Abstract
C2H12N2S4W, orthorhombic, Pnma (no. 62), a = 9.6317(3) Å, b = 7.0104(2) Å, c = 15.7286(6) Å, V = 1062.03(6) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0230, wRref(F2) = 0.0520, T = 223 K.
1 Source of material
(NH4)2WS4 (0.030 g, 0.086 mmol) and MeNH3Cl (0.069 g, 1.0 mmol) were charged to a Pyrex tube with diameter of 9 mm and about 0.5 mL MeOH was added as a solvent. While the solvent was being frozen, the Pyrex tube was evacuated and sealed with a flame. The sealed tube was placed in an oven and heated at 110 °C for 3 days, then cooled to room temperature. Light yellow needle crystals were isolated by filtration and washed with MeOH and diethyl ether several times. Crystals of (MeNH3)2[WS4] were obtained in 9 % yield, based on the W metal used (Table 1).
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow needle |
| Size: | 0.14 × 0.13 × 0.09 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 11.6 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 8592, 1417, 0.036 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1,228 |
| N(param)refined: | 57 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX 2 , WinGX 3 , DIAMOND 4 |
2 Experimental details
H atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding, with C–H = 0.97 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) and N–H = 0.90 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(N).
3 Comment
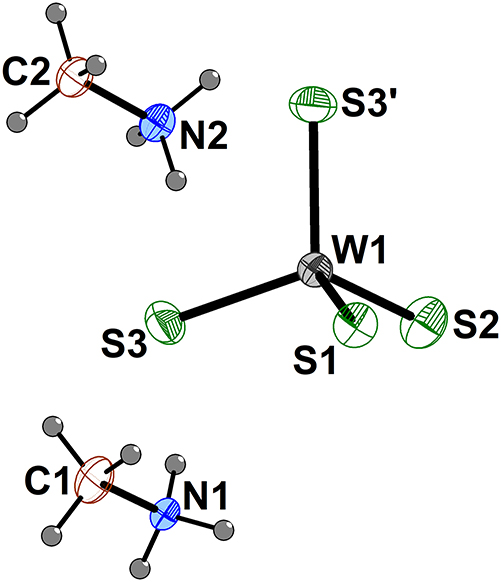
The title compound, (CH3NH3)2[WS4] was prepared by the methanothermal reaction of (NH4)2WS4 and CH3NH3Cl, and it consists of a [WS4]2− anion and two charge-balancing CH3NH3+ cations. As one of the most extensively studied and structurally characterized thiometallate anions, the tetrathiotungstate [WS4]2− anion has been stabilized with numerous cations including NH4+, 5 , 6 Rb+, 7 [Ni(tren)2]2+ (tren = tris(2-aminoethyl)amine) 8 and various organic cations. Organic cations employed for the stabilization of the [WS4]2− anion include Ph4P+, 9 tetraalkylammonium (Me4N+, Et4N+, Pr4N+), 10 alkylammonium with N–H bonds (H3NCH2CH2NH32+, i-PrNH3+, etc.), 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 and mixed tetraalkylammonium (BuMe3N+, BenzylMe3N+). 16 , 17 As the smallest organic cation and a member of the alkylammonium family with N–H bonds, CH3NH3+ methylammonium ion is also demonstrated to be adequate for the stabilization of the [WS4]2− anion.
In the structure of (CH3NH3)2[WS4], there is one half of a crystallographically independent [WS4]2− anion, in which the W(1), S(1) and S(2) atoms lie on the mirror plane. The tetrahedral coordination geometry around the W(1) atom is nearly ideal, with S–W–S bond angles between 107.86(4)° and 110.61(6)°. The W–S bond distances range from 2.185(2) Å to 2.197(1) Å. Compared to the other [WS4]2− compounds, (CH3NH3)2[WS4] exhibits a relatively small Δ value, 0.012 Å for the difference between the longest and the shortest W–S bond distances. The shortest S…H contacts occur between S(3) and H(1NB) with 2.453(1) Å, and between S(2) and H(1NA) with 2.454(2) Å, respectively. There are three additional S…H contacts less than 2.80 Å in the pairs of S(3)…H(2NA), S(1)…H(1NC), and S(2)…H(1NB). In both crystallographically independent CH3NH3+ cations, C and N atoms lie on the mirror plane resulting in an occupancy of 0.5 for all H atoms. Based on the short S…H contacts, it is evident that both CH3NH3+ cations are positioned with –NH3 side, instead of –CH3 side, heading toward [WS4]2− anion. The orientation of the CH3NH3+ cations relative to the [WS4]2− anion can be attributed to the positive charge on N atoms and better H-bonding between N and S atoms.
