Abstract
The Hamiltonian and wavefunctions of two-dimensional two-electron quantum dots (2D2eQD) in parabolic confinement are determined. The ground and excited state energies are calculated solving the Schrödinger equation analytically and numerically. To determine the energy eigen-value of the system variational method is employed due to the large coupling constant
1 Introduction
Zero-dimensional semiconductor systems or quantum dots with one electron are widely used in the nano physics [1,2]. Recently, quantum dots have gained considerable attention due to their wide range of potential applications in optoelectronic devices [3,4]. Few of these applications are single electron transistors [5], quantum lasers, quantum computing [8], optical memories [9], infrared photodetectors [6], and high-speed optical modulators [7]. The advancement of technology leads to the possibility of fabricating quantum dots with two or more electrons where the Coulomb interaction between them must be taken into account [10,11,12]. Due to the localization of the electrons in low-dimensional system the Coulomb interaction can exceed the average kinetic energy of electrons that considerably complicates the analytic solution of the Schrödinger equation [13]. At a temperature smaller than the distance between the ground and excited states, the two-electron quantum dot consists of the para- and ortho-states [13]. These states play a crucial role for quantum information processing [14,15,16]. Due to quantum confinement, engineering the electronic structure of materials by controlling its shape and size leads to the possibility of designing the energy spectrum to produce suitable optical transitions [17]. These characteristics are helpful for developing optoelectronic devices with tunable transmission or emission properties. As the result, nonlinear optical properties of quantum dots have been studied theoretically and experimentally [18,19]. Intraband nonlinear optical properties of
In this article, the ground and first excited states of 2D2eQDs with parabolic confinement are considered. Our system is the simplest quantum dot that consists of two electrons confined in a 2D parabolic potential. In this model, the two electrons each with an effective mass
2 Statement of the problem
The Hamiltonian of 2D2eQD with soft or parabolic confinement potential is expressed as:
In equation (1), the first term indicates the kinetic energy of two electrons, the second term is the parabolic potential for confining electrons and the last term is the electron electron interaction which includes pure Coulombic and exchange correlation part. Using the dimensionless variables
where
3 Ground state energy of 2D2eQD
The energy eigen values of complicated systems are estimated using variational technique. It is based on full minimization of the energy functional with respect to the two-electron wavefunction. In this method, the energy computed from a guessed wavefunction is an upper bound to the true ground state energy. In this section, we are going to determine the ground state energy of 2D2eQD with parabolic confinement. The gaussed wavefunction when two electrons in the ground state may be given as:
The total ground state energy is the expectation value of the Hamiltonian and described by,
The kinetic energy of the first electron is
The kinetic energy of the second electron is given by,
The expectation value of the potential energies of the two electrons are
The Coulombic part is given by,
After evaluation of equation (9) the Coulombic part becomes
Solving all terms in equation (4) and gathering all values give
The total minimum energy of equation (11) can be obtained from its first derivative with respect to the variational parameter
Ground state energy,
|
|
0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
|
|
1.00 | 0.969 | 0.914 | 0.865 | 0.820 | 0.781 | 0.746 |
|
|
2.00 | 2.124 | 2.367 | 2.604 | 2.834 | 3.058 | 3.277 |
4 Excited state energy of 2D2eQD
The wave function of the first excited state in parabolic confinement is given by the symmetrical and anti-symmetrical combination
where
where
Similarly, the total excited state energy is the expectation value of the Hamiltonian and described by
Solving equation (15) yields
The minimum value of the excited state energy in equation (12) can be obtained from the condition
The variational parameter
Excited state energy,
|
|
0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 |
|
|
1.000 | 0.992 | 0.975 | 0.959 | 0.944 | 0.929 | 0.915 |
|
|
4.000 | 4.067 | 4.201 | 4.334 | 4.466 | 4.597 | 4.727 |
Using the obtained variational parameters
The variational parameters
The computation of the average Hamiltonian (2) with respect to the gaussed wavefunction (12) gives
where,
The first excited state energies: para-state energy with singlet spin and ortho-state energy with triplet spin for different values of coupling constant are described in Table 3.
