Abstract
Our commentary is focused on three studies that used microRNA overexpression methods for directed differentiation of stem cells into insulin-producing cells. Islet transplantation is the only cell-based therapy used to treat type 1 diabetes mellitus. However, due to the scarcity of cadaveric donors and limited availability of good quality and quantity of islets for transplant, alternate sources of insulin-producing cells are being studied and used by researchers. This commentary provides an overview of distinct studies focused on manipulating microRNA expression to optimize differentiation of embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells into insulin-producing cells. These studies have used different approaches to overexpress microRNAs that are highly abundant in human islets (such as miR-375 and miR-7) in their differentiation protocol to achieve better differentiation into functional islet beta (β)-cells.
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) mellitus is characterized by immune-mediated destruction of insulin-producing β-cells in the pancreatic islets [1]. The management plan for T1D consists of exogenous insulin injections or continuous glucose monitors with/without insulin pumps. Although effective, these treatment options fail to completely recapitulate the true biology of a healthy pancreas to control real-time fluctuations in circulating glucose. Currently, this can be achieved only through total pancreas or islet transplantation, which replace the lost insulin-producing β-cells. Islet transplantation has developed over the years to be the only cell-based therapy to treat T1D. In 2000, Shapiro et al. [2] described a procedure for the transplantation of allogeneic islets from the human cadaveric pancreas (The Edmonton Protocol) in recipients with T1D. This study demonstrated that patients with T1D can achieve independence from exogenous insulin administration with excellent metabolic control when glucocorticoid-free immunosuppression is combined with the infusion of an adequate islet mass. While the results are very promising, this technique will continue to be limited by low numbers of cadaveric donors and the restricted yield of good quality and quantity of islets for transplantation. This has led researchers to pursue alternative cell sources with the potential to differentiate into insulin-producing cells for transplantation [3,4]. This targeted differentiation has been achieved via multiple different protocols including the application of growth factors and the use of small molecules as signaling inducers as well as recapitulating stepwise process of differentiation of embryonic definitive endoderm into fully differentiated β-cells. In this commentary, we describe three studies where microRNAs (miRs) are used for direct differentiation of stem cells toward β-cells.
In pursuit of an alternative source of islet cells for transplantation, Lahmy et al. [5] chose to explore the differentiation capacity of the human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) into an insulin-producing phenotype utilizing lentiviral-mediated overexpression of a single miR. MiRs are small, noncoding RNA molecules that are now recognized as one of the regulators of gene expression, fine-tuning several pathological and physiological processes. The authors presented a novel strategy to generate insulin-producing cells in vitro using miR-375 overexpression in the absence of additional extrinsic factors. MiR-375 is known to be one of the most abundant miRs in human islets and is involved in regulating insulin secretion, β-cell development, and proliferation [6]. The authors generated hiPSC lines from human foreskin fibroblasts and then transduced those hiPSCs using lentiviral particles containing miR-375 (pCDH-375) and noncoding controls (pCDH-NCs) at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 25. Differentiated miR-375 overexpressing cells reorganized themselves into small bud-like aggregates, demonstrated dual immune-positive labels for insulin and C-peptide, and glucose-responsive insulin secretion following a standard glucose challenge protocol. Cells transduced to overexpress miR-375 had higher transcript levels of β-cell-related genes, including HNF4α, PDX1, NKX6.1, and PAX6, suggesting that miR-375 upregulation alone could facilitate the differentiation of hiPSCs into an islet-like phenotype. The authors also demonstrated that overexpression of miR-375 can induce directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) into insulin-producing pancreatic lineage [7].
Similar to miR-375, miR-7 is also one of the most abundant endocrine miRs in rodents [8] and human islets [9]. In a recent study, Lopez-Beas et al. [10] overexpressed miR-7 in (HS181) hESCs and differentiated them into a β-cell-like phenotype with an established multistep differentiation protocol [11]. The authors initially performed a microarray analysis to detect differentially expressed miRs in hESCs (that are undifferentiated, differentiated, or spontaneously differentiated), human islets, as well as human pancreas. They confirmed that miR-7 is the most abundant miR in human islets. The miR expression analysis during different stages of differentiation of hESCs into insulin-producing β-like cells was performed using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). MiR-7 was found to be abundant at very early stages of differentiation with a gradual reduction in the expression at later stages of directed differentiation. The fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) method also validated miR-7 expression to be high across differentiating hESCs in the early stages and reducing later. The authors observed that the β-like cells obtained after directed differentiation of hESCs with their protocol do not have high expression of miR-7 as is seen in the human islets. Therefore, they extrinsically increased miR-7 expression during the differentiation process to understand if that would enhance pancreatic differentiation of hESCs.
A scrambled control and miR-7 mimic were transiently transfected into the differentiating hESCs at day 14 of the multistep differentiation protocol and were incubated for 24 h in the differentiation medium. A 100 nM concentration of miR-7 mimic was found to be optimum with a significant increase in the miR-7 levels as well as an increase in insulin transcripts. The expression of pancreatic transcription factors, FOXA2 and PDX1, was also significantly increased in miR-7 mimic-transfected cells compared to that in the controls.
