Abstract
C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 6.0166(6) Å, b = 15.2792(14) Å, c = 11.5833(12) Å, β = 100.295(1)°, V = 1047.70(18) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0412, wRref(F2) = 0.0884, T = 298 K.
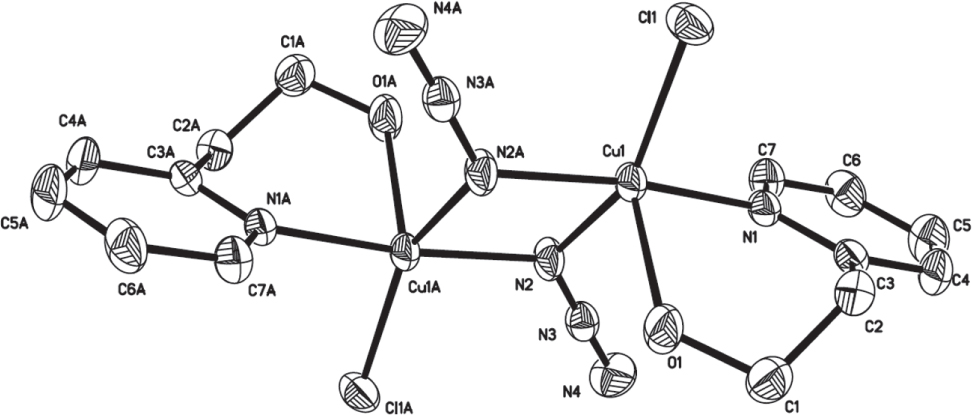
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Black block |
| Size: | 0.41 × 0.18 × 0.15 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 23.1 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 50°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 5221, 1842, 0.048 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1331 |
| N(param)refined: | 127 |
| Programs: | SHELX [7] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.16199(8) | 0.57579(3) | 0.55314(4) | 0.03893(19) |
| Cl1 | 0.39785(18) | 0.65706(8) | 0.46611(9) | 0.0557(3) |
| N1 | 0.3382(5) | 0.5948(2) | 0.7136(3) | 0.0383(8) |
| N2 | 0.0393(6) | 0.4569(2) | 0.5965(3) | 0.0475(9) |
| N3 | 0.0188(6) | 0.4345(2) | 0.6939(3) | 0.0420(8) |
| N4 | 0.0068(7) | 0.4122(3) | 0.7863(3) | 0.0672(12) |
| O1 | −0.1133(5) | 0.6531(2) | 0.6040(3) | 0.0709(10) |
| H1 | −0.2567 | 0.6469 | 0.5589 | 0.085* |
| C1 | −0.0892(8) | 0.7109(3) | 0.6993(4) | 0.0590(13) |
| H1A | −0.1360 | 0.6827 | 0.7660 | 0.071* |
| H1B | −0.1828 | 0.7622 | 0.6788 | 0.071* |
| C2 | 0.1546(7) | 0.7369(3) | 0.7294(4) | 0.0520(12) |
| H2A | 0.1677 | 0.7851 | 0.7845 | 0.062* |
| H2B | 0.2020 | 0.7581 | 0.6587 | 0.062* |
| C3 | 0.3144(7) | 0.6658(3) | 0.7813(3) | 0.0410(10) |
| C4 | 0.4407(8) | 0.6732(3) | 0.8924(4) | 0.0583(13) |
| H4 | 0.4242 | 0.7223 | 0.9376 | 0.070* |
| C5 | 0.5904(9) | 0.6089(4) | 0.9369(4) | 0.0685(15) |
| H5 | 0.6743 | 0.6139 | 1.0122 | 0.082* |
| C6 | 0.6156(8) | 0.5372(3) | 0.8694(4) | 0.0598(13) |
| H6 | 0.7173 | 0.4930 | 0.8972 | 0.072* |
| C7 | 0.4857(7) | 0.5328(3) | 0.7592(4) | 0.0483(11) |
| H7 | 0.5011 | 0.4838 | 0.7136 | 0.058* |
Source of material
All reagents and solvents were of high purity grade and were purchased from commercial sources and received unless noted otherwise. To a methanolic solution (30 mL) of 2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol (224 mg, 2.04 mmol) and copper(II) acetate monohydrate (75 mg, 1.02 mmol), a methanol solution (10 mL) of NaN3 (99.12 mg, 1.02 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature for several days. Dark green crystals formed, and were filtered off and dried in vacuo. Yield 80%, Combustion Anal. Calc. for Cu2C14H18Cl2N8O2: C, 31.83; H, 3.43; N, 21.21. Found: C, 31.78; H, 3.40; N, 21.19.
Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C).
Discussion
A large number of dinuclear copper complexes have been reported recently as model compounds for the active sites of biological metalloenzymes. The best-investigated binuclear proteins are hemocyanin, and tyrosinase or catechol oxidase.
As shown in figure, the Cu atom exhibits a tetrahedral coordination geometry with basal positions occupied by one nitrogen atom of azido group, one oxygen atom and one nitrogen atom of the organic ligand, and one chlorine atom. The three nitrogen atoms of the azido group are as expected nearly collinear (177.6°). The azido group makes an average angle Cu—N—N of 126.49°. The bond lengths between the Cu atom and the nitrogen atoms of the two coordinating azido groups are 1.993(3) and 2.056(3) Å, respectively. The bonding distance between the Cu atom and the nitrogen atom of the pyridinyl nitrogen atom is 1.990(3) Å. The Cu—O bond length is 2.199(3) Å. The Cu—Cl bond length is 2.4545(11) Å.
Each hydroxy group of the neutral organic ligand forms a OH ⋯Cl hydrogen bond to an adjacent complex, creating a chain structure along the [100] direction.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Key Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities, Henan Province (Nos. 16A150001, 16A430012).
References
1 Hanson, K.; Calin, N.; Bugaris, D.; Scancella, M.; Sevov, S. C.: Reversible repositioning of zinc atoms within single crystals of a zinc polycarboxylate with an open-framework structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 (2004) 10502–10503.10.1021/ja0474190Search in Google Scholar
2 Kitagawa, S.; Uemura, K.: Dynamic porous properties of coordination polymers inspired by hydrogen bonds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 34 (2005) 109–119.10.1039/b313997mSearch in Google Scholar
3 Zeng, M. H.; Feng, X. L.; Chen, X. M.: Crystal-to-crystal transformations of a microporous metal–organic laminated framework triggered by guest exchange, dehydration and readsorption. Dalton Trans. (2004) 2217–2223.10.1039/B404483PSearch in Google Scholar
4 Kitajima, N.; Moro-Oka, Y.: Copper-dioxygen complexes. inorganic and bioinorganic perspectives. Chem. Rev. 94 (1994) 737–757.10.1021/cr00027a010Search in Google Scholar
5 Ryan, S.; Adams, H.; Fenton, D. E.; Becker, M.; Schindler, S.: Intramolecular ligand hydroxylation: mechanistic studies on the reaction of a copper(I) Schiff base complex with dioxygen. Inorg. Chem. 37 (1998) 2134–2140.10.1021/ic971010cSearch in Google Scholar
6 Fernandes, C.; Neves, A.; Bortoluzzi, A. J.; Mangrich, A. S.; Rentschler, E.; Azpoganicz, B.; Schwingel, E.: A new dinuclear unsymmetric copper(II) complex as model for the active site of catechol oxidase. Inorg. Chim. Acta 320 (2001) 12–21.10.1016/S0020-1693(01)00470-4Search in Google Scholar
7 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
©2017 Wang Xin et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16

