Abstract
C19H16F4O3, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 9.5792(5) Å, b = 9.5542(4) Å, c = 17.6986(9) Å, β = 99.508(5)∘, V = 1597.55(14) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0481, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1153, T = 293 K.
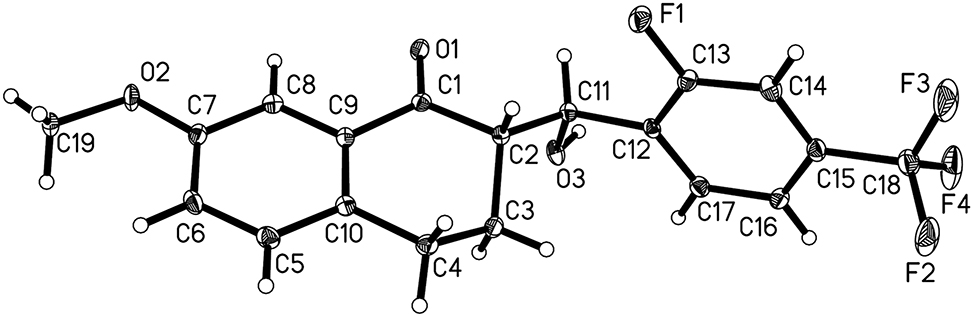
The crystal structure is shown in the Figure. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40 % probability level.
Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.12 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: μ: |
Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) 0.13 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: θ max, completeness: |
SuperNova, 25.5°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured , N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7486, 2984, 0.028 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2502 |
| N(param)refined: | 237 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.5783 (2) | 0.2291 (2) | 0.90120 (11) | 0.0129 (4) |
| C2 | 0.4323 (2) | 0.2717 (2) | 0.91677 (11) | 0.0126 (4) |
| H2 | 0.443743 | 0.361583 | 0.943790 | 0.015* |
| C3 | 0.3316 (2) | 0.2974 (2) | 0.84093 (12) | 0.0152 (5) |
| H3A | 0.323081 | 0.212900 | 0.810155 | 0.018* |
| H3B | 0.238366 | 0.322276 | 0.851173 | 0.018* |
| C4 | 0.3905 (2) | 0.4162 (2) | 0.79752 (12) | 0.0160 (5) |
| H4A | 0.330365 | 0.428978 | 0.748260 | 0.019* |
| H4B | 0.389467 | 0.502565 | 0.826261 | 0.019* |
| C5 | 0.5940 (2) | 0.4459 (2) | 0.72495 (12) | 0.0175 (5) |
| H5 | 0.536793 | 0.505706 | 0.691771 | 0.021* |
| C6 | 0.7316 (2) | 0.4195 (2) | 0.71239 (12) | 0.0171 (5) |
| H6 | 0.765118 | 0.460905 | 0.671324 | 0.021* |
| C7 | 0.8182 (2) | 0.3306 (2) | 0.76195 (12) | 0.0146 (4) |
| C8 | 0.7667 (2) | 0.2699 (2) | 0.82302 (11) | 0.0137 (4) |
| H8 | 0.824690 | 0.211162 | 0.856419 | 0.016* |
| C9 | 0.6285 (2) | 0.2962 (2) | 0.83480 (11) | 0.0121 (4) |
| C10 | 0.5396 (2) | 0.3859 (2) | 0.78526 (11) | 0.0131 (4) |
| C11 | 0.3767 (2) | 0.1676 (2) | 0.97036 (11) | 0.0139 (4) |
| H11 | 0.451738 | 0.150908 | 1.014224 | 0.017* |
| C12 | 0.2467 (2) | 0.2205 (2) | 1.00053 (11) | 0.0126 (4) |
| C13 | 0.2563 (2) | 0.3275 (2) | 1.05421 (12) | 0.0155 (4) |
| C14 | 0.1444 (2) | 0.3740 (2) | 1.08781 (12) | 0.0178 (5) |
| H14 | 0.156028 | 0.445362 | 1.124055 | 0.021* |
| C15 | 0.0140 (2) | 0.3102 (2) | 1.06534 (12) | 0.0160 (5) |
| C16 | −0.0024 (2) | 0.2048 (2) | 1.01059 (12) | 0.0168 (5) |
| H16 | −0.090617 | 0.163869 | 0.995184 | 0.020* |
| C17 | 0.1134 (2) | 0.1609 (2) | 0.97897 (12) | 0.0159 (5) |
| H17 | 0.101724 | 0.089981 | 0.942492 | 0.019* |
| C18 | −0.1117 (2) | 0.3531 (2) | 1.09992 (13) | 0.0217 (5) |
| C19 | 1.0140 (2) | 0.3652 (3) | 0.69570 (12) | 0.0216 (5) |
| H19A | 0.955676 | 0.347368 | 0.647115 | 0.032* |
| H19B | 1.107654 | 0.330063 | 0.695010 | 0.032* |
| H19C | 1.018278 | 0.464145 | 0.705200 | 0.032* |
| F1 | 0.38489 (13) | 0.38979 (13) | 1.07585 (7) | 0.0224 (3) |
| F2 | −0.21041 (16) | 0.41932 (17) | 1.05058 (9) | 0.0416 (4) |
| F3 | −0.07929 (17) | 0.4326 (2) | 1.16122 (10) | 0.0587 (6) |
| F4 | −0.18188 (16) | 0.24189 (16) | 1.12227 (9) | 0.0406 (4) |
| O1 | 0.65304 (15) | 0.14541 (15) | 0.94221 (8) | 0.0171 (3) |
| O2 | 0.95477 (16) | 0.29652 (16) | 0.75505 (8) | 0.0194 (4) |
| O3 | 0.34839 (16) | 0.03904 (15) | 0.92984 (8) | 0.0167 (3) |
| H3 | 0.345647 | −0.024889 | 0.960473 | 0.025* |
1 Source of material
The raw material 7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalene-1(2H)-one was obtained according to a literature [4]. The raw material (0.53 g, 3.0 mmol) and 2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde (0.58 g, 3.0 mmol) were dissolved in 15 mL of methanol. About 5.0 mL of 20 % NaOH solution was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for about 1 h, and detected the reaction process by Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC). The solvent was then removed by pouring, and the residues were purified on a silica gel by column chromatography using petroleum ether/EtOAc (2:1, v/v) as the eluent to obtain the light yellow solid of the title compound in 82.2 % yield.
2 Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d(C–H) = 0.96 Å(methyl), U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C); d(C–H) = 0.97 Å(methylene), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C); U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C); d(C–H) = 0.93 Å(aromatic), U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C); and d(O–H) = 0.82 Å(hydroxyl), U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O), respectively.
3 Comment
3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one is an active fragment with potential for the treatment of allergies and inflammatory phenomena among others [5]. In our previous study, we demonstrated that compounds with 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one fragment could have inhibitory effects on the NF-κB signaling pathway [6], so we introduced electron-withdrawing groups fluorine atoms and trifluoromethyl side chains based on the original compounds with aromatic aldehydes through the Claisen–Schmidt reaction because their lipophilicity could enhance the membrane permeability of the drug, the stabilized C–F bond could improve the metabolic stability and prolong the duration of in vivo action. It is well known that fluorine atoms are the strongly electronegative that can form hydrogen bonds with the target proteins, thus enhancing the inhibitory effect of the drug against NF-κB [7]. Previously, we reported a series of condensation products with electron-donoring and electron-withdrawing groups, which were obtained by Claisen–Schmidt condensation reaction between aromatic aldehydes and 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one [8], [9], [10], [11]. The common structural features is the formation of α,β-unsaturated ketones. In this study, we still expected the compound containing the α,β-unsaturated ketone, but our structural analysis of the title compound revealed that there is β-hydroxyketone unit [12] but not β-unsaturated ketone unit.
Single-crystal structure analysis reveals that there is only a title molecule in the asymmetric unit (cf. the Figure). The bond lengths and bond angles of the title compound are within the normal range and are in agreement with previous reports [7, 9, 11, 13]. The parent nucleus of this compound is 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one with a methoxy group attached to C(7), while a 2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl substituted β-hydroxyketone attached to C(2). Interestingly, C(11) is a chiral carbon atom. In the solid state, the molecules crystallize in a centrosymmetric space group, P21/n, and the whole does not show chiral properties. In addition, the benzene ring is substituted with electron-withdrawing substituents (–F and –CF3), and the substituted benzene ring is not coplanar with the parent nucleus with a big dihedral angle of about 85.20(2)∘. The C(11)-substituted hydroxyl group and C(1)=O(1) group did not form the intramolecular hydrogen bond, and the torsion angle of C(1)–C(2)–C(1)–O(3) is about −68.3(2)∘, and the torsion angle of O(1)=C(1)–C(2)–C(11) is about −17.7(3)∘, respectively. The C(11)-substituted hydroxyl group and the C(13)-substituted fluorine atom are in the trans structure, so that the torsion angle of O(3)–C(11)–C(12)–C(13) is about 166.92(17)∘, and the torsion angle of C(11)–C(12)–C(13)–F(1) is about 3.8(3)∘, respectively.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2023MH190).
