CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Ziao Wang
Abstract
2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19, previously known as novel coronavirus pneumonia) was first discovered in December 2019 and spread widely in China and all over the world in 2020. The initial symptoms of most patients include fever, cough, and fatigue. Dyspnea may occur with the progress of the disease, and acute respiratory distress syndrome may occur in severe cases. The CT manifestations of this disease are mainly ground-glass opacity (GGO) in the lung, which may be accompanied by patchy consolidation, and fibrous changes may appear in the lung at the later stage of the disease. Combined with typical clinical and imaging findings and positive nucleic acid test results, the disease can be diagnosed. We report the first case of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Heilongjiang Province, China. The patient was seriously ill, who felt that he suffered from fever, fatigue, cough, and expectoration and sought medical treatment, with a history of contact with Wuhan. The leukocyte count was normal, and the lymphocyte count was decreased. CT imaging showed large GGO and partial patchy consolidation in both lungs. The patient recovered and was discharged after 26 days of treatment. This study is helpful for early diagnosis and timely clinical management by mastering the typical imaging of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
1 Introduction
Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19, previously known as novel coronavirus pneumonia [NCP]) is an acute pulmonary inflammation caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. In December 2019, several cases with pneumonia caused by unknown reasons occurred in Hubei Province, China. Most of these patients worked or lived nearby the local Huanan China Seafood Wholesale Market. Some of them rapidly developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and other complications after a few days of onset. In January 2020, the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention found and confirmed the virus for the first time, which is known as SARS-CoV-2. In the next several months, the disease spread widely in China and other countries, infecting more than 2,00,000 people. On 30 January 2020, WHO declared the outbreak of COVID-19 as a public health emergency of international concern. In this article, the first case with severe NCP in Heilongjiang Province, China, was reported, aiming to state related knowledge for reference by colleagues, improve the understanding for imaging manifestations of COVID-19, facilitate the early diagnosis of this disease, and guide the next clinical decision-making.
2 Case details
A 69-year-old man who suffered from fever, fatigue, myalgia, cough, and expectoration went to the hospital for medical treatment; temperature at admission: 38.2 ℃; heart rate: 78 times/min; respiration: 22 times/min; and blood pressure: 142/75 mm Hg. The patient stated that he had traveled back to Harbin from Wuhan, Hubei Province, by aircraft 1 day before and returned to Mudanjiang city, Heilongjiang Province from Harbin by high-speed railway. The patient stated that he had a smoking history, no drinking history, and suffered hypertension. The results of laboratory examination after admission are as follows: normal leucocyte count (6.17 × 109/L), decreased lymphocyte count (0.72 × 109/L), increased C-reactive protein (64.5 mg/L), increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (28 mm/h), and increased D-dimer (1.44 µg/mL). CT examination showed that the two lungs had a large area of ground-glass opacity (GGO) and a small area of patchy consolidation. The lesions had an obscure boundary, which distributed mainly in a subpleural area. CT images also reveal “air bronchography sign,” enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes, and bilateral pleura thickening. The patient was admitted to the hospital for antiviral treatment and symptomatic supportive treatment.
Two days after admission, the patient developed dyspnea. Because the patient was seriously ill, he was admitted to the ICU for the treatment and received tracheal cannula and continuously underwent symptomatic supportive treatment, antiviral treatment, and prophylactic antibacterial treatment. After 9 days of admission, the nucleic acid test showed that the result of SARS-CoV-2 was positive, and the patient was diagnosed with COVID-19, who was the first case in Heilongjiang Province, which was imported. During the period of hospitalization, the general situation of the patients was relatively stable. After 16 days of admission, CT examination was performed again: large areas of GGO and consolidation were still seen in both lungs, mainly distributed in the lower lobes of both lungs. However, compared with the previous images, the area of GGO was reduced and more tended to be distributed in subpleural. The area of patchy consolidation increased slightly. The grid shadow appeared near the pleura of both lungs, showing the fibrous change.
The condition of the patient gradually improved. On the 20th day after admission, the reexamination of CT showed that the areas of GGO and consolidation shadow in both lungs were significantly reduced, and the lesions were absorbed. There were more grid shadows in both lungs, main subpleural distribution, and fibrous changes in both lungs. The patient continued to receive supportive treatment. The patient was generally in good condition with normal body temperature, and the laboratory examination indicators gradually returned to normal. Then, the patient presented the pathogen test of SARS-CoV-2 RNA twice, and the results were all negative. The patient was discharged on the 26th day after admission and was clinically cured.
3 Discussion
Since the discovery of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Wuhan, Hubei Province, in December 2019, the number of cases has increased rapidly, showing a spreading trend in China and other countries overseas. By 20:00 on 21 March 2020, there were 81,457 confirmed cases and 3,261 dead cases in China, and 2,01,577 cases were confirmed in overseas areas, involving more than 100 countries. COVID-19 has become pandemic all over the world. For the first visit, the common clinical manifestations of patients showed fever, weakness, dry cough, and myalgia, while some patients showed headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea for the first time. With the progress of the disease, some patients suffered dyspnea about 1 week after admission. Severe patients might have shock, arrhythmia, and ARDS [1].
Imaging examination is an important method to diagnose COVID-19. Chest radiography shows a patchy shadow in the lung field, which is a preliminary judgment of the disease. However, chest radiography has a low diagnostic rate for small lesions and is not the first choice because of the blocking effect of mediastinal shadow. We can find lesions from the tomography and carry out three-dimensional reconstruction by CT examination to diagnose COVID-19 more accurately. It can accurately assess the size, distribution, involved range, and severity of the lesion. Therefore, the CT examination plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of NCP.
The main CT imaging feature of COVID-19 includes bilateral GGO, mainly with the subpleural distribution. The imaging of mild cases shows the focal distribution. CT findings of severe cases show the diffuse distribution in double lung fields such as the case we reported. GGO can be accompanied by consolidation, which is mainly seen in critically ill patients with “white lung” changes [2]. “Air bronchography sign,” thickened vascular shadow were seen in lesions. Thickened interlobular septa and “crazy-paving pattern” can also be seen in CT imaging [3]. Because the patient we reported is under the severe condition, lesions on the CT are quite obvious. CT imaging shows large areas of GGO, which is a classical manifestation. With the development of the disease, fibrous changes can be formed, which is manifested as a grid shadow. Fibrous changes illustrate the destruction of lung tissues, especially in severe cases. In the third CT examination of our patient, fibrous stripes exist definitely. Some patients have enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, and pleural effusion is rare. There are also a small number of patients with negative CT manifestations, which should be noted [4]; thus, the diagnosis of COVID-19 should not depend only on radiology.
COVID-19 can be divided into four stages according to its imaging characteristics and lung involved: early stage, progressive stage, critical stage, and remission stage [3]. We report the case in a dynamic course. As the patient was admitted to the hospital in a critical stage, we did not obtain the classical imaging of early stage and progressive stage. However, we can see the recovery of the patient by CT imaging. The areas of GGO reduced obviously as the lesions were absorbed. The fibrous changes emerged later (Figures 1–4).

First CT scans of the patient (a: axial noncontrast CT image; b: coronal thin-section noncontrast CT image; and c: sagittal thin-section noncontrast CT image) showing large areas of GGO distributed mainly in subpleural (black arrows), thickened vascular shallow (white arrow), and bronchus shallow (white asterisk).

CT scans obtained 16 days after admission (a: axial non-contrast CT image; b: coronal thin-section noncontrast CT image; and c: sagittal thin-section noncontrast CT image) showing the range of lesions reduced compared with the previous images; partial patchy consolidation (black arrows).
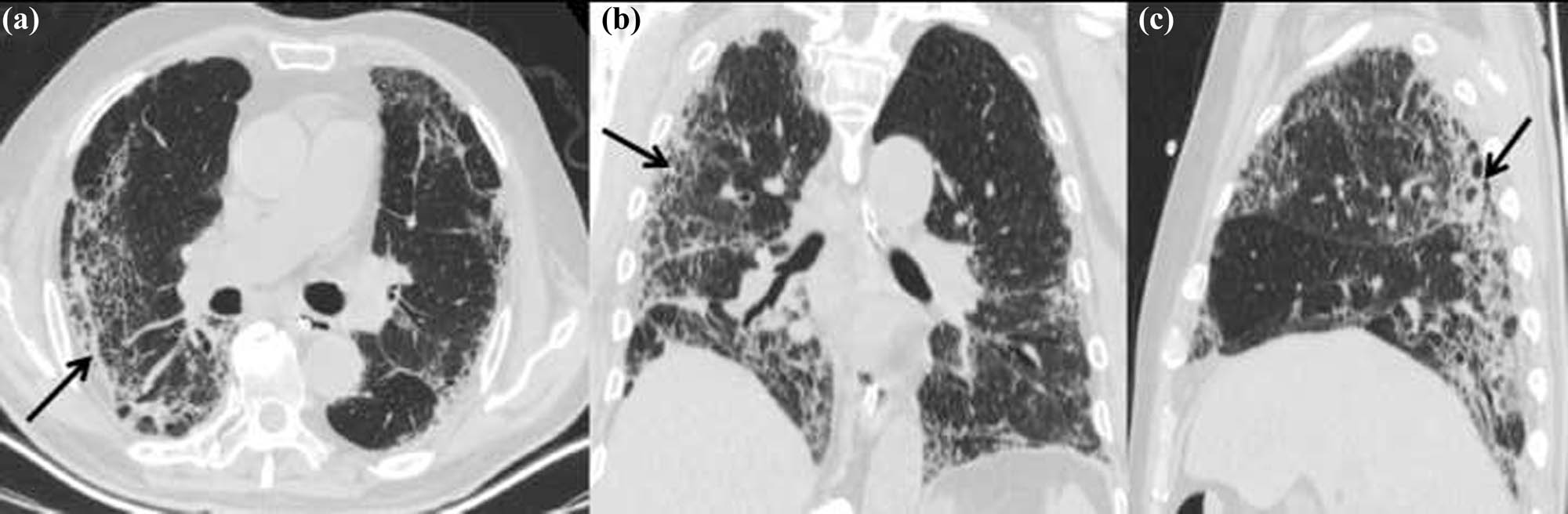
CT scans obtained 20 days after admission (a: axial non-contrast CT image; b: coronal thin-section non-contrast CT image; and c: sagittal thin-section noncontrast CT image) showing the range of lesions reduced significantly compared with previous images; fibrous changes in subpleural (black arrows).

First CT scans (axial mediastinal noncontrast image) showing mediastinal enlarged lymph nodes (white arrow, a) and local thickening of the pleural (white arrow, b).
According to the related epidemiological history of the patients, the typical symptoms such as fever, dry cough, and fatigue, combined with the imaging manifestations of typical viral pneumonia and the results of laboratory examination, can make a preliminary diagnosis. The final diagnosis needs to be tested by the viral nucleic acid. If it is positive, the final diagnosis can be made.
Funding information: This study was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFC0118100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671760 and 81873910), Scientific Research Transformation Special Fund of Heilongjiang Academy of Medical Sciences (2018415); Scientific Research Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Heilongjiang Province (201812 and 201622).
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020, Feb 07. 10.1001/jama.2020.1585.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Pan Y, Guan H, Zhou S, et al. Initial CT findings and temporal changes in patients with the novel coronavirus pneumonia (2019-nCoV): a study of 63 patients in Wuhan, China. Eur Radiol. 2020;30(6):3306–9. 10.1007/s00330-020-06731-x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Pan F, Ye T, Sun P, et al. Time course of lung changes at chest CT during recovery from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Radiol. 2020;295(3):715–21. 10.1148/radiol.2020200370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Kanne JP. Chest CT findings in 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections from Wuhan, China: key points for the radiologist. Radiol. 2020;295(1):16–7. 10.1148/radiol.2020200241.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2020 Ziao Wang et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway

