Abstract
C28H29AsCl2Ru, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 15.4135(9) Å, b = 9.2514(5) Å, c = 35.444(2) Å, β = 97.000(3)°, V = 5016.5(5) Å3, Z = 8, R gt (F) = 0.0537, wRref(F2) = 0.1127, T = 100 K.
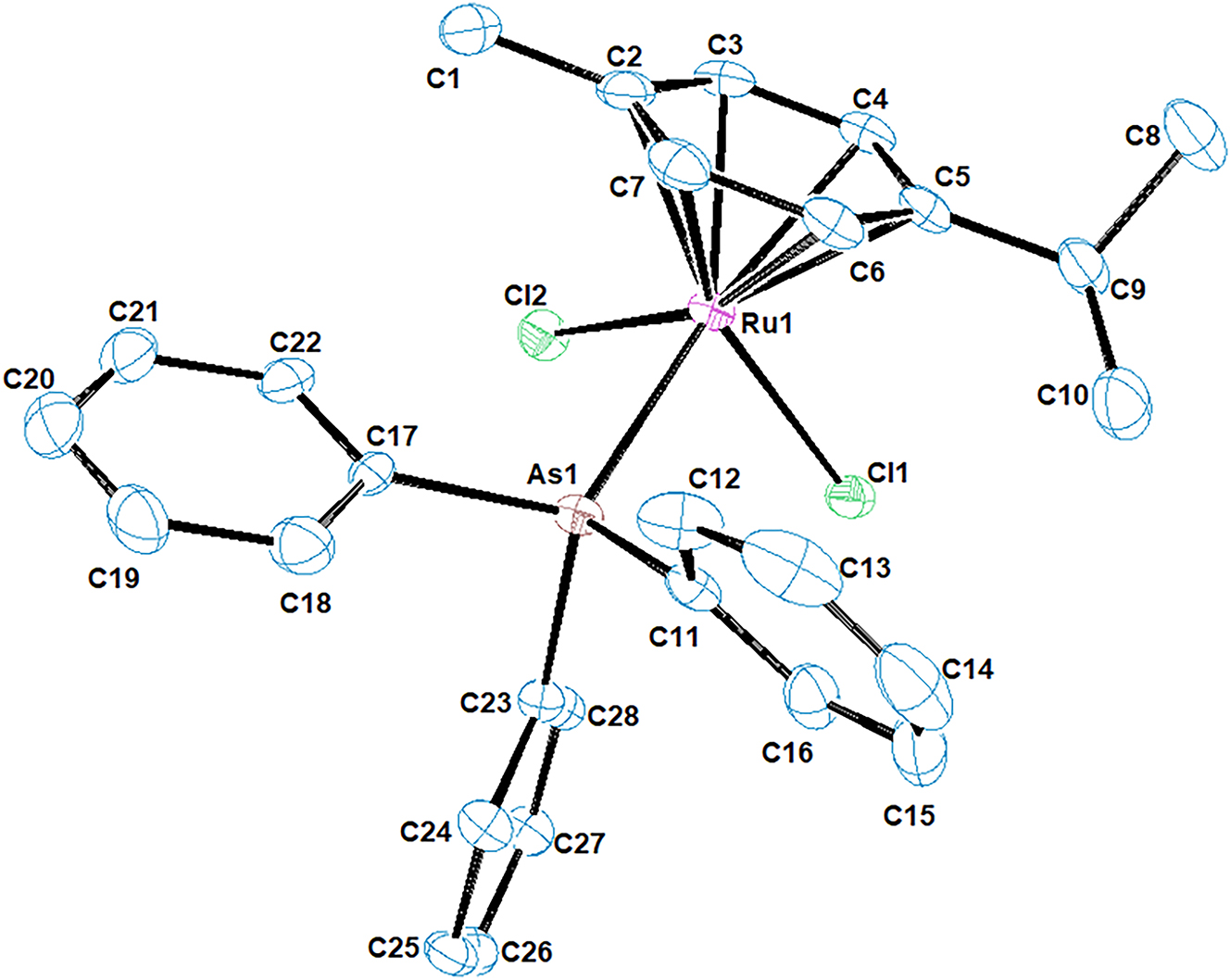
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red hexagonal |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.45 × 0.62 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.16 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker (D8 Quest), φ and ω scan |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 273096, 12482, 0.085 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 10,807 |
| N(param)refined: | 583 |
| Programs: | Bruker 1 , SHELX 2 , Olex2 3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.4307 (4) | 0.9230 (6) | 0.70430 (16) | 0.0354 (13) |
| H1A | 0.494189 | 0.922206 | 0.711286 | 0.053* |
| H1B | 0.403079 | 0.976654 | 0.723490 | 0.053* |
| H1C | 0.416717 | 0.969654 | 0.679484 | 0.053* |
| C2 | 0.3971 (3) | 0.7706 (6) | 0.70224 (14) | 0.0255 (10) |
| C3 | 0.4232 (3) | 0.6699 (6) | 0.73213 (13) | 0.0232 (10) |
| H3 | 0.462326 | 0.700278 | 0.753451 | 0.028* |
| C4 | 0.3922 (3) | 0.5272 (5) | 0.73059 (12) | 0.0213 (9) |
| H4 | 0.409672 | 0.463234 | 0.751082 | 0.026* |
| C5 | 0.3347 (3) | 0.4768 (6) | 0.69863 (13) | 0.0217 (9) |
| C6 | 0.3077 (3) | 0.5759 (6) | 0.66936 (13) | 0.0238 (10) |
| H6 | 0.267683 | 0.545901 | 0.648306 | 0.029* |
| C7 | 0.3395 (3) | 0.7197 (6) | 0.67094 (14) | 0.0250 (10) |
| H7 | 0.321726 | 0.783537 | 0.650461 | 0.030* |
| C8 | 0.2275 (4) | 0.3145 (7) | 0.72268 (17) | 0.0409 (14) |
| H8A | 0.247831 | 0.346449 | 0.748610 | 0.061* |
| H8B | 0.206771 | 0.214438 | 0.723255 | 0.061* |
| H8C | 0.179512 | 0.376924 | 0.711736 | 0.061* |
| C9 | 0.3032 (3) | 0.3234 (6) | 0.69827 (14) | 0.0275 (11) |
| H9 | 0.352044 | 0.262438 | 0.710762 | 0.033* |
| C10 | 0.2754 (4) | 0.2605 (7) | 0.65864 (16) | 0.0410 (15) |
| H10A | 0.226086 | 0.316188 | 0.646019 | 0.061* |
| H10B | 0.257773 | 0.159411 | 0.661003 | 0.061* |
| H10C | 0.324528 | 0.265606 | 0.643562 | 0.061* |
