Abstract
C27H18N6NiO7, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 8.0981(15) Å, b = 21.660(3) Å, c = 14.170(2) Å, β = 95.215(4)°, V = 2475.1(7) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0418, wRref(F2) = 0.0965, T = 293 K.
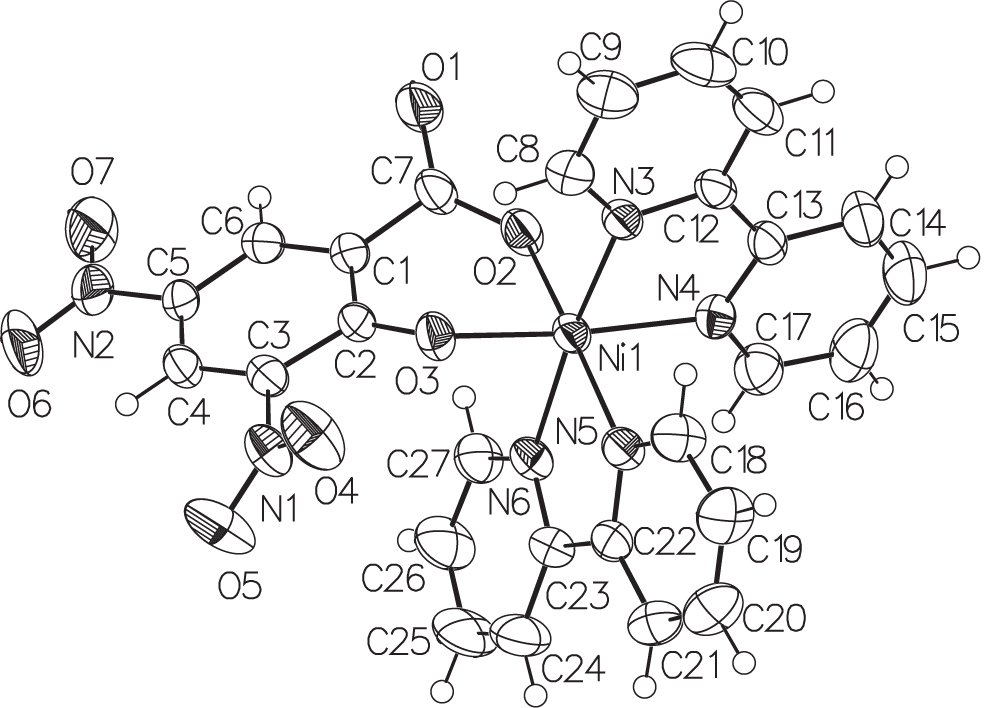
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Green block |
| Size: | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 8.5 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Weissenberg IP, ω-scans |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 55°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique: | 5669, 5669 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3438 |
| N(param)refined: | 370 |
| Programs: | SHELX [8], TeXan [9] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni1 | 0.63824(5) | 0.369630(15) | 0.82529(2) | 0.03136(10) |
| N1 | 0.4773(3) | 0.32126(12) | 0.51319(17) | 0.0447(6) |
| N2 | 0.7725(4) | 0.49713(13) | 0.40091(18) | 0.0518(7) |
| N3 | 0.4443(3) | 0.40647(10) | 0.89026(15) | 0.0345(5) |
| N4 | 0.7371(3) | 0.37073(10) | 0.96577(15) | 0.0360(5) |
| N5 | 0.5721(3) | 0.27725(10) | 0.84337(15) | 0.0351(5) |
| N6 | 0.8285(3) | 0.32325(10) | 0.76747(15) | 0.0358(5) |
| O1 | 0.6898(4) | 0.54809(10) | 0.73997(15) | 0.0802(9) |
| O2 | 0.7257(3) | 0.45594(9) | 0.80703(12) | 0.0416(5) |
| O3 | 0.5161(2) | 0.37271(9) | 0.69458(12) | 0.0383(5) |
| O4 | 0.3583(3) | 0.30630(12) | 0.55192(17) | 0.0703(8) |
| O5 | 0.5333(3) | 0.28864(11) | 0.45306(18) | 0.0724(8) |
| O6 | 0.7607(4) | 0.47301(12) | 0.32309(15) | 0.0781(9) |
| O7 | 0.8426(4) | 0.54636(12) | 0.41698(17) | 0.0773(8) |
| C1 | 0.6580(4) | 0.46127(12) | 0.64086(18) | 0.0357(7) |
| C2 | 0.5725(3) | 0.40326(12) | 0.62811(17) | 0.0317(6) |
| C3 | 0.5564(4) | 0.38101(12) | 0.53290(18) | 0.0338(6) |
| C4 | 0.6198(4) | 0.41060(13) | 0.45965(19) | 0.0374(7) |
| H4A | 0.6086 | 0.3938 | 0.3990 | 0.045* |
| C5 | 0.7002(4) | 0.46530(13) | 0.47659(18) | 0.0377(7) |
| C6 | 0.7174(4) | 0.49082(13) | 0.56618(19) | 0.0399(7) |
| H6A | 0.7702 | 0.5287 | 0.5757 | 0.048* |
| C7 | 0.6922(4) | 0.49141(13) | 0.7361(2) | 0.0436(8) |
| C8 | 0.3002(4) | 0.42438(13) | 0.8469(2) | 0.0444(8) |