Ground state energy,
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 3.000 | 3.000 |
| 0.1 | 0.969 | 0.992 | 0.108 | 0.030 | 3.131 | 3.085 |
| 0.3 | 0.914 | 0.975 | 0.316 | 0.070 | 3.391 | 3.251 |
| 0.5 | 0.865 | 0.959 | 0.515 | 0.118 | 3.645 | 3.409 |
| 0.7 | 0.820 | 0.944 | 0.705 | 0.167 | 3.894 | 3.560 |
| 0.9 | 0.781 | 0.929 | 0.886 | 0.217 | 4.139 | 3.705 |
| 1.1 | 0.746 | 0.915 | 1.059 | 0.268 | 4.378 | 3.843 |
Thus, in the first excited state the system of energy levels of 2D2eQD splits into two classes: para- and ortho-state energies. The ortho-state energy lies below the para-state energy. The transition between these two states is very improbable as the spin–spin interaction is too small. If the 2D2eQD is in a state with parallel spins, it is therefore very unlikely that its state will change to one with anti parallel spins in normal situations.
5 Optical properties of two-dimensional two-electron ZnO quantum dots
Zinc oxide is a wide band gap material that has got considerable attention due to its potential application in short wave length optoelectronic devices [22]. This optoelectronic applications include devices such as blue or ultra-violet light emitting diodes and laser. All these interesting applications are based on the nonlinear optical properties such as the optical absorptions and refractive index changes.
In this section, the linear and nonlinear refractive index and absorption coefficients of 2D2eQD can be calculated by employing the density matrix formalism and iterative procedure [23]. It is assumed that 2D2e ZnO QD in parabolic confinement interacts with polarized monochromatic electric field.
The evolution of density matrix
where
The electronic polarization of quantum dot due to the field
where
For the third-order term,
where
The linear and nonlinear absorption coefficient and refractive index are related to the imaginary and real parts of the susceptibility (a measure of how much the polarization is built up in the medium by the incident field).
where
where
where
The total absorption is the sum of linear and nonlinear absorption coefficients and is approximated by
Similarly, the total refractive index is the sum of linear and nonlinear refractive index and given by
The linear and nonlinear absorption coefficients and changes in refractive index of 2D2eQD are determined in equations (29), (30), (31), and (32), respectively. The parameters used in this calculation are the carrier density
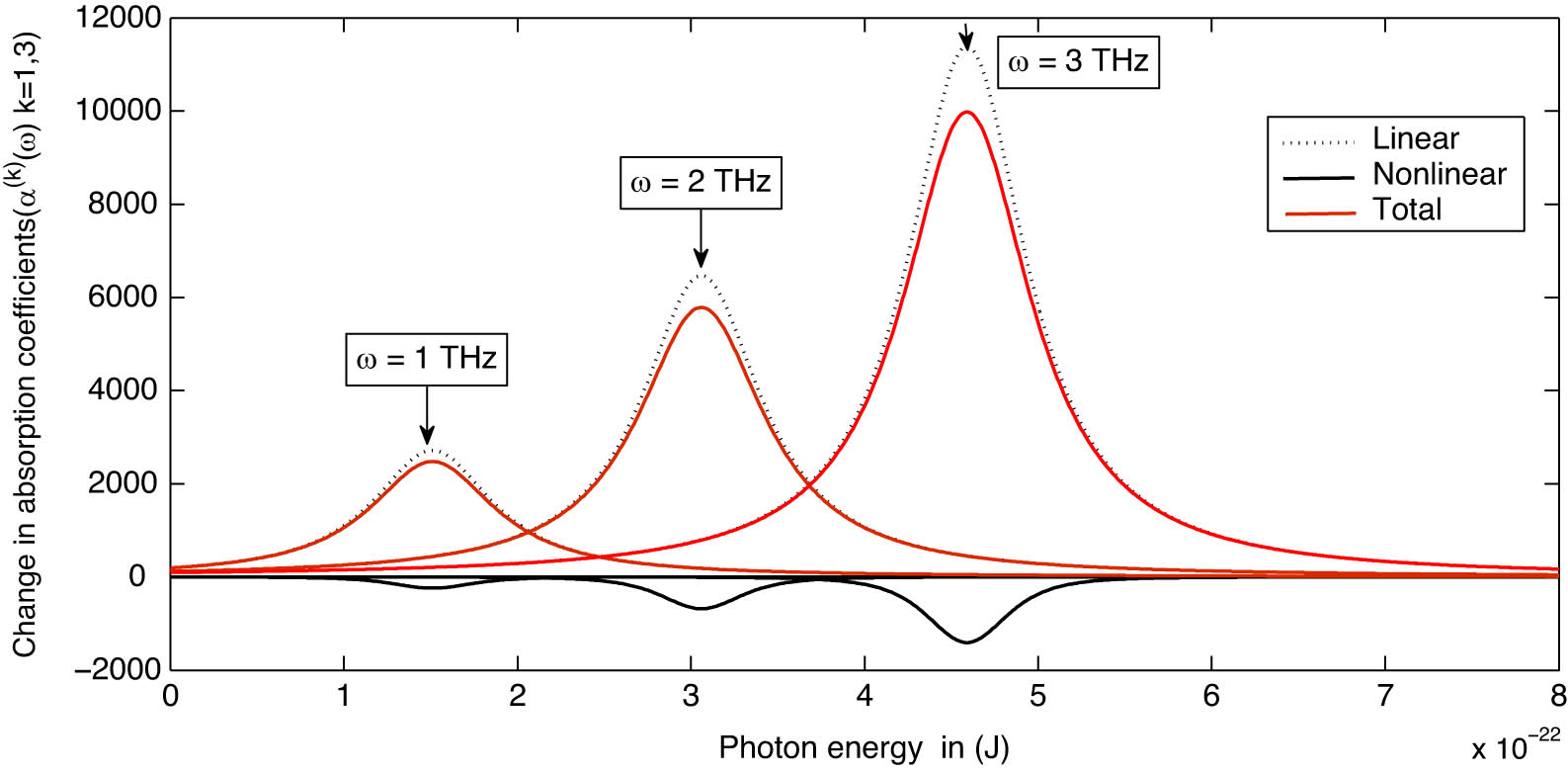
Absorption coefficients of 2D2eQD for confining frequencies of

Refractive index changes of 2D2eQD for confining frequencies of
As it can be seen from Figure 1, the magnitude of the absorption coefficients (linear, nonlinear, and total) are magnified, as the confining frequency of the 2D2eQD increases from 1 to 3 THz. Moreover the maximas shift toward the high energy or frequency. This property is useful for device application at different frequency regimes.
