Abstract
C17H12O2, monoclinic, P21/c, a = 11.982(2) Å, b = 5.8563(11) Å, c = 17.894(3) Å, β = 99.892(4)°, V = 1237.0(4) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0506, wRref(F2) = 0.1221, T = 296.15 K.
1 Source of materials
The synthesis of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one (DBIO) primarily referred to the literature of Jungang Wang and coworkers. 5 A reaction mixture containing 1,2-bis(bromomethyl)benzene (3.2 g, 12 mmol), 1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione (1.5 g, 10 mmol), and Cs2CO3 (6.5 g, 20 mmol) was dissolved in DMSO (25 ml) and stirred at 80 °C for 12 h. Afterwards, the mixture was pouring into 250 ml of 1 M hydrochloric acid solution and subsequently extracted with ethyl acetate three times. The combined organic layers were dried using anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent was evaporated to concentrate the mixture. The crude product was then purified via silica gel column chromatography using a petroleum ether/ethyl acetate eluent (40:1) to yield the final product as a yellow solid. To obtain the crystal of DBIO. A sample of DBIO (2.0 mmol) was transferred into a 20 ml glass tube containing a pre-mixed solvent composed of methanol and dichloromethane (10 ml, 1:1 v/v). The mixture was left for crystallization. After several days, well defined block crystals were isolated, washed with anhydrous methanol, and subsequently dried under air, yield 67 % (based on DBIO). The reagents and chemicals used in the synthesis were purchased from Anhui Zesheng Technology Co., Ltd.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Clear light colourless block |
| Size: | 0.22 × 0.21 × 0.19 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.09 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART APEX2, φ and ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 7020, 2774, 0.039 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1,649 |
| N(param)refined: | 172 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
2 Experimental details
The crystal data obtained from the X-ray single-crystal diffractometer show excellent quality parameters. The initial structural determination of the title compound was achieved through the application of the intrinsic phasing method with the SHELXT program. Subsequent refinement was executed utilizing the SHELXL program (Table 1).
3 Comment
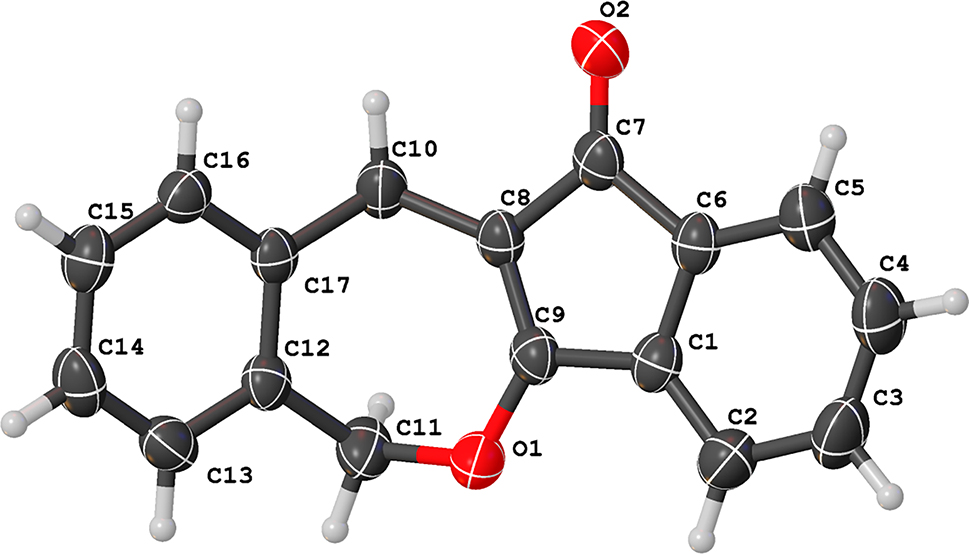
As an organic compound used as a pharmaceutical intermediate, the crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one (DBIO) has been reported in the literature. 5 However, the exploration of its crystalline forms is far from exhausted. In this work, we have successfully synthesized a new crystalline form of DBIO by optimizing the crystallization conditions. The crystal structure of this new form of DBIO is completely different from the previously reported structure. This result not only enriches the crystalline structural diversity of the compound but may also exhibit unique physical and chemical properties. For example, the change in crystal form may have a significant impact on the solubility, safety and stability of medicine, thereby providing new possibilities for its applications in pharmaceuticals and other fields. 6 , 7 , 8 The new DBIO crystal was obtained by slow solvent evaporation at room temperature. X-ray single-crystal structure determination reveals that the compound crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system and belonging to the P21/c space group. The asymmetric unit comprises a complete DBIO molecule, with all atoms exhibiting full occupancy and no disorder observed. The C–C and C–O distances are of 1.340(2)–1.512(2) Å and 1.223(2)–1.340(2) Å, respectively. These bond lengths are similar to the reported isomeric DBIO crystal structure and crystals formed from structures analogous to DBIO. 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 The DBIO molecule can be regarded as consisting of two parts: a polycyclic structure (C1–C2–C3–C4–C5–C6–C7–C8–C9, including O1 and O2 connected to C7 and C9) and a benzene ring (C12–C13–C14–C15–C16–C17). These two parts are connected by C10 and C11, forming a certain angle, which ultimately results in the DBIO molecule not being a planar structure. Specifically, the angles of C8–C10–C17 and O1–C11–C12 are 111.295° and 112.937°, respectively. It is precisely this non-planar angular structure that enables the formation of isomers. Through calculations using the PLATON software and analysis with the Mercury software, 14 , 15 it is found that the aggregation of DBIO molecules in the DBIO crystal structure mainly relies on weak C–H⋯O interactions (C11–H11B⋯O2x, 1+y, z and C15–H15⋯O2x, −1/2−y, 1/2+z) and p-p stacking interactions. It is worth noting that the effective overlap between the aromatic rings of adjacent DBIO molecules is minimal, preventing the formation of classical face-to-face sandwich or T-shaped stacking. Instead, a parallel-displaced stacking with significant slippage between the centroids is formed. This type of stacking results in relatively weak π-π interactions, with the perpendicular distance between the aromatic rings ranging from 3.6142 to 3.6206 Å, and the slippage ranging from 2.446 to 2.736 Å. In the end, the DBIO molecules form a final three-dimensional framework through the weak attractive interactions mentioned above.