Abstract
C16H10N2O7Pb, tetragonal, I41/a (no. 88), a = 15.1344(2) Å, b = 15.1344(2) Å, c = 26.5431(6) Å, V = 6079.7(2) Å3, Z = 16, R gt (F) = 0.0419, wRref (F 2) = 0.0991, T = 150 K.
CCDC no.: 2251224
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.2 × 0.16 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 11.1 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 26.4°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 41,734, 3109, 0.060 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2739 |
| N(param)refined: | 235 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb01 | −1.36051 (2) | −0.25288 (2) | 0.19622 (2) | 0.03489 (12) |
| O1 | −1.2516 (4) | −0.2270 (4) | 0.1347 (2) | 0.0392 (13) |
| O2 | −1.3728 (4) | −0.2461 (4) | 0.0887 (2) | 0.0402 (13) |
| O3 | −1.3387 (4) | −0.2349 (4) | −0.1014 (2) | 0.0488 (15) |
| O4 | −1.2018 (5) | −0.2318 (6) | −0.1307 (2) | 0.070 (2) |
| O5 | −0.6507 (4) | 0.0434 (4) | −0.0616 (2) | 0.0392 (13) |
| O6 | −0.5836 (4) | 0.0190 (4) | 0.0109 (2) | 0.0429 (14) |
| O7 | −1.4080 (4) | −0.2186 (4) | 0.2993 (3) | 0.073 (2) |
| H7A | −1.394837 | −0.256468 | 0.321763 | 0.110* |
| H7B | −1.455967 | −0.196438 | 0.288363 | 0.110* |
| N1 | −0.9674 (4) | −0.1218 (4) | 0.0585 (2) | 0.0324 (14) |
| H1 | −0.987865 | −0.135539 | 0.088540 | 0.039* |
| N2 | −0.9592 (4) | −0.1026 (4) | −0.0235 (3) | 0.0349 (14) |
| H2 | −0.973982 | −0.101619 | −0.055515 | 0.042* |
| C1 | −1.2920 (5) | −0.2309 (5) | 0.0934 (3) | 0.0334 (16) |
| C2 | −1.2373 (5) | −0.2123 (5) | 0.0466 (3) | 0.0282 (15) |
| C3 | −1.2739 (5) | −0.2261 (5) | −0.0015 (3) | 0.0306 (15) |
| H3 | −1.332638 | −0.247415 | −0.005006 | 0.037* |
| C4 | −1.2224 (5) | −0.2077 (5) | −0.0440 (3) | 0.0333 (16) |
| C5 | −1.2555 (6) | −0.2260 (6) | −0.0964 (3) | 0.0420 (19) |
| C6 | −1.1371 (5) | −0.1781 (5) | −0.0386 (3) | 0.0333 (17) |
| H6 | −1.102107 | −0.167880 | −0.067767 | 0.040* |
| C7 | −1.1007 (5) | −0.1628 (5) | 0.0095 (3) | 0.0285 (15) |
| C8 | −1.1517 (5) | −0.1817 (5) | 0.0518 (3) | 0.0290 (15) |
| H8 | −1.127439 | −0.173589 | 0.084455 | 0.035* |
| C9 | −1.0112 (5) | −0.1295 (5) | 0.0147 (3) | 0.0293 (15) |
| C10 | −0.8851 (5) | −0.0892 (5) | 0.0481 (3) | 0.0329 (16) |
| C11 | −0.8142 (5) | −0.0695 (5) | 0.0793 (3) | 0.0374 (18) |
| H11 | −0.817439 | −0.078421 | 0.114665 | 0.045* |
| C12 | −0.7391 (5) | −0.0366 (5) | 0.0569 (3) | 0.0344 (17) |
| H12 | −0.689633 | −0.022016 | 0.077321 | 0.041* |
| C13 | −0.7339 (5) | −0.0242 (5) | 0.0044 (3) | 0.0319 (16) |
| C14 | −0.6520 (5) | 0.0142 (5) | −0.0173 (3) | 0.0325 (16) |
| C15 | −0.8032 (5) | −0.0437 (5) | −0.0269 (3) | 0.0327 (16) |
| H15 | −0.799646 | −0.035106 | −0.062330 | 0.039* |
| C16 | −0.8792 (5) | −0.0768 (5) | −0.0040 (3) | 0.0306 (15) |
1 Source of materials
Pb(NO3)2 (0.2 mmol 0.0662 g) and 2-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-6-carboxyl 1H-benzimidazole (0.1 mmol 0.0326 g) were added sequentially to a 25 mL Teflon reactor liner, then, 9 mL of deionized water and 1 mL of N,N-Dimethylformamide in sequence, were added and finally add 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. At room temperature, the reactor stir for half an hour to ensure that the reaction is complete. The inner lining of the stirred reactor is put into the stainless steel reactor, and the reactor is heated to 140 Celsius degree and the reaction temperature is maintained for 3 days. After the reaction is finished, the reactor is allowed to cool naturally to room temperature, the product was rinsed repeatedly with water and DMF (9:1, v/v) and selected to produce block crystals. The selected crystals were dried at 60 °C for 24 h. The calculated yield of the crystal is 60 %.