| C11 | 0.3700 (3) | 0.5365 (5) | 0.57964 (12) | 0.0199 (9) |
| C12 | 0.2939 (3) | 0.6151 (7) | 0.56979 (14) | 0.0322 (12) |
| H12 | 0.292474 | 0.715114 | 0.575757 | 0.039* |
| C13 | 0.2200 (4) | 0.5485 (9) | 0.55126 (15) | 0.0422 (16) |
| H13 | 0.167908 | 0.602775 | 0.544955 | 0.051* |
| C14 | 0.2218 (4) | 0.4037 (8) | 0.54195 (16) | 0.0451 (17) |
| H14 | 0.171576 | 0.358633 | 0.528760 | 0.054* |
| C15 | 0.2969 (4) | 0.3250 (7) | 0.55196 (16) | 0.0384 (14) |
| H15 | 0.298354 | 0.225320 | 0.545663 | 0.046* |
| C16 | 0.3705 (3) | 0.3899 (6) | 0.57109 (14) | 0.0279 (11) |
| H16 | 0.421467 | 0.333947 | 0.578406 | 0.033* |
| C17 | 0.4810 (3) | 0.8107 (5) | 0.59428 (13) | 0.0205 (9) |
| C18 | 0.4470 (4) | 0.8569 (6) | 0.55764 (14) | 0.0304 (11) |
| H18 | 0.413324 | 0.792822 | 0.540802 | 0.037* |
| C19 | 0.4632 (4) | 0.9972 (6) | 0.54625 (16) | 0.0350 (13) |
| H19 | 0.439648 | 1.029364 | 0.521670 | 0.042* |
| C20 | 0.5133 (4) | 1.0902 (6) | 0.57039 (18) | 0.0369 (13) |
| H20 | 0.525621 | 1.184597 | 0.561918 | 0.044* |
| C21 | 0.5459 (4) | 1.0472 (6) | 0.60689 (17) | 0.0323 (12) |
| H21 | 0.579263 | 1.111986 | 0.623646 | 0.039* |
| C22 | 0.5285 (3) | 0.9061 (5) | 0.61865 (14) | 0.0260 (10) |
| H22 | 0.549767 | 0.875907 | 0.643699 | 0.031* |
| C23 | 0.5661 (3) | 0.5256 (5) | 0.58785 (13) | 0.0188 (9) |
| C24 | 0.5621 (3) | 0.5325 (5) | 0.54825 (13) | 0.0223 (9) |
| H24 | 0.512470 | 0.573603 | 0.533638 | 0.027* |
| C25 | 0.6308 (3) | 0.4791 (5) | 0.53023 (13) | 0.0223 (9) |
| H25 | 0.628239 | 0.484284 | 0.503347 | 0.027* |
| C26 | 0.7028 (3) | 0.4184 (5) | 0.55155 (14) | 0.0234 (10) |
| H26 | 0.749857 | 0.382344 | 0.539283 | 0.028* |
| C27 | 0.7066 (3) | 0.4101 (5) | 0.59090 (13) | 0.0230 (10) |
| H27 | 0.755980 | 0.367583 | 0.605381 | 0.028* |
| C28 | 0.6381 (3) | 0.4639 (5) | 0.60922 (13) | 0.0208 (9) |
| H28 | 0.640823 | 0.458269 | 0.636100 | 0.025* |
| C29 | 0.9346 (4) | 0.4444 (6) | 0.70343 (15) | 0.0334 (12) |
| H29A | 0.919499 | 0.400617 | 0.678305 | 0.050* |
| H29B | 0.907027 | 0.389262 | 0.722375 | 0.050* |
| H29C | 0.998164 | 0.443182 | 0.710084 | 0.050* |
| C30 | 0.9023 (3) | 0.5979 (5) | 0.70270 (13) | 0.0239 (10) |
| C31 | 0.9299 (3) | 0.6959 (5) | 0.73296 (13) | 0.0222 (9) |
| H31 | 0.969439 | 0.663320 | 0.753878 | 0.027* |
| C32 | 0.9001 (3) | 0.8385 (5) | 0.73253 (12) | 0.0205 (9) |
| H32 | 0.919500 | 0.901062 | 0.753081 | 0.025* |
| C33 | 0.8404 (3) | 0.8914 (5) | 0.70137 (13) | 0.0213 (9) |
| C34 | 0.8125 (3) | 0.7961 (6) | 0.67152 (13) | 0.0248 (10) |
| H34 | 0.772602 | 0.828562 | 0.650693 | 0.030* |
| C35 | 0.8432 (3) | 0.6524 (6) | 0.67221 (13) | 0.0265 (11) |
| H35 | 0.823757 | 0.590099 | 0.651597 | 0.032* |
| C36 | 0.7320 (4) | 1.0455 (7) | 0.72675 (17) | 0.0380 (13) |
| H36A | 0.685373 | 0.982954 | 0.714637 | 0.057* |
| H36B | 0.709749 | 1.144171 | 0.728467 | 0.057* |
| H36C | 0.751857 | 1.009258 | 0.752337 | 0.057* |
| C37 | 0.8091 (3) | 1.0455 (6) | 0.70291 (14) | 0.0258 (10) |
| H37 | 0.857327 | 1.104123 | 0.716768 | 0.031* |
| C38 | 0.7828 (4) | 1.1161 (7) | 0.66429 (15) | 0.0391 (14) |
| H38A | 0.832641 | 1.114829 | 0.649565 | 0.059* |
| H38B | 0.764972 | 1.216295 | 0.667981 | 0.059* |
| H38C | 0.733964 | 1.062572 | 0.650540 | 0.059* |
| C39 | 0.8681 (3) | 0.8490 (5) | 0.58198 (12) | 0.0193 (9) |
| C40 | 0.8693 (3) | 0.9987 (5) | 0.57829 (13) | 0.0221 (9) |
| H40 | 0.920043 | 1.051568 | 0.587952 | 0.027* |
| C41 | 0.7968 (4) | 1.0709 (6) | 0.56058 (14) | 0.0301 (11) |
| H41 | 0.798523 | 1.172933 | 0.557751 | 0.036* |
| C42 | 0.7218 (4) | 0.9957 (7) | 0.54697 (15) | 0.0346 (13) |
| H42 | 0.672265 | 1.045707 | 0.534849 | 0.041* |
| C43 | 0.7196 (4) | 0.8479 (7) | 0.55112 (16) | 0.0375 (13) |
| H43 | 0.668048 | 0.796025 | 0.542036 | 0.045* |
| C44 | 0.7927 (3) | 0.7733 (6) | 0.56861 (14) | 0.0291 (11) |
| H44 | 0.790732 | 0.671245 | 0.571327 | 0.035* |
| C45 | 0.9779 (3) | 0.5701 (5) | 0.59173 (13) | 0.0198 (9) |
| C46 | 0.9485 (3) | 0.5336 (5) | 0.55429 (13) | 0.0235 (10) |
| H46 | 0.918296 | 0.603272 | 0.537948 | 0.028* |
| C47 | 0.9628 (4) | 0.3963 (6) | 0.54060 (14) | 0.0288 (11) |
| H47 | 0.942400 | 0.372135 | 0.515008 | 0.035* |
| C48 | 1.0069 (3) | 0.2947 (5) | 0.56437 (15) | 0.0273 (11) |
| H48 | 1.017525 | 0.201028 | 0.554959 | 0.033* |
| C49 | 1.0357 (3) | 0.3293 (5) | 0.60189 (15) | 0.0272 (10) |
| H49 | 1.064601 | 0.258375 | 0.618245 | 0.033* |
| C50 | 1.0225 (3) | 0.4666 (5) | 0.61565 (13) | 0.0233 (10) |
| H50 | 1.043623 | 0.490535 | 0.641187 | 0.028* |
| C51 | 1.0612 (3) | 0.8582 (5) | 0.58628 (12) | 0.0189 (9) |
| C52 | 1.0477 (3) | 0.8685 (5) | 0.54684 (13) | 0.0220 (9) |
| H52 | 0.994276 | 0.836105 | 0.533268 | 0.026* |
| C53 | 1.1124 (3) | 0.9262 (5) | 0.52743 (14) | 0.0254 (10) |
| H53 | 1.103465 | 0.933335 | 0.500493 | 0.030* |
| C54 | 1.1901 (3) | 0.9735 (5) | 0.54731 (14) | 0.0281 (11) |
| H54 | 1.235116 | 1.010530 | 0.533956 | 0.034* |
| C55 | 1.2024 (3) | 0.9669 (5) | 0.58674 (15) | 0.0270 (11) |
| H55 | 1.254858 | 1.003032 | 0.600287 | 0.032* |
| C56 | 1.1382 (3) | 0.9076 (5) | 0.60658 (13) | 0.0220 (9) |
| H56 | 1.147038 | 0.901059 | 0.633524 | 0.026* |
| As1 | 0.47082 (3) | 0.61244 (5) | 0.61142 (2) | 0.01673 (10) |
| As2 | 0.96982 (3) | 0.76514 (5) | 0.61146 (2) | 0.01582 (10) |
| Cl1 | 0.50618 (7) | 0.33441 (12) | 0.67030 (3) | 0.0221 (2) |
| Cl2 | 0.60144 (7) | 0.65452 (13) | 0.69402 (3) | 0.0231 (2) |
| Cl3 | 1.10543 (7) | 0.71071 (13) | 0.69237 (3) | 0.0232 (2) |
| Cl4 | 1.01233 (7) | 1.03494 (12) | 0.67217 (3) | 0.0211 (2) |
| Ru1 | 0.45179 (2) | 0.57596 (4) | 0.67819 (2) | 0.01608 (8) |
| Ru2 | 0.95617 (2) | 0.79378 (4) | 0.67898 (2) | 0.01528 (8) |
1 Source of materials
All manipulations were carried out using Schlenck techniques under an inert atmosphere of argon. A solution of [Ru(η6-p-cymene)Cl2]2 (0.254 g, 0.106 mmol) and AsPh3 (0.320 g, 0.001 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (20 ml) were refluxed for 15 h. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was washed with hexane (3 × 10 ml) to afford an orange-red solid. The ruthenium complex was crystallized by slow diffusion of petroleum ether 40–60 °C into a concentrated dichloromethane solution at ambient temperature. Red hexagonal crystals were obtained overnight. Yield (0.276 g, 86 %).
2 Experimental details
Intensity data was determined on a Bruker D8 Quest Microfocus with a Photon III detector diffractometer at 173 K. Data reduction was carried out using the SAINT-Plus version 6.02.6 software program, and SADABS was used to process empirical absorption correction. 1 The aromatic H atoms were placed in geometrically idealised positions and constrained to maintain fixed distances relative to their parent carbon atoms, with a specified C–H bond length of 0.93 Å for aromatic C–H bonds with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C). 2 The structure was solved in the Olex2-1.5 suite of programs, using charge flipping and refined with SHELXL-2019/3 refinement package. 3 , 4 Diagrams and publication material were generated using ORTEP-3. 5
3 Discussion
Drug resistance to cancer and malaria poses a significant challenge concerning therapeutic interventions. Recent investigations into the anticancer and antimalarial properties of half-sandwich ruthenium(II)-arene complexes have highlighted the efficacy of this class of complexes against various cancers and malaria. 6 , 7 Notably, p-cymene ruthenium(II) complexes exhibit potential as therapeutic agents due to their unique properties and mechanisms of action. 8 , 9 In this paper, we report the crystal structure of the ruthenium complex, [RuCl2(η6-p-cymene)(AsPh3)].
The asymmetric unit contains two molecules (Ru1 and Ru2) which both exhibit a pseudo-octahedral structure. In this arrangement, the ruthenium centre is coordinated with two chloride ions, a triphenylarsine ligand and a hexahapto p-cymene ligand. The molecular structures of the two ruthenium complexes are nearly identical, with minor differences. The η6-p-cymene ring is planar, while the C=C bonds within the ring have slightly unequal bond lengths, ranging from 1.403 Å to 1.431 Å and 1.404 Å to 1.435 Å for complexes Ru1 and Ru2 respectively. The p-cymene ligand is asymmetrically bonded to ruthenium, with Ru1–C(Arene) bond lengths in the range 2.173–2.223 Å, to accommodate the sterically demanding AsPh3 ligand. The Ru–Arene(centroid) distance was also measured as 1.686 Å and 1.688 Å for Ru1 and Ru2 complexes, respectively, which is within the range of similar reported structures in literature. 8 These measurements indicate favourable proximity that allows for adequate overlap between the metal d-orbital and the π-system of the cymene ligand, which is crucial for stabilizing the overall structure. 10 The Ru–As bond lengths are measured at 2.4430(5) Å and 2.4424(5) Å for Ru1 and Ru2 complexes, respectively. The average Ru–Cl bond length is 2.417 Å for both complexes, and falls within the range of 2.2971–2.4357 Å for previously reported complexes of this type. 11 , 12 Furthermore, the Cl–Ru–Cl angles measured at 88.29(4)° and 88.23(4)° for Ru1 and Ru2, respectively, supports the pseudo-octahedral geometry assigned to the molecule and is comparable to values reported for similar complexes. 13 , 14
Weak intramolecular non-covalent interactions were identified in the structure, including hydrogen bonds and T-type intermolecular π–π stacking. The structural analysis reveals that the coordination environment around the ruthenium centre is influenced by both steric and electronic factors, contributing to the overall stability of the complex. The bond distances and angles are in agreement with previously reported data for ruthenium(II)–arene complexes.
