Abstract
C18H16O5, Triclinic,
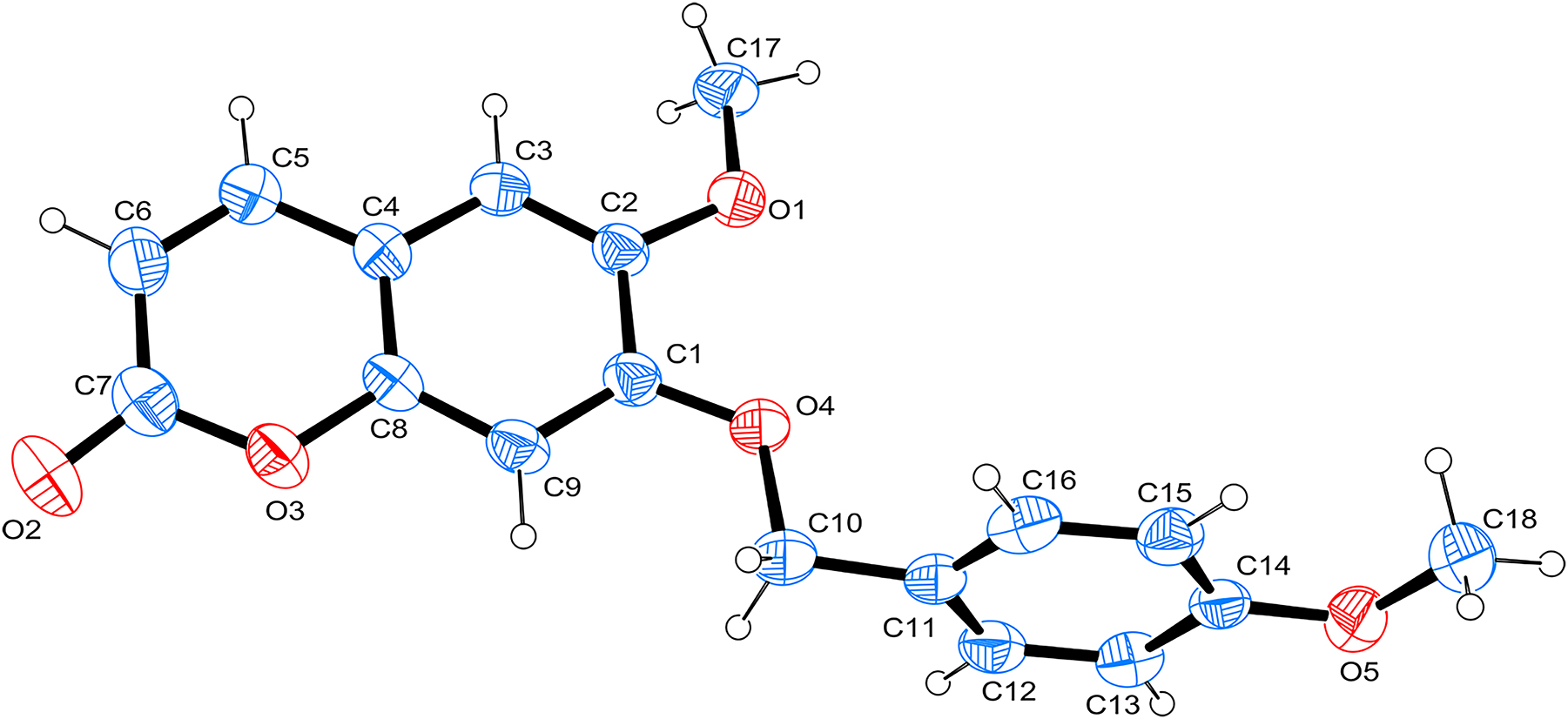
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.24 × 0.18 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.10 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II CCD, φ and ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.7°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 8452, 2872, 0.029 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1,603 |
| N(param)refined: | 210 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 SHELX 2 , 3 , WinGx 4 |
1 Source of material
All chemicals were purchased from commercial sources and used as received without further purification. The scopoletin (1.0 mmol, 0.192 g), 4-methoxybenzylchloride (3.0 mmol, 0.469 g), potassium carbonate (2 mmol, 0.276 g), and sodium iodide (0.1 mmol, 0.015 g) was suspended in anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide (30 mL) in a dry round bottom flask at room temperature. The mixture was warmed to 60 °C and stirred for 12 h under N2. All solvents were removed by vacuum distillation to obtain a crude product. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel to yield the pure title compound. The crystal was obtained by slow evaporating chloroform at room temperature.
2 Experimental details
All H-atoms bonded to C atoms were placed geometrically and refined using a riding model with common isotropic displacement factors Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5 Ueq (parent C-atom).
3 Comment
Natural products have always been an important source of medicines for the treatment of various diseases. Among the various natural product scaffolds, benzopyrone compounds play an important role in biologically active compounds. 5 Scopoletin is a natural benzopyrone compound extracted from the ethnopharmacology Prismatomeris tetrandra (Prismatomerisconnata Y. Z. Ruan), which has various biological activities. 6 , 7 , 8 Currently, the benzopyrone class of compounds has shown great potential in drug development. Therefore, the synthesis and crystal structure of the benzopyrone derivative are important significance for the study of the application.
Single-crystal structure analysis revealed that the title compound crystallized in the triclinic space group
-
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work were supported by Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2024GXNSFAA010466), Natural Science Foundation Key Project of Guangxi International Zhuang Medicine Hospital (No. 2023GZYJKT002), Innovation Team for Research and Development of Characteristic Pharmaceutics of Zhuang & Yao Medicine (No. GZCX20231203).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: An Update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Sharma, V.; Sharma, A.; Wadje, B. N.; Bharate, S. B. Benzopyrone, A Privileged Scaffold in Drug Discovery: An Overview of FDA-Approved Drugs and Clinical Candidates. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 2035–2077; https://doi.org/10.1002/med.22032.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Parama, D.; Girisa, S.; Khatoon, E.; Kumar, A.; Alqahtani, M. S.; Abbas, M.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A. B. An Overview of the Pharmacological Activities of Scopoletin against Different Chronic Diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 179, 106202; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106202.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Antika, L.; Tasfiyati, A.; Hikmat, H.; Septama, A. Scopoletin: A Review of Its Source, Biosynthesis, Methods of Extraction, and Pharmacological Activities. Z. Naturforsch. C 2022, 77, 303–316; https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2021-0193.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Firmansyah, A.; Winingsih, W.; Manobi, J. D. Y. Review of Scopoletin: Isolation, Analysis Process, and Pharmacological Activity. Biointerface Res. App. 2021, 11, 12006–12019; https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC114.1200612019.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Ikemura, A.; Karuo, Y.; Uehashi, Y.; Agou, T.; Ebihara, M.; Kubota, Y.; Inuzuka, T.; Omote, M.; Funabiki, K. 3-Perfluoroalkylated Fluorescent Coumarin Dyes: Rational Molecular Design and Photophysical Properties. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2024, 9, 332; https://doi.org/10.1039/D4ME00006D.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

