Abstract
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has become one of the most popular methods for the rapid and cost-effective detection of clinical pathogenic microorganisms. This study aimed to evaluate and compare the diagnostic performance of MALDI-TOF MS with that of conventional approaches for the direct identification of pathogens from urine samples. A systematic review was conducted based on a literature search of relevant databases. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR) and area under the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of the combined studies were estimated. Nine studies with a total of 3920 subjects were considered eligible and included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity was 0.85 (95% CI 0.79-0.90), and the pooled specificity was 0.93 (95% CI 0.82-0.97). The PLR and NLR were 11.51 (95% CI 4.53-29.26) and 0.16 (95% CI 0.11-0.24), respectively. The area under the SROC curve was 0.93 (95% CI 0.91-0.95). Sensitivity analysis showed that the results of this meta-analysis were stable. MALDI-TOF MS could directly identify microorganisms from urine samples with high sensitivity and specificity.
1 Introduction
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common clinical infectious diseases and are also a major cause of hospital-acquired infections [1,2]. The clinical symptoms of UTIs range from simple cases such as cystitis to severe cases such as uroseptic shock. In addition, the etiology of UTIs varies, although Escherichia coli is the leading causative agent, and pathogen resistance to common antibiotics largely depends on the geographical location [3]. Currently, the definitive diagnosis of urinary tract infections relies on urine culture [4]. Typical laboratory diagnosis of a UTI requires culture of the pathogen for 18-48 hours, and antibiotic susceptibility testing results require an additional 24-48 hours [5]. Before a final diagnosis is obtained, the UTI patient may be treated empirically with an inappropriate antimicrobial therapy, which could lead to a higher mortality rate [6]. Hence, the rapid and correct identification of pathogens from urine samples is urgent and important.
In recent years, protein analysis based on the technique matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has been implemented and is known as a rapid and reliable method for bacterial identification [7]. Several institutions have applied this method to identify bacteria in conjunction with antibiotic stewardship, which aids in providing timely antibiotic therapy and decreasing unnecessary antibiotic use [8, 9, 10]. In light of its promise, MALDI-TOF MS technology was described as “a revolution in clinical microbiology” [11] . Currently, four main commercial systems are in more popular use worldwide: the MALDI Biotyper (Bruker Daltonics, Germany), the Vitek MS (bioMérieux, France) ,Shimadzu and Applied Biosystems [12,13]. Each system has its own characteristics. Many studies have reported the direct detection and identification of bacterial pathogens from urine samples using MALDI-TOF MS [14, 15]. However, these studies only included a few strains, and the results are somewhat inconsistent.
Therefore, the present work aimed to analyze and compare the performance of MALDI-TOF MS with that of common methods for the diagnosis of pathogens from urine samples by performing a meta-analysis that synthesized large amounts of data to improve the reliability of the results.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
We systematically searched original papers published in PubMed, Embase,Web of Science, and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases. These databases were queried with the following keywords and subject terms: “maldi” or “Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption Ionization”, “urine” or “urinary tract infections” or “infection”, and “identification”. Disagreements were resolved by consultation with a third researcher. To obtain relevant studies, the articles were first screened by title and abstract; then, full articles were further evaluated. The search was limited to publications in Chinese or English. We searched the databases for relevant articles published from inception to March 31, 2018.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies evaluating and comparing the accuracy of MALDI-TOF MS with that of routine identification methods for the identification of clinical pathogens in urinary tract infections were considered eligible for the meta-analysis. Typically, routine identification methods included the Vitek II system, API system, MicroScan WalkAway system or other routine biochemical tests and/or 16S rRNA sequencing (molecular biology). We required sufficient information to construct 2Í2 contingency tables. We contacted the authors for additional data for analysis if needed.
We also applied the following exclusion criteria: (i) studies that did not investigate urinary tract infections; (ii) studies lacking urine specimens; (iii) studies lacking reference methods, a comparator method or gold standard; and (iv) studies identifying clinical pathogens by mass spectrometry methods other than MALDI-TOF MS.
2.3 Data extraction
Two reviewers (MT and JY) independently extracted pertinent data from each study. Any inconsistencies were resolved in a consensus meeting or through discussion with the third author (YL). The quality of eligible studies was assessed by using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS) 2 questionnaire [16]. The following data were included: first author, year of publication, country, number of patients, MALDI-TOF MS system, TP (true positive), FP (false positive), FN (false negative), and TN (true negative), and the method of specimen handling.