To examine the insulin secretion potential, differentiated cells were incubated under different glucose conditions (2 and 20 mM) with or without the membrane depolarizing agent potassium chloride (KCl; 30 mM). The miR-7 mimic transfected cells demonstrated increased insulin secretion in response to the increasing glucose concentration compared to scramble/mock control and anti-miR-7 transfected cells. Double immunofluorescence and MetaMorph-based quantitative analysis also confirmed that higher levels of insulin and C-peptide were observed after the differentiation of miR-7 mimic transfected hESCs.
The aforementioned studies [5,7,10] presented a novel strategy to generate insulin-producing cells in vitro by miR overexpression. Immunocytochemistry, gene expression profile, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion assays confirmed that miR overexpressing cells share characteristics with those of mature islets. These studies illustrate the potential of miR manipulations on directed differentiation of stem cells into endocrine pancreatic lineage.
To generate more β-cells for transplantation, many groups around the world have explored methods to reliably induce the differentiation of progenitor or stem cell populations into endocrine pancreatic cells, using a variety of techniques. These include the use of growth/differentiation factors in islet-derived cells [12] or stepwise application of small molecules in embryonic stem cells [13,14]. An alternative to culture-based methods to induce differentiation is direct gene expression intervention. When Pdx1, Ngn3 (also referred to as Neurog3), and MafA are reexpressed in an experimental context, these three primary factors have been shown to induce the differentiation of exocrine pancreatic acinar cells into functional insulin-producing cells, indistinguishable from endogenous islet β-cells [15]. Unfortunately, currently, there are no small molecules or pharmaceuticals capable of inducing the expression of Pdx1 or Ngn3, rendering genetic manipulation as the only available technique.
Lahmy et al. [5,7] and Lopez-Beas et al. [10] have explored an alternative to direct transcription factor manipulation. These studies have demonstrated that the overexpression of miR (miR-375 or miR-7) has the potential to drive the differentiation process to endocrine pancreatic lineage. It will be interesting to understand the combined effect of overexpression of multiple β-cell-specific miRs in the differentiation of stem/progenitor cells. The miRs associated with pancreas development, biology, and disease have been investigated and thoroughly reviewed [16,17], offering a wealth of potential miRs for overexpression experiments. The success of these studies represents a proof of concept application for miR-based approaches to alter cell identity in cell replacement therapies. This technique could also be applied to a variety of other cell types, disease states, and clinical applications.
Stem cell differentiation to generate β-cells suitable for clinical transplantation to treat T1D has been studied for more than a decade and has shown substantial progress over the years. It still faces many challenges and requires more optimization and refinement. Current protocols [13,14] can be further fine-tuned by using regulatable miRs/other noncoding RNAs or miR inhibitors at specific stages during the differentiation process to closely resemble a true β-cell (Figure 1). Identification of an approach to generate β-cells in vitro would highly benefit people with T1D by making β-cell transplantation readily available as a treatment.
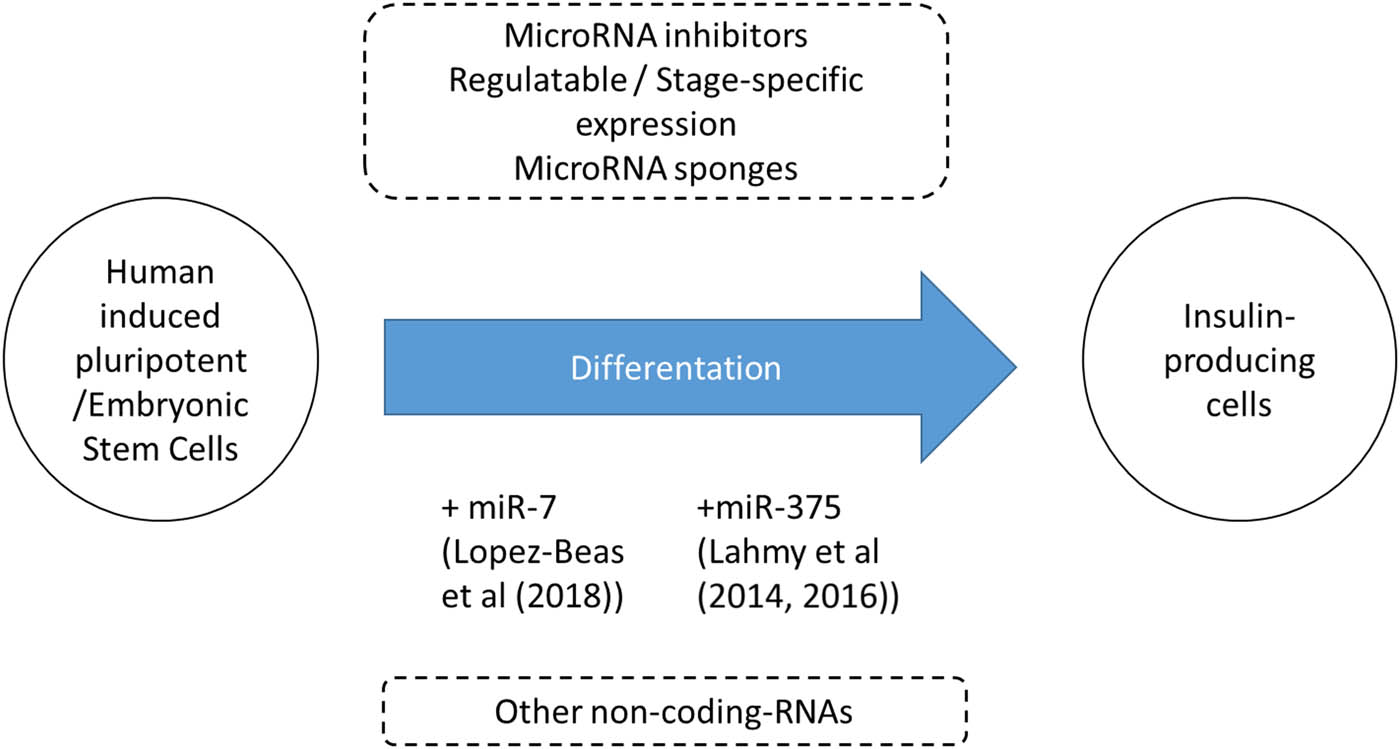
This commentary describes distinct studies (by Lopez-Beas et al and Lahmy et al) that used miR-7 and miR-375 for directed differentiation of stem cells into insulin-producing cells respectively. While innovative, other approaches (in dashed boxes) such as miR inhibitors or other noncoding RNAs can also be used in the future to enhance the β-cell differentiation process.
