Abstract
C13H12Cl2N2OS, orthorhombic, Pna21 (no. 33), a = 30.2415(19) Å, b = 6.0253(4) Å, c = 7.8933(6) Å, V = 1438.27(17) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0428, wRref (F 2) = 0.1046, T = 285 K.
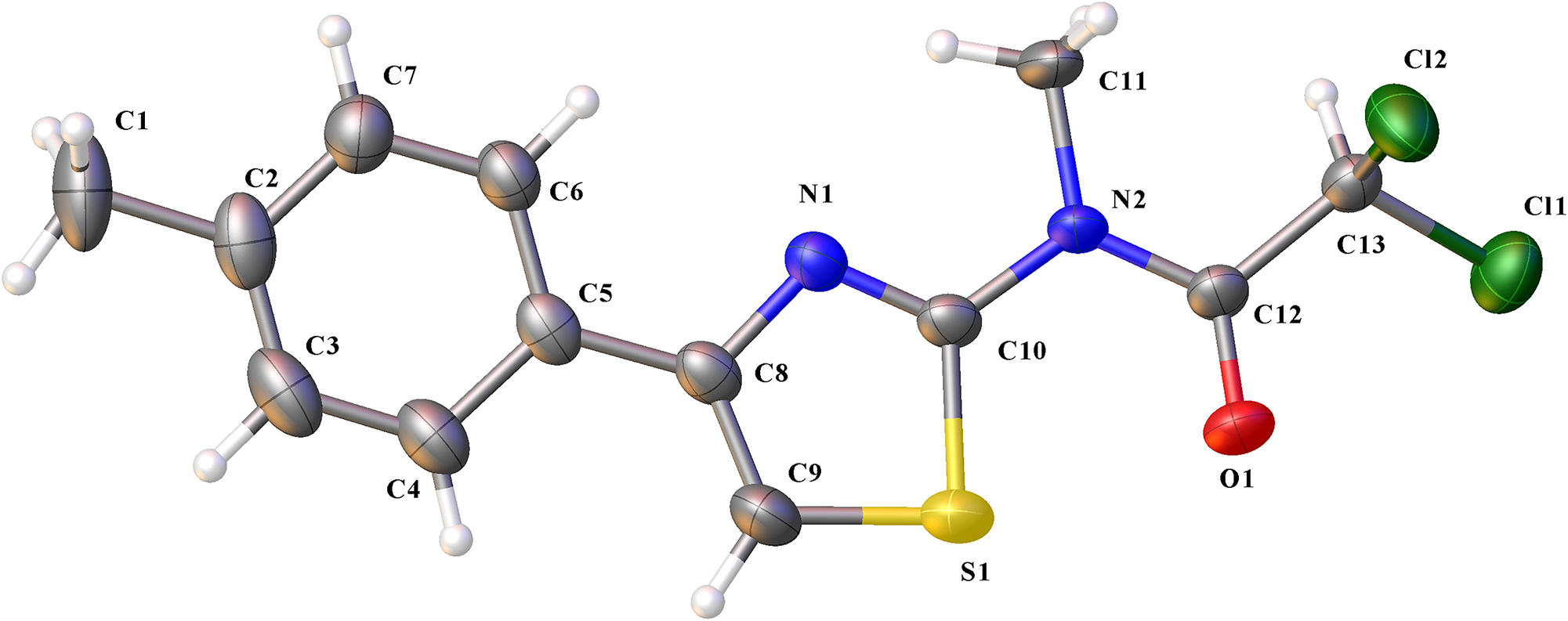
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains the crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.15 × 0.13 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.59 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX II, φ and ω scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.5°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 27472, 3288, 0.032 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3231 |
| N(param)refined: | 173 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 , 3 SHELX 4 |
1 Source of material
The title compound was synthesized according to literature with slight modification. 5 , 6 A solution was formed consisting of 5.76 mmol (1.23 g) of 2-bromo-4′-methylacetophenone, 5.49 mmol (0.56 g) of triethylamine and 25 mL of ethanol. N-methylthiourea (0.92 g, 5.49 mmol) was added to the mixture by drops followed by heated to reflux. After the reaction was completed, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation. The obtained substance was dissolved in dichloromethane, then washed three times with saturated salt water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filtered, and the solvent was then evaporated under reduced pressure to yield intermediate (N-methyl-4-p-tolylthiazol-2-amine). The intermediate (1.02 g, 5.00 mmol) and triethylamine (1.52 g, 15.00 mmol) were added to 30 mL of acetonitrile. Subsequently, dichloracetyl chloride (1.47 g, 10.00 mmol) was added dropwise with stirring at room temperature for 2.00 h. After removing the solvent by rotary evaporation, the product was purified via column chromatography on silica gel (petroleum ether: EtOAc = 10:1, v/v). Crystals of the title compound were obtained by using a mixed solvent of EtOAc and petroleum ether at room temperature.
2 Experimental details
The structures was solved by direct methods with the SHELXS program. 4 All hydrogen atoms were placed in geometrically calculated positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.
