Abstract
C16H13N2O9.5, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 7.3757(4) Å, b = 7.7827(5) Å, c = 15.2903(10) Å, α = 79.473(4)°, β = 82.927(4)°, γ = 72.069(4)°, V = 818.92(9) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0444, wRref(F2) = 0.1317, T = 298 K.
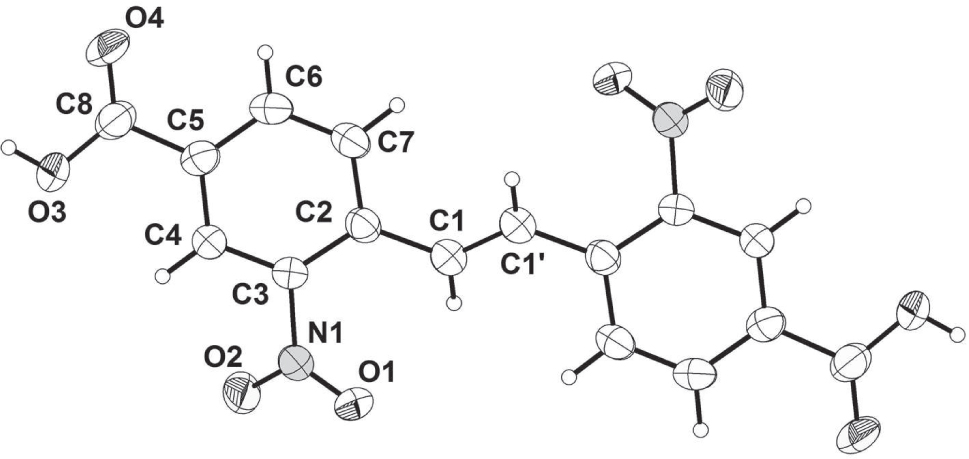
One of the two crystallographically independent molecules of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details of the measurement method and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.45 × 0.30 × 0.21 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.3 cm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 50°, 98.2% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 4108, 2841, 0.027 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2130 |
| N(param)refined: | 260 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], Bruker programs [2], DIAMOND [3] |
Source of material
Put 45 mL of pure ethanol into a 250 mL beaker, slowly add 5.74 g KOH (0.0970 mol) and dissolve it. Then add 5.00 g 4-(chloromethyl)-3-nitrobenzoic acid (0.0230 mol). A brown precipitate should immediately emerge, which is the potassium salt of the target compound. Keep reacting at room temperature for about 45 min. Then apply vacuum filtration and dissolve the solid in about 70 mL H2O. Then add HCl to adjust the pH to 1 when the solid matter emerges. Recrystallization from tetrahydrofuran gives yellow crystals of the target compound with a 75% yield after oven dry. 1H-NMR (200 MHz; DMSO) δ = 7.62 (s, 2H); 7.89 (d, 2H); 8.52 (d, 2H); 9.06 (s, 2H)
Experimental details
The aromatic CH as well as the OH groups were idealized and refined using rigid groups (AFIX 43 and 83 options of SHELX program system [1]), with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O), respectively.