2.4 Statistical analysis
We adopted the recommended standard methods for a meta-analysis of diagnostic research evaluations [17]. Analyses were performed using STATA version 12.0. To obtain accurate and objective results, we defined the following terms used to assess the sensitivity and specificity of MALDI-TOF MS identification: true positive: the MALDI-TOF MS and culture results were consistent, and only one microorganism was isolated in culture; false positive: the MALDI-TOF MS and culture results differed; false negative: a positive culture in the absence of MALDI-TOF MS identification; and true negative: no MALDI-TOF MS identification of samples with a negative culture.
The summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve was plotted to depict a simultaneous non-linear relationship between sensitivity and specificity and calculated to evaluate the overall diagnostic performance of MALDI-TOF MS. Statistical heterogeneity was tested through the Q statistic and the inconsistency index (I2) (a P value of Q<0.05 or I2 >50% was considered the threshold indication of heterogeneity). The source of heterogeneity was further investigated by using sensitivity analysis that ascertained whether the results were stable.
Publication bias was determined by performing Deek’s funnel plot asymmetry test. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05 or an asymmetric funnel plot.
3 Results
3.1 Results of the systematic literature search
A total of 298 studies were retrieved by searching the indicated databases. After reviewing titles and/or abstracts, we excluded 247 articles. We further excluded 42 studies based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Finally, 9 studies were considered eligible and used in the meta-analysis (Figure 1).
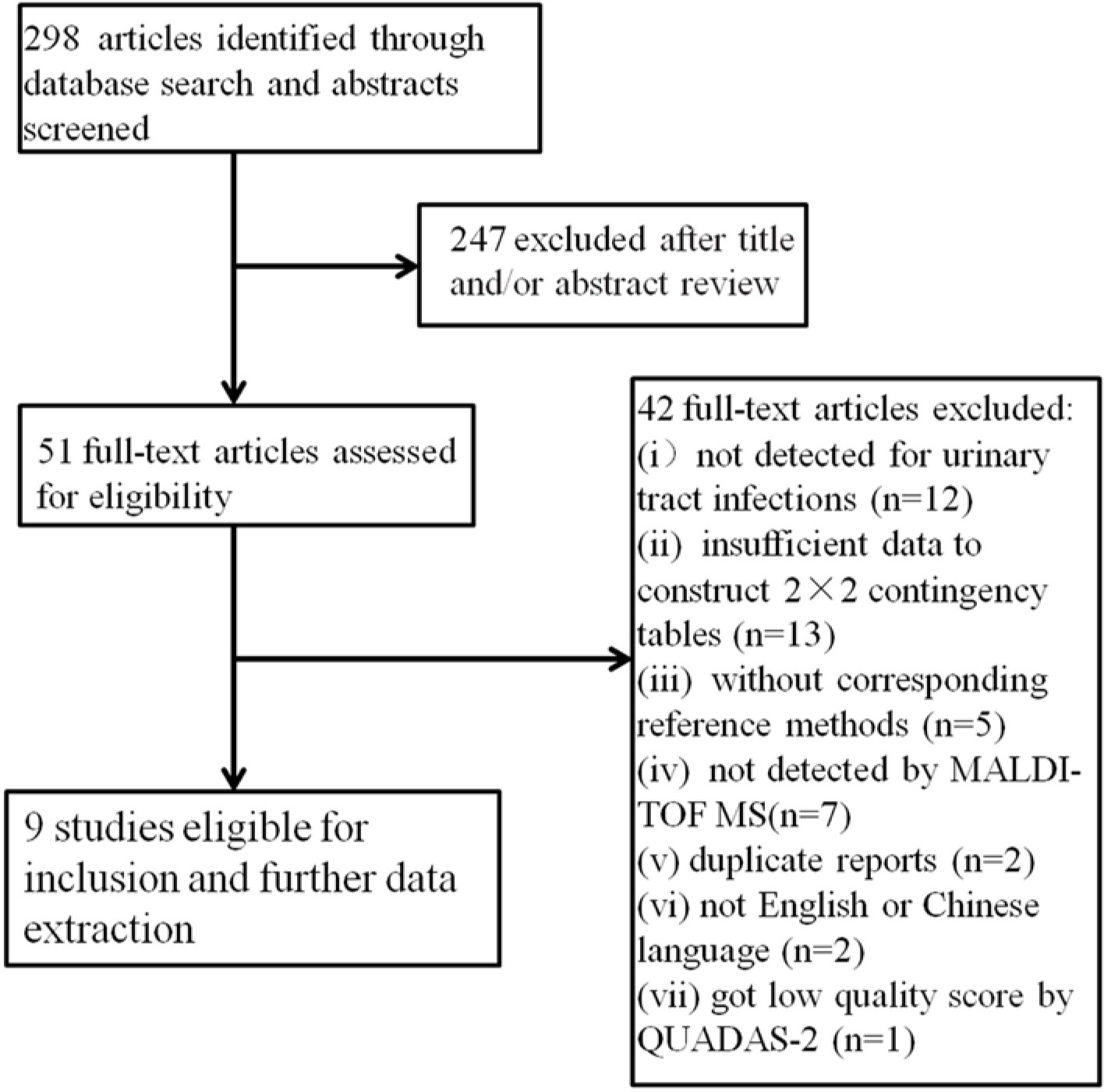
Flowchart describing the systematic literature search and study selection process for the meta-analysis.