2 Experimental details
The data were collected and processed using CrysAlisPRO [1]. And the structure was solved by direct methods using Olex2 software [2] and refined with the SHELXL [3]. The hydrogen atom positions were fixed geometrically at the calculated distances and allowed to ride on the parent atoms. The U iso of the H-atoms were set to 1.2 times U eq of the parent atoms with C–H = 0.93 Å (aromatic).
3 Comment
Coordination polymers constructed with N-heterocyclic carboxylic acid ligands have gained much attention due to their rich structures and functionalities [4], [5], [6], [7]. Many coordination polymers constructed with N-heterocyclic carboxylic acid ligands have been synthesized and structural characterized in our group [8], [9], [10], [11].
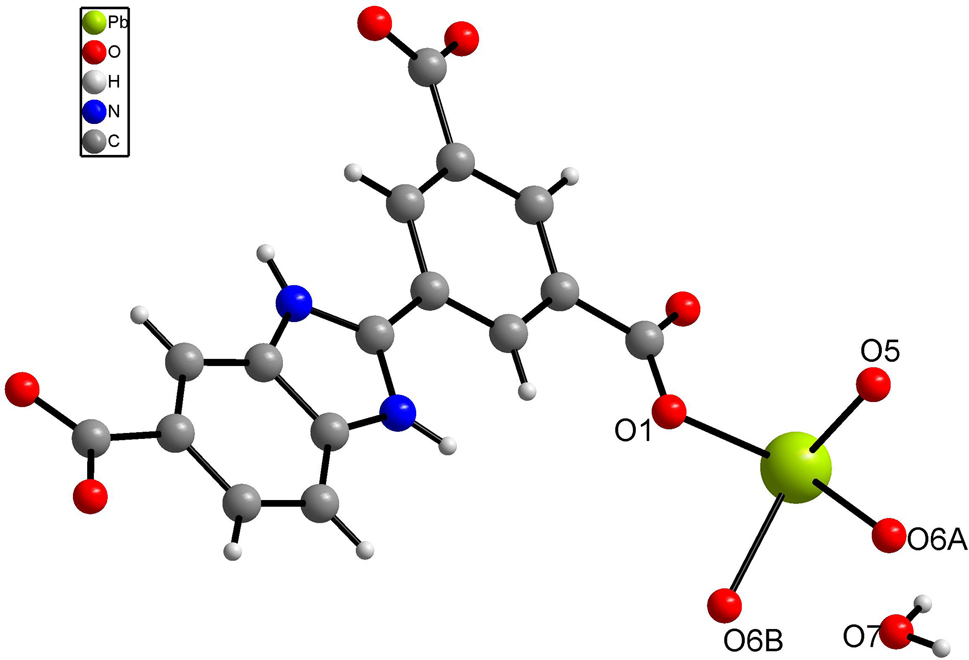
As shown in the figure, the asymmetric unit of the title structure contains one Pb(II) ion, one 2-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-6-carboxyl 1H-benzimidazole ligand and one lattice water molecule. The Pb(II) ion is four-coordinated by four O atoms from different 2-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-6-carboxyl 1H-benzimidazole ligands. The Pb–O bond lengths are in the range of 2.354(5)–2.618(6) Å, which are comparable to other lead(II) complexes [12]. The O–Pb–O angles are ranging from 52.52(19) to 100.48(18) degrees. Two adjacent lead ions are bridged by two oxygen atoms to form a binuclear unit, each binuclear lead structural unit is surrounded by four aromatic carboxylic acid ligands, which results in a three-dimensional framework.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: None declared.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Agilent Technologies. CrysAlisPRO Software System (version [171.]38.43f); Agilent Technologies UK Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sun, L. B., Li, Y., Liang, Z. Q., Yu, J. H., Xu, R. R. Structures and properties of lanthanide metal-organic frameworks based on a 1,2,3-triazole-containing tetracarboxylate ligand. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 12790–12796; https://doi.org/10.1039/c2dt31717f.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Zhang, X. T., Fan, L. M., Fan, W. L., Li, B., Liu, G. Z., Liu, X. Z., Zhao, X. A series of lanthanide coordination polymers based on designed bifunctional 1,4-bis(imidazol-1-yl)terephthalic acid ligand: structural diversities, luminescence, and magnetic properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3993–4004; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.6b00540.Search in Google Scholar
6. Li, H. H., Han, Y. B., Shao, Z. C., Li, N., Huang, C., Hou, H. W. Water-stable Eu–MOF fluorescent sensors for trivalent metal ions and nitrobenzene. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12201–12208; https://doi.org/10.1039/c7dt02590d.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Li, Z. D., Zhan, Z. Y., Jia, Y. J., Li, Z., Hu, M. A water-stable europium–MOF as a multifunctional luminescent sensor for some inorganic ions and dichloromethane molecule. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 97, 180–187; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.12.036.Search in Google Scholar