References
1. Bruker. Apex2 and Saint; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8, https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and Ortep for Windows: An Update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. Diamond. Visual Crystal Structure Information System; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Sasvári, K. The Crystal Structure of Ammonium Thiotungstate (NH4)2WS4. Acta Cryst. 1963, 16, 719–724; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0365110x63001894.Search in Google Scholar
6. Srinivasan, B. R.; Poisot, M.; Näther, C.; Bensch, W. Diammonium tetrathiotungstate(VI), (NH4)2[WS4], at 150 K. Acta Cryst. 2004, E60, i136–i138; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536804023761.Search in Google Scholar
7. Yao, J.; Ibers, J. A. Dirubidium Tetrathiotungstate, Rb2[WS4]. Acta Cryst 2004, E60, i10–i11; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536804000169.Search in Google Scholar
8. Ellermeier, J.; Stähler, R.; Bensch, W. Two New [Ni(tren)2]2+ Complexes: [Ni(tren)2]Cl2 and [Ni(tren)2]WS4. Acta Cryst. 2002, C58, m70–m73; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108270101015992.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Bailen, P. L.; Powell, A. V.; Vaqueiro, P. Bis(tetraphenylphosphonium) Tetrasulfidotungstate(VI). Acta Cryst. 2008, E64, m574.10.1107/S1600536808007472Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
10. Poisot, M.; Näther, C.; Synthesis, B. W. Spectroscopic and X–Ray Structure Characterisation of Bis(tetramethylammonium), Bis(tetraethylammonium) and Bis(tetrapropylammonium) Tetrathiotungstates. Z. Naturforsch. 2006, 61b, 1061–1066.10.1515/znb-2006-0903Search in Google Scholar
11. Srinivasan, B. R.; Dhuri, S. N.; Näther, C.; Bensch, W. Ethylenediammonium Tetrathiotungstate(VI). Acta Cryst. 2002, E58, m622–m624; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536802017841.Search in Google Scholar
12. Srinivasan, B. R.; Dhuri, S. N.; Näther, C.; Bensch, W. 1,3-Propanediammonium Tetrathiotungstate and N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediammonium Tetrathiotungstate. Acta Cryst. 2003, C59, m124–m127; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108270103002543.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Srinivasan, B. R.; Dhuri, S. N.; Näther, C.; Bensch, W. 1,4-Dimethylpiperazinium Tetrathiotungstate(VI). Acta Cryst. 2003, E59, m681–m683.10.1107/S1600536803016040Search in Google Scholar
14. Srinivasan, B. R.; Dhuri, S. N.; Näther, C.; Bensch, W. Synthesis, X-Ray Structures, Spectroscopic and Thermal Characterization of Two New Organic Ammonium Tetrathiotungstates. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2005, 631, 1087–1094.10.1002/zaac.200400513Search in Google Scholar
15. Srinivasan, B. R.; Näther, C.; Dhuri, S. N.; Bensch, W. On the Importance of H-Bonding Interactions in Organic Ammonium Tetrathiotungstates. Monatsh. Chem. 2006, 137, 397–411; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-005-0456-y.Search in Google Scholar
16. Kim, K.-W.; Yoo, Y.-H. Crystal Structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylbutanaminium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (BuMe3N)2[WS4]. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2024, 239, 627–629; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0110.Search in Google Scholar
17. Kim, K.-W.; Yoo, Y.-H. Crystal Structure of Bis(benzyltrimethylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), {(C6H5CH2)(CH3)3N}2[WS4]. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2024, 239, 907–910; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0228.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