3.2 Study characteristics
The main characteristics of the enrolled eligible studies are shown in Table 1. These studies originated from 5 countries and had a total of 3920 subjects. The most common reference method for pathogen identification was a biochemistry test after incubating for 18-48 hours. Among the included articles, six studies [18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23] reported on the identification performance of the Biotyper system, and the remaining three studies [24, 25, 26] reported on the identification performance of the Vitek MS system.
Main characteristics of the enrolled studies
| Author | Year | Country | N1[a] | N2[b] | N | TP | FP | FN | TN | system | specimen handling[c] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferreira (18) | 2010 | Spain | 260 | 5 | 255 | 205 | 2 | 28 | 20 | MALDI Biotyper | ICM and PEM |
| Ferreira (19) | 2011 | Spain | 238 | 0 | 238 | 193 | 11 | 14 | 20 | MALDI Biotyper | ICM and PEM |
| Wang (20) | 2013 | China | 1456 | 44 | 1412 | 387 | 8 | 35 | 982 | MALDI Biotyper | PEM |
| Burillo (21) | 2014 | Spain | 207 | 8 | 199 | 130 | 8 | 36 | 25 | MALDI Biotyper | PEM |
| Veron (24) | 2015 | France | 103 | 6 | 97 | 74 | 1 | 11 | 11 | VITEK MS | Short time culture |
| Haiko (25) | 2016 | Finland | 207 | 49 | 158 | 94 | 2 | 46 | 16 | VITEK MS | Short time culture |
| Zboromyrska (22) | 2016 | Spain | 140 | 36 | 104 | 89 | 0 | 12 | 3 | MALDI Biotyper | PEM |
| Huang (26) | 2017 | China | 1167 | 9 | 1158 | 295 | 69 | 47 | 747 | VITEK MS | PEM |
| Kitagawa (23) | 2017 | Japan | 142 | 0 | 142 | 90 | 0 | 43 | 9 | MALDI Biotyper | PEM |
N: the number of calculated indexes after removing contaminated or/and 2 morphology samples.
3.3 The methods of specimen handling
In order to obtain a certain amount of bacteria, the urine samples were often concentrated. The enrolled studies included roughly three methods for specimen handing prior to MALDI-TOF MS measurement (Table 1). Ferreira L et.al [19] described the general workflow of ICM (intact cell method)and PEM(protein extraction method).
3.4 Overall meta-analysis
Notably, current MALDI-TOF MS data software analysis is unable to reliably identify all microorganisms present in a mixture of microorganisms [27,28]. As such, contaminated urine samples often appear to produce insignificant results. Therefore, we calculated indexes after removing such samples. The pooled sensitivity was 0.85 (95% CI 0.79-0.90), and the pooled specificity was 0.93 (95% CI 0.82-0.97; Figure 2). The PLR and NLR were 11.51 (95% CI 4.53-29.26) and 0.16 (95% CI 0.11-0.24), respectively (Figure 3). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (SROC) was 0.93 (95% CI 0.91-0.95; Figure 4).
