Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
-
Franca Vergalito
, Giulio Petronio Petronio
Abstract
The healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) occur in patients both in nosocomial environments and in community. More often HCAIs are associated to the use of medical devices and bacterial biofilm development on these equipments. Due to the clinical and economic relevance of this topic, new strategies for the treatment of infections caused by biofilm proliferation are unceasingly searched by scientists.
The present study investigated the role of vitamin E to reduce the biofilm formation for a larger panel of human pathogens, including strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas putida.
This potential activity was tested by placing a preparation of vitamin E (α-Tocopheryl acetate) as interface between the bacterial culture and the polystyrene walls of a 96 well plate at different concentrations of glucose, used as a biofilm enhancer.
The Staphylococcus genus was further investigated by spreading the vitamin E on a silicone catheter lumen and evaluating its influence on the bacterial colonization.
From our results, vitamin E has been able to interfere with bacterial biofilm and prevent in vitro biofilm formation. Furthermore, the ability of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis to colonize the catheter surface decreased as a result of vitamin E application.
1 Introduction
Healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) occur in patients subjected to the care process in any setting such as hospitals or patient’s own homes [1, 2, 3]. A consistent part of HCAIs are associated with the use of medical devices, and this is an important cause for patients morbidity and mortality increasing [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. Consequently, there is a global needs to reduce the social and economic implications of HCAIs [9].
A wide range of Gram positive bacteria (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Enterococcus faecalis), Gram negative bacteria (e.g. Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas putida and Chlamydophila pneumoniae) and also yeasts (particularly Candida species) are implicated in HCAIs onset [2,3,9, 10, 11]. These microorganisms are responsible for numerous diseases like ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), lower respiratory tract infections (22.8 % of cases), catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs, 17.2 % of cases) and surgical-site infections (SSIs; 15.7 % of cases) [5,12,13]. The ability of these microorganisms to grow forming biofilm makes the medical treatment of infections more difficult and in some cases leads to its failure [14,15].
A biofilm is a cellular assembly of one or more microorganisms surrounded by a complex self-produced polymeric matrix which commonly includes components from the host, such as fibrin, platelets or immunoglobulins [16, 17, 18, 19]. This complex encapsulating structure protects the microbial cells against the host immune-response system and provides a site for the adhesion of other bacterial cells [20, 21, 22]. Moreover, antibiotics may not penetrate into the biofilm layers, and also the presence of characteristic water channels inside the biofilm matrix can determine a partial antibiotics leaking together with an alteration of the environment inside the biofilm matrix that can antagonize the antibiotic action [23, 24, 25]. Finally, mechanisms of plasmid gene transferring may conduce to the onset of resistant bacterial strains which can generate molecules that antagonize the antibiotics inducing a reduction of their therapeutic role [26,27]. Indeed, there are many scientific evidences that bacteria living in a mature biofilm can tolerate antibiotics concentrations 10-1000 higher compared to planktonic bacteria [24,28,29].
Due to the clinical and economical relevance of this topic, new strategies for the treatment of infections caused by the biofilm proliferation are unceasingly searched by scientists [30,31].
The evidence of a potential role of vitamins as antibiofilm/antimicrobial agent is not recent. In 1999 Habash et al. investigated the role of vitamin C in the reduction of adhesion of some uropathogens onto biomaterials utilized within the urinary tract [32].
More recent studies hypothesized a similar function for vitamin E. The capability of Staphylococcus ssp. and E. coli to form biofilm onto different biomaterials blended with vitamin E was investigated. Although not consistent results have been obtained by different studies due to the different methods used and different pathogens tested [1,33, 34, 35, 36].
Therefore, the present study investigated the role of vitamin E to reduce the biofilm formation for a larger panel of human pathogens, including S. aureus, S. epidermidis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa and P. putida. This activity was tested placing a preparation of vitamin E as an interface between the bacterial culture and the polystyrene wells of a 96 well plate at different concentrations of glucose, used as a biofilm formation enhancer. Moreover, bacterial species which commonly cause the infections associated with the use of urinary catheters belonging to the Staphylococcus genus were further investigated. More precisely, the vitamin E was directly spread on a silicone catheter lumen to evaluate its influence on the bacterial colonization and biofilm formation.
2 Methods
Ethical approval: the conducted research is not related to either human or animals use
2.1 Chemicals
Tryptic Soy Broth (Sigma Aldrich), glucose (Sigma Aldrich), vitamin E (α-Tocopheryl acetate) (≥96%, 0.95 g/ml, Sigma Aldrich), 96 well cell culture plate flat bottom (Orange Scientific), NaCl (Sigma Aldrich), methanol solution (for HPLC, ≥99.9%, Sigma-Aldrich), glacial acetic acid (≥99.85%, Sigma Aldrich), 2% crystal violet solution (from the Gram color kit Liofilchem).
2.2 Tested strains
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228, Escherichia coli ATCC 11775, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603, Proteus mirabilis ATCC 29906, Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 and Pseudomonas putida ATCC 12633.
2.3 In vitro toxicity test
The in vitro toxicity of vitamin E was estimated through a microdilution assay as suggested by Tintino et al. with some modifications [37]. Tested bacterial strains were grown in Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) and TSB with 1 and 2.5% glucose, at 37°C for 24 hours. All cultures were diluted to the cell concentration of 108 CFU/ml, and 100 ul serial dilutions were prepared in triplicates in the 96 well microtiter plates. Vitamin E was added to the subsequent wells at the range of final concentration from 100 to 400 mg/ml, with concentration increments of 100 mg/ml. Also, triplicates of different media and inocula only were prepared in plate wells as controls. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours and bacterial growth was determined plating proper dilutions of the bacterial cultures on 1.8% agarose TSB by colony counting after 24 hours of incubation. The highest concentration of vitamin E that did not interfere with the growth of all the tested bacterial strains, i.e. the concentration of 200 mg/ml, was used in subsequent in vitro experiments for biofilm eradication.