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Bluestone JA, Herold K, Eisenbarth G. Genetics, pathogenesis and clinical interventions in type 1 diabetes. Nature. 2010;464(7293):1293–300.10.1038/nature08933Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Shapiro AM, Lakey EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(4):230–8.10.1056/NEJM200007273430401Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Sahu S, Tosh D, Hardikar AA. New sources of beta-cells for treating diabetes. J Endocrinol. 2009;202(1):13–6.10.1677/JOE-09-0097Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Gangaram-Panday ST, Faas MM, de Vos P. Towards stem-cell therapy in the endocrine pancreas. Trends Mol Med. 2007;13(4):164–73.10.1016/j.molmed.2007.02.002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Lahmy R, Soleimani M, Sanati MH, Behmanesh M, Kouhkan F, Mobarra N. MiRNA-375 promotes beta pancreatic differentiation in human induced pluripotent stem (hiPS) cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(4):2055–66.10.1007/s11033-014-3054-4Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Eliasson L. The small RNA miR-375 – a pancreatic islet abundant miRNA with multiple roles in endocrine beta cell function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017;456:95–101.10.1016/j.mce.2017.02.043Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Lahmy R, Soleimani M, Sanati MH, Behmanesh M, Kouhkan F, Mobarra N. Pancreatic islet differentiation of human embryonic stem cells by microRNA overexpression. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(6):527–34.10.1002/term.1787Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Bravo-Egana V, Rosero S, Molano RD, Pileggi A, Ricordi C, Domínguez-Bendala J, et al. Quantitative differential expression analysis reveals miR-7 as major islet microRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;366(4):922–6.10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.12.052Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Joglekar MV, Joglekar VM, Hardikar AA. Expression of islet-specific microRNAs during human pancreatic development. Gene Expression Patterns. 2009;9(2):109–13.10.1016/j.gep.2008.10.001Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Lopez-Beas J, Capilla-González V, Aguilera Y, Mellado N, Lachaud CC, Martín F, et al. miR-7 modulates hESC differentiation into insulin-producing beta-like cells and contributes to cell maturation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;12:463–77.10.1016/j.omtn.2018.06.002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Pezzolla D, López-Beas J, Lachaud CC, Domínguez-Rodríguez A, Smani T, Hmadcha T, et al. Resveratrol ameliorates the maturation process of beta-cell-like cells obtained from an pptimized differentiation protocol of human embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119904.10.1371/journal.pone.0119904Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Gershengorn MC, Hardikar AA, Wei C, Geras-Raaka E, Marcus-Samuels B, Raaka BM. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition generates proliferative human islet precursor cells. Science. 2004;306(5705):2261–4.10.1126/science.1101968Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Rezania A, Bruin JE, Arora P, Rubin A, Batushansky I, Asadi A, et al. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(11):1121–33.10.1038/nbt.3033Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Pagliuca FW, Millman JR, Gürtler M, Segel M, Van Dervort A, Ryu JH, et al. Generation of functional human pancreatic beta cells in vitro. Cell. 2014;159(2):428–39.10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.040Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Zhou Q, Brown J, Kanarek A, Rajagopal J, Melton DA. In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine cells to beta-cells. Nature. 2008;455(7213):627–32.10.1038/nature07314Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Williams MD, Mitchell GM. MicroRNAs in insulin resistance and obesity. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012;484696.10.1155/2012/484696Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Joglekar MV, Parekh VS, Hardikar AA. Islet-specific microRNAs in pancreas development, regeneration and diabetes. Indian J Exp Biol. 2011;49(6):401–8.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2020 Michael D. Williams et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway