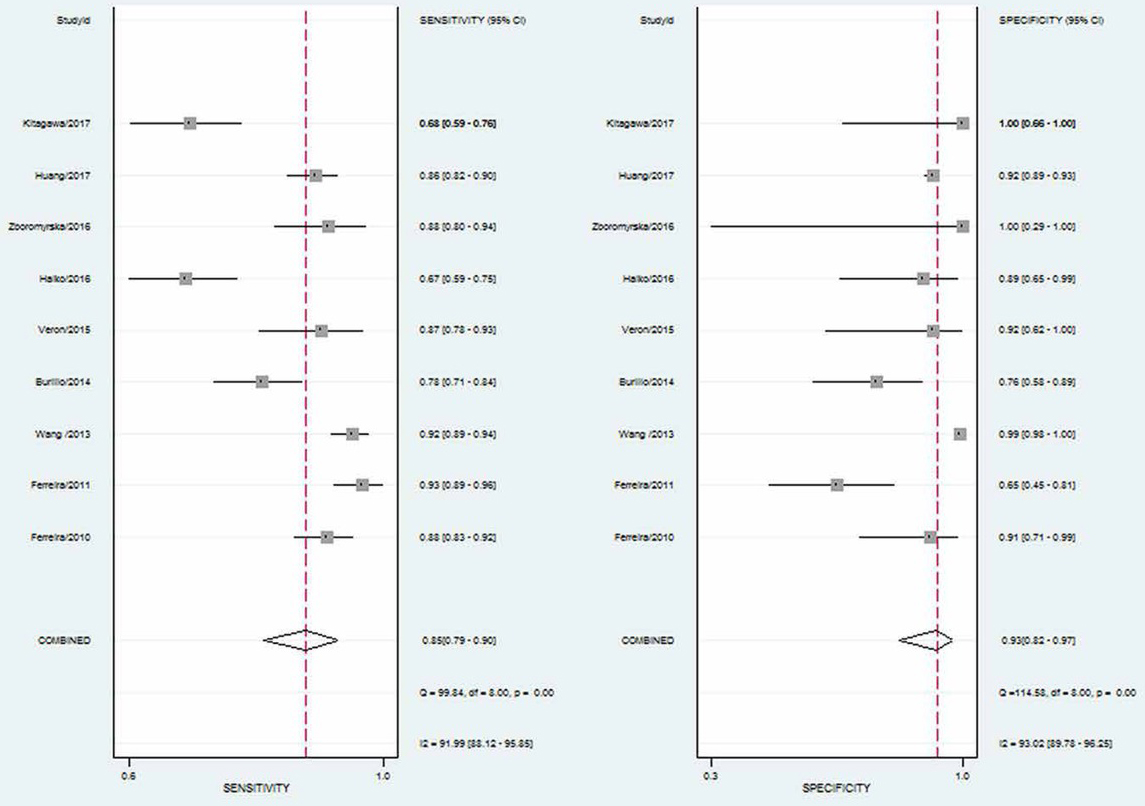
Forest plot of the pooled sensitivity and specificity of MALDI-TOF MS for identifying pathogens.
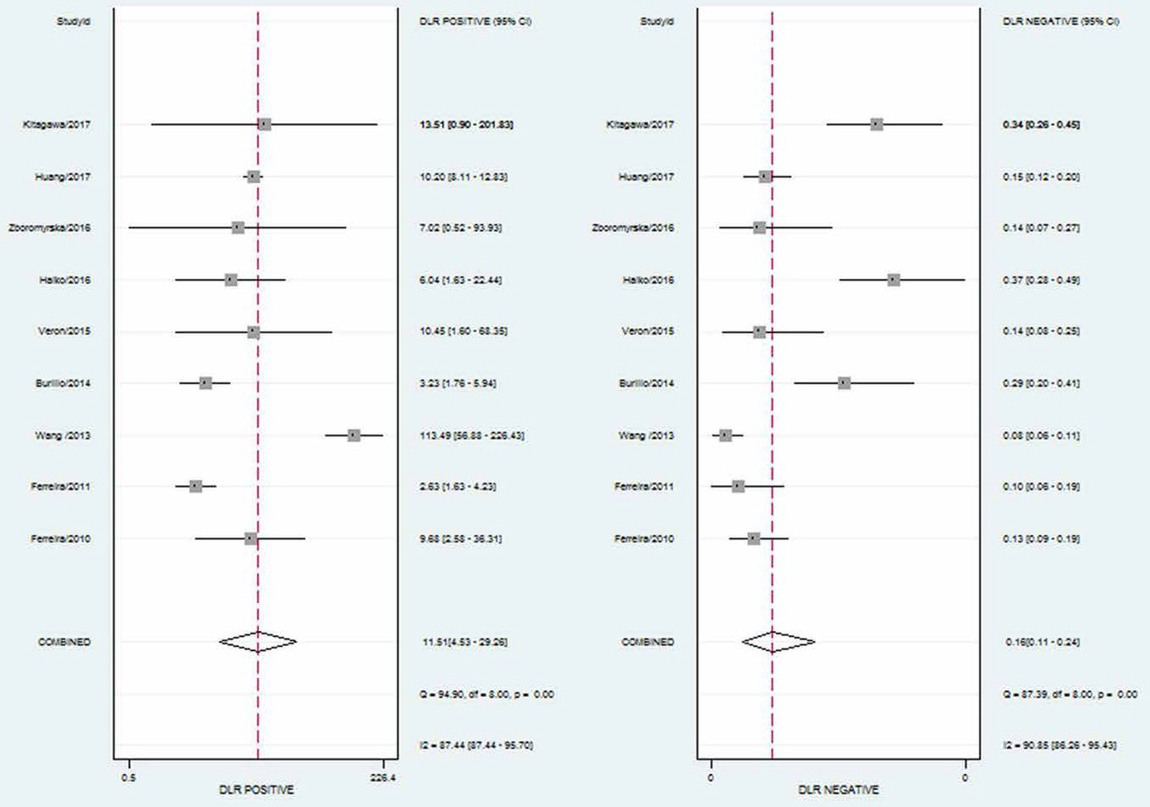
Forest plot of positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio.