As it is demonstrated from Figure 2, the magnitude of the refractive index changes (nonlinear and total) are amplified, for the increment of confining frequency from 1 to 3 THz. Moreover blue shift is observed as magnitude of the confining frequency increases. The intensity-dependent nonlinear and total absorption coefficient and refractive index changes are described in Figures 3 and 4, respectively. In Figure 3, it is observed that as the intensity of the source increases, the magnitude of the nonlinear absorption coefficient increases. However, the total absorption coefficient decreases since the linear absorption coefficient does not depend on optical intensity. This nonlinear optical property is a fundamental for developing optical limiting devices. In Figure 4, it is demonstrated that as the intensity of the source increases, the magnitude of the change in nonlinear refractive index increases. But, the total refractive index decreases. The linear refractive index is constant and does not be affected with an increment of optical intensity.

Nonlinear and total absorption coefficients of 2D2eQD for different values of intensity.

Linear, nonlinear, and total refractive index changes of 2D2eQD for different values of intensity.
6 Conclusion
The ground and excited state energies of 2D2e ZnO QD in parabolic confinement are calculated for different values of coupling constant using variational technique. There are para- and ortho states in 2D2eQD in which quantum transition between them is almost improbable unless electron bombardment is considered. The ortho state of the 2D2eQD with triplet level lies above the ground sate and below the first excited para-state. This state is metastable and the charge carriers stay for long time. The singlet spin wavefunction of the ground state and the triplet spin wavefunction of the lowest ortho state are the states responsible for quantum information processing. Using the calculated energy eigen value, the linear, third order nonlinear, and total absorption coefficient and refractive index changes are studied between the ground state and the first excited para state. The optical study shows that increasing the confining frequency of the 2D2eQD in parabolic confinement alters both the magnitude and position of peak of the linear, third-order nonlinear and total absorption coefficient and refractive index changes. Increasing the confining frequency magnifies the magnitude of the linear, nonlinear, and total absorption coefficient and refractive index changes. Moreover, increasing the confining frequency results in blue shift of the peak for both optical parameters. Increasing the optical intensity of the system while fixing all other parameters constant amplifies the magnitude of the nonlinear absorption and refractive index changes. As the result, the total absorption coefficient and refractive index diminish as the magnitude of the optical intensity increases.
Acknowledgements
The author is thankful to the Department of Physics of Jimma University for material support.
-
Funding information: The author states no funding involved.
-
Conflict of interest: The author declares there is no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data relevant to this publication are included in the text and hence available to every one.