2.4 In vitro biofilm formation assay
Cultures of tested strains were grown in TSB at 37°C for 24 hours, centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min and the pellet was re-suspended to the final concentration of 108 CFU/ml in 2 ml of fresh TSB, TSB with 1 and 2.5% glucose, respectively. 200 ul aliquots of each culture were added to a polystirene 96 well plate as well as 200 ul triplicates of TSB and TSB with 1, and 2.5 % glucose without inocula were prepared as controls. Vitamin E was added to all wells at the final concentration of 200 mg/ml. Another plate was generated with the same samples and controls without vitamin E. Both plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. After incubation time the biofilm production was estimated through the method proposed by Stepanović et al. with some modification [38]. The wells were emptied and washed three times using 250 ul of 0.9% NaCl. Therefore, 200 ul of methanol solution were added incubating for 15 min to fix the cells which eventually adhered to the tubes. The methanol solution was discarded, and the plates were dried under the biological laminar flow in upset-down position. Subsequently, 200 ul of crystal violet solution were added to wells and maintained in incubation for 5 min. Then, the excess of staining was removed washing the plates under a moderate tap water flow.
The dye bound to the adherent cells was resolubilized with 160 μl of 33% glacial acetic acid and the Optical Density (O.D.) at 570 nm for each well was measured using the VICTOR X5 multilabel plate reader (Perkin-Elmer) [38, 39, 40]. For each considered strain the comparison between O.D. values obtained with/without vitamin E was performed, and consequently, the strains attitude to form biofilm under the presence/absence of vitamin E was established.
Furthermore, the effect of two different glucose concentrations was assessed adding 1% or 2.5% sugar to TSB during bacterial growth.
For each strain, the O.D. values obtained in all tested conditions under vitamin E presence were compared to those obtained under vitamin E absence and considered as the maximum rate of their biofilm formation capability (100%). Therefore, the percentage reduction of biofilm formation under vitamin E influence was calculated as the mean value between the percentage reduction in all tested conditions.
The biofilm producing strains more susceptible to vitamin E action were subjected to further investigation to evaluate the possible application of vitamin E for the prevention of biofilm formation on the surface of medical devices.
2.5 In vitro biofilm formation on the surface of medical devices
The influence of vitamin E on the ability of the Staphylococcus strains to form biofilm layers on the lumen of silicone urinary catheters was also investigated.
The lumen of silicone catheters sections (continuous irrigation balloon catheters DBK-Dufour UROMED) of 2 cm in length were previously homogeneously layered by the same concentration of vitamin E used in the in vitro biofilm assay (200 mg/ml) and subsequently covered by 200 ul of strains suspensions (108 cells/ml) and media for which in this study the more relevant effect of the vitamin E was observed. Also, controls were prepared applying 200 ul of each medium only on the surface of catheter sections with vitamin E layer, as well as sections of the device with vitamin E only were prepared. All catheter sections were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours.
After incubation time sections were washed and stained as described above and the stain was re-suspended using 200 ul of 33% glacial acetic acid. The stain suspensions were distributed to a 96 well plate for the O. D. measurement as described above.
The effect of the vitamin E layer in reducing the biofilm formation of Staphylococcus strains on the catheter surface was evaluated: the O.D. values obtained for the sections inoculated with bacteria and pre-treated with the vitamin E were compared to those obtained for sections not previously layered by vitamin E.
3 Statistical analysis
Statistical data analysis was performed using SigmaPlot version 12.0, from Systat Software, Inc. (San Jose California, USA). For each strain firstly the normality of data was evaluated through Shapiro-Wilk test. The values groups resulted as normal distributed were subjected to the ANOVA analysis with post-hoc Tukey HSD test (p<0.05). The values series not normally distributed were statistically analysed using the not parametric Kruskal-Wallis test FDR corrected (p<0.05).
4 Results
4.1 In vitro toxicity test
Vitamin E concentration of 200 mg/ml did not interfere with the growth of all tested bacteria (data not shown) and therefore this dosage was used for the in vitro biofilm experiments.
4.2 In vitro biofilm formation
The inhibitory action of vitamin E (α-Tocopheryl acetate) on biofilm formation was evaluated for all tested strains. Although for E. coli, K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa no significant results were obtained (ANOVA analysis with post-hoc Tukey HSD test and not parametric Kruskal-Wallis test FDR corrected, p<0.05), a reduction of biofilm formation was observed at least in one of tested conditions (Figure 1). In detail, both with and without glucose adding a reduction trend between 9-19% was calculated for E. coli as well as 38-51% for P. aeruginosa (Figure 1, Table 1). An inhibitory effect of vitamin E alone and in association with 1% glucose was detected for K. pneumoniae with reduction percentages of 24 and 18% respectively (Figure 1, Table 1). Finally, for A. baumannii the reduction trend was observed only by application of vitamin E alone with a biofilm decreasing of 24% (Figure 1, Table 1).
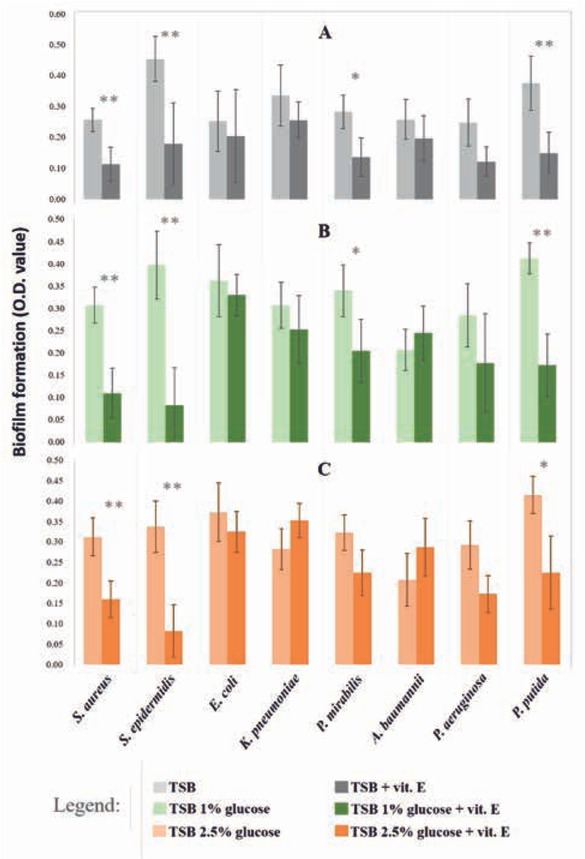
Influence of vitamin E and glucose on the biofilm formation by common human pathogens. Bars indicate the biofilm formed by strains in A) TSB with (dark grey) and without (light grey) vitamin E B) TSB 1% glucose with (dark green) and without (light green) vitamin E C) TSB 2.5% glucose with (dark orange) and without (light orange) vitamin E. The estimation of biofilm formed is based on the optical density of solutions obtained through the resuspension of the stain (see section Methods). Asterisks indicate significance of these comparisons, with «*» for p<0.05 and «**» for p<0.01 (ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis test, with p<0.05).
On the contrary, for S. aureus, S. epidermidis and P. putida the application of vitamin E both with and without glucose adding caused a significant decreasing of biofilm formation meanly larger than 50%. More precisely, in presence of vitamin E alone and in association with 1 and 2.5% of glucose the biofilm of S. aureus was reduced of 56, 64 and 49% respectively, for S. epidermidis of 61, 79 and 76% and for P. putida of 61, 58 and 46% (Figure 1, Table 1).
Moreover, for P. mirabilis the biofilm formation resulted significantly reduced of 52 and 40% applying vitamin E alone and in association with the lowest glucose concentration; a trend of biofilm reduction was also observed when vitamin E was applied with the highest glucose concentration even though this variation resulted not significant (Figure 1, Table 1).
Regarding the effect of glucose in association with vitamin E on biofilm formation, we verified that glucose was not significantly influential in biofilm reduction when associated with vitamin E. No significant differences were obtained between vitamin E treatments with and without glucose adding, whereas significant variations were obtained with vitamin E adding respect to the media without it (ANOVA analysis with post-hoc Tukey HSD test and not parametric Kruskal-Wallis test FDR corrected, p<0.05).
Variation of biofilm formation in media added with vitamin E respect to media not added by vitamin E. For each strains is reported the percentage of reduction (red bars) or increasing (blue bars) of biofilm formation in media added with vitamin E respect to the same media not added with vitamin E. The negative and positive numbers indicate percentages of decrement or increment of biofilm respectively.
 |
4.3 In vitro biofilm formation on the surface of medical devices
The influence of vitamin E on the ability of both Staphylococcus strains to colonize the lumen of catheter section was evaluated. The O.D. values measured for suspensions from catheter sections incubated into Staphylococcus cultures and pre-treated with vitamin E were lower than the ones measured for sections untreated. More precisely, the ability of S. aureus and S. epidermidis to colonize the catheter surface decreased 17% and 36% (Student t-test, p<0,05) respectively with the application of vitamin E (Figure 2).
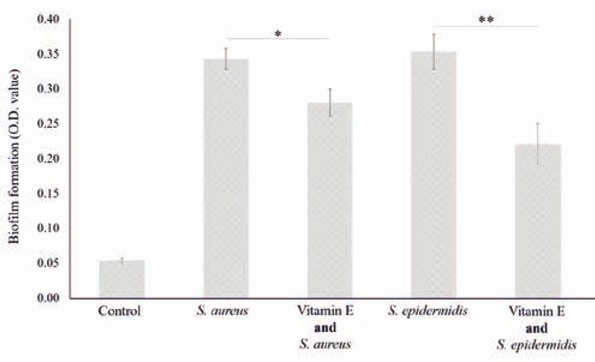
Effect of vitamin E pre-treatment of catheter surfaces on the biofilm formation ability of Staphylococcus strains. «Control» stands for medium not added with vitamin E and not inoculated by considered strains. Statistical significance of interesting comparisons is indicated by asterisks, with «*» for p< 0.05 and «**» for p<0.01 (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey HSD, p<0.05).
5 Discussion
Biofilm forming microorganisms are commonly responsible for HCAIs. More relevant, into the biofilm assembles these bacteria are protected by the action of antibiotics and this leads to the failure of clinical treatments or at least to the prolonging of the pathologic conditions.
In this context, S. aureus and S. epidermidis are Gram positive biofilm producer bacteria that play an important role in HCAIs onset [41,42]. Although the infection caused by these pathogens included a low percentage of HCAIs, it should not be underestimated. Indeed, in urinary tract infections (UTI) a significant relationship between biofilm formation by S. aureus strains and some antibiotic resistance have been demonstrated [43]. For this reason, it is necessary to intervene in the initial phases of biofilm formation to prevent bacterial colonization.
In last years, alternative approaches for the treatment of biofilm-related infections appear as necessity firstly for the treatment of the most common HCAIs due to the use of urinary catheters [44, 45, 46, 47]. Many natural substances and synthetic molecules compatible with both human physiology and the constitutive materials of medical devices, and potentially capable of interfering with pathogen attachment to surfaces have been evaluated [46,47].
In the present study we analyzed the in vitro effects of vitamin E, well known for its beneficial activity on human and animals, in biofilm formation evaluating its ability to interfere with bacterial colonization of medical devices by a large panel of human pathogens implicated in HCAIs onset including S. aureus, S. epidermidis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa and P. putida.
Results related to biofilm formation have shown that, although the concentration used does not inhibit bacterial growth (200 mg/ml), it is still able to reduce the biofilm production capacity of all the strains tested, with a variable efficacy between strains without any correlation to the Gram negative or positive group. The low antibacterial activity, i.e. low toxicity, was confirmed by Bidossi et al. [48] testing a soluble form of vitamin E (α-tocopheryl phosphate) against different strains of S. aureus, S. epidermidis and P.aeruginosa and reporting MIC values very close to one of the liposoluble forms used in our study (100-200 mg/ml) [48]. The sensible value variation may be likely due to the different strains tested and to the enhanced solubility of the phosphate form compared to α-Tocopheryl acetate [48]. Moreover, a recent study by Naguib et al. [49] demonstrated the low antibacterial activity of vitamin E alone compared to its combination with norfloxacin or ceftazidemime that increased antimicrobial sensitivity to B. cenocepacia and P. aeruginosa through the inhibition of the bacterial lipocalin antibiotic binding [49].
Furthermore, the effect of different glucose concentrations (1% and 2.5% w/v) on the action of vitamin E has provided interesting results. Although the role of glucose as biofilm enhancer is well known, we verified that no significant differences could be appreciated between vitamin E treatments with and without glucose adding for all tested strains. This suggests that the inhibition of biofilm formation was ascribable mainly to the vitamin E action able to mask the enhancing effect of glucose.
Moreover, although the increased biofilm formation by staphylococcal species has been reported in response to increased glucose concentrations [50], our results suggest a potential synergistic and inhibitory effect of vitamin E/glucose at low concentrations tested.
Regarding the ability of vitamin E to prevent Staphylococcus strains adhesion on surfaces, our data have confirmed the results of previous studies [48,51] even though conflicting results have been observed in these studies due to the different materials and strains tested. Results obtained with polystyrene plates and silicone catheters highlight the importance of the material constituting the devices when the formation of biofilms is tested in vitro. The biofilm reduction percentage of S. aureus and S. epidermidis in silicone cathers, under the same experimental conditions, is significantly lower compared to polystyrene plates.
These results obtained for these specific strains related to glucose addition could be explained by a hypothesis formulated by Campocia et al. [34]; according to the authors the surface physico-chemical properties of biomaterials variably affect the adherence of the microorganism and the formation of biofilms, while the vitamin E action determines a conditioning of the bacterial surfaces, rather than of the biomaterial surfaces.
This hypothesis seems to be confirmed by numerous studies conducted on the antibiofilm action of polymers made with the addition of vitamin E against Staphylococcus spp. which is demonstrated as the reduced bacterial adhesion was not dependant by the adding of vitamin E to all the polymers tested [35,36,52,53].
Concluding, our results together showed that vitamin E could significantly reduce in vitro biofilm formation of some bacterial strains generally considered to be the most frequent pathogens responsible for HCAIs onset.
Furthermore, it was found that S. aureus and S. epidermidis were more susceptible to the action of vitamin E. A potential role of vitamin E for prevention of biofilm formation on the surface of medical devices was also demonstrated.
Although in our experiments an antimicrobial effect of vitamin E at high concentrations was observed, further studies are needed to better clarify the mechanisms, the spectrum of activity and the influence on that of glucose adding.
However, our findings together prospect the promising use of vitamin E as coating molecule to prevent implant-associated infections and improve post-operative course.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the free donation H32F16000180007 assigned from “Panin s.r.l.” to Prof. Roberto di Marco and Prof. Germano Guerra as scientifica at University of Molise.
Abbreviations
- HCAIs
(healthcare-associated infections)
- VAP
(ventilator-associated pneumonia)
- CAUTIs
(catheter-associated urinary tract infections)
- SSIs
(surgical-site infections)
- TSB
(Tryptic Soy Broth)
- O.D.
(Optical Density)
- UTI
(urinary tract infections)
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflicts of interest.
References
[1] van Kleef E, Robotham J V., Jit M, Deeny SR, Edmunds WJ. Modelling the transmission of healthcare associated infections: A systematic review. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13(1)10.1186/1471-2334-13-294Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Khan HA, Baig FK, Mehboob R. Nosocomial infections: Epidemiology, prevention, control and surveillance. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2017;7(5):478–482. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.01.01910.1016/j.apjtb.2017.01.019Search in Google Scholar
[3] Haque M, Sartelli M, McKimm J, Bakar MA. Health care-associated infections – An overview. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:2321–233310.2147/IDR.S177247Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] 4. Donlan R. Biofilms on Central Venous Catheters: Is Eradication Possible? Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Feb 1;322:133–16110.1007/978-3-540-75418-3_7Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Percival SL, Suleman L, Vuotto C, Donelli G. Healthcare-Associated infections, medical devices and biofilms: Risk, tolerance and control. J Med Microbiol. 2015;64(4):323–33410.1099/jmm.0.000032Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Ripabelli G, Salzo A, Mariano A, Sammarco ML, Tamburro M. Healthcare-associated infections point prevalence survey and antimicrobials use in acute care hospitals (PPS 2016–2017) and long-term care facilities (HALT-3): a comprehensive report of the first experience in Molise Region, Central Italy, and targeted in. J Infect Public Health. 2019;12(4):509–515. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2019.01.06010.1016/j.jiph.2019.01.060Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Ripabelli G, Sammarco ML, Scutellà M, Felice V, Tamburro M. Carbapenem-Resistant KPC- and TEM-Producing Escherichia coli ST131 Isolated from a Hospitalized Patient with Urinary Tract Infection: First Isolation in Molise Region, Central Italy, July 2018 . Microb Drug Resist. 2019;00(00)10.1089/mdr.2019.0085Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] M. A. Lo Bue, R. M. Di Marco, I. Milazzo, D. Nicolosi, G. Calì, B. Rossetti GB. Microbiological and clinical periodontal effects of fixed orthodontic appliances in pediatric patients. New Microbiol. 2008;(31):299–302Search in Google Scholar
[9] Stone PW. Economic burden of healthcare-associated infections: An American perspective. Expert Rev Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Res. 2009;9(5):417–42210.1586/erp.09.53Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Donlan RM. Biofilm Formation: A Clinically Relevant Microbiological Process. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33(8):1387–19210.1086/322972Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Revelas A. Healthcare - associated infections: A public health problem. Niger Med J. 2012;53(2):5910.4103/0300-1652.103543Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Hopkins S, Karen S, Lisa S. Healthcare Protection Agency (2012) English National Point Prevalence Survey on Healthcare-associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use, 2011: Preliminary data. Healthc Assoc Infect Guid data Anal. 2012;1–140. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/healthcare-associated-infections-hcai-point-prevalence-survey-englandSearch in Google Scholar
[13] Ripabelli G, Tamburro M, Guerrizio G, Fanelli I, Flocco R, Scutellà M, et al. Tracking Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from an Italian Hospital: Molecular Epidemiology and Surveillance by PFGE, RAPD and PCR-Based Resistance Genes Prevalence. Curr Microbiol. 2018;75(8):977–98710.1007/s00284-018-1475-3Search in Google Scholar
[14] Römling U, Balsalobre C. Biofilm infections, their resilience to therapy and innovative treatment strategies. J Intern Med. 2012;272(6):541–56110.1111/joim.12004Search in Google Scholar
[15] Baldassarri L, Creti R, Recchia S, Imperi M, Facinelli B, Giovanetti E, et al. Therapeutic failures of antibiotics used to treat macrolide-susceptible Streptococcus pyogenes infections may be due to biofilm formation. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44(8):2721–272710.1128/JCM.00512-06Search in Google Scholar
[16] Flemming H-C, Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8(9):623–33. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro241510.1038/nrmicro2415Search in Google Scholar
[17] Lindsay D, von Holy A. Bacterial biofilms within the clinical setting: what healthcare professionals should know. J Hosp Infect. 2006;64(4):313–32510.1016/j.jhin.2006.06.028Search in Google Scholar
[18] Percival SL, Hill KE, Malic S, Thomas DW, Williams DW. Antimicrobial tolerance and the significance of persister cells in recalcitrant chronic wound biofilms. Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19(1):1–910.1111/j.1524-475X.2010.00651.xSearch in Google Scholar
[19] Signorelli SS, Anzaldi M, Libra M, Navolanic PM, Malaponte G, Mangano K, et al. Plasma Levels of Inflammatory Biomarkers in Peripheral Arterial Disease: Results of a Cohort Study. Angiology. 2016;67(9):870–87410.1177/0003319716633339Search in Google Scholar
[20] Domenech M, Ramos-Sevillano E, García E, Moscoso M, Yuste J. Biofilm formation avoids complement immunity and phagocytosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae Infect Immun. 2013;81(7):2606–261510.1128/IAI.00491-13Search in Google Scholar
[21] Leid JG. Bacterial biofilms resist key host defenses. Microbe. 2009;4(2):66–70Search in Google Scholar
[22] Blandino G, Fazio D, Di Marco R. Probiotics: Overview of microbiological and immunological characteristics. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008;6(4):497–50810.1586/14787210.6.4.497Search in Google Scholar
[23] Steward PS, Costdrton JW. Antibiotic resistance of baqteria in biofilms. Lancet. 2001;358(9276):135–13810.1016/S0140-6736(01)05321-1Search in Google Scholar
[24] Olsen I. Biofilm-specific antibiotic tolerance and resistance. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34(5):877–88610.1007/s10096-015-2323-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Balcázar JL, Subirats J, Borrego CM. The role of biofilms as environmental reservoirs of antibiotic resistance. Front Microbiol. 2015;6(OCT):1–910.3389/fmicb.2015.01216Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Hall CW, Zhang L, Mah TF. PA3225 is a transcriptional repressor of antibiotic resistance mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(8):1–2010.1128/AAC.02114-16Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Ridenhour BJ, Metzger GA, France M, Gliniewicz K, Millstein J, Forney LJ, et al. Persistence of antibiotic resistance plasmids in bacterial biofilms. Evol Appl. 2017;10(6):640–64710.1111/eva.12480Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] El-Gebaly E, Essam T, Hashem S, El-Baky RA. Effect of levofloxacin and vitamin C on bacterial adherence and preformed biofilm on urethral catheter surfaces. J Microb Biochem Technol. 2012;4(6):131–13610.4172/1948-5948.1000083Search in Google Scholar
[29] Macià MD, Rojo-Molinero E, Oliver A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm-growing bacteria. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(10):981–99010.1111/1469-0691.12651Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Shorr AF, Haque N, Taneja C, Zervos M, Lamerato L, Kothari S, et al. Clinical and economic outcomes for patients with health care-associated Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(9):3258–326210.1128/JCM.02529-09Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Wu H, Moser C, Wang HZ, Høiby N, Song ZJ. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilm infections. Int J Oral Sci. 2015;7(July 2014):1–710.1038/ijos.2014.65Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Habash MB, Van der Mai HC, Busscher HJ, Reid G. The effect of water, ascorbic acid, and cranberry derived supplementation on human urine and uropathogen adhesion to silicone rubber. Can J Microbiol. 1999;45(8):691–69410.1139/w99-065Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Banche G, Allizond V, Bracco P, Bistolfi A, Boffano M, Cimino A, et al. Interplay between surface properties of standard, vitamin E blended and oxidised ultra high molecular weight polyethylene used in total joint replacement and adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli Bone Jt J. 2014;96 B(4):497–50110.1302/0301-620X.96B4.32895Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Campoccia D, Visai L, Renò F, Cangini I, Rizzi M, Poggi A, et al. Bacterial adhesion to poly-(D,L)lactic acid blended with vitamin E: Toward gentle anti-infective biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res - Part A. 2015;103(4):1447–145810.1002/jbm.a.35284Search in Google Scholar
[35] Gómez-Barrena E, Esteban J, Molina-Manso D, Adames H, Martínez-Morlanes MJ, Terriza A, et al. Bacterial adherence on UHMWPE with vitamin E: An in vitro study. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(7):1701–170610.1007/s10856-011-4340-5Search in Google Scholar
[36] Kyomoto M, Shobuike T, Moro T, Yamane S, Takatori Y, Tanaka S, et al. Prevention of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation on a vitamin E-blended, cross-linked polyethylene surface with a poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) layer. Acta Biomater. 2015;24:24–34. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.05.03410.1016/j.actbio.2015.05.034Search in Google Scholar
[37] Tintino SR, Morais-Tintino CD, Campina FF, Pereira RL, Costa M do S, Braga MFBM, et al. Original article : ACTION OF CHOLECALCIFEROL AND ALPHA-TOCOPHEROL ON. EXCLI J. 2016;15:315–322Search in Google Scholar
[38] Stepanović S, Vuković D, Dakić I, Savić B, Švabić-Vlahović M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J Microbiol Methods. 2000;40(2):175–17910.1016/S0167-7012(00)00122-6Search in Google Scholar
[39] Stepanović S, Ćirković I, Ranin L, Švabić-Vlahović M. Biofilm formation by Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes on plastic surface. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2004;38(5):428–43210.1111/j.1472-765X.2004.01513.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Pietrangelo L, Bucci A, Maiuro L, Bulgarelli D, Naclerio G. Unraveling the composition of the root-associated bacterial microbiota of Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia Front Microbiol. 2018;9(AUG):1–1310.3389/fmicb.2018.01650Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Soto SM. Importance of Biofilms in Urinary Tract Infections: New Therapeutic Approaches. Adv Biol. 2014;2014:1–1310.1155/2014/543974Search in Google Scholar
[42] Delcaru C, Alexandru I, Podgoreanu P, Grosu M, Stavropoulos E, Chifiriuc MC, et al. Microbial biofilms in urinary tract infections and prostatitis: Etiology, pathogenicity, and combating strategies. Pathogens. 2016;5(4)10.3390/pathogens5040065Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Yousefi M, Pourmand MR, Fallah F, Hashemi A, Mashhadi R, Nazari-Alam A. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation in urinary tract infection. Iran J Public Health. 2016;45(4):485–493Search in Google Scholar
[44] Jacobsen SM, Stickler DJ, Mobley HLT, Shirtliff ME. Complicated catheter-associated urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008;21(1):26–5910.1128/CMR.00019-07Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Nicolle LE. Catheter associated urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2014;3(1):23. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-2994-3-2310.1186/2047-2994-3-23Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Siddiq DM, Darouiche RO. New strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Nat Rev Urol. 2012;9(6):305–14. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2012.6810.1038/nrurol.2012.68Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Singha P, Locklin J, Handa H, Author AB. A Review of the Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Coatings for Urinary Catheters Graphical Abstract HHS Public Access Author manuscript. Acta Biomater. 2017;50(706):20–40. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5316300/pdf/nihms837082.pdf10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.070Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] Bidossi A, Bortolin M, Toscano M, De Vecchi E, Romanò CL, Mattina R, et al. In vitro comparison between α-tocopheryl acetate and α-tocopheryl phosphate against bacteria responsible of prosthetic and joint infections. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):1–1210.1371/journal.pone.0182323Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Naguib MM, Valvano MA. Vitamin E Increases Antimicrobial Sensitivity by Inhibiting Bacterial Lipocalin Antibiotic Binding. mSphere. 2018;3(6):1–1410.1128/mSphere.00564-18Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Waldrop R, McLaren A, Calara F, McLemore R. Biofilm Growth Has a Threshold Response to Glucose in Vitro. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(11):3305–331010.1007/s11999-014-3538-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[51] Banche G, Bracco P, Allizond V, Bistolfi A, Boffano M, Cimino A, et al. Do Crosslinking and Vitamin E Stabilization Influence Microbial Adhesions on UHMWPE-based Biomaterials? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(3):974–98610.1007/s11999-014-4024-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Williams DL, Vinciguerra J, Lerdahl JM, Bloebaum RD. Does Vitamin E-blended UHMWPE Prevent Biofilm Formation? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(3):928–93510.1007/s11999-014-3673-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[53] Banche G, Bracco P, Bistolfi A, Allizond V, Boffano M, Costa L, et al. Vitamin e blended Uhmwpe may have the potential to reduce bacterial adhesive ability. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(11):1662–166710.1002/jor.21432Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2020 Franca Vergalito et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Article
- MicroRNA-451b participates in coronary heart disease by targeting VEGFA
- Case Report