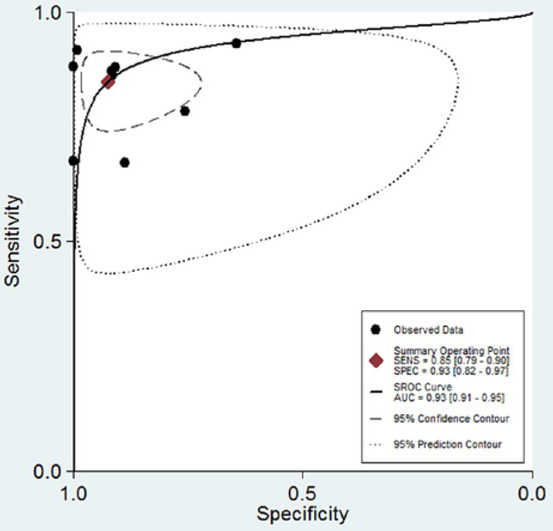
Summary receiver operating characteristic curve. The figure also shows 95% confidence contour and 95%prediction contour.
3.5 Performance of MS systems
The meta-analysis included two MS systems: the MALDI Biotyper and the Vitek MS. We compared the diagnostic accuracy of the MALDI Biotyper and the Vitek MS and found that the estimated specificity and sensitivity of all studies using the MALDI Biotyper were 0.94 (95% CI 0.75-0.99) and 0.86 (95% CI 0.79-0.91), respectively, while the specificity and sensitivity of the Vitek MS were 0.91 (95% CI 0.87-0.94) and 0.81 (95% CI 0.70-0.89), respectively.
3.6 Heterogeneity analysis and sensitivity analysis
There was substantial heterogeneity among the studies (overall I2for the bivariate model: 95%, 95% CI 91-99 and P<0.001). However, we recorded no evidence of a threshold effect. Therefore, we further investigated the source of heterogeneity with a sensitivity analysis. This analysis was performed by inspecting pooled estimates that were calculated by omitting one study at a time. As shown in Supplementary Figure S1, there was no evidence that any individual study had an obvious effect on the combined overall results. Hence, the results of this meta-analysis were stable.
3.7 Assessment of publication bias
Publication bias among the included studies was analyzed by performing Deek’s funnel plot asymmetry test using STATA software. The results indicated that there was no publication bias among studies (P=0.15) (Supplementary Figure S2).
4 Discussion
As one of the most popular technologies in clinical microbiology, MALDI-TOF MS demonstrates great advantages for microbial species identification [29]. Currently, MALDI-TOF MS is considered the holy grail of rapid and cheap microbial identification. Moreover, it produces final results more quickly than conventional methods, and it directly identifies microbes from positive blood cultures, which may enhance the quality of patient management [30]. In this meta-analysis, we performed a systematic review and evaluated the ability of MALDI-TOF MS systems to accurately and directly identify clinical pathogens in urine samples.
MALDI-TOF MS demonstrated high accuracy for the direct identification of pathogens from urine samples, with a pooled sensitivity of 0.85 and a pooled specificity of 0.93. As reported by Kim et al., higher PLR values indicate the greater likelihood of an association between a test result and a disease, and lower NLR values forecast the greater likelihood that a test result is related to the absence of a disease[31] .Therefore, based on the PLR and NLR values obtained for MALDI-TOF MS, this method is reliable for the direct detection of pathogenic microorganisms from urine samples. Furthermore, the SROC value was 0.93, which indicated a high degree of overall diagnostic accuracy.