| H8A | 0.2819 | 0.4191 | 0.7817 | 0.053* |
| C9 | 0.1765(4) | 0.45034(15) | 0.8943(2) | 0.0557(9) |
| H9A | 0.0764 | 0.4623 | 0.8621 | 0.067* |
| C10 | 0.2057(5) | 0.45804(15) | 0.9905(3) | 0.0585(9) |
| H10A | 0.1246 | 0.4755 | 1.0247 | 0.070* |
| C11 | 0.3529(4) | 0.44020(14) | 1.0359(2) | 0.0494(8) |
| H11A | 0.3732 | 0.4452 | 1.1011 | 0.059* |
| C12 | 0.4724(4) | 0.41454(12) | 0.98418(19) | 0.0356(7) |
| C13 | 0.6366(4) | 0.39508(12) | 1.02631(19) | 0.0369(7) |
| C14 | 0.6877(5) | 0.40219(15) | 1.1212(2) | 0.0551(9) |
| H14A | 0.6178 | 0.4199 | 1.1622 | 0.066* |
| C15 | 0.8427(6) | 0.38273(18) | 1.1540(2) | 0.0682(11) |
| H15A | 0.8795 | 0.3875 | 1.2177 | 0.082* |
| C16 | 0.9438(5) | 0.35632(17) | 1.0935(2) | 0.0629(10) |
| H16A | 1.0489 | 0.3421 | 1.1149 | 0.075* |
| C17 | 0.8849(4) | 0.35148(14) | 0.9996(2) | 0.0484(8) |
| H17A | 0.9531 | 0.3337 | 0.9578 | 0.058* |
| C18 | 0.4495(4) | 0.25710(14) | 0.8913(2) | 0.0472(8) |
| H18A | 0.3721 | 0.2855 | 0.9093 | 0.057* |
| C19 | 0.4315(5) | 0.19650(15) | 0.9156(2) | 0.0564(9) |
| H19A | 0.3457 | 0.1845 | 0.9509 | 0.068* |
| C20 | 0.5403(5) | 0.15414(15) | 0.8874(2) | 0.0558(9) |
| H20A | 0.5293 | 0.1127 | 0.9029 | 0.067* |
| C21 | 0.6657(4) | 0.17290(13) | 0.8362(2) | 0.0463(8) |
| H21A | 0.7398 | 0.1444 | 0.8150 | 0.056* |
| C22 | 0.6808(4) | 0.23533(12) | 0.81622(18) | 0.0339(6) |
| C23 | 0.8154(4) | 0.26097(13) | 0.7653(2) | 0.0379(7) |
| C24 | 0.9238(5) | 0.22531(16) | 0.7204(2) | 0.0604(10) |
| H24A | 0.9147 | 0.1825 | 0.7202 | 0.072* |
| C25 | 1.0465(5) | 0.25398(18) | 0.6756(3) | 0.0723(12) |
| H25A | 1.1199 | 0.2306 | 0.6436 | 0.087* |
| C26 | 1.0603(5) | 0.31717(16) | 0.6781(3) | 0.0618(10) |
| H26A | 1.1440 | 0.3371 | 0.6491 | 0.074* |
| C27 | 0.9486(4) | 0.34994(15) | 0.7241(2) | 0.0462(8) |
| H27A | 0.9567 | 0.3928 | 0.7252 | 0.055* |
Source of material
A mixture of Ni(OAc)2⋅2H2O (0.1 mmol), 2,2′-bipyridine (0.1 mmol), 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (0.2 mmol) in distilled water (10 mL) was filled in a 20 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor. The solution was heated to 453 K for 3 days, then slowly cooled to room temperature to get green block-like crystals.
