Abstract
C15H20FN7O2, triclinic, P1̅ (no. 2), a = 5.8088(18) Å, b = 11.667(4) Å, c = 13.104(4) Å, α = 68.724(4)°, β = 84.660(5)°, γ = 84.859(4)°, V = 822.4(4) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0501, wRref(F2) = 0.1394, T = 293(2) K.
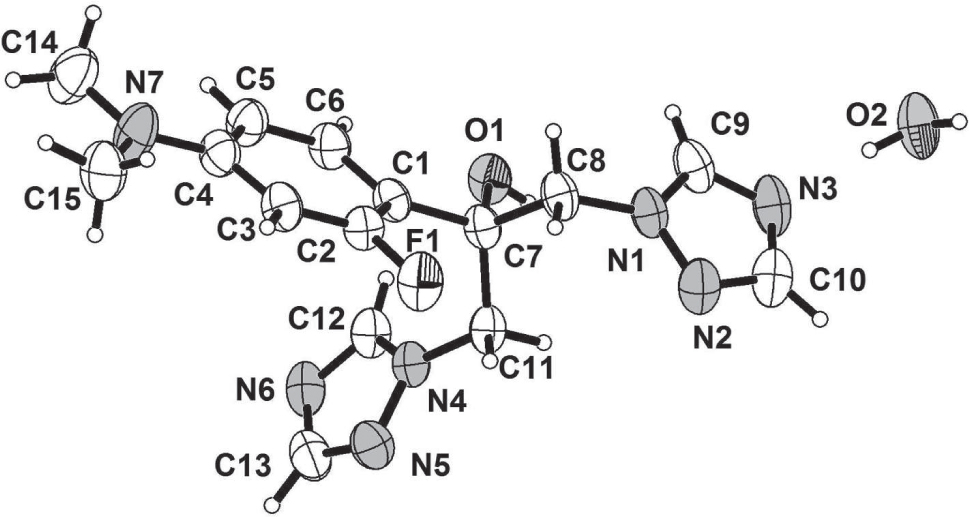
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.28 × 0.22 × 0.18 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.1 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 50°, 98.4% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 4390, 2838, 0.024 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1857 |
| N(param)refined: | 229 |
| Programs: | DIAMOND [1], SHELX [2], Bruker programs [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.0295(2) | 0.37080(12) | 0.55389(11) | 0.0549(4) |
| O1 | 0.5429(3) | 0.31464(15) | 0.77918(13) | 0.0481(4) |
| H1 | 0.5116 | 0.3183 | 0.8403 | 0.072* |
| N1 | 0.2555(3) | 0.53275(16) | 0.76014(15) | 0.0454(5) |
| N2 | 0.0400(4) | 0.56043(19) | 0.79813(18) | 0.0586(6) |
| N3 | 0.3129(4) | 0.60236(19) | 0.88777(17) | 0.0607(6) |
| N4 | 0.1645(3) | 0.14260(16) | 0.83728(14) | 0.0405(5) |
| N5 | −0.0201(4) | 0.07588(19) | 0.84265(17) | 0.0533(6) |
| N6 | 0.2914(4) | −0.04937(18) | 0.90646(16) | 0.0525(6) |
| N7 | 0.5224(4) | 0.1484(2) | 0.37448(18) | 0.0665(7) |
| C1 | 0.3884(4) | 0.29169(19) | 0.62792(17) | 0.0386(5) |
| C2 | 0.2352(4) | 0.3080(2) | 0.54847(18) | 0.0413(5) |
| C3 | 0.2731(4) | 0.2644(2) | 0.46452(18) | 0.0475(6) |
| H3 | 0.1618 | 0.2793 | 0.4139 | 0.057* |
| C4 | 0.4802(4) | 0.1974(2) | 0.45503(18) | 0.0473(6) |
| C5 | 0.6400(4) | 0.1815(2) | 0.5327(2) | 0.0500(6) |
| H5 | 0.7817 | 0.1392 | 0.5279 | 0.060* |
| C6 | 0.5937(4) | 0.2264(2) | 0.61587(18) | 0.0455(6) |
| H6 | 0.7048 | 0.2124 | 0.6665 | 0.055* |
| C7 | 0.3383(4) | 0.3394(2) | 0.72168(17) | 0.0386(5) |
| C8 | 0.2878(4) | 0.4789(2) | 0.67541(19) | 0.0462(6) |
| H8A | 0.4153 | 0.5165 | 0.6244 | 0.055* |
| H8B | 0.1492 | 0.4973 | 0.6350 | 0.055* |
| C9 | 0.4139(5) | 0.5588(2) | 0.8145(2) | 0.0535(7) |
| H9 | 0.5733 | 0.5477 | 0.8022 | 0.064* |
| C10 | 0.0879(5) | 0.6018(2) | 0.8747(2) | 0.0625(8) |
| H10 | −0.0272 | 0.6286 | 0.9166 | 0.075* |
| C11 | 0.1355(4) | 0.27625(19) | 0.79894(18) | 0.0408(6) |
| H11A | 0.1198 | 0.3023 | 0.8618 | 0.049* |
| H11B | −0.0063 | 0.3027 | 0.7609 | 0.049* |
| C12 | 0.3457(4) | 0.0662(2) | 0.87588(19) | 0.0463(6) |
| H12 | 0.4910 | 0.0908 | 0.8807 | 0.056* |
| C13 | 0.0679(5) | −0.0370(2) | 0.8848(2) | 0.0568(7) |
| H13 | −0.0195 | −0.1047 | 0.8989 | 0.068* |
| C14 | 0.7389(5) | 0.0819(3) | 0.3639(3) | 0.0767(9) |
| H14A | 0.8587 | 0.1388 | 0.3342 | 0.115* |
| H14B | 0.7248 | 0.0379 | 0.3156 | 0.115* |
| H14C | 0.7777 | 0.0245 | 0.4347 | 0.115* |
| C15 | 0.3518(5) | 0.1536(3) | 0.3005(2) | 0.0691(8) |
| H15A | 0.2259 | 0.1048 | 0.3406 | 0.104* |
| H15B | 0.4203 | 0.1220 | 0.2458 | 0.104* |
| H15C | 0.2950 | 0.2375 | 0.2657 | 0.104* |
| O2 | 0.5413(3) | 0.72228(15) | 1.00420(13) | 0.0637(6) |
| H2A | 0.4974 | 0.6680 | 0.9860 | 0.096* |
| H2B | 0.4817 | 0.7926 | 0.9817 | 0.096* |
Source of material
Fluconazole (C13H12F2N6O, 20 mg) was dissolved in a water and DMF (v:v = 4:1, 5 mL) solution. Then the solution was transferred to a Teflon-lined stainless vessel and heated to 313 K for 72 h. It was then cooled to room temperature at a rate of 1 K/h to afford colorless block crystals of the title compound in ca. 30% yield.