References
[1] Rink SS, Miller DAB, Chemla DS. Theory of the linear and nonlinear optical properties of semiconductor microcrystallites. Phys Rev B. 1986;35:8114. 10.1103/PhysRevB.35.8113. Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Bryant GW. Theory for quantum-dot quantum wells: pair correlation and internal quantum confinement in nanoheterostructures. Phys Rev B. 1995;52:R16997. 10.1103/PhysRevB.52.R16997. Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Harrison P. Quantum wells, wires and dots. Chichester: Wiley; 2005. 10.1002/0470010827Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Sahin M. Photoionization cross section and intersublevel transitions in a one-and two-electron spherical quantum dot with a hydrogenic impurity. Phys Rev B. 2008;77:045317. 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.045317. Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Leobandung E, Guo L, Chou SY. Single hole quantum dot transistors in silicon. Appl Phys Lett. 1995;67:2338. 10.1063/1.114337. Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Likharev KK. Correlated discrete transfer of single electrons in ultrasmall tunnel junctions. IBM J Res Dev. 1998;32:1444. 10.1147/rd.321.0144Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Yuen SY. Fast relaxing absorptive nonlinear refraction in superlattices. Appl Phys Lett. 1983;43:813. 10.1063/1.94518. Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Loss D, DiVincenzo DP. Quantum computation with quantum dots. Phys Rev A. 1998;57:120. 10.1103/PhysRevA.57.120. Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Imamura K, Sugiyama Y, Nakata Y, Murol S, Yokoyama N. New optical memory structure using self assembled InAs quantum dots. Jpn Appl Phys. 1995;11:L1445–47. 10.1143/JJAP34L1445. Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Wei-Ping L, Jing-Lin X, Ji-Wen Y, Yi-Fu Y, Zi-Wu W. The energy levels of a two-electron two-dimensional parabolic quantum dot. Chin Phys B. 2010;19(4):047102. 10.1088/1674-1056/19/4/047102. Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Woldemariam MM. Nonlinear absorption coefficient and refractive index changes of two-dimensional two-electron quantum dot in rigid confinement. Int J Modern Phys B. 2019;33(9):1950078. 10.1142/S0217979219500784. Suche in Google Scholar
[12] Mengesha M, Mal’nev V. Optical properties of two-electron quantum dots in low lying para-and ortho-states. Superlatt Microstruct. 2012;52(1):1–10. 10.1016/j.spmi.2012.04.008. Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Menberu M, Mal’nev VN. Two electron quantum dots with parabolic confinement (Low lying para- and ortho-states). Ukr J Phys. 2011;56(11):ISSN 2071-0194. Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Einstein A, Podolsky B, Rosen N. Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete? Phys Rev. 1935;47:777. 10.1103/PhysRev.47.777. Suche in Google Scholar
[15] He L, Bester G, Zunger A. Singlet-triplet splitting, correlation, and entanglement of two electrons in quantum dot molecules. Phys Rev B. 2005;72:195307. 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.199903. Suche in Google Scholar
[16] Ferron A, Osenda O, Serra P. Entanglement in resonances of two-electron quantum dots. Phys Rev A. 2009;79:032509. 10.1103/PhysRevA.79.032509. Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Planells J, Rajadel F, Royo M. Dielectric control of spin in semiconductor spherical quantum dots. J Appl Phys. 2008;104:014313. 10.1063/1.2952070. Suche in Google Scholar
[18] Huang LL, Chang HJ, Chou YY, Wang CH, Chen TT, Chen YF, et al. Optical properties of InGaN quantum dots grown by SiNx nanomasks. J Appl Phys. 2007;101:083501. 10.1063/1.2717258. Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Yilmaz S, Şafak H. Oscillator strengths for the intersubband transitions in a CdS-SiO2 quantum dot with hydrogenic impurity. Phys E. 2007;36(1):40–4. 10.1016/j.physe.2006.07.040. Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Turkoglu A, Dakhlaoui H, Durmuslar AS, Mora-Ramos ME, Ungan F. Nonlinear optical properties of a quantum well with inversely quadratic Hellman potential. Eur Phys J B. 2021;94:111. 10.1140/epjb/s10051-021-00129-4. Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Turkoglu A, Aghoutane N, Feddi E, Mora-Ramos ME, Ungan F. Non-resonant intense laser field effect on the nonlinear optical properties associated to the inter-and intra-band transitions in an anharmonic quantum well submitted to electric and magnetic field. Solid State Commun. 2021;334–335:114390. 10.1016/j.ssc.2021.114390. Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Kiliani G, Schneider R, Litvinov D, Gerthsen D, Fonin M, Rüdiger U, et al. Ultraviolet photoluminescence of ZnO quantum dots sputtered at room-temperature. Optics Express. 2011 Jan 17;19(2):1641–7. 10.1364/OE.19.001641. Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Boyd RW. Nonlinear optics. New York: Rochester; 2007. Suche in Google Scholar
[24] Rezaei G, Vaseghi B, Taghizadh F, Vahdani MRK, Karimi MJ. Intersubband optical absorption coefficient changes and refractive index changes in a two-dimensional quantum pseudodot system. Superlatt Microstruct. 2010;48(5):450–7. 10.1016/j.spmi.2010.08.009. Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Vahdani MR, Rezaei G. Intersubband optical absorption coefficients and refractive index changes in a parabolic cylinder quantum dot. Phys Lett A. 2010 Jan 11;374(4):637–43. 10.1016/j.physleta.2009.06.042. Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Menberu Mengesha Woldemariam, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Circular Rydberg states of helium atoms or helium-like ions in a high-frequency laser field
- Closed-form solutions and conservation laws of a generalized Hirota–Satsuma coupled KdV system of fluid mechanics
- W-Chirped optical solitons and modulation instability analysis of Chen–Lee–Liu equation in optical monomode fibres
- The problem of a hydrogen atom in a cavity: Oscillator representation solution versus analytic solution
- An analytical model for the Maxwell radiation field in an axially symmetric galaxy
- Utilization of updated version of heat flux model for the radiative flow of a non-Newtonian material under Joule heating: OHAM application
- Verification of the accommodative responses in viewing an on-axis analog reflection hologram
- Irreversibility as thermodynamic time
- A self-adaptive prescription dose optimization algorithm for radiotherapy
- Algebraic computational methods for solving three nonlinear vital models fractional in mathematical physics
- The diffusion mechanism of the application of intelligent manufacturing in SMEs model based on cellular automata
- Numerical analysis of free convection from a spinning cone with variable wall temperature and pressure work effect using MD-BSQLM
- Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic oscillation of side-by-side double-floating-system with a narrow gap in waves
- Closed-form solutions for the Schrödinger wave equation with non-solvable potentials: A perturbation approach
- Study of dynamic pressure on the packer for deep-water perforation
- Ultrafast dephasing in hydrogen-bonded pyridine–water mixtures
- Crystallization law of karst water in tunnel drainage system based on DBL theory
- Position-dependent finite symmetric mass harmonic like oscillator: Classical and quantum mechanical study
- Application of Fibonacci heap to fast marching method
- An analytical investigation of the mixed convective Casson fluid flow past a yawed cylinder with heat transfer analysis
- Considering the effect of optical attenuation on photon-enhanced thermionic emission converter of the practical structure
- Fractal calculation method of friction parameters: Surface morphology and load of galvanized sheet
- Charge identification of fragments with the emulsion spectrometer of the FOOT experiment
- Quantization of fractional harmonic oscillator using creation and annihilation operators
- Scaling law for velocity of domino toppling motion in curved paths
- Frequency synchronization detection method based on adaptive frequency standard tracking
- Application of common reflection surface (CRS) to velocity variation with azimuth (VVAz) inversion of the relatively narrow azimuth 3D seismic land data
- Study on the adaptability of binary flooding in a certain oil field
- CompVision: An open-source five-compartmental software for biokinetic simulations
- An electrically switchable wideband metamaterial absorber based on graphene at P band
- Effect of annealing temperature on the interface state density of n-ZnO nanorod/p-Si heterojunction diodes
- A facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic adsorption material 5A zeolite for oil–water separation with potential use in floating oil
- Shannon entropy for Feinberg–Horodecki equation and thermal properties of improved Wei potential model
- Hopf bifurcation analysis for liquid-filled Gyrostat chaotic system and design of a novel technique to control slosh in spacecrafts
- Optical properties of two-dimensional two-electron quantum dot in parabolic confinement
- Optical solitons via the collective variable method for the classical and perturbed Chen–Lee–Liu equations
- Stratified heat transfer of magneto-tangent hyperbolic bio-nanofluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms: Keller-Box solution technique
- Analysis of the structure and properties of triangular composite light-screen targets
- Magnetic charged particles of optical spherical antiferromagnetic model with fractional system
- Study on acoustic radiation response characteristics of sound barriers
- The tribological properties of single-layer hybrid PTFE/Nomex fabric/phenolic resin composites underwater
- Research on maintenance spare parts requirement prediction based on LSTM recurrent neural network
- Quantum computing simulation of the hydrogen molecular ground-state energies with limited resources
- A DFT study on the molecular properties of synthetic ester under the electric field
- Construction of abundant novel analytical solutions of the space–time fractional nonlinear generalized equal width model via Riemann–Liouville derivative with application of mathematical methods
- Some common and dynamic properties of logarithmic Pareto distribution with applications
- Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model
- Fractional modeling of COVID-19 epidemic model with harmonic mean type incidence rate
- Liquid metal-based metamaterial with high-temperature sensitivity: Design and computational study