3 Comment
N-dichloroacetamides herbicide safeners have generated considerable commercial interest and research activity for their application to crops to alleviate the injury from herbicides. 7 , 8 Thiazole derivatives, due to their unique physiological activities, are extensively utilized in the development of active small molecules for applications in pesticides and pharmaceuticals. 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 In view of the principle of fragment splicing, 14 the thiazole derivative and dichloroacetyl were spliced together to design and synthesize novel potential 2-dichloroacetyl thiazole derivatives herbicide safeners.
Single-crystal structure analysis revealed that the title compound belongs to orthorhombic system, The space group type is Pna21. Bond lengths and angles are all in normal ranges. 15 , 16 There is only a drug molecule in the asymmetric unit (see the Figure). Obviously, there is π–π conjugation effect in amide moiety, which cause shorter N(2)–C(12) (1.360(3) Å) bond than the normal N–C (1.47 ∼ 1.50 Å). Besides, the torsion angle of N(1)–C(8)–C(5)–C(4) and N(1)–C(8)–C(5)–C(6) are 175.3(3)° and −5.0(3)°, respectively, which indicate the benzene ring and thiazole ring are almost coplanar. The torsion angles of N(1)–C(10)–N(2)–C(12) and S(1)–C(10)–N(2)–C(12) are 176.9(3)° and −2.1(3)°, respectively, so the carbon atom C(12) and thiazole ring are almost coplanar. Weak intermolecular C–H⋯O and C–H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds are founded.
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30900953), Undergraduate SIPT Program of Northeast Agricultural University (X202410224231).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refifinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment-Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. A 2015, 71, 59–75. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. A Short History of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, A64, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Sun, M.; Xu, Q.; Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, D.; Guan, Q.; Bao, K.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W. Synthesis and Bioevaluation of N,4-Diaryl-1,3-Thiazole-2-Amines as Tubulin Inhibitors with Potent Antiproliferative Activity. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0174006. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174006.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Lu, W.; Ma, Z. Y.; Dong, X. N.; Li, Y. J. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Safen Activity of Some New N-Dichloroacetylindole Derivatives. Indian J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2023, 33, 165–171; https://doi.org/10.59467/ijhc.2023.33.165.Search in Google Scholar
7. Sivey, J. D.; Lehmler, H. J.; Salice, C. J.; Ricko, A. N.; Cwiertny, D. M. Environmental Fate and Effe of Dichloroacetamide Herbicide Safeners: “Inert” Yet Biologically Active Agrochemical Ingredients. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 2, 260–269. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00220.Search in Google Scholar
8. Kazinczi, G.; Biro, K.; Horvath, J.; Takács, P. A.; Béres, I. Effect of Acenit 50 EC (Acetochlor) and Acenit A 500 EC Acetochlor+AD-67 Safener (52-Dichloro-Acetyl-11-Oxo-Azaspiro-(4,5)-Decane) on the Early Root Development of Maize. Növénytermelés 2003, 52, 657–666.Search in Google Scholar
9. Ekler, Z.; Stephenson, G. R. Comparative Effectiveness and Mode of Action of Safeners for Chloroacetamide Herbicides in Maize Seedlings. Z. Naturforsch., C: Biosci. 1991, 46, 828–835. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-1991-9-1018.Search in Google Scholar
10. Bondock, S.; Fadaly, W.; Metwally, M. A. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Thiazole, Thiophene and Pyrazole Derivatives Containing Benzothiazole Moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3692–3701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.05.018.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Kashyap, S. J.; Garg, V. K.; Sharma, P. K.; Kumar, N.; Dudhe, R.; Gupta, J. K. Thiazoles: Having Diverse Biological Activities. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 2123–2132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9685-2.Search in Google Scholar
12. Mo, W.; Shi, Y.; He, J.; Li, B.; Peng, H. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Ethyl 4-Alkyl-2-(2-(substituted phenoxy)acetamido) thiazole-5-carboxylate. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2016, 53, 183–187. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.2302.Search in Google Scholar
13. Zhao, L.; Yin, M.; Wang, Q.; Zou, Y. L.; Ren, T.; Gao, S.; Fu, Y.; Ye, F. Novel Thiazole Phenoxypyridine Derivatives Protect Maize from Residual Pesticide Injury Caused by PPO-Inhibitor Fomesafen. Biomolecules 2019, 9 (10). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100514.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Deng, X.; Zheng, W.; Jin, C.; Bai, L. Synthesis of Novel 6-Aryloxy-4-chloro-2-phenylpyrimidines as Fungicides and Herbicide Safeners. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 23996–24004. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03300.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
15. Li, Y.; Zhong, H.; Guo, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhou, T. The Crystal Structure of 2,2,5-Trimethyl-3-(4-(4-(5-phenyl-4,5-dihydroisoxazol- 3-yl)thiazol-2-yl) phenyl)Imidazolidin-4-one, C24H24N4O2S. Z. Kristallogr. New. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 1017–1019. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0266.Search in Google Scholar
16. Geng, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y. X. Crystal Structure of N-(Benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-2-chloroacetamide, C9H7ClN2OS. Z. Kristallogr. New. Cryst. Struct. 2024, 239, 639–640. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0116.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