Experimental details
H atoms bonded to aromatic and methylene C atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93 and 0.97 Å, respectively) and included in the refinement as the riding-model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). Hydroxyl and water H atoms were refined as rigid groups with O—H = 0.82 Å that were allowed to rotate but not tip, with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O).
Comment
Fluconazole (C13H12F2N6O), 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-propan-2-ol, a good antifungal agent, has been effectively applied in clinical treatment and also plays a great role in preventing the opportunistic fungal infections for HIV patients [4, 5] . In order to enhance fluconazole’s biomedical application, numberous research groups have been engaged in new polymorphs of fluconazole, which resulted in the formation of several polymorphs, salts, solvates and cocrystals [6, 7] . In this context, we initial the solvothermal treatment of fluconazole in water and DMF solution. An unexpectant crystalline product resulting from the SNAr reaction of the aryl fluoride, namely 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate (C15H20FN7O2), was obtained and characterized by X-ray single-crystal diffraction.
In the asymmetric unit, there is one 2-(4-(dimethyl-amino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol and a water molecule. The torison angles of C2–C1–C7–O1, C7–C8–N1–N2 and C7–C11–N4–N5 are −174.8(2), −99.3(2), and −138.2(2), respectively. The dihedral angles between the aryl ring and the triazole rings are 26.0(1) and 68.5(1)°, respectively. Two terminal pyridyl rings make a dihedral angle of 68.0(1)° with each other. In contrast to the polymorphs of fluconazole [7], the title compound has not been found to form a dimer. The resultant hydrogen-bonding array is an infinite waving tape built by the O–H⋅⋅⋅O and O–H⋅⋅⋅N interactions between the host substituted fluconazole and the water molecule. Weak π⋅⋅⋅π interactions have to be taken into account, to construct the final 3D supramolecular arrangement.
References
1 Brandenburg, K.: Diamond. Version 3.0d. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany, 2005.Search in Google Scholar
2 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3 Bruker. SADABS, SMART and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2007.Search in Google Scholar
4 Ritter, J. M.; Lewis, L. D.; Mant, T. G. K.: A Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology. Arnold, London, 1999; 54–75.Search in Google Scholar
5 Caira, M. R.; Alkhamis, K. A.; Obaidat, R. M.: Preparation and crystal characterization of a polymorph, a monohydrate, and an ethyl acetate solvate of the antifungal fluconazole. J. Pharm. Sci. 93 (2004) 601–611.10.1002/jps.10541Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6 Kastelic, J.; Hodnik, Z.; Sket, P.; Plavec, J.; Lah, N.; Leban, I.; Pajk, M.; Planinek, O; Kikelj, D.: Fluconazole cocrystals with dicarboxylic acids. Cryst. Growth Des. 10 (2010) 4943–4953.10.1021/cg1010117Search in Google Scholar
7 Karanam, M.; Dev, S.; Choudhury, A. R.: New polymorphs of fluconazole: results from cocrystallization experiments. Cryst. Growth Des. 12 (2012) 240–252.10.1021/cg201005ySearch in Google Scholar
©2017 Shao-Hua Liu et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16