- Biosynthesis and characterization of Saudi propolis-mediated silver nanoparticles and their biological properties
- New trigonometric B-spline approximation for numerical investigation of the regularized long-wave equation
- Modal characteristics of harmonic gear transmission flexspline based on orthogonal design method
- Revisiting the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations
- Time-periodic pulse electroosmotic flow of Jeffreys fluids through a microannulus
- Exact wave solutions of the nonlinear Rosenau equation using an analytical method
- Computational examination of Jeffrey nanofluid through a stretchable surface employing Tiwari and Das model
- Numerical analysis of a single-mode microring resonator on a YAG-on-insulator
- Review Articles
- Double-layer coating using MHD flow of third-grade fluid with Hall current and heat source/sink
- Analysis of aeromagnetic filtering techniques in locating the primary target in sedimentary terrain: A review
- Rapid Communications
- Nonlinear fitting of multi-compartmental data using Hooke and Jeeves direct search method
- Effect of buried depth on thermal performance of a vertical U-tube underground heat exchanger
- Knocking characteristics of a high pressure direct injection natural gas engine operating in stratified combustion mode
- What dominates heat transfer performance of a double-pipe heat exchanger
- Special Issue on Future challenges of advanced computational modeling on nonlinear physical phenomena - Part II
- Lump, lump-one stripe, multiwave and breather solutions for the Hunter–Saxton equation
- New quantum integral inequalities for some new classes of generalized ψ-convex functions and their scope in physical systems
- Computational fluid dynamic simulations and heat transfer characteristic comparisons of various arc-baffled channels
- Gaussian radial basis functions method for linear and nonlinear convection–diffusion models in physical phenomena
- Investigation of interactional phenomena and multi wave solutions of the quantum hydrodynamic Zakharov–Kuznetsov model
- On the optical solutions to nonlinear Schrödinger equation with second-order spatiotemporal dispersion
- Analysis of couple stress fluid flow with variable viscosity using two homotopy-based methods
- Quantum estimates in two variable forms for Simpson-type inequalities considering generalized Ψ-convex functions with applications
- Series solution to fractional contact problem using Caputo’s derivative
- Solitary wave solutions of the ionic currents along microtubule dynamical equations via analytical mathematical method
- Thermo-viscoelastic orthotropic constraint cylindrical cavity with variable thermal properties heated by laser pulse via the MGT thermoelasticity model
- Theoretical and experimental clues to a flux of Doppler transformation energies during processes with energy conservation
- On solitons: Propagation of shallow water waves for the fifth-order KdV hierarchy integrable equation
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part II
- Numerical study on heat transfer and flow characteristics of nanofluids in a circular tube with trapezoid ribs
- Experimental and numerical study of heat transfer and flow characteristics with different placement of the multi-deck display cabinet in supermarket
- Thermal-hydraulic performance prediction of two new heat exchangers using RBF based on different DOE
- Diesel engine waste heat recovery system comprehensive optimization based on system and heat exchanger simulation
- Load forecasting of refrigerated display cabinet based on CEEMD–IPSO–LSTM combined model
- Investigation on subcooled flow boiling heat transfer characteristics in ICE-like conditions
- Research on materials of solar selective absorption coating based on the first principle
- Experimental study on enhancement characteristics of steam/nitrogen condensation inside horizontal multi-start helical channels
- Special Issue on Novel Numerical and Analytical Techniques for Fractional Nonlinear Schrodinger Type - Part I
- Numerical exploration of thin film flow of MHD pseudo-plastic fluid in fractional space: Utilization of fractional calculus approach
- A Haar wavelet-based scheme for finding the control parameter in nonlinear inverse heat conduction equation
- Stable novel and accurate solitary wave solutions of an integrable equation: Qiao model
- Novel soliton solutions to the Atangana–Baleanu fractional system of equations for the ISALWs
- On the oscillation of nonlinear delay differential equations and their applications
- Abundant stable novel solutions of fractional-order epidemic model along with saturated treatment and disease transmission
- Fully Legendre spectral collocation technique for stochastic heat equations
- Special Issue on 5th International Conference on Mechanics, Mathematics and Applied Physics (2021)
- Residual service life of erbium-modified AM50 magnesium alloy under corrosion and stress environment
- Special Issue on Advanced Topics on the Modelling and Assessment of Complicated Physical Phenomena - Part I
- Diverse wave propagation in shallow water waves with the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili–Benjamin–Bona–Mahony and Benney–Luke integrable models
- Intensification of thermal stratification on dissipative chemically heating fluid with cross-diffusion and magnetic field over a wedge
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Circular Rydberg states of helium atoms or helium-like ions in a high-frequency laser field
- Closed-form solutions and conservation laws of a generalized Hirota–Satsuma coupled KdV system of fluid mechanics
- W-Chirped optical solitons and modulation instability analysis of Chen–Lee–Liu equation in optical monomode fibres
- The problem of a hydrogen atom in a cavity: Oscillator representation solution versus analytic solution
- An analytical model for the Maxwell radiation field in an axially symmetric galaxy
- Utilization of updated version of heat flux model for the radiative flow of a non-Newtonian material under Joule heating: OHAM application
- Verification of the accommodative responses in viewing an on-axis analog reflection hologram
- Irreversibility as thermodynamic time
- A self-adaptive prescription dose optimization algorithm for radiotherapy
- Algebraic computational methods for solving three nonlinear vital models fractional in mathematical physics
- The diffusion mechanism of the application of intelligent manufacturing in SMEs model based on cellular automata
- Numerical analysis of free convection from a spinning cone with variable wall temperature and pressure work effect using MD-BSQLM
- Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic oscillation of side-by-side double-floating-system with a narrow gap in waves
- Closed-form solutions for the Schrödinger wave equation with non-solvable potentials: A perturbation approach
- Study of dynamic pressure on the packer for deep-water perforation
- Ultrafast dephasing in hydrogen-bonded pyridine–water mixtures
- Crystallization law of karst water in tunnel drainage system based on DBL theory
- Position-dependent finite symmetric mass harmonic like oscillator: Classical and quantum mechanical study
- Application of Fibonacci heap to fast marching method
- An analytical investigation of the mixed convective Casson fluid flow past a yawed cylinder with heat transfer analysis
- Considering the effect of optical attenuation on photon-enhanced thermionic emission converter of the practical structure
- Fractal calculation method of friction parameters: Surface morphology and load of galvanized sheet
- Charge identification of fragments with the emulsion spectrometer of the FOOT experiment
- Quantization of fractional harmonic oscillator using creation and annihilation operators
- Scaling law for velocity of domino toppling motion in curved paths
- Frequency synchronization detection method based on adaptive frequency standard tracking
- Application of common reflection surface (CRS) to velocity variation with azimuth (VVAz) inversion of the relatively narrow azimuth 3D seismic land data
- Study on the adaptability of binary flooding in a certain oil field
- CompVision: An open-source five-compartmental software for biokinetic simulations
- An electrically switchable wideband metamaterial absorber based on graphene at P band
- Effect of annealing temperature on the interface state density of n-ZnO nanorod/p-Si heterojunction diodes
- A facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic adsorption material 5A zeolite for oil–water separation with potential use in floating oil
- Shannon entropy for Feinberg–Horodecki equation and thermal properties of improved Wei potential model
- Hopf bifurcation analysis for liquid-filled Gyrostat chaotic system and design of a novel technique to control slosh in spacecrafts
- Optical properties of two-dimensional two-electron quantum dot in parabolic confinement
- Optical solitons via the collective variable method for the classical and perturbed Chen–Lee–Liu equations
- Stratified heat transfer of magneto-tangent hyperbolic bio-nanofluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms: Keller-Box solution technique
- Analysis of the structure and properties of triangular composite light-screen targets
- Magnetic charged particles of optical spherical antiferromagnetic model with fractional system
- Study on acoustic radiation response characteristics of sound barriers
- The tribological properties of single-layer hybrid PTFE/Nomex fabric/phenolic resin composites underwater
- Research on maintenance spare parts requirement prediction based on LSTM recurrent neural network
- Quantum computing simulation of the hydrogen molecular ground-state energies with limited resources
- A DFT study on the molecular properties of synthetic ester under the electric field
- Construction of abundant novel analytical solutions of the space–time fractional nonlinear generalized equal width model via Riemann–Liouville derivative with application of mathematical methods
- Some common and dynamic properties of logarithmic Pareto distribution with applications
- Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model
- Fractional modeling of COVID-19 epidemic model with harmonic mean type incidence rate
- Liquid metal-based metamaterial with high-temperature sensitivity: Design and computational study
- Biosynthesis and characterization of Saudi propolis-mediated silver nanoparticles and their biological properties
- New trigonometric B-spline approximation for numerical investigation of the regularized long-wave equation
- Modal characteristics of harmonic gear transmission flexspline based on orthogonal design method
- Revisiting the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations
- Time-periodic pulse electroosmotic flow of Jeffreys fluids through a microannulus
- Exact wave solutions of the nonlinear Rosenau equation using an analytical method
- Computational examination of Jeffrey nanofluid through a stretchable surface employing Tiwari and Das model
- Numerical analysis of a single-mode microring resonator on a YAG-on-insulator
- Review Articles
- Double-layer coating using MHD flow of third-grade fluid with Hall current and heat source/sink
- Analysis of aeromagnetic filtering techniques in locating the primary target in sedimentary terrain: A review
- Rapid Communications
- Nonlinear fitting of multi-compartmental data using Hooke and Jeeves direct search method
- Effect of buried depth on thermal performance of a vertical U-tube underground heat exchanger
- Knocking characteristics of a high pressure direct injection natural gas engine operating in stratified combustion mode
- What dominates heat transfer performance of a double-pipe heat exchanger
- Special Issue on Future challenges of advanced computational modeling on nonlinear physical phenomena - Part II
- Lump, lump-one stripe, multiwave and breather solutions for the Hunter–Saxton equation
- New quantum integral inequalities for some new classes of generalized ψ-convex functions and their scope in physical systems
- Computational fluid dynamic simulations and heat transfer characteristic comparisons of various arc-baffled channels
- Gaussian radial basis functions method for linear and nonlinear convection–diffusion models in physical phenomena
- Investigation of interactional phenomena and multi wave solutions of the quantum hydrodynamic Zakharov–Kuznetsov model
- On the optical solutions to nonlinear Schrödinger equation with second-order spatiotemporal dispersion
- Analysis of couple stress fluid flow with variable viscosity using two homotopy-based methods
- Quantum estimates in two variable forms for Simpson-type inequalities considering generalized Ψ-convex functions with applications
- Series solution to fractional contact problem using Caputo’s derivative
- Solitary wave solutions of the ionic currents along microtubule dynamical equations via analytical mathematical method
- Thermo-viscoelastic orthotropic constraint cylindrical cavity with variable thermal properties heated by laser pulse via the MGT thermoelasticity model
- Theoretical and experimental clues to a flux of Doppler transformation energies during processes with energy conservation
- On solitons: Propagation of shallow water waves for the fifth-order KdV hierarchy integrable equation
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part II
- Numerical study on heat transfer and flow characteristics of nanofluids in a circular tube with trapezoid ribs
- Experimental and numerical study of heat transfer and flow characteristics with different placement of the multi-deck display cabinet in supermarket
- Thermal-hydraulic performance prediction of two new heat exchangers using RBF based on different DOE
- Diesel engine waste heat recovery system comprehensive optimization based on system and heat exchanger simulation
- Load forecasting of refrigerated display cabinet based on CEEMD–IPSO–LSTM combined model
- Investigation on subcooled flow boiling heat transfer characteristics in ICE-like conditions
- Research on materials of solar selective absorption coating based on the first principle
- Experimental study on enhancement characteristics of steam/nitrogen condensation inside horizontal multi-start helical channels
- Special Issue on Novel Numerical and Analytical Techniques for Fractional Nonlinear Schrodinger Type - Part I
- Numerical exploration of thin film flow of MHD pseudo-plastic fluid in fractional space: Utilization of fractional calculus approach
- A Haar wavelet-based scheme for finding the control parameter in nonlinear inverse heat conduction equation
- Stable novel and accurate solitary wave solutions of an integrable equation: Qiao model
- Novel soliton solutions to the Atangana–Baleanu fractional system of equations for the ISALWs
- On the oscillation of nonlinear delay differential equations and their applications
- Abundant stable novel solutions of fractional-order epidemic model along with saturated treatment and disease transmission
- Fully Legendre spectral collocation technique for stochastic heat equations
- Special Issue on 5th International Conference on Mechanics, Mathematics and Applied Physics (2021)
- Residual service life of erbium-modified AM50 magnesium alloy under corrosion and stress environment
- Special Issue on Advanced Topics on the Modelling and Assessment of Complicated Physical Phenomena - Part I
- Diverse wave propagation in shallow water waves with the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili–Benjamin–Bona–Mahony and Benney–Luke integrable models
- Intensification of thermal stratification on dissipative chemically heating fluid with cross-diffusion and magnetic field over a wedge

