order to understand more about the supramolecular interactions stabilising the crystal, the structure was further evaluated using Crystal Explorer 17 [13] to calculate the Hirshfeld surfaces along with the full and delineated fingerprint plots guided by established procedures [14]. The analysis of the calculated Hirshfeld surface for the complete asymmetric unit of the title structure revealed a myriad of different types of contacts with the most prevalent being F⋯H/H⋯F at 26.2% but, at separations greater than the sum of the van der Waals radii. Other major contributors to the contacts were found to be H⋯H [14.1%], C⋯H/H⋯C [13.4%], O⋯H/H⋯O [9.3%], I⋯C/C⋯I [9.1%] and I⋯H/H⋯I [7.6%], with only the H⋯O contacts being less than the sum of the respective van der Waals radii; I⋯N/N⋯I interactions only amounted to 3.1% of all surface contacts.
The calculations were also performed on the individual co-crystal co-formers. For 4LH2, reflecting the composition of the molecule, the percentage contributions from H⋯H [21.7%], C⋯H/H⋯C [17.3%] and O⋯H/H⋯O [14.7%] contacts all increased in significance while F⋯H/H⋯F [19.9%], I⋯C/C⋯I [2.7%] and [I⋯H/H⋯I [5.0%] decreased. As expected, the opposite trends in surface contacts are evident for the 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene molecule with diminished contributions from H⋯H [0.0%], C⋯H/H⋯C [5.4%] and O⋯H/H⋯O [0.0%] contacts but, significantly increased contributions from F⋯H/H⋯F [33.3%], I⋯C/C⋯I [18.6%] and [I⋯H/H⋯I [16.2%] contacts to the calculated surface.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant no. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: CrysAlisPRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England (2017).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
5. Nguyen, T. L.; Scott, A.; Dinkelmeyer, B.; Fowler, F. W.; Lauher, J. W.: Design of molecular solids: utility of the hydroxyl functionality as a predictable design element. New J. Chem. 22 (1998) 129–135.10.1039/a707642hSearch in Google Scholar
6. Tiekink, E. R. T.: Multi-component crystals: synthesis, concepts, function. (Ed. Tiekink E. R. T. and Schpector-Zukerman J.), p. 289–319. De Gruyter, Singapore (2017).10.1515/9783110464955-013Search in Google Scholar
7. Nguyen, T. L.; Fowler, F. W.; Lauher, J. W.: Commensurate and incommensurate hydrogen bonds. an exercise in crystal engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123 (2001) 11057–11064.10.1021/ja016635vSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Goroff, N. S.; Curtis, S. M.; Webb, J. A.; Fowler, F. W.; Lauher, J. W.: Designed cocrystals based on the pyridine-iodoalkyne halogen bond. Org. Lett. 7 (2005) 1891–1893.10.1021/ol050184sSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Hursthouse M. B.; Gelbrich, T.; Plater M. J.: Private communication to the Cambridge Structural Database. Z. Kristallogr. NCS (2003).Search in Google Scholar
10. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: N,N′-bis(4-Pyridylmethyl)oxalamide benzene solvate: crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and computational study. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 1133–1139.10.1107/S2056989019009551Search in Google Scholar
11. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of the 1:2 co-crystal between N,N′-bis(4-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide and acetic acid as a dihydrate, C14H14N4O2⋅2C2H4O2⋅2H2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 1109–1111.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0477Search in Google Scholar
12. Tan, S. L.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of the co-crystal N,N′-bis(3-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide acetic acid (1/2), C14H14N4O2⋅2C2H4O2. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 234 (2019) 1113–1116.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0478Search in Google Scholar
13. Turner, M. J.; Mckinnon, J. J.; Wolff, S. K.; Grimwood, D. J.; Spackman, P. R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. A.: Crystal Explorer v17. The University of Western Australia, Australia (2017).Search in Google Scholar
14. Tan, S. L.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 308–318.10.1107/S2056989019001129Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2019 Sang Loon Tan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ8-1,1′:2′,1′′-terphenyl-3,3′′,4′,5′-tetracarboxylato-κ8O1:O2:O3:O4:O5:O6:O7:O8)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-ylimino)methyl)-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C22H27N3O
- Crystal structure of (4-ethoxynaphthalen-1-yl)(furan-2-yl)methanone, C17H14O3
- Crystal structure of 1-nonylpyridazin-1-ium iodide, C13H23N2I
- Crystal structure of bis[diaqua(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N, N′)-copper(II)]diphenylphosphopentamolybdate dihydrate, C36H38Cu2Mo5N4O27P2