Comment
Photoconductive materials are characterized by an increase of their conductivity upon illumination [4], [5], [6]. It was believed that molecular alignment in the mesophase should bring about an intermolecular overlap of p-orbitals of the charge carriers convenient for charge transport properties [7], [8], [9]. This paper reports the crystal structure of a sanidic liquid crystal material based on a nitro group functionalized trans-stilbene dicarboxylate linker.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 0.1021(3) | 0.7725(2) | 0.29535(11) | 0.0403(5) |
| N2 | 0.6989(3) | 0.1090(2) | 0.38924(11) | 0.0424(5) |
| O1 | 0.1170(3) | 0.8345(2) | 0.36141(10) | 0.0552(5) |
| O2 | 0.0533(3) | 0.8676(2) | 0.22441(11) | 0.0688(6) |
| O3 | 0.4251(3) | 0.3417(2) | 0.07963(10) | 0.0617(5) |
| H3 | 0.484(4) | 0.292(4) | 0.0360(14) | 0.093* |
| O4 | 0.4451(3) | 0.0618(2) | 0.15212(11) | 0.0687(6) |
| O5 | 0.7291(4) | 0.0785(2) | 0.46809(11) | 0.0854(7) |
| O6 | 0.6843(3) | −0.0055(2) | 0.34846(12) | 0.0594(5) |
| O7 | 0.9385(2) | 0.3404(2) | 0.08215(9) | 0.0535(5) |
| O8 | 0.8693(3) | 0.6411(2) | 0.07617(9) | 0.0537(5) |
| H8 | 0.922(4) | 0.643(4) | 0.0250(10) | 0.081* |
| O9 | 0.6246(3) | 0.1829(3) | 0.94810(11) | 0.0669(5) |
| H9C | 0.6029 | 0.1108 | 0.9178 | 0.080* |
| H9D | 0.7234 | 0.1129 | 0.9732 | 0.080* |
| O10a | 0.9480(6) | −0.0041(5) | 0.0378(2) | 0.0668(10) |
| H10Ca | 0.9708 | 0.0955 | 0.0401 | 0.080* |
| H10Da | 0.9784 | −0.0641 | 0.0888 | 0.080* |
| C1 | −0.0049(3) | 0.5456(3) | 0.45883(12) | 0.0339(5) |
| H1 | −0.0829 | 0.6657 | 0.4505 | 0.041* |
| C2 | 0.1002(3) | 0.4687(3) | 0.37965(12) | 0.0310(5) |
| C3 | 0.1460(3) | 0.5744(2) | 0.30057(12) | 0.0304(4) |
| C4 | 0.2402(3) | 0.5022(3) | 0.22505(12) | 0.0319(5) |
| H4 | 0.2678 | 0.5780 | 0.1740 | 0.038* |
| C5 | 0.2921(3) | 0.3142(3) | 0.22760(13) | 0.0348(5) |
| C6 | 0.2474(3) | 0.2054(3) | 0.30447(14) | 0.0391(5) |
| H6 | 0.2829 | 0.0793 | 0.3064 | 0.047* |
| C7 | 0.1512(3) | 0.2806(3) | 0.37810(13) | 0.0382(5) |
| H7 | 0.1194 | 0.2044 | 0.4280 | 0.046* |
| C8 | 0.3954(3) | 0.2262(3) | 0.14919(14) | 0.0408(5) |
| C9 | 0.5110(3) | 0.4375(3) | 0.47404(12) | 0.0326(5) |
| H9 | 0.4669 | 0.3373 | 0.4969 | 0.039* |
| C10 | 0.6005(3) | 0.4472(3) | 0.38278(11) | 0.0280(4) |
| C11 | 0.6857(3) | 0.2936(3) | 0.34057(12) | 0.0296(4) |
| C12 | 0.7670(3) | 0.3025(3) | 0.25410(12) | 0.0302(4) |
| H12 | 0.8207 | 0.1971 | 0.2284 | 0.036* |
| C13 | 0.7666(3) | 0.4725(3) | 0.20650(12) | 0.0303(5) |
| C14 | 0.6806(3) | 0.6292(3) | 0.24518(12) | 0.0332(5) |
| H14 | 0.6788 | 0.7433 | 0.2131 | 0.040* |
| C15 | 0.5982(3) | 0.6154(3) | 0.33099(12) | 0.0318(5) |
| H15 | 0.5388 | 0.7218 | 0.3553 | 0.038* |
| C16 | 0.8639(3) | 0.4844(3) | 0.11530(12) | 0.0349(5) |
aOccupancy: 0.5.
This title crystal structure is only built up by the C16H10N2O8 molecules and water molecules, in which all bond lengths are in normal ranges. Both crystallographically independent organic molecules of the title structure have a crystallographic inversion center and adopts an E configuration with respect to the C = C bond (cf. the figure). In both molecules, the carboxyl groups are roughly coplanar with the ethene-1,2-diphenyl moieties. The bond lengths of the central C = C bond are 1.326(4) and 1.325(4) Å, respectively.
Acknowledgement
I acknowledge support for the publication fee by the Scientific Research Foundation of Yunnan Provincial Education Department No. 2016zzx107.