References
1. Bruker. APEX-5, SAINT-Plus (Version 8.8.4.0, Including XPREP) and SADABS (Version 2016); Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison,Wisconsin. USA, 2019.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
4. Bourhis, L. J.; Dolomanov, O. V.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A.; Puschmann, H. The Anatomy of a Comprehensive Constrained, Restrained Refinement Program for the Modern Computing Environment – Olex2 Dissected. Acta Crystallogr. A: Found. Adv. 2015, A71, 59–75. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar
5. Farrugia, L. J. ORTEP-3 for Windows (Version 2020.1). J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Search in Google Scholar
6. Graux, L. V.; Giorgi, M.; Buono, G.; Clavie, H. [RuCl2(η6-p-cymene)] Complexes Bearing Phosphinous Acid Ligands: Preparation, Application in C–H Bond Functionalization and Mechanistic Investigations. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 6491–6502. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5dt04683a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Ma, X.; Guillet, S. G.; Peng, M.; Van Hecke, K.; Nolan, S. P. A Simple Synthesis of [RuCl2(NHC)(p-cymene)] Complexes and Their Use in Olefin Oxidation Catalysis. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 3959–3965. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1dt00030f.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Latiş, S.; Marschner, C.; Baumgartner, J.; Prince, S.; Biswas, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Garcia, K. G.; Heeren, R. M. A.; Van Nuffel, S.; Blom, B. Synthesis and In Vitro Anticancer Studies of Arene Ruthenium(II) and Arene Osmium(II) Complexes Bearing Arsine and Stibine Co-Ligands on Breast Cancer Cell-Lines. J. Organomet. Chem. 2023, 1001, 122891–122901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2023.122891.Search in Google Scholar
9. Elsegood, M. R. J.; Smith, M. B.; Sanchez-Ballester, N. M. Dichloro(η6-p-Cymene)(Triphenylphosphine)Ruthenium(II). Acta Crystallogr. 2006, E62, m2838–m2840. https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536806039869.Search in Google Scholar
10. Betanzos-Lara, S.; Habtemariam, A.; Clarkson, G. J.; Sadler, P. J. Organometallic cis–Dichlorido Ruthenium(II) Ammine Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 3257–3264. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201100250.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Adeniyi, A. A.; Ajibade, P. A. Exploring the Ruthenium–Ligands Bond and Their Relative Properties at Different Computational Methods. J. Chem. 2016, 672062.10.1155/2016/3672062Search in Google Scholar
12. Kang, L.; Wang, B.; Thetford, A.; Wu, K.; Danaie, M.; He, Q.; Gibso, E. K.; Sun, L. D.; Asakura, H.; Catlow, C. R. A.; Wang, F. R. Design, Identification, and Evolution of a Surface Ruthenium(II/III) Single Site for CO Activation. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 1212–1219. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202008370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
13. Rafols, L.; Josa, D.; Aguilà, D.; Barrios, L. A.; Roubeau, O.; Cirera, J.; Soto-Cerrato, V.; Pérez–Tomás, R.; Martínez, M.; Grabulosa, A.; Gamez, P. Piano-Stool Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Delayed Cytotoxic Activity: Origin of the Lag Time. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 7974–7990. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00507.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Allison, M.; Caramés-Méndez, P.; Hofmann, B. J.; Pask, C. M.; Phillips, R. M.; Lord, R. M.; McGowan, P. C. Cytotoxicity of Ruthenium(II) Arene Complexes Containing Functionalized Ferrocenyl β-Diketonate Ligands. Organometallics 2023, 42, 1869–1881. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.organomet.2c00553.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