Experimental details
H atoms were positioned geometrically and were included in the refinement in the riding-model approximation [C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C)].
Discussion
A lot of attention has been paid to salicylate complexes because of their structural features and biological applications. Complexs with salicylato and N-donor ligands, were found to display diverse structure types [1], [2], [3]. A large number of hydrogen-bonded supramolecular architectures based on bipyridine and carboxylato ligands have been reported [4]. Though the functional groups such as NO2 are able to form robust and strong hydrogen bond, the syntheses of metal-organic supramolecular assemblies employing organic ligands with NO2 groups are limited [5]. Up to now, only 3,5-dinitrosalicylato complexes have been reported [6, 7] .
In the title crystal structure the Ni(II) atom exhibits an octahedral coordination geometry, defined by four N atoms of two 2,2′-bipy ligands and two O atoms from one 3,5-(NO2)2sal ligand. The Ni-N(4) and Ni-N(6) distances are equivalent, while the Ni—N(3) bond (2.053 Å) is significantly shorter than Ni—N(3) (2.093 Å). The bipyridine rings of 2,2′-bipy containing N3 and N4 are approximately coplanar, exhibiting a dihedral angle of 2.0(1)°, while the bipyridine rings of the other 2,2′-bipy containing N5 and N6 are non-coplanar with a dihedral angle of 11.4(2)°. The 3,5-(NO2)2sal ligand is coordinated to Ni(II) atom via one oxygen atom of the carboxylate group (O2) and one oxygen atom from the phenolate group (O3). The carboxylate group of the 3,5-(NO2)2sal ligand is rotated relatively to the aromatic ring with a dihedral angle of 36.8(2)°. The adjacent mononuclear units are further connected to each other by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds formed between the NO2 groups of 3,5-(NO2)2sal ligands and phenyl hydrogens of 2,2′-bipy.
Acknowledgement
We thank the Foundation of Education Department of Fujian Province, PR China (No. JB12220, JB12214, JK2012048).
References
1 Khalaji, A. D.; Ghoran, S. H.; Rohlicek, J.; Dusek, M.: Characterization and crystal structure of a 17-membered macrocyclic Schiff base compound MeO-sal-pn-bn. J. Struct. Chem. 56 (2015) 259–265.10.1134/S0022476615020080Search in Google Scholar
2 Vieira, B. J.; Coutinho, J. T.; Dias, J. C.; Nunes, J. C.; Santos, I. C.; Pereira, L. C.; Waerenborgh, J. C.: Crystal structure and spin crossover behavior of the [Fe(5-Cl-qsal)2][Ni(dmit)2]⋅2CH3CN complex. Polyhedron 85 (2015) 643–651.10.1016/j.poly.2014.09.038Search in Google Scholar
3 Varughese, S.; Pedireddi, V. R.: Hydrogen bond mediated open-frame networks in coordination polymers: supramolecular assemblies of Pr (III) and 3, 5-dinitro-4-methylbenzoic acid with aza-donor compounds. Chem. Commun. 14 (2005) 1824–1826.10.1039/b417754aSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
4 Ye, B. H.; Tong, M. L.; Chen, X. M.: Metal-organic molecular architectures with 2,2′-bipyridyl-like and carboxylate ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 249 (2005) 545–565.10.1016/j.ccr.2004.07.006Search in Google Scholar
5 Pedireddi, V. R.; Varughese, S.: Solvent-dependent coordination polymers: cobalt complexes of 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid and 3,5-dinitro-4-methylbenzoic acid with 4,4′-bipyrdine. Inorg. Chem. 43 (2004) 450–457.10.1021/ic0349499Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6 He, X.; Bi, M. H.; Ye, K. Q.; Fang, Q. R.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J. N.; Wang, Y.: Self-assembly of a 1D helical manganese coordination polymer and a tetranuclear lanthanum complex with 1, 10-phenanthroline and 3, 5-dinitrosalicylato dianion. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 9 (2006) 1165–1168.10.1016/j.inoche.2006.07.017Search in Google Scholar
7 Wen, D. C.; Liu, S. X.; Ribas, J.: Syntheses, structures and magnetic property of two copper complexes with cyclic dimer and 2D herringbone-like network built from helical motif. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 10 (2007) 661–665.10.1016/j.inoche.2007.02.025Search in Google Scholar
8 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9 TeXan: Texray Structural Analysis Package Molecular Structure Corp. The Woodlands, TX, (1998).Search in Google Scholar
©2017 Guixiang Xie et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16