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(imidazole)-copper(I) hexafluorophosphate, C12H16CuF6PN8
- The crystal structure of dimethyl ((3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)(phenyl)methyl)phosphonate, C23H33O4P
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(1,10-phenanthroline κ2N,N′)nickel(II) trifluoroacetate- trifluoroacetic acid (1/1), C30H21F9N4NiO8
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,8-naphthyridine, C18H12N2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of a new polymorph of diisopropylammonium trichloroacetate, C8H16Cl3NO2
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)cadmium(II) C34H34CdN12O2S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2,2-difluoro-2-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C14H12F2O5
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)] bis[1′-(diphenylphosphino-κP)-1-cyanoferrocene]disilver(I), C56H56Ag2Fe2N4P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis(di-n-butylammonium) tetrachloridodiphenylstannate(IV), C28H50Cl4N2Sn
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ5-2-((5-bromo-3-formyl-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)benzenesulfonato-κ6O:O:O,O′:O′:O′′)sodium(I)], C13H9O4NSBrNa
- Crystal structure of catena-{poly[bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-S)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)-zinc(II)] di-acetonitrile solvate}, {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn ⋅ 2 C2H3N}n
- Halogen and hydrogen bonding in the layered crystal structure of 2-iodoanilinium triiodide, C6H7I4N
- Crystal structure of cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium 2-[(2-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate — dimethylformamide — monohydrate (1/1/1), [C6H16N2][C14H8O4S2] ⋅ C3H7NO⋅H2O
- The synthesis and crystal structure of isobutyl 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C16H13Cl2F6N3O3S
- Isolation and crystal structure of bufotalinin — methanol (1/1), C25H34O7
- Crystal structure of benzylbis(1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′) chloridotin(IV), C37H29ClO4Sn
- Crystal structure of Bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}diiodidocadmium(II), [Cd(C11H11N5)2I2], C22H22N10I2Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-isobutoxybenzaldehyde oxime, C11H15NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(N′-hydroxypyrimidine-2-carboximidamide-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) — methanol (1/2), C14H18MnN8O6, 2(CH3OH)′
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-bis(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)amine-κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)cadmium(II)], C36H30CdN12O6
- Crystal structure and optical properties of 1,6-bis(methylthio)pyrene, C18H14S2
- The crystal structure of hexaquamagnesium(II) bis(3,4-dinitropyrazol-1-ide), C6H14MgN8O14
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3:5,4-terpyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure and photochromic properties of a novel photochromic perfluordiarylethene containing a triazole bridged pyridine group moiety, C24H18F6N4S2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ3-oxido)-(μ2-(N,N-diisopropylthiocarbamoylthio) acetato-κ2O,O′)-((N,N-diisopropylthiocarbamoylthio)acetato-κO)-bis(di-4-methylbenzyl-tin(IV))], C100H136N4O10S8Sn4
- Crystal structure of dibromidobis(4-bromobenzyl)tin(IV), C14H12Br4Sn
- The crystal structure of (4Z)-2-[(E)-(1-ethyl-3,3-dimethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-ylidene)methyl]-4-[(1-ethyl-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indolium-2-yl)methylidene]-3-oxocyclobut-1-en-1-olate, C30H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-5,5-dimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-one, C18H23NO
- Crystal structure of dihydrazinium 1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate, C5H12N6O4
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-4-sulfidobenzoate-κ2O:S)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C42H44Co2N8O7S2
- Crystal structure of 8-(3,4-dimethylbenzylidene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C17H18O4
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-bromo-4-(6-morpholino-3-phenyl-3H-benzo[f]chromen-3-yl) cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-yl)morpholine, C33H31BrN2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((1-phenyl-3-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one, C23H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,1′-(oxybis(4,1-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole)-κ2N,N′)(μ2-1,3-benzenecarboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)zinc(II)] dihydrate, C26H22N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(cinnamato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II), C18H18ZnO6
- Crystal structure of 2-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1-naphthaldehyde, C14H10O2
