Abstract
C14H11N3O4S, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14),a = 20.6433(8) Å, b = 6.9795(3) Å, c = 20.9482(8) Å, β = 112.440(1)∘, V = 2789.67(19) Å3, Z = 8, R gt (F) = 0.0344, wR ref (F2) = 0.0972, T = 170 K.
1 Source of materials
A representative purification of the crude title compound was performed as follows: Ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate (0.3 g, 1 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane and washed with water under stirring for 10 min. After phase separation, the organic layer was treated with activated charcoal and filtered through a sand core funnel. Following an additional phase separation, the organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure until precipitation occurred. The resulting viscous solid was dissolved in n-hexane and filtered in an ice-water bath, yielding a yellow solid upon evaporation that was suitable for single crystal growth (Table 1).
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | yellow block |
| Size: | 0.48 × 0.26 × 0.19 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.26 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Venture, φ and ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.1°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 45938, 6145, 0.036 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 5,351 |
| N(param)refined: | 399 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX. 3 , 4 |
The suitable single crystals for X-ray diffraction were obtained through the slow evaporation method.
n–Hexane solvent was added dropwise to the clean crystal growth tube containing the title compound. Care was taken to achieve near saturation of the solution. The crystal growth tube was then covered with aluminum foil, which was perforated with a needle to allow for ventilation. Subsequently, the crystal growth tube was placed in a dark cabinet to facilitate the slow evaporation of the n–hexane solvent.
During this equilibration process, yellow crystalline particles of the title compound were formed within approximately one week, and a suitable crystal was selected for X-ray crystallography.
2 Experimental details
Uiso values of hydrogen atoms were set to 1.2Ueq of the parent atoms for all C(H) groups, C(H,H) groups, and 1.5Ueq for all C(H,H,H) groups.
Secondary hydrogen atoms, were refined using riding coordinates. The phenyl hydrogen atoms, along with the imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole hydrogen atoms, wer refined as aromatic hydrogen using riding coordinates. The methyl hydrogen atoms, C14(H14A, H14B, H14C) and C14A(H14D, H14E, H14F), were refined as a idealized rotating group.
3 Comment
The title compound, a derivative of imidazothiazoles, is a high-value pharmaceutical intermediate for the synthesis of various drugs. 5
The synthesis method of the title compound has been reported in the literature. 6 , 7
The structural determination of the title compounds containing the moiety of heterocyclic imidazothiazole has been documented in several publications. 8 , 9 , 10
As part of our ongoing research interest on the structure-activity relationship about the antimicrobial agent, and understanding of hydrogen bonding schemes of related compounds, 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 this study presents the first successful preparation of single crystals of the title compound and provides a determination of its structure.
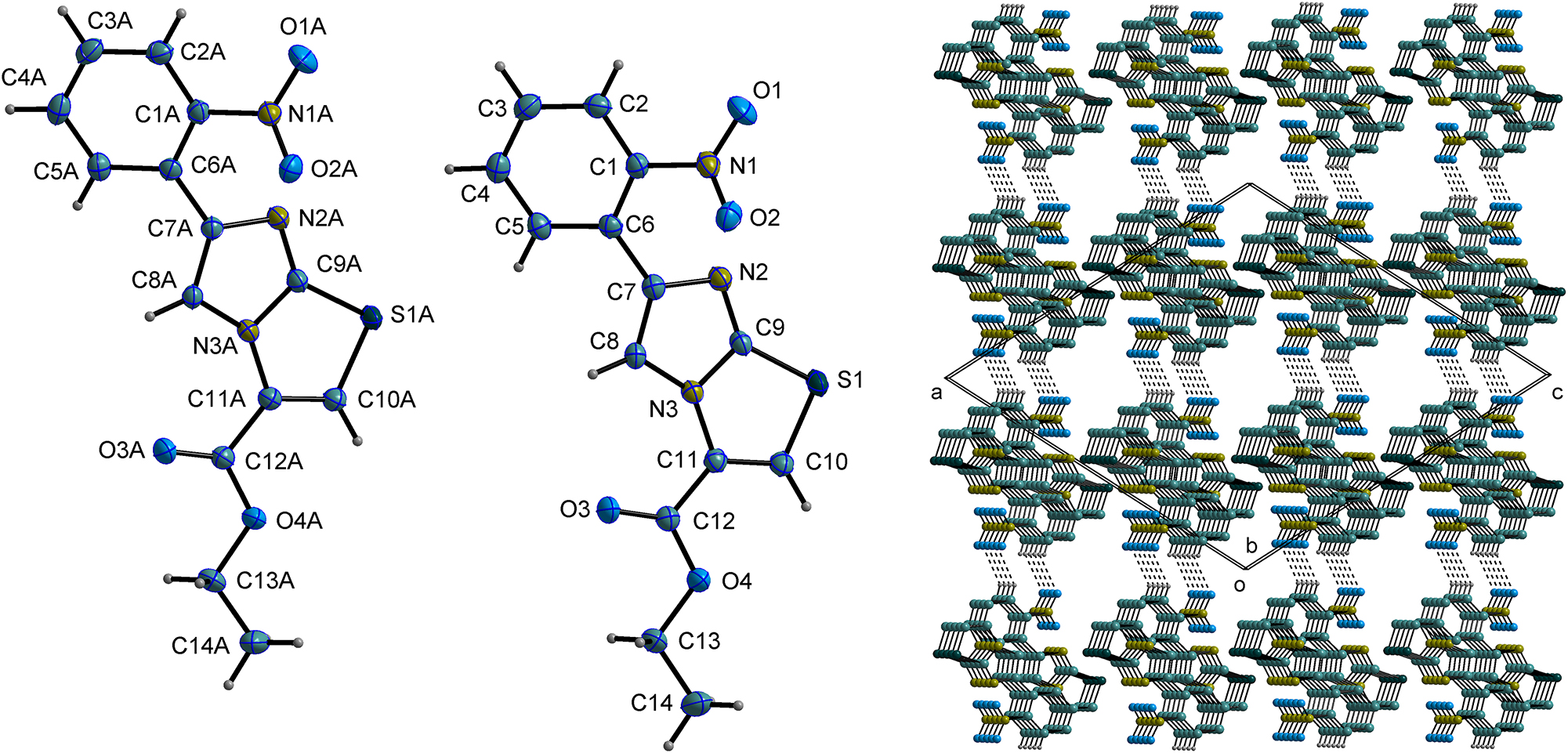
The asymmetric unit comprises two molecules of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate (cf. left part of the figure).
The two molecules are indeed independent in the asymmetric unit.
First, the two molecules exhibit slightly different spatial conformations. The angle between the ring planes S1–C9–N3–C11–C10 and C9–N2–C7–C8–N3 is measured at 4.06(7)∘, while in another molecule, the corresponding angle is 2.85(7)∘. And, the angle between the eight-membered ring plane S1–N2–N3–C7–C8–C9–C10–C11 and the phenyl ring plane C1–C2–C3–C4–C5–C6 is 39.36(5)∘. In contrast, in another molecule, this corresponding angle is 38.97(5)∘.
Furthermore, the crystallographic independence of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit was confirmed by Platon, 15 , 16 analysis. The ADDSYM routine, which searches for additional symmetry elements, found no missed or pseudo symmetry that could relate these two molecules. The analysis confirmed that the P21/n space group is correct and complete, with no higher symmetry possible. This crystallographic evidence, combined with the distinct conformational differences between the two molecules, conclusively proves that these are indeed two crystallographically independent molecules.
In the title compound molecule, the imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole moiety and the 2-nitrophenyl moiety form an interesting case of atropisomerism due to restricted rotation around the single bond (C6–C7) connecting them.
Our calculation using MM2 force field method, 17 shows the rotation energy barriers of the title compound is about 22 kcal/mol. According to literature, 18 , 19 the interconversion half life of this atropisomers is about 0.2 h. That means this atropisomers are usually used as mixture. But in our crystal prepared, only one atropisomeric enantiomer is present, because crystal packing forces may favor one atropisomer over another in the crystal solid state.
No classic hydrogen bonds were identified. However, two C–H⋯O nonclassic hydrogen interactions were observed (cf. right part of the figure. Some hydrogen atoms and ethyl carboxylate group are omitted for clarity).
These two hydrogen bonds (C2⋯O1A′ = 3.3250(19) Å′ = 2-x, 1-y, 2-z), and( C2A⋯O1
The imidazothiazole and phenyl ring planes arrange themselves in a layered configuration along the ac-plane of the crystal lattice.
Simultaneously, multiple π-π weak interactions between imidazothiazole and phenyl rings form a chain-like structure that connects the molecules along the b-axis.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support by School of Chemical Engineering, Ningbo Polytechnic, Ningbo Polytechnic Zhejiang Collaborative Innovation Center, and Ningbo Polytechnic Academician Workstation.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker Smart and Saint; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2019.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: a Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. C 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxt – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. A 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Cesur, N.; Cesur, Z.; Guner, H.; Kasimoullari, B. O. Fused Heterocycles: Synthesis of Some New Imidazothiazoles. Heterocycl. Commun. 2002, 8, 433–438; https://doi.org/10.1515/hc.2002.8.5.433.Search in Google Scholar
6. Klimesová, V.; Kocí, J.; Pour, M.; Stachel, J.; Kaustová, J.; Kaustová, J. Synthesis and Preliminary Evaluation of Benzimidazole Derivatives as Antimicrobial Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 37, 409–418; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0223-5234(02)01342-9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Nunes, J. J.; Milne, J.; Bemis, J.; Xie, R.; Vu, C. B.; Ng, P. Y.; Disch, J. S. Benzimidazole Derivatives as Sirtuin Modulators. World Intellectual Property Organization, International Patent. WO2007019416A1, 2007.Search in Google Scholar
8. Giorgi, G.; Salvini, L.; Andreani, A.; Locatelli, A.; Leoni, A. Molecular Structure, Characterization and Stereochemical Properties of New Biologically Interesting 3-(5-Imidazo[2,1-b]thiazolylmethylene)-2-Indolinones. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 524, 189–199; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2860(99)00463-9.Search in Google Scholar
9. Yıldırım, S. Ö.; Akkurt, M.; Ur, F.; Cesur, Z.; Cesur, N.; Heinemann, F. W. 6–Methyl–N-(3-oxo-1-thia-4-azaspiro[4.4]non-4-yl)imidazo [2,1-b][1,3]thiazole-5-carboxamide Monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. Sec. E 2005, 61, o2357–o2359.10.1107/S1600536805020088Search in Google Scholar
10. Lynch, D. E.; McClenaghan, I. Ethyl 2-Amino-4-tert.-Butyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylate and 6-methylimidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-2-amino-1,3-thiazole (1/1). Acta Crystallogr. Sec. C 2004, 60, o592–o594; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108270104015471.Search in Google Scholar
11. Li, Y.; Wu, Y.-D.; Wang, J. The Crystal Structure of 4-(3-Chloro-4-fluorophenylamino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-ol, C15H11ClFN3O2. Z. Kristallogr. – New Cryst. Struct. 2019, 234, 437–438; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2018-0445.Search in Google Scholar
12. Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. The Crystal Structure of Ethyl 2,3,5-trifluoro-4-(4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyridin-1(2H)-yl)benzoate, C14H12F3NO3. Z. Kristallogr. – New Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 1087–1089; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0412.Search in Google Scholar
13. Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. The Crystal Structure of 3-((4-Chloro–N-(2-methoxyethyl)benzamido)methyl)phenyl methanesulfonate. C18H20ClNO5S. Z. Kristallogr. – New Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 1033–1036; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0376.Search in Google Scholar
14. Li, Y.; Wang, J. The Crystal Structure of 4-(Methoxycarbonyl)benzoic acid, C9H8O4. Z. Kristallogr. – New Cryst. Struct. 2019, 234, 349–350; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2018-0408.Search in Google Scholar
15. Spek, A. L. Single-crystal Structure Validation with the Program Platon. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889802022112.Search in Google Scholar
16. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sec. D 2009, D65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
17. Dudek, M. J.; Ponder, J. W. Accurate Modeling of the Intramolecular Electrostatic Energy of Proteins. J. Comput. Chem. 1995, 16, 791–816; https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.540160702.Search in Google Scholar
18. Laplante, S. R.; Edwards, P. J.; Fader, L. D.; Jakalian, A.; Hucke, O. Revealing Atropisomer Axial Chirality in Drug Discovery. Chemmedchem 2015, 6; https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201000485.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
19. Smyth, J. E.; Butler, N. M.; Keller, P. A. A Twist of Nature – the Significance of Atropisomers in Biological Systems. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1562–1583; https://doi.org/10.1039/c4np00121d.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