8. You, L. X., Zhang, L., Cao, S. Y., Liu, W. L., Xiong, G., Deun, R. V., He, Y. K., Ding, F., Dragutan, V., Sun, Y. G. Synthesis, structure and luminescence of 3D lanthanide metal-organic frameworks based on 1,3-bis(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl) imidazolium chloride. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 543, 121181; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.121181.Search in Google Scholar
9. Li, C., He, Y. K., Shao, N., Xiong, G., Wu, S. Y., You, L. X., Sun, Y. G., Tao, X., Mao, P., Ma, X. R. Syntheses, structures and photoluminescence of novel lanthanide-organic frameworks based on 1,4-bis(3,5-dicarboxylic pyrazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene. Chinese J. Struct. Chem. 2020, 39, 960–966; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-020-01572-z.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Xiong, G., Qi, D., He, Y. K., You, L. X., Ren, B. Y., Sun, Y. G. Lanthanide contraction and anion-controlled structure diversity in two types of novel 3d-4f heterometallic coordination polymers: crystal structure and magnetic properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 483, 299–304; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2018.08.044.Search in Google Scholar
11. Xiong, G., Wang, B. B., He, Y. K., You, L. X., Ren, B. Y., Sun, Y. G. Syntheses, structures, and luminescence of a series of novel trimetallic coordination polymers constructed by Cu–I clusters and alkaline-carboxyl-alkaline-earth building units. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 265, 393–401; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2018.06.026.Search in Google Scholar
12. Kowalik, M., Masternak, J., Kazimierczuk, K., Kupcewicz, B., Khavryuchenko, O. V., Barszcz, B. Exploring thiophene-2-acetate and thiophene-3-acetate binding modes towards the molecular and supramolecular structures and photoluminescence properties of Pb(II) polymers. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 7025–7035; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ce01224f.Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of a polymorph of potassium picrate, C6H2KN3O7
- The crystal structure of (1E,2E)-1,2-bis(quinolin-2-ylmethylene)hydrazine, C20H14N4
- 5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluoro-N-(N-isopropyl-N-methylsulfamoyl) benzamide, C11H15O3ClFN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-N 1,N 8-bis(2-cyanoethyl)-5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane, C22H42N6
- The crystal structure of [N-{[2-(oxy)-4-methoxyphenyl](phenyl)methylidene}alaninato]-diphenyl-silicon(IV) – chloroform (1/1), C29H25NO4Si·CHCl3
- Crystal structure of tetracarbonyl-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N,P,P-triphenylphosphinