Abstract
C19H13N2ZnCl5, monoclinic, I2/a, a = 15.2859(2) Å, b = 14.7894(1) Å, c = 18.0569(2) Å, β = 97.311(1)°, V = 4048.92(8) Å3, Z = 8, R gt (F) = 0.0260, wR ref (F2) = 0.0722, T = 296 K.
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data.
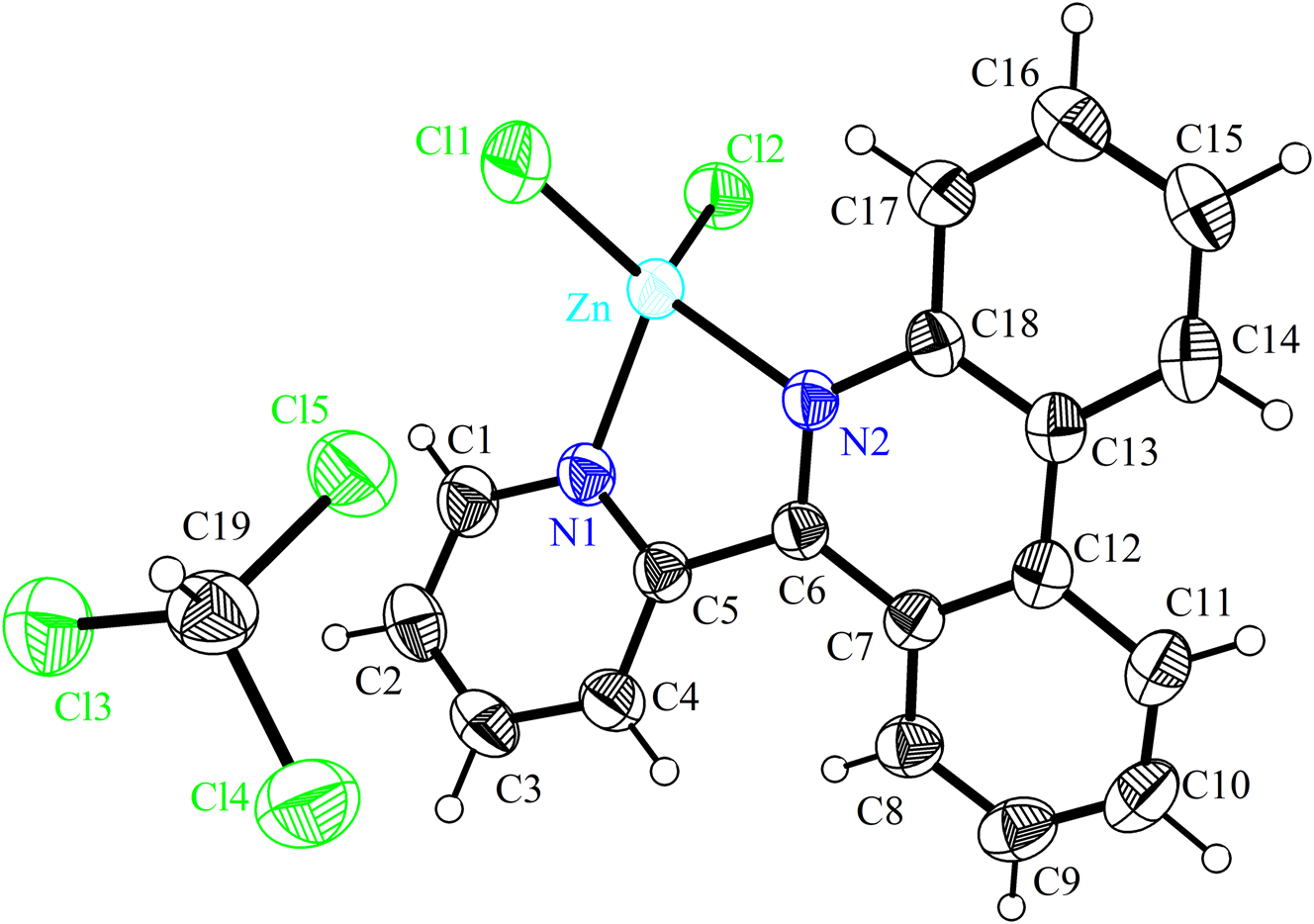
Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif- file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Clear yellowish colourless block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.15 × 0.14 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 7.82 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Rigaku Synergy, ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 77.6°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 25,997, 4,217, 0.035 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3,828 |
| N(param)refined: | 245 |
| Programs: | Rigaku, 1 SHELX, 2 Olex2 3 |
1 Source of materials
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used as received without further purification. 6-(Pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine was prepared as reported. 4 , 5 A solution of 6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine (0.01 mmol) in chloroform (4 mL) was added to a stirred solution of ZnCl2 (0.01 mmol) in acetonitrile (2 mL) at room temperature for 2 h. After filtration, slow diffusion of diethyl ether into the filtrate over 72 h afforded block yellow crystals.
2 Experimental details
The structure solution followed standard methods; the SHELXL 2 refinement package were employed to refine the crystal structure. The Olex2 3 was used to visualize the crystal structure. All hydrogen atoms were placed in idealized positions. Their Uiso values were set to 1.2Ueq of the parent atoms.
3 Comment
Symmetric chelating ligands such as 2,2′-bipyridine and phenanthroline play important roles in the fields of coordination chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, catalytic chemistry, and optoelectronic materials. 6 , 7 Asymmetric chelating ligands with flexible and versatile structures can provide richer electronic and spatial effects and shows potential application value in the field of functional complexes. 8 , 9 The unsymmetric chelating ligand composed of phenanthrene ring and pyridine ring coordinated with Zn(II) to form the planar structure and the rigid structures of the complex can reduce the non-radiative transition process, thereby improving the luminescence efficiency of the Zn(II) complex. 10
Each Zn(II) shows a tetrahedral coordination geometry and is ligated by one N atom from one pyridine, one N atom from phenanthridine moiety, 11 and two chlorido ligands (see the Figure). In addition, there is a free chloroform molecule present in the crystal structure. For C19H13N2ZnCl5, The Zn–Cl bond lengths range are 2.1970(5)–2.2182(6) Å, while the Zn–N bond lengths are 2.0500(15)–2.0673(13) Å. The Cl–Zn–Cl, and N–Zn–N angles are 116.82(2) and 80.07(6)°, respectively, while those for N–Zn–Cl are 111.10(5)–115.96(5)°. The C–N–Zn angles range from 113.20(11) to 125.51(13)°. It should be noted that the above bond lengths and angles are consistent with the reported Zn-based complexes. 12
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support by the NSFC of China (21703291), the NSF of Guangdong Province (2017A030310258), the Education Department of Guangdong Province (2022ZDJS027) and Jiangmen Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (Jiangke 2020-135, Jiangke 2021-76).
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Research funding: NSFC of China (21703291), the NSF of Guangdong Province (2017A030310258), the Education Department of Guangdong Province (2022ZDJS027) and Jiangmen Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (Jiangke 2020-135, Jiangke 2021-76).
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
References
1. Meyer, M.; Paciorek, W.; Kowalski, A.; Muszynski, A.; Wisniewski, A.; Pol, M., Przewozniczek, M., et al.. CrysAlisPRO Software System, Version 171.42.94a; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Rigaku Corporation: Wroclaw, 2023.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8, https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Mandadapu, A. K.; Saifuddin, M.; Agarwal, P. K.; Kundu, B. A New Entry to Phenanthridine Ring Systems via Sequential Application of Suzuki and the Modified Pictet–Spengler Reactions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2796–2803; https://doi.org/10.1039/b905696c.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Q. Bronsted Acid-Mediated Reactions of Aldehydes with 2-Vinylaniline and Biphenyl-2-Amine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 2280–2282; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2014.02.090.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Kaes, C.; Katz, A. Bipyridine: The Most Widely Used Ligand. A Review of Molecules Comprising at Least Two 2,2-Bipyridine Units. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3553–3590; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr990376z.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Su, M. M.; Ni, J.; Guo, Z. C.; Liu, S. Q.; Zhang, J. J.; Meng, C. G. Long-Wavelength NIR Luminescence of 2,2′-Bipyridyl-Pt(ii) Dimers Achieved by Enhanced Pt–Pt Interaction. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 4192–4199; https://doi.org/10.1039/d1qi00546d.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Payce, E. N.; Knighton, R. C.; Platts, J. A.; Horton, P. N.; Coles, S. J.; Pope, S. J. A. Luminescent Pt(II) Complexes Using Unsymmetrical Bis(2-Pyridylimino)isoindolate Analogues. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 8273–8285; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c00558.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Elgar, C. E.; Otaif, H. Y.; Beames, J. M.; Horton, P. N.; Coles, S. J.; Hallett, A. J.; O’Kell, S. P.; Pope, S. J. A. Deep Red Emitting Heteroleptic Ir(III) Complexes that Incorporate Unsymmetrical 4-quinoline Carboxylic Acid Derived Ligands. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 26; e202300102; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.202300102.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Xiong, J.; Li, K.; Teng, T.; Chang, X.; Wei, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, C. Dinuclear ZnII Complexes Exhibiting Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence and Luminescence Polymorphism. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26 (30), 6887–6893; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202000572.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Carver, C. T.; Williams, B. N.; Ogilby, K. R.; Diaconescu, P. L. Coupling of Aromatic N-Heterocycles Mediated by Group 3 Complexes. Organometallics 2010, 29, 835; https://doi.org/10.1021/om900943m.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Liu, Q. D.; Wang, R.; Wang, S. Blue Phosphorescent Zn(II) and Orange Phosphorescent Pt(II) Complexes of 4,4′-Diphenyl-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′- bipyrimidine. Dalton Trans. 2004, 14, 2073–2079, https://doi.org/10.1039/b404905e.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