References
1 Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
2 Bruker: APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA, (2009).Search in Google Scholar
3 Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version3.2i. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany, (2012).Search in Google Scholar
4 Adam, D.; Schuhmacher, P.; Simmerer, J.; Häussling, L.; Siemensmeyer, K.; Etzbach, K. H.; Ringsdorf, H.; Haarer, D.: Fast photoconduction in the highly ordered columnar phase of a discotic liquid crystal. Nature 371 (1994) 141–143.10.1038/371141a0Search in Google Scholar
5 Haristoy, D.; Mery, S.; Heinrich, B.; Mager, L.; Nicoud, J. F.; Guillon, D.: Structure and photoconductive behaviour of a sanidic liquid crystal. Liq. Cryst. 27 (2000) 321–328.10.1080/026782900202769Search in Google Scholar
6 Doty, F. P.; Bauer, C. A.; Skulan, A. J.; Grant, P. G.; Allendorf, M. D.: Scintillating Metal-Organic Frameworks: a new class of radiation detection materials. Adv. Mater. 21 (2009) 95–101.10.1002/adma.200801753Search in Google Scholar
7 James, S. L.: Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 32 (2003) 276–288.10.1039/b200393gSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
8 Rowsell, J. L. C.; Yaghi, O. M.: Strategies for hydrogen storage in metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44 (2005) 4670–4679.10.1002/anie.200462786Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9 Bahr, D. F.; Reid, J. A.; Mook, W. M.; Bauer, C. A.; Stumpf, R.; Skulan, A. J.; Moody, N. R. ; Simmons, B. A.; Shindel, M. M.; Allendorf, M. D.: Mechanical properties of cubic zinc carboxylate IRMOF-1 Metal-Organic Framework crystals. Phys. Rev. B 76 (2007) 184106.10.1103/PhysRevB.76.184106Search in Google Scholar
©2017 Li Song et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2,5-diiodo-4-nitro-1H-imidazole hemihydrate, C6H4I4N6O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[μ2-2,2′-(1,3-phenylene)diacetato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ2-1,6-bis(2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)hexane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C32H34CdN4O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(2,2′-bipyridine-κN,N′)-(μ4-5,5′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)-bis(oxy)diisophthalato κ8O1,O2:O3,O4:O5,O6:O7,O8)manganese(II)], C21H21MnN2O7
- Crystal structure of poly-[(μ2-((1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)(μ2-4-tert-butyl-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)] monohydrate, C29H30CoN4O5
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-5-(oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene)-3-carbonitrile – ethanol (1/1), C21H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-benzyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylate, C19H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(1-benzyl-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-5-(4-nitrobenzylthio)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C25H19N5O3S
- Structure and photochromism of 1,2-bis[2-methyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-thienyl]-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-1-ene, C27H16Cl2F6S2
- The crystal structure of the Schiff base (E)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)aniline, C18H22N2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C10H14Br2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (bis(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′))-(3,5-dinitrosalicylato-κ2O,O′)nickel(II), C27H18N6NiO7
- Crystal structure of 1-(diethoxy phosphonomethyl) 2-benzoyl-3-chloro-2-cyclohexen-1-ol, C18H24ClO5P
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(1,3-benzimidazol-3-ium-1,3-diacetato-κO)copper(II) hemihydrate, C22H27CuN4O12.50
- Crystal structure of 1α,11-dihydroxyeremophil-9-en-8-one, C15H24O3
- Crystal structure of 1-ferrocenylsulfonyl-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, C16H13FeN3O2S
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-κ2N:N)-dichlorido-bis(μ2-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethan-1-ol-κ2O,N)dicopper(II), C14H18Cl2Cu2N8O2
- Crystal structure of (5,15-cis-bis(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-10-phenyl-20-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-porphyrinato)-(pyridine)-zinc(ii) pyridine solvate, C67H47N7O3Zn
- Crystal structure of (μ2-[2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene oxide-κ2O,P])-iodido copper(I), C44H32CuIOP2
- Crystal structure of 6,8-diphenyl-2-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(3H)-one, C27H20FNO
- Crystal structure of 5,11,17,23-tetra(tert-butyl)-25,26,27,28-tetrahexoxycalix[4]arene, C68H104O4
- Crystal structure of N,N′–bis(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxamide dihydrate, C18H20N6O4