-
Competing interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sun, Y., Gao, Z. F., Wang, C. H., Hou, G. G. Synthesis, crystal structures and anti-inflammatory activity of fluorine-substituted 1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine derivatives. Acta Crystallogr. 2019, C75, 1157–1165; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229619010118.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Barlow, J. W., Zhang, T., Woods, O., Byrne, A. J., Walsh, J. J. Novel mast cell-stabilising amine derivatives of 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one and 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[7]annulen-5-one. Med. Chem. 2011, 7, 213–223; https://doi.org/10.2174/157340611795564222.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Kirby, A. J., Le, L. R., Maharlouie, F., Mason, P., Nicholls, P. J., Smith, H. J. Inhibition of retinoic acid metabolising enzymes by 2-(4-aminophenylmethyl)-6-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one and related compounds. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2003, 18, 27–33; https://doi.org/10.1080/1475636021000049221.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Luan, M. Z., Wang, H. Y., Zhang, M., Song, J., Hou, G. G., Zhao, F. L., Meng, Q. G. Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 61–63; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0446.Search in Google Scholar
8. Sun, Y., Zhou, Y. Q., Liu, Y. K., Zhang, H. Q., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G., Hou, Y. Potential anti-neuroinflammatory NF-κB inhibitors based on 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one derivatives. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1631–1640; https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1804899.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Zhang, Y. L., Liu, S. L., Hou, G. G., Zhang, X. F., Wang, L., Xin, W. Y. Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H15BrO2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 945–947; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0315.Search in Google Scholar
10. Zhang, X. F., Luan, M. Z., Yan, W. B., Zhao, F. L., Hou, Y., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of novel 5,6-dihydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine derivatives in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114322; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114322.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Qi, Q. B., Li, W. X., Hou, G. G., Li, C. B. Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H23BrN2O. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 235–237; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0590.Search in Google Scholar
12. Yang, Y., Gao, Z. F., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G., Hou, Y. Discovery of anti-neuroinflammatory agents from 1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[2,3]oxepino[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2-amine derivatives by regulating microglia polarization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 259, 115688; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115688.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Dai, Z.-Y., Nong, Z.-S., Wang, P.-S. Light-mediated asymmetric aliphatic C–H alkylation with hydrogen atom transfer catalyst and chiral phosphoric acid. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 4786–4790; https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c00610.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of bis(dimethylammonium) poly[(μ4-1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato))-κ6O1, N2:O2:O3:O1′,N2′]nickel (II)], C22H26N6NiO8
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)] – 4,4′-bipyridine – water (1/2/2)
- Crystal structure of (2S,3S,4S,5S, Z)-2,3,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)-4-hydroxyhexanal oxime, C34H37NO6
- The crystal structure of hexakis(3-thiophenecarboxylato-κ2O,O″)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) trimanganese(II), C54H34N4O12S6Mn3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(4-bromobenzoate-κ2O:O′)-(μ-2-bromobenzoate-κ2O,O′)nickel(II)] – water (2/1), C30H21Br2N2NiO4.5
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ3-1,3-phenylenedioxydiacetate-κ5O,O,O′,O″,O‴)-bis(4′-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-4,2′:6′,4″-terpyridine-kN) cadmium(II)], C58H42CdN10O6
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-6′-methyl-3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-1′-ium 4-methylbenzenesulfonate
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ-benzoato)-(μ-cis-4–hydroxy-D-proline)lithium], C12H14LiNO5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3N,O,O′)-copper(II)] monohydrate, C7H6NO6ICu
- The crystal structure of catena-[diaqua-(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ2O,O)-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ3O,O:O)-dihydrate-lanthanum(III)]–4,4′-bipyridine (2/1), C35H35NO14La
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-iodopyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,O′′)(4-imidazol-1-yl-pyridine-κN)copper(II)], C15H9N4O4ICu
- Crystal structure of polybis(μ 4-3,5-dicarboxylatopyrazol-1-yl)-bis(N,N-dimethylformamide)tri-copper(II)–acetonitrile (1/2), C20H22Cu3N8O10
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-5-hydroxy-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O″,O‴)-(μ2-1,5-bis(imidazol-2-methyl)pentane-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], C21H24CdN4O5
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bi(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)bis(μ2-4,4′-methylenebis(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate)-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C35H24CoN4O6
- The crystal structure of a cobalt-vanadium-oxido hydrate
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-2H-1,2,3-triazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)-(μ 2-1,3-bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ 2 N,N′) zinc(II)], C18H15N7O4Zn
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(bis(m2-1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene)-κ2N,N′-manganese] dichloride, C28H32MnN8O2Cl2
- The crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino [3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium (E)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)acrylate pentahydrate, C29H34N2O13
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ6-ammoniotris(methylene))tris(hydrogen phosphonato)cadmium(II)], C3H10CdNO9P3
- Crystal structure of Zn2[(1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-(pyridin-3-yl)urea))·(H2O)2·(DMF)2·(SO4)2], C24H50N8O18S2Zn2
- The crystal structure of 2-anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone, C10H11NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(2-(4-(diethylamino)styryl)-1-ethyl-1,4-dihydroquinolin-4-yl) malononitrile, C26H26N4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-((2,6-dichloro-4-(cyanomethyl)phenyl) amino)benzoate, C17H14Cl2N2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H13NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile-κ1N)tetrakis(μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)rhodium(II) (Rh–Rh), C32H18F8O8N2Rh2
- The crystal structure of a new polymorph of 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, C11H8O3
- The crystal structure of [(8-carboxymethoxy-quinoline-2-carboxylate-κ4N,O,O,O)-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N-copper(II)] tetrahydrate, C22H23N3O9Cu
- The crystal structure of ethyl 4-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C23H19NO7
- Crystal structure of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C10H10O2
- Crystal structure of bis(tetrapropylammonium) dodecacarbonyltetratelluridotetraferrate(2-), (Pr4N)2[Fe4Te4(CO)12]
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2−3−aminopyridine−4−carboxylato−κ2N:O)Zinc(II)], [Zn(C6H5N2O2)2] n
- The crystal structure of methyl 5-nitro-2-(tosyloxy)benzoate, C15H13NO7S
- The crystal structure of 18-crown-6 ― tetraaqua-dichlorido-di-μ2-chloridodicopper(II) (2/1), C12H32O10Cu2Cl4
- Crystal structure of 6,6a,7,8,9,10-hexahydro-5H-pyrazino [2,3-e]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine, C10H14N4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly-{diaqua-bis[μ-(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)](μ2-4, 4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)} dihydrate, C26H30Cl2CoN4O12S2
- Crystal structure of bis{N′-[1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-N-phenylcarbamohydrazonothioato}zinc(II), C44H36N6S2Zn
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)glycinato-κO)cobalt(II) dihydrate, C16H26Cl2CoN2O14S2
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-phenyl-1-(quinolin-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol, C24H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 2-((2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)(hydroxy)methyl)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1((2H))-one, C19H16F4O3
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-methoxy-1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-3-ium chloride, C20H18ClF4N3O
- Crystal structure of (2-phenylimino methylquinoline-κ 2 N,N′)-bis(1–phenylpyrazole-κ 2 C,N)-iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C34H26F6IrN6P
- Crystal structure of (3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methanone, C12H15NO3
- The crystal structure of bis(trimethylsulfoxonium) catena-poly[µ2-hexabromido-indium(III)sodium(I)] C6H18O2S2NaInBr6
- Crystal structure of N-cyclopropyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C11H13NO3
- The crystal structure of (bis(benzimidazol-2-yl-methyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N″ )-(dihydrogen L-malate-κ2O,O ′)copper(II) perchlorate dihydrate, CuC20H24ClN5O12
- Crystal structure of (1E,1′E)-4,4′-(9,9-diethyl-9H-fluorene-2,7-diyl)dibenzaldehyde dioxime, C31H28N2O2
- Crystal structure of diethyl 1,9-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,6-diphenylhexahydro-3H-2,7,3,5-(epimethanetriyliminomethanetriyl)cyclopenta [b]pyridine-3,7(2H)-dicarboxylate, C40H36F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(benzene-1 carboxylato-O 3,5-carboxyl-κ1O)-[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)nickel(II) ─ benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid ─ water (1/2/4), C52H66N4NiO28
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)benzene-1,4-diol, C12H16Br2O4
- Crystal structure of dicarbonyl[N,N′-(1,2-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediylidene)bis[2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)benzenamine]-N,N′]nickel(0), C30H40N2NiO2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-dibromo-2,5-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzene, C12H8Br2O2
- Crystal structure of O-(3-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-yl) O-phenyl carbonothioate, C24H15NO2S2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-N-(4,5-dihydropyren-2-yl)methanimine, C24H16N2S
- Crystal structure of 3-((4-bromophenyl)thio)-1H-indole, C14H10BrNS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carboxylate monohydrate, C22H22N2O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (3E,5S,10S,13S,14S,17Z)-17-ethylidene-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-3-one O-(methacryloyl) oxime, C50H74N2O4
- Crystal structure of the hydrogen storage active phase La12Mg46LiMn
- The crystal structure of the salt: 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)carbamoyl)pyridine-1-ium 2-carboxybenzoate, C14H10N3O3·C8H5O4
- Crystal structure of (2-(2-pyridine)-benzimidazole-κ2 N,N′)-bis(1-phenylpyrazole-κ2 C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate, C30H22F6IrN7P
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis[2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridine-κ1N]platinum(II), C22H14Cl2F4N2Pt
- Crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R, 17S,17Z)-2-((3-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3