- Crystal structure and photochromic properties of 1-(2-methyl-5-phenyl-3-thienyl)-2-{2-methyl-5-[4-(9-fluorenone hydrazone)-phenyl]-3-thienyl}perfluorocyclopentene, C41H26F6N2S2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of cylo[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-1,4-bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)but-2-ene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4-nitro-phthalate-κ2O,O′)dinickel(II)], C26H23N5O8Ni
- Crystal structure of 3-[methyl(phenyl)amino]-1-phenylthiourea, C14H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-[methyl(phenyl)amino]thiourea, C14H14ClN3S
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C10H13N3
- Crystal structure of 5-carboxy-2-(2-carboxyphenyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium-4-carboxylate dihydrate, C12H8N2O6⋅2(H2O)
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-μ2-dichlorido-(η2-1,4-bis(4-vinylbenzyl)-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-1,4-diium)dicopper(I), C24H30N2Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl (Z)-N-(adamantan-1-yl)morpholine-4-carbothioimidate, C22H29BrN2OS
- Crystal structure of (4S,4aS,6aR,6bR,12aS,12bR,14aS,14bR)-3,3,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyloctadecahydro-1H,3H-4,14b-ethanophenanthro[1,2-h]isochromene-1(6bH)-one, C30H48O2
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl (Z)-N′-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-phenylpiperazine-1-carbothioimidate, C30H33F6N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-methoxyphenanthridin-6(5H)-one, C14H11NO2
- Crystal structure of 4-(5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-3H,5H-5λ4-dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-10-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidoferrate(III), C18H19BF2FeI4N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-3-((phenylsulfonyl)methyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C21H18N2O3S
- Crystal structure of [(2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II) perchlorate, C29H50Cl2N4NiO8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-6-(dimethylamino)-3,3-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-2-(2-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)hydrazinyl)-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one, C35H35N7O
- 5-Methyl-N′-[5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbonyl]-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbohydrazide, C22H22N8O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-dichloro-6-methoxyquinoxaline, C9H6Cl2N2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 7-chloro-2-(ethylsulfinyl)-6-fluoro-3-(1H-pyrazole-1-yl)-4H-thiochromen-4-one, C13H10FN3OS2
- Crystal structure of 4-ethylpiperazine-1-carbothioic dithioperoxyanhydride, C14H26N4S4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)naphthalen-1-yl)pyrimidine, C20H15N3
- The crystal structure of N′-((1E,2E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-ylidene)-3-methylbenzohydrazide, C23H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-isophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(2,5-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3N,N′,N′′)zinc(II)] — water (2/5), C26H21N6O6.5Zn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)-1-((4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C53H38Cl2F6N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-oxido)-bis(N,N′-o-phenylenebis(salicylideneiminato))diiron(III) — N,N′-dimethylformamide, C47H43Fe2N4O9
- Crystal structure of N1,N3-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-N1, N1,N3,N3-tetramethylpropane-1,3-diaminium dibromide, C11H28Br2N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine, C12H9ClN2
- Crystal structure of 8-bromo-6-oxo-2-phenyl-6H-pyrrolo[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-5-carbaldehyde, C18H11BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(2-azidoethyl)piperazine-1,4-diium dichloride trihydrate, C8H18N8Cl2 ⋅ 3 H2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-bromo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethylene)aniline, C12H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(3-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ-O)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Br2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of (1E,2E)-2-methyl-4-((7-oxo-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-9-yl)oxy)but-2-enal O-isonicotinoyl oxime–trichloromethane (3/1), C67H49Cl3N6O18
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate(V), C8H13F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(2-bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κO)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II) hemihydrate C42H65Br2N4NiO8.5
- The crystal structure of N-(7-(4-fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbonothioyl)benzamide, C28H23F2N3OS