- Crystal structure of a diaqua-bis(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)pyridine-κN)-bis(2-(4-carboxy-phenyl)acetato-κO]manganese(II), C40H36MnN10O10
- Crystal structure of 4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester, C21H25NO5
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,4′-(ethene-1,2-diyl)bis(3-nitrobenzoic acid) 1.5 hydrate, C16H13N2O9.5
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(furan-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-5-((4-fluorophenyl)diazenyl)-4-methylthiazole, C23H17F2N5OS
- Crystal structure of the co-crystalline adduct 4-((4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)methylamino)-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide - acetic acid (1/1), C21H24N4O4S ⋅ C2H4O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-((5-chlorobenzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)amino)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-3-ium tetraphenylborate, C33H29BClN5S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(3-ferrocenyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methanone, C21H14ClF3FeN2O
- Crystal structure of (S)-benzyl 3-(benzylcarba-moyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate, C25H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 5-acetyl-3-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)oxazolidin-2-one, C15H17FN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-perimidin-3-ium iodide, C19H16FIN2
- Crystal structure of methyl 1H-indole-2-carboxylate, C10H9NO2
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-[(dipropylamino)acetyl]-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C28H37N3O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propan-1-one, C13H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,9-dibromo-1,10-phenanthroline, C12H6Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-(adamantan-1-yl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C18H20FN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-bis((E)-7-oxo-4-(phenyldiazenyl)cyclohepta-1,3,5-trien-1-olato)-κ2O,O′)-bis(pyridine-κN)cobalt(II), C36H28CoN6O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methyl-3-phenylthiazol-2(3H)-ylidene)malononitrile, C13H9N3S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-S-benzylisothiourea, C24H27ClN2S
- Crystal structure of chlorido{[3-(η5-cyclopenta-dienyl)-2,2,3-trimethyl-1-phenylbutylidene] azanido-κN}[η2(N,O)-N,N-dimethylhydroxylaminato]titanium(IV), C20H27ClN2OTi
- Crystal Structure of 1,1′-dimethyl-[4,4′-bipyridine]-1,1′-diium tetrachloridozincate(II), C12H14Cl4N2Zn
- Crystal structure of 5-nitro-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)benzaldehyde, C11H12N2O3
- Crystal structure of 2,3-diphenyl-1-(morpholin-4-ylacetyl)-1,3-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one, C26H31N3O3
- Crystal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-benzo[c]chromene-1,6(2H)-dione, C15H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis(2-(2-hydroxymethyl)pyridine-κ2N,O)-bis(pivalato-κO)nickel(II), C22H32N2NiO6
- Crystal structure of (1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II) trihydrate, C20H20N6O7Mn
- The crystal structure of 3-aminopropan-1-aminium iodide, C3H11N2I
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4 carboxylate, C12H12ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-((1Z,1′Z)-2,2′-(2,5-diethoxy-1,4-phenylene)bis(ethene-2,1-diyl))dipyridine, C24H24N2O2
- Crystal structure of (16S)-12,16-epoxy-11,14-dihydroxy-17(15/16)-abeo-3a,18-cyclo-8,11,13-abietatrien-7-one, C20H24O4
- Crystal structure of aquadichlorido(2,4,6-tri-2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine-κ3N,N′,N′′)nickel(II) monohydrate, C18H16Cl2N6NiO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[dichlorido-(μ-ethane-1,2-diyl-bis-(pyridyl-4-carboxylate-κN:N′)mercury(II)], C15H14Cl2HgN2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-acetamido-5-chlorbenzoate, C10H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-3,3-dimethylacrylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(2-aminopyrimidine-κN) dicopper(II), C28H38Cu2N6O8
- Crystal structure of 3-amino-8-methoxy-1-phenyl-1H-benzo[f]chromene-2-carbonitrile, C21H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4-(2-ammonioethyl)morpholin-4-ium dichloride monohydrate, C6H18Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-((5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethanone O-benzyl oxime, C22H19BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-(dimethylamino)-2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol monohydrate, C15H20FN7O2
- Crystal structure of 4-bromo-2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C9H7BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethyl-1,3-cyclopentadiene, C10H16