This study also investigated the performance of different MS systems. The Biotyper system demonstrated better performance in six studies that were enrolled and synthesized in this meta-analysis, with a higher specificity and sensitivity than that of the Vitek MS system. However, it remains uncertain whether the identification accuracy of the Biotyper system is generally superior to that of the other three systems of interest. On the one hand, the present study only included two different detection systems, and no included study performed a sufficient direct comparison of these systems. On the other hand, identification performance can be influenced by many factors (for example, the reference library version, the number of studies, or the method for handling samples), as revealed by the substantial heterogeneity of the included studies. Therefore, additional studies should be conducted to confirm our results.
To obtain good results with MALDI-TOF MS directly from clinical samples, the bacterial count and pathogenic species seem to be the critical issues. Wang et. al considered that Gram-positive cocci samples with bacterial counts of <105 CFU/ml did not provide reliable MALDI-TOF results and Gram-negative bacilli samples could be accurately identified when bacterial counts were <105 CFU/ml [20]. It migh be possible that the cell wall of Gram-negative bacilli were more easily lysed and the proteins were more easily detected. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the sensitivity of MALDI-TOF MS and reduce the threshold of detection. And to obtain sufficient spectra for MALDI-TOF MS detecting, the sample must be concentrated. The included studies used various concentration procedures to facilitate identification, including a centrifugation (low and high speed)/wash protocol that yields pure microbial pellets and added formic acid and acetonitrile to destroy the cell wall more fully[18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 26]. Ferreira et.al [19] compared the ICM with PEM and showed that the intact cell method (ICM) provided excellent results for urine. They considered that the ICM should initially be applied to all samples and, if reliable identification is not achieved, the PEM should be applied to increase the possibility of identification. An alternative method for concentration was “short incubation”, in which samples are cultured for 3-5 hours followed by sample preparation [24, 25]. Although the “short culture” method required a longer time than direct methods to obtain results, the overall efficiency was similar among all methods. Compared with the conventional method (culture for 18-48 h), these alternative protocols saved a substantial amount of time, which considerably improved patient treatment.
It was not feasible to apply more elaborate meta-regression to investigate the source of heterogeneity with only nine enrolled studies. Therefore, we performed a sensitivity analysis to analyze the heterogeneity. As shown in Supplementary figure S1, the pooled index was not appreciably affected by omitting any single study, which indicated the stability of our results.
We must acknowledge certain limitations of the present work. First, although we attempted to search for all relevant studies, some data were inevitably missing. The studies enrolled in the meta-analysis were restricted only to articles published in Chinese or English. Hence, the number of included studies was small. Second, given the current limitations of the technique, MALDI-TOF MS was unable to identify all microorganisms present in a mixture of microorganisms. Additionally, it was unable to distinguish the most abundant pathogen in a mixture. Therefore, we eliminated samples that were contaminated or contained two or more pathogens, which may have resulted in the overestimation of accuracy. Improved algorithms are needed to interpret the spectra obtained for combinations of bacteria resulting from the direct testing of urine samples [32]. Third, in its current iteration, MALDI-TOF MS does not produce quantifiable results. It is uncertain whether MALDI-TOF MS meets the requirements for a UTI diagnostic method. Clinically, we suggested that urine samples should first be screened by flow cytometry or Gram-staining, and then bacteriuria-positive samples could be directly analyzed with MALDI-TOF MS. Meanwhile, we could not but acknowledge MALDI-TOF MS currently has some other limitations. The cost of purchasing and maintaining the instrument is high, it is difficult to discriminate some closely related species such as Escherichia coli and Shigella and it is difficult for the method to detect antimicrobial resistance.
The results of the meta-analysis suggested that MALDI-TOF MS could directly identify microorganisms from urine samples with higher sensitivity and specificity than routine methods. More studies should be conducted to confirm the performance this technology and many aspects of MALDI-TOF MS must be improved, such as the ability to provide information about the antimicrobial susceptibility of pathogens in clinical samples.
Funding information: This study was supported by the construction of clinical medicine strain resource base and application platform, the Sichuan science and technology infrastructure platform project (2018TJPT0011) and the Sichuan science and technology planning project (Grant No. 14JC0047).