- The crystal structure of N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide, C18H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(ethylamino)-2,7-dimethyl-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-((6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – methanol (1/1), C34H37N5O3
- Crystal structure of 2-oxo-1-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-5l4-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-olate, C20H13F3N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O1: O2: O3)(μ2-4-(pyridin-4-yl)pyridine-κ2N1:N1′)zinc(II)], C19H11N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,8-dihydropyren-1-yl)-methylene)picolinohydrazide, C23H15N3O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{[μ2-1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane]dichloridocadmium(II)}, C26H24CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of the 1:2 co-crystal between N,N′-bis(4-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide and acetic acid as a dihydrate, C14H14N4O2⋅2 C2H4O2⋅2 H2O
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal N,N′-bis(3-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide acetic acid (1/2), C14H14N4O2⋅2C2H4O2
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal N,N′-bis(4-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide and 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-di-iodobenzene (1/1), C14H14N4O2⋅C6F4I2
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 4-[(4-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid–(1E,4E)-1-N,4-N-bis(pyridin-4-ylmethylidene)cyclohexane-1,4-diamine (1/1), C14H10O4S2⋅C18H20N4
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-bis(μ2-di-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S:S′)-di-rhenium(I), C20H28N2O6Re2S4
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-morpholine-κN-(morpholinocarbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)rhenium(I), C12H17N2O5ReS2
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ8-1,1′:2′,1′′-terphenyl-3,3′′,4′,5′-tetracarboxylato-κ8O1:O2:O3:O4:O5:O6:O7:O8)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2O10
- Crystal structure of 2-((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-ylimino)methyl)-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol, C22H27N3O
- Crystal structure of (4-ethoxynaphthalen-1-yl)(furan-2-yl)methanone, C17H14O3
- Crystal structure of 1-nonylpyridazin-1-ium iodide, C13H23N2I
- Crystal structure of bis[diaqua(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N, N′)-copper(II)]diphenylphosphopentamolybdate dihydrate, C36H38Cu2Mo5N4O27P2
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(imidazole)-copper(I) hexafluorophosphate, C12H16CuF6PN8
- The crystal structure of dimethyl ((3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)(phenyl)methyl)phosphonate, C23H33O4P
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(1,10-phenanthroline κ2N,N′)nickel(II) trifluoroacetate- trifluoroacetic acid (1/1), C30H21F9N4NiO8
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,8-naphthyridine, C18H12N2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of a new polymorph of diisopropylammonium trichloroacetate, C8H16Cl3NO2
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-bis(1-((2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-κN)-bis(thiocyanato-κN)cadmium(II) C34H34CdN12O2S2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2,2-difluoro-2-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acetate, C14H12F2O5
- The crystal structure of bis[μ2-(N,N-diethylcarbamodithioato-κS:κS,κS′)] bis[1′-(diphenylphosphino-κP)-1-cyanoferrocene]disilver(I), C56H56Ag2Fe2N4P2S4
- Crystal structure of bis(di-n-butylammonium) tetrachloridodiphenylstannate(IV), C28H50Cl4N2Sn
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ5-2-((5-bromo-3-formyl-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)benzenesulfonato-κ6O:O:O,O′:O′:O′′)sodium(I)], C13H9O4NSBrNa
- Crystal structure of catena-{poly[bis(O,O′-diethyldithiophosphato-S)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)-zinc(II)] di-acetonitrile solvate}, {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn ⋅ 2 C2H3N}n
- Halogen and hydrogen bonding in the layered crystal structure of 2-iodoanilinium triiodide, C6H7I4N
- Crystal structure of cyclohexane-1,4-diammonium 2-[(2-carboxylatophenyl)disulfanyl]benzoate — dimethylformamide — monohydrate (1/1/1), [C6H16N2][C14H8O4S2] ⋅ C3H7NO⋅H2O
- The synthesis and crystal structure of isobutyl 5-amino-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-((trifluoromethyl)sulfinyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C16H13Cl2F6N3O3S
- Isolation and crystal structure of bufotalinin — methanol (1/1), C25H34O7
- Crystal structure of benzylbis(1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′) chloridotin(IV), C37H29ClO4Sn
- Crystal structure of Bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-methyl-imidazol)}diiodidocadmium(II), [Cd(C11H11N5)2I2], C22H22N10I2Cd
- Crystal structure of 4-isobutoxybenzaldehyde oxime, C11H15NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(acetato-κ1O)-bis(N′-hydroxypyrimidine-2-carboximidamide-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) — methanol (1/2), C14H18MnN8O6, 2(CH3OH)′
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-bis(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)amine-κ2N:N′)-bis(nitrato-κO)cadmium(II)], C36H30CdN12O6
- Crystal structure and optical properties of 1,6-bis(methylthio)pyrene, C18H14S2
- The crystal structure of hexaquamagnesium(II) bis(3,4-dinitropyrazol-1-ide), C6H14MgN8O14
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3:5,4-terpyridine – 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure and photochromic properties of a novel photochromic perfluordiarylethene containing a triazole bridged pyridine group moiety, C24H18F6N4S2
- Crystal structure of bis[(μ3-oxido)-(μ2-(N,N-diisopropylthiocarbamoylthio) acetato-κ2O,O′)-((N,N-diisopropylthiocarbamoylthio)acetato-κO)-bis(di-4-methylbenzyl-tin(IV))], C100H136N4O10S8Sn4
- Crystal structure of dibromidobis(4-bromobenzyl)tin(IV), C14H12Br4Sn
- The crystal structure of (4Z)-2-[(E)-(1-ethyl-3,3-dimethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-ylidene)methyl]-4-[(1-ethyl-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indolium-2-yl)methylidene]-3-oxocyclobut-1-en-1-olate, C30H32N2O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-5,5-dimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-one, C18H23NO
- Crystal structure of dihydrazinium 1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylate, C5H12N6O4
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-1,4-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-4-sulfidobenzoate-κ2O:S)cobalt(II)] dihydrate, C42H44Co2N8O7S2
- Crystal structure of 8-(3,4-dimethylbenzylidene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C17H18O4
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-bromo-4-(6-morpholino-3-phenyl-3H-benzo[f]chromen-3-yl) cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-yl)morpholine, C33H31BrN2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((1-phenyl-3-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene)-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one, C23H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,1′-(oxybis(4,1-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazole)-κ2N,N′)(μ2-1,3-benzenecarboxylato-κ3O,O′:O′′)zinc(II)] dihydrate, C26H22N4O7Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(cinnamato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II), C18H18ZnO6
- Crystal structure of 2-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1-naphthaldehyde, C14H10O2
- Crystal structure and photochromic properties of 1-(2-methyl-5-phenyl-3-thienyl)-2-{2-methyl-5-[4-(9-fluorenone hydrazone)-phenyl]-3-thienyl}perfluorocyclopentene, C41H26F6N2S2
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of cylo[tetraaqua-bis(μ2-1,4-bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)but-2-ene-κ2N:N′)-bis(μ2-4-nitro-phthalate-κ2O,O′)dinickel(II)], C26H23N5O8Ni
- Crystal structure of 3-[methyl(phenyl)amino]-1-phenylthiourea, C14H15N3S
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-[methyl(phenyl)amino]thiourea, C14H14ClN3S
- Crystal structure of 2-tert-butyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C10H13N3
- Crystal structure of 5-carboxy-2-(2-carboxyphenyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium-4-carboxylate dihydrate, C12H8N2O6⋅2(H2O)
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-μ2-dichlorido-(η2-1,4-bis(4-vinylbenzyl)-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-1,4-diium)dicopper(I), C24H30N2Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzyl (Z)-N-(adamantan-1-yl)morpholine-4-carbothioimidate, C22H29BrN2OS
- Crystal structure of (4S,4aS,6aR,6bR,12aS,12bR,14aS,14bR)-3,3,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyloctadecahydro-1H,3H-4,14b-ethanophenanthro[1,2-h]isochromene-1(6bH)-one, C30H48O2
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl (Z)-N′-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-phenylpiperazine-1-carbothioimidate, C30H33F6N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-methoxyphenanthridin-6(5H)-one, C14H11NO2
- Crystal structure of 4-(5,5-difluoro-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-3H,5H-5λ4-dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinin-10-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidoferrate(III), C18H19BF2FeI4N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-3-((phenylsulfonyl)methyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine, C21H18N2O3S
- Crystal structure of [(2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ2O,O′) (5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II) perchlorate, C29H50Cl2N4NiO8
- Crystal structure of (Z)-6-(dimethylamino)-3,3-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-2-(2-(quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)hydrazinyl)-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one, C35H35N7O
- 5-Methyl-N′-[5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbonyl]-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbohydrazide, C22H22N8O2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-dichloro-6-methoxyquinoxaline, C9H6Cl2N2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 7-chloro-2-(ethylsulfinyl)-6-fluoro-3-(1H-pyrazole-1-yl)-4H-thiochromen-4-one, C13H10FN3OS2
- Crystal structure of 4-ethylpiperazine-1-carbothioic dithioperoxyanhydride, C14H26N4S4
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)naphthalen-1-yl)pyrimidine, C20H15N3
- The crystal structure of N′-((1E,2E)-4-(7-methoxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-8-yl)-2-methylbut-2-en-1-ylidene)-3-methylbenzohydrazide, C23H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-isophthalato-κ2O:O′)-(2,5-di(pyrazin-2-yl)-4,4′-bipyridine-κ3N,N′,N′′)zinc(II)] — water (2/5), C26H21N6O6.5Zn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(3-nitrobenzylidene)-1-((4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one — dichloromethane (2/1), C53H38Cl2F6N6O14S2
- Crystal structure of (μ2-oxido)-bis(N,N′-o-phenylenebis(salicylideneiminato))diiron(III) — N,N′-dimethylformamide, C47H43Fe2N4O9
- Crystal structure of N1,N3-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-N1, N1,N3,N3-tetramethylpropane-1,3-diaminium dibromide, C11H28Br2N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine, C12H9ClN2
- Crystal structure of 8-bromo-6-oxo-2-phenyl-6H-pyrrolo[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-5-carbaldehyde, C18H11BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(2-azidoethyl)piperazine-1,4-diium dichloride trihydrate, C8H18N8Cl2 ⋅ 3 H2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-bromo-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethylene)aniline, C12H9BrN2
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(3-bromophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κ-O)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II), C40H60Br2N4NiO8
- The crystal structure of (1E,2E)-2-methyl-4-((7-oxo-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-9-yl)oxy)but-2-enal O-isonicotinoyl oxime–trichloromethane (3/1), C67H49Cl3N6O18
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate(V), C8H13F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of bis[(2-(2-bromophenyl)-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylato-κO)-(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)]nickel(II) hemihydrate C42H65Br2N4NiO8.5
- The crystal structure of N-(7-(4-fluorobenzylidene)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3,3a,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-2H-indazole-2-carbonothioyl)benzamide, C28H23F2N3OS
- The crystal structure of N1,N4-bis(pyridin-3-yl)cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxamide, C18H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,6-bis(ethylamino)-2,7-dimethyl-9H-xanthen-9-yl)-N′-((6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide – methanol (1/1), C34H37N5O3
- Crystal structure of 2-oxo-1-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1,2-dihydro-5l4-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-olate, C20H13F3N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-9H-carbazole-3,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O1: O2: O3)(μ2-4-(pyridin-4-yl)pyridine-κ2N1:N1′)zinc(II)], C19H11N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((1,8-dihydropyren-1-yl)-methylene)picolinohydrazide, C23H15N3O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{[μ2-1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane]dichloridocadmium(II)}, C26H24CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of the 1:2 co-crystal between N,N′-bis(4-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide and acetic acid as a dihydrate, C14H14N4O2⋅2 C2H4O2⋅2 H2O
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal N,N′-bis(3-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide acetic acid (1/2), C14H14N4O2⋅2C2H4O2
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal N,N′-bis(4-pyridylmethyl)oxalamide and 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-di-iodobenzene (1/1), C14H14N4O2⋅C6F4I2
- Crystal structure of the co-crystal 4-[(4-carboxyphenyl)disulfanyl]benzoic acid–(1E,4E)-1-N,4-N-bis(pyridin-4-ylmethylidene)cyclohexane-1,4-diamine (1/1), C14H10O4S2⋅C18H20N4
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-bis(μ2-di-n-propyldithiocarbamato-κ3S,S′:S;κ3S:S:S′)-di-rhenium(I), C20H28N2O6Re2S4
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-morpholine-κN-(morpholinocarbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)rhenium(I), C12H17N2O5ReS2