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2021QB053), and research startup funds of Weifang University (No. 196100040020).
References
1. Bruker. Saint and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxt – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Xiang, J.; Xi, H.; Wu, A. Generation of O-Quinodimethanes (O–QDMs) from Benzo[c]oxepines and the Synthetic Application for Polysubstituted Tetrahydronaphthalenes. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 7687–7694; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2015.07.062.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Datta, S.; Grant, D. J. Crystal Structures of Drugs: Advances in Determination, Prediction and Engineering. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 42–57; https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1280.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Haleblian, J. K. Characterization of Habits and Crystalline Modification of Solids and Their Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Pharm. Sci. 1975, 64, 1269–1288; https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600640805.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Xia, Y.-P. Crystal Structure of N-(diaminomethylene)-1-(dimethylamino)-1-iminiomethanaminium Dichloride, C4H13Cl2N5. Z. Kristallogr. – New Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 799–800; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023-0218.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Zhou, N.-N.; Ning, S.-S.; Li, L.-Q.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Fan, M.-J.; Yang, D.-S.; Zhu, H.-T. Bronsted-acid-catalyzed One-Pot Tandem Annulation/[5 + 2]-Cycloaddition of O-Propargyl Alcohol Benzaldehydes with Alkynes: Regioselective and Stereoselective Synthesis of Dibenzo[a,f]azulen-12-Ones. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 2664–2669; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0qo00522c.Suche in Google Scholar
10. He, Y. W.; Ma, W. Q.; Han, Y.; Sun, J.; Yan, C. G. Construction of Unique Spiro[dibenzo[a,f]azulene-6,2′-indenes] via Unprecedented Annulation of Ortho–C–H Bond of Benzylidene Group. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 14911–14927; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.3c01246.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Dunand, A.; Gerdil, R. The Crystal and Molecular Structure of endo-1,2,3,4,4a,9a-Hexahydro-1,4-(peri-Naphthaleno)fluoren-9-One. Acta Cryst. B 1977, 33, 2776–2779; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0567740877009455.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Zhu, H. T.; Liang, C. M.; Li, T. Y.; Li, L. Y.; Zhang, R. L.; Wang, J. N.; Qi, R. Q.; Zhang, J. M.; Yang, R. H.; Yang, Y. Q.; Zhou, A. X.; Jin, X.; Zhou, N. N. Dual Proton/Silver-Catalyzed Serial (5 + 2)-Cycloaddition and Nazarov Cyclization of (E)-2-Arylidene-3-hydroxyindanones with Conjugated Eneynes: Synthesis of Indanone-Fused Benzo[cd]azulenes. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 3409–3423; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.2c02247.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Uemura, N.; Ishikawa, H.; Tamura, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Mino, T.; Kasashima, Y.; Sakamoto, M. Stereoselective Photodimerization of 3-Arylindenones in Solution and in the Solid State. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 2256–2262; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.7b03147.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Macrae, C. F.; Edgington, P. R.; Mccabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Shields, G. P.; Taylor, R.; Towler, M.; Van De Streek, J. Mercury: Visualization and Analysis of Crystal Structures. J. Appl. Crystal. 2006, 39, 453–457; https://doi.org/10.1107/s002188980600731x.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Spek, A. L. Structure Validation in Chemical Crystallography. Acta Cryst. D 2009, 65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O