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
[1] Flores-Mireles AL., Walker JN., Caparon M., Hultgren SJ., Urinary tract infections: epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options,Nat Rev Microbiol,2015,13(5),269-284; DOI:10.1038/nrmicro343210.1038/nrmicro3432Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Schwab S., Jobin K., Kurts C., Urinary tract infection: recent insight into the evolutionary arms race between uropathogenic Escherichia coli and our immune system, Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2017, 32,1-7; DOI:10.1093/ndt/ gfx02210.1093/ndt/gfx022Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Tandogdu Z., Wagenlehner FM., Global epidemiology of urinary tract infections,Curr Opin Infect Dis,2016, 29(1), 73-79;DOI: 10.1097/QCO.000000000000022810.1097/QCO.0000000000000228Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Gupta K., Grigoryan L., Trautner B., Urinary Tract Infection,Ann Intern Med ,2017,167(7), ITC49-ITC64; DOI:10.7326/AITC20171003010.7326/AITC201710030Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Montgomery S., Roman K., Ngyuen L., Cardenas AM., Knox J., Tomaras AP., et al., Prospective Evaluation of Light Scatter Technology Paired with Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Rapid Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections,J Clin Microbiol,2017,55(6): 1802-1811; DOI:10.1128/JCM.00027-1710.1128/JCM.00027-17Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] March Rossello GA., Gutierrez Rodriguez MP., Ortiz de Lejarazu Leonardo R., Orduna Domingo A., Bratos Perez MA., New procedure for rapid identification of microorganisms causing urinary tract infection from urine samples by mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF),Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin,2015, 33(2): 89-94; DOI: 10.1016/j.eimc.2014.02.02210.1016/j.eimc.2014.02.022Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Kostrzewa M., Application of the MALDI Biotyper to clinical microbiology: progress and potential, Expert Rev Proteomics, 2018,15(3):193-202;DOI: 10.1080/14789450.2018.143819310.1080/14789450.2018.1438193Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Huang AM., Newton D., Kunapuli A., Gandhi TN.,Washer LL., Isip J.,et al., Impact of rapid organism identification via matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight combined with antimicrobial stewardship team intervention in adult patients with bacteremia and candidemia, Clin Infect Dis ,2013,57(9):1237-1245;DOI: 10.1093/cid/cit49810.1093/cid/cit498Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Perez KK., Olsen RJ., Musick WL., Cernoch PL.,Davis JR., Peterson LE., et al.,Integrating rapid diagnostics and antimicrobial stewardship improves outcomes in patients with antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteremia, J Infect, 2014,69(3): 216-225 ;DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.05.00510.1016/j.jinf.2014.05.005Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Wenzler E., Goff DA., Mangino JE., Reed EE., Wehr A., Bauer KA., Impact of rapid identification of Acinetobacter Baumannii via matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with antimicrobial stewardship in patients with pneumonia and/ or bacteremia, Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, 2016,84(1):63-68;DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.09.01810.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2015.09.018Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Lavigne JP., Espinal P., Dunyach-Remy C., Messad N., Pantel A., Sotto A., Mass spectrometry: a revolution in clinical microbiology? Clin Chem Lab Med ,2013,51(2):257-270;DOI:10.1515/cclm-2012-029110.1515/cclm-2012-0291Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Ling HZ., Yuan ZJ., Shen JL., Wang ZX., Xu YH., Accuracy of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Identification of Clinical Pathogenic Fungi: a Meta-Analysis, J Clin Microbiol, 2014,52(7):2573-2582;DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00700-1410.1128/JCM.00700-14Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Chen JH., Ho PL., Kwan GS., She KK., Siu GK., Cheng VC., et al., Direct Bacterial Identification in Positive Blood Cultures by Use of Two Commercial Systems Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization−Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry Systems, J clin microbiol,2013,51(6):1733-1739;DOI: 10.1128/JCM.03259-1210.1128/JCM.03259-12Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Inigo M., Coello A., Fernandez-Rivas G., Rivaya B., Hidalgo J., Quesada MD., et al., Direct Identification of Urinary Tract Pathogens from Urine Samples, Combining Urine Screening Methods and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry, J clin microbiol, 2016, 54(4): 988-993;DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02832-15.10.1128/JCM.02832-15Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Kohling HL., Bittner A., Muller KD., Buer J., Becker M.,Rubben H.,et al., Direct identification of bacteria in urine samples by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and relevance of defensins as interfering factors,J Med Microbiol, 2012; 61(pt3): 339-344;DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.032284-010.1099/jmm.0.032284-0Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Whiting PF., Rutjes AWS., Westwood ME., Mallett S., Deeks JJ., Reitsma JB., et al.,QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies,Ann Intern Med ,2011,155(8): 529-536;DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-0000910.