Abstract
C6H18S2O2CoCl4, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 8.4397(3) Å, b = 15.6692(5) Å, c = 12.5989(4) Å, β = 93.8580(10)°, V = 1662.35(10) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0408, wRref(F2) = 0.0965, T = 293(2) K.
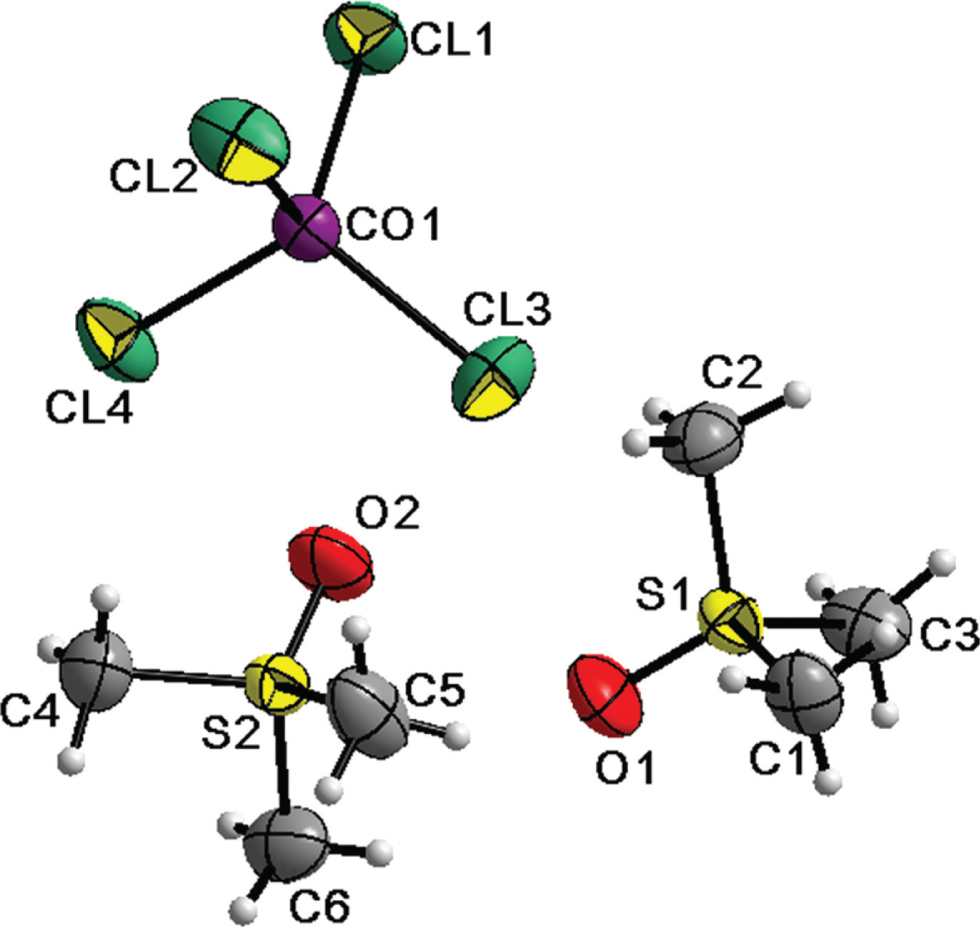
The asymmetric unit of the title structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Blue plate |
| Size: | 0.17 × 0.10 × 0.03 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.91 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Venture, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 24807, 4145, 0.051 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2695 |
| N(param)refined: | 208 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4], Diamond [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co1 | 0.72195(5) | 0.09385(3) | 0.73655(3) | 0.04694(13) |
| Cl1 | 0.77928(12) | 0.09471(7) | 0.91518(7) | 0.0701(3) |
| Cl2 | 0.92334(13) | 0.15793(7) | 0.65821(8) | 0.0829(3) |
| Cl3 | 0.48827(13) | 0.15965(7) | 0.69899(10) | 0.0852(3) |
| Cl4 | 0.71007(15) | −0.04238(6) | 0.68017(8) | 0.0799(3) |
| S1 | 0.73731(10) | 0.83701(5) | 0.00564(7) | 0.0513(2) |
| S2 | 0.76471(10) | 0.39074(5) | 0.84130(6) | 0.0524(2) |
| O1 | 0.7364(3) | 0.75429(16) | 0.0527(2) | 0.0820(8) |
| O2 | 0.7328(4) | 0.40322(18) | 0.72946(19) | 0.0815(8) |
| C1 | 0.7771(7) | 0.9174(3) | 0.0997(4) | 0.0715(12) |
| C2 | 0.5589(5) | 0.8644(4) | −0.0625(5) | 0.0747(12) |
| C3 | 0.8786(6) | 0.8481(4) | −0.0882(4) | 0.0722(12) |
| C4 | 0.6212(6) | 0.3301(4) | 0.9002(5) | 0.0788(13) |
| C5 | 0.7792(10) | 0.4861(3) | 0.9106(4) | 0.0860(16) |
| C6 | 0.9412(6) | 0.3345(4) | 0.8709(4) | 0.0766(13) |
| H1 | 0.695(5) | 0.911(2) | 0.140(3) | 0.077(13)* |
| H2 | 0.770(5) | 0.969(3) | 0.063(4) | 0.106(17)* |
| H3 | 0.873(6) | 0.906(3) | 0.128(4) | 0.096(18)* |
| H4 | 0.488(5) | 0.863(3) | −0.009(3) | 0.081(13)* |
| H5 | 0.572(5) | 0.920(3) | −0.096(3) | 0.088(14)* |
| H6 | 0.538(5) | 0.821(3) | −0.101(4) | 0.099(18)* |
| H7 | 0.972(5) | 0.837(3) | −0.056(3) | 0.084(14)* |
| H8 | 0.865(5) | 0.903(3) | −0.122(4) | 0.102(16)* |
| H9 | 0.851(5) | 0.805(3) | −0.132(4) | 0.100(17)* |
| H10 | 1.006(5) | 0.374(3) | 0.854(3) | 0.076(14)* |
| H11 | 0.926(6) | 0.281(3) | 0.835(4) | 0.12(2)* |
| H12 | 0.943(5) | 0.329(3) | 0.946(4) | 0.085(13)* |
| H13 | 0.657(6) | 0.325(3) | 0.978(4) | 0.119(18)* |
| H14 | 0.608(6) | 0.284(4) | 0.862(4) | 0.12(2)* |
| H15 | 0.539(6) | 0.370(3) | 0.894(4) | 0.102(17)* |
| H16 | 0.796(5) | 0.476(3) | 0.984(4) | 0.105(16)* |
| H17 | 0.865(5) | 0.512(3) | 0.887(4) | 0.088(17)* |
| H18 | 0.687(6) | 0.511(3) | 0.893(4) | 0.097(19)* |
Source of material
The starting materials of CoCl2 ⋅ 6 H2O (0.238 g, 1 mmol) and trimethylsulfoxonium chloride (0.129 g, 1 mmol) were dissolved in deionized water with two drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid (37 wt%), resulting in a clear red solution. With slow evaporation at room temperature, blue plate crystals of the title compound were obtained within 2 days.
Experimental details
The structure was solved by direct methods and refined by full-matrix least-squares calculations. All the calculations were performed using the SHELX package [2], [3] and WinGX [4]. Hydrogen atoms were picked from difference Fourier maps and refined without any constraints or restraints.
Comment
Organic-inorganic hybrid compounds often exhibit a great variety of interesting structures as well as physical properties. The inorganic components, if containing transition metals, are likely to be a source to activate electrical transport, magnetism, ferroelectric properties, while the organic counterparts usually serve as a guest and sometimes account for additional variations in polarizability, luminescence, and chromophoric group [6]. As composed of both organic and inorganic components, hybrid compounds are expected to adopt combined properties that arise from both components or emerge new properties. In organometallic complexes, transition metals with one or more empty d-orbitals enable ligand-field-assisted d–d transitions, usually resulting in absorption in visible light range.
In the crystal structure, two types of discrete motifs with opposite charges exist. Co(II) is tetrahedrally coordinated with Cl, forming a distorted negatively-charged tetrahedron [CoCl4]2−, which is surrounded by the organic cation trimethylsulfoxonium [(CH3)3SO]+, to stabilize the structure by electrostatic force. The Co—Cl bond lengths vary from 2.2474(11) Å to 2.2700(10) Å. Compared with the reported values for [CoCl4]2− in other hybrids [7], [8], [9], these bond lengths are slightly shorter, presumably due to the absence of hydrogen bonding. The Cl—Co—Cl angles are in an expected range of 107.63(5)° to 112.31(5)°. The [(CH3)3SO]+ motif is of pyramidal geometry with an approximate 3m symmetry, similar to that in trimethylsulfoxonium metal-halides [10], [11]. Within this motif, the S—C bond lengths (1.731(5)–1.749(5) Å) and the O—S—C angles (112.3(2)°–113.8(2)°) lie in known ranges. There are no hydrogen bonds detected in the crystal structure, unlike the positively-charged or neutral organic motifs in some other hybrids [7], [8], [9], [12].
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51532010). Thanks X. L. Chen and S. F. Jin for valuable discussions.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2012).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT-Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Suche in Google Scholar
5. Putz, H.; Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND – Crystal and Molecular Structure Visualization. Ver. 3.0. Crystal Impact, 102, 53227 Bonn, Germany (2005).Suche in Google Scholar
6. Saparov, B.; Mitzi, D. B.: Organic-inorganic perovskites: structural versatility for functional materials design. Chem. Rev. 116 (2016) 4558–4596.10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00715Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Williams, I. D.; Brown, P. W.: 235 K Structural phase transition in dimethylammonium tetrachlorocobaltate(II). Acta Crystallogr. C48 (1992) 263–266.10.1107/S010827019101020XSuche in Google Scholar
8. Wiesner, J. R.; Srivastava, R. C.; Kennard, C. H. L.; DiVaira, M.; Lingafelter, E. C.: The crystal structures of tetramethylammonium tetrachloro-cobaltate (II), -nickelate (II), and -zincate (II). Acta Crystallogr. 23 (1967) 565–574.10.1107/S0365110X67003214Suche in Google Scholar
9. Reiss, G. J.; Sergeeva, A.: The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4CoN2O. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 232 (2017) 159–161.10.1515/ncrs-2016-0245Suche in Google Scholar
10. Knop, O.; Linden, A.; Vincent, B. R.; Choi, S. C.; Cameron, T. S.; Boyd, R. J.: The lone electron pair and crystal packing: observations on pyramidal YEL3ϵ species, ab initio calculations, and the crystal structures of Me3SOI, Et3SI, (Me3S)2SnCl6, (Me3SO)2SnCl6, and (Et3S)2SnCl6. Can. J. Chem. 67 (1989) 1984–2008.10.1139/v89-310Suche in Google Scholar
11. Puget, R.; Jannin, M.; Brauer, C. D.; Perret, R.: Structures of trimethyloxosuifonium salts. V. the catena-tri-μ-chloro-cadmate and the catena-tri-μ-bromo-cadmate. Acta Crystallogr. C47 (1991) 1803–1805.10.1107/S0108270190013701Suche in Google Scholar
12. Zhao, L. L.; Wang, D.; Huang, Q. Z.; Wu, H.; Sun, R. J.; Fan, X.; Song, Y. P.; Jin, S. F.; Chen, X. L.: Structural evolution and phase diagram of the superconducting iron selenides Lix(C2H8N2)yFe2Se2 (x = 0 ∼0.8). Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 99 (2019) 094503.10.1103/PhysRevB.99.094503Suche in Google Scholar
©2020 Xin Zhong et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4