- A combination therapy for Kawasaki disease with severe complications: a case report
- Vitamin E for prevention of biofilm-caused Healthcare-associated infections
- Research Article
- Differential diagnosis: retroperitoneal fibrosis and oncological diseases
- Optimization of the Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Detection of Skin Cancer
- NEAT1 promotes LPS-induced inflammatory injury in macrophages by regulating miR-17-5p/TLR4
- Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 as prognostic biomarkers in critically ill patients
- Effects of extracorporeal magnetic stimulation in fecal incontinence
- Case Report
- Mixed germ cell tumor of the endometrium: a case report and literature review
- Bowel perforation after ventriculoperitoneal-shunt placement: case report and review of the literature
- Research Article
- Prognostic value of lncRNA HOTAIR in colorectal cancer : a meta-analysis
- Case Report
- Treatment of insulinomas by laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation: case reports and literature review
- Research Article
- The characteristics and nomogram for primary lung papillary adenocarcinoma
- Undiagnosed pheochromocytoma presenting as a pancreatic tumor: A case report
- Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma
- Diagnostic value of recombinant heparin-binding hemagglutinin adhesin protein in spinal tuberculosis
- Primary cutaneous DLBCL non-GCB type: challenges of a rare case
- LINC00152 knock-down suppresses esophageal cancer by EGFR signaling pathway
- Case Report
- Life-threatening anaemia in patient with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome)
- Research Article
- QTc interval predicts disturbed circadian blood pressure variation
- Shoulder ultrasound in the diagnosis of the suprascapular neuropathy in athletes
- The number of negative lymph nodes is positively associated with survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in China
- Differentiation of pontine infarction by size
- RAF1 expression is correlated with HAF, a parameter of liver computed tomographic perfusion, and may predict the early therapeutic response to sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates colorectal cancer cells by miR-205/YAP1 axis
- Tissue coagulation in laser hemorrhoidoplasty – an experimental study
- Classification of pathological types of lung cancer from CT images by deep residual neural networks with transfer learning strategy
- Enhanced Recovery after Surgery for Lung Cancer Patients
- Case Report
- Streptococcus pneumoniae-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in an immunosuppressed adult
- Research Article
- The characterization of Enterococcus genus: resistance mechanisms and inflammatory bowel disease
- Case Report
- Inflammatory fibroid polyp: an unusual cause of abdominal pain in the upper gastrointestinal tract A case report
- Research Article
- microRNA-204-5p participates in atherosclerosis via targeting MMP-9
- LncRNA LINC00152 promotes laryngeal cancer progression by sponging miR-613
- Can keratin scaffolds be used for creating three-dimensional cell cultures?
- miRNA-186 improves sepsis induced renal injury via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/P53 pathway
- Case Report
- Delayed bowel perforation after routine distal loopogram prior to ileostomy closure
- Research Article
- Diagnostic accuracy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the direct identification of clinical pathogens from urine
- The R219K polymorphism of the ATP binding cassette subfamily A member 1 gene and susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population
- miR-92 regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting neogenin
- Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- NF2 inhibits proliferation and cancer stemness in breast cancer
- Body composition indices and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes. CV biomarkers are not related to body composition
- S100A6 promotes proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells via increased ubiquitin-dependent degradation of p53
- Review Article
- Focus on localized laryngeal amyloidosis: management of five cases
- Research Article
- NEAT1 aggravates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by sponging miR-22-3p
- Pericentric inversion in chromosome 1 and male infertility
- Increased atherogenic index in the general hearing loss population
- Prognostic role of SIRT6 in gastrointestinal cancers: a meta-analysis
- The complexity of molecular processes in osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Interleukin-6 gene −572 G > C polymorphism and myocardial infarction risk
- Case Report
- Severe anaphylactic reaction to cisatracurium during anesthesia with cross-reactivity to atracurium
- Research Article
- Rehabilitation training improves nerve injuries by affecting Notch1 and SYN
- Case Report
- Myocardial amyloidosis following multiple myeloma in a 38-year-old female patient: A case report
- Research Article
- Identification of the hub genes RUNX2 and FN1 in gastric cancer
- miR-101-3p sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to irradiation
- Distinct functions and prognostic values of RORs in gastric cancer
- Clinical impact of post-mortem genetic testing in cardiac death and cardiomyopathy
- Efficacy of pembrolizumab for advanced/metastatic melanoma: a meta-analysis
- Review Article
- The role of osteoprotegerin in the development, progression and management of abdominal aortic aneurysms
- Research Article
- Identification of key microRNAs of plasma extracellular vesicles and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in melanoma
- miR-30a-3p participates in the development of asthma by targeting CCR3
- microRNA-491-5p protects against atherosclerosis by targeting matrix metallopeptidase-9
- Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus
- Case Report
- Mycobacterial identification on homogenised biopsy facilitates the early diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal tuberculosis
- Research Article
- The will of young minors in the terminal stage of sickness: A case report
- Extended perfusion protocol for MS lesion quantification
- Identification of four genes associated with cutaneous metastatic melanoma
- Case Report
- Thalidomide-induced serious RR interval prolongation (longest interval >5.0 s) in multiple myeloma patient with rectal cancer: A case report
- Research Article
- Voluntary exercise and cardiac remodeling in a myocardial infarction model
- Electromyography as an intraoperative test to assess the quality of nerve anastomosis – experimental study on rats
- Case Report
- CT findings of severe novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A case report of Heilongjiang Province, China
- Commentary
- Directed differentiation into insulin-producing cells using microRNA manipulation
- Research Article
- Culture-negative infective endocarditis (CNIE): impact on postoperative mortality
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling
- Bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A meta-analysis
- Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Problems and solutions of personal protective equipment doffing in COVID-19
- Evaluation of COVID-19 based on ACE2 expression in normal and cancer patients
- Review Article
- Gastroenterological complications in kidney transplant patients
- Research Article
- CXCL13 concentration in latent syphilis patients with treatment failure
- A novel age-biomarker-clinical history prognostic index for heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction
- Case Report
- Clinicopathological analysis of composite lymphoma: A two-case report and literature review
- Trastuzumab-induced thrombocytopenia after eight cycles of trastuzumab treatment
- Research Article
- Inhibition of vitamin D analog eldecalcitol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo
- CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer
- Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on adipokine level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed high-fat diet
- 72 hour Holter monitoring, 7 day Holter monitoring, and 30 day intermittent patient-activated heart rhythm recording in detecting arrhythmias in cryptogenic stroke patients free from arrhythmia in a screening 24 h Holter
- FOXK2 downregulation suppresses EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Case Report
- Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Research Article
- Clinical prediction for outcomes of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure associated with HBV infection: A new model establishment
- Case Report
- Combination of chest CT and clinical features for diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia
- Research Article
- Clinical significance and potential mechanisms of miR-223-3p and miR-204-5p in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck: a study based on TCGA and GEO
- Review Article
- Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in noncirrhotic liver. A case report and systematic review
- Research Article
- Voltage-dependent anion channels mediated apoptosis in refractory epilepsy
- Prognostic factors in stage I gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Circulating irisin is linked to bone mineral density in geriatric Chinese men
- Case Report
- A family study of congenital dysfibrinogenemia caused by a novel mutation in the FGA gene: A case report
- Research Article
- CBCT for estimation of the cemento-enamel junction and crestal bone of anterior teeth
- Case Report
- Successful de-escalation antibiotic therapy using cephamycins for sepsis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia: A sequential 25-case series
- Research Article
- Influence factors of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis
- Assessment of knowledge of use of electronic cigarette and its harmful effects among young adults
- Predictive factors of progression to severe COVID-19
- Procedural sedation and analgesia for percutaneous trans-hepatic biliary drainage: Randomized clinical trial for comparison of two different concepts
- Acute chemoradiotherapy toxicity in cervical cancer patients
- IGF-1 regulates the growth of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition in pelvic organ prolapse
- NANOG regulates the proliferation of PCSCs via the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway
- An immune-relevant signature of nine genes as a prognostic biomarker in patients with gastric carcinoma
- Computer-aided diagnosis of skin cancer based on soft computing techniques
- MiR-1225-5p acts as tumor suppressor in glioblastoma via targeting FNDC3B
- miR-300/FA2H affects gastric cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Hybrid treatment of fibroadipose vascular anomaly: A case report
- Surgical treatment for common hepatic aneurysm. Original one-step technique
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms, quality of life and caregivers’ burden in dementia
- Predictor of postoperative dyspnea for Pierre Robin Sequence infants
- Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT in glioma by sponging miR-506-5p
- Analysis of expression and prognosis of KLK7 in ovarian cancer
- Circular RNA circ_SETD2 represses breast cancer progression via modulating the miR-155-5p/SCUBE2 axis
- Glial cell induced neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells
- Case Report
- Moraxella lacunata infection accompanied by acute glomerulonephritis
- Research Article
- Diagnosis of complication in lung transplantation by TBLB + ROSE + mNGS
- Case Report
- Endometrial cancer in a renal transplant recipient: A case report
- Research Article
- Downregulation of lncRNA FGF12-AS2 suppresses the tumorigenesis of NSCLC via sponging miR-188-3p
- Case Report
- Splenic abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus bacteremia secondary to urinary tract infection: a case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Advances in the role of miRNAs in the occurrence and development of osteosarcoma
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of pleural empyema
- Effect of miRNA-200b on the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting RhoA
- LncRNA NEAT1 promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-1294/AKT1 axis
- Key pathways in prostate cancer with SPOP mutation identified by bioinformatic analysis
- Comparison of low-molecular-weight heparins in thromboprophylaxis of major orthopaedic surgery – randomized, prospective pilot study
- Case Report
- A case of SLE with COVID-19 and multiple infections
- Research Article
- Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007121 regulates proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of trophoblast cells by miR-182-5p/PGF axis in preeclampsia
- SRPX2 boosts pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by activating PI3K/AKT axis
- Case Report
- A case report of cervical pregnancy after in vitro fertilization complicated by tuberculosis and a literature review
- Review Article
- Serrated lesions of the colon and rectum: Emergent epidemiological data and molecular pathways
- Research Article
- Biological properties and therapeutic effects of plant-derived nanovesicles
- Case Report
- Clinical characterization of chromosome 5q21.1–21.3 microduplication: A case report
- Research Article
- Serum calcium levels correlates with coronary artery disease outcomes
- Rapunzel syndrome with cholangitis and pancreatitis – A rare case report
- Review Article
- A review of current progress in triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Case Report
- Peritoneal-cutaneous fistula successfully treated at home: A case report and literature review
- Research Article
- Trim24 prompts tumor progression via inducing EMT in renal cell carcinoma
- Degradation of connexin 50 protein causes waterclefts in human lens
- GABRD promotes progression and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
- The lncRNA UBE2R2-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell growth in vitro
- LncRNA FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-182-5p relieves murine allergic rhinitis via TLR4/NF-κB pathway