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Devillé WL., Buntinx F., Bouter LM., Montori VM., de Vet HC., van der Windt DA., et al., Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: didactic guidelines, BMC Med Res Methodol, 2002, 2(9): 1-13;DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-2-910.1186/1471-2288-2-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Ferreira L., Sánchez-Juanes F., González-Avila M., Cembrero-Fuciños D., Herrero-Hernández A., González-Buitrago JM., et al., Direct identification of urinary tract pathogens from urine samples by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry, J clin microbiol, 2010,48(6): 2110-2115;DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02215-0910.1128/JCM.02215-09Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Ferreira L., Sánchez-Juanes F., Muñoz-Bellido JL., González-Buitrago JM., Rapid method for direct identification of bacteria in urine and blood culture samples by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: intact cell vs. extraction method, Clin Microbiol Infect ,2011,17(7): 1007-1012;DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03339.x10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03339.xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Wang XH., Zhang G., Fan YY., Yang X., Sui WJ., Lu XX., Direct identification of bacteria causing urinary tract infections by combining matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry with UF-1000i urine flow cytometry,J Microbiol Methods ,2013, 92(3): 231-235 ;DOI: 10.1016/j. mimet.2012.12.01610.1016/j.mimet.2012.12.016Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Burillo A., Rodríguez-Sánchez B., Ramiro A., Cercenado E., Rodríguez-Créixems M., Bouza E.,Gram-Stain Plus MALDI-TOF MS (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry) for a Rapid Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection, PloS one ,2014, 9(1): e86915;DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.008691510.1371/journal.pone.0086915Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Zboromyrska Y., Rubio E., Alejo I., Vergara A., Mons A., Campo I., et al.,Development of a new protocol for rapid bacterial identification and susceptibility testing directly from urine samples, Clin Microbiol Infet, 2016, 22(6): 561.e1- 561. e6;DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.01.02510.1016/j.cmi.2016.01.025Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Kitagawa K., Shigemura K., Onuma KI., Nishida M., Fujiwara M., Kobayashi S., et al., Improved bacterial identification directly from urine samples with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, J Clin Lab Anal, 2018, 32(3):e22301.1-7;DOI: 10.1002/jcla.2230110.1002/jcla.22301Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Veron L., Mailler S., Girard V., Muller BH., L’Hostis G., Ducruix C., et al., Rapid urine preparation prior to identification of uropathogens by MALDI-TOF MS, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 2015,34(9): 1787-1795;DOI: 10.1007/s10096-015-2413-y10.1007/s10096-015-2413-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Haiko J., Savolainen LE., Hilla R., Pätäri-Sampo A., Identification of urinary tract pathogens after 3-hours urine culture by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, J Microbiol Methods ,2016, 129: 81-84,DOI: 10.1016/j. mimet.2016.08.00610.1016/j.mimet.2016.08.006Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Huang B., Zhang L., Zhang WZ., Liao K., Zhang SH., Zhang ZQ., et al., Direct Detection and Identification of Bacterial Pathogens from Urine with Optimized Specimen Processing and Enhanced Testing Algorithm, J clini microbiol, 2017, 55(5): 1488-1495 ;DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02549-1610.1128/JCM.02549-16Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Bizzini A., Greub G., Matrix-Assisted Laser DesorptionIonization Time-of Flight Mass Spectrometry,a revolution in clinical microbial identification, Clin Microbiol Infect ,2010, 16: 1614-1619;DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03311.x10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03311.xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] van Belkum A., Welker M., Pincus D., Charrier J., Girard V., Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Microbiology: What Are the Current Issues? Ann Lab Med, 2017,37(6): 475-483;DOI: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.6.47510.3343/alm.2017.37.6.475Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Croxatto A., Prod’hom G., Greub G., Applications of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical diagnostic microbiology, FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2012, 36(2): 380-407 ;DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00298.x10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00298.xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Lagace-Wiens PR., Adam HJ., Karlowsky JA., Nichol KA.,Pang PF.,Guenther J.,et al., Identification of blood culture isolates directly from positive blood cultures by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry and a commercial extraction system: analysis of performance, cost, and turnaround time, J Clin Microbiol, 2012, 50(10): 3324-3328;DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01479-1210.1128/JCM.01479-12Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Kim KW., Lee J., Choi SH., Huh J., Park SH., Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part I. General Guidance and Tips,Korean J Radiol, 2015, 16(6): 1175-1187;DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.117510.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1175Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Davenport M., Mach KE., Shortliffe LMD., Banaei N., Wang TH., Liao JC., New and developing diagnostic technologies for urinary tract infections, Nat Rev Urol,2017,14(5): 296-310;DOI: 10.1038/nrurol.2017.2010.1038/nrurol.2017.20Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2020 Min Tang et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway

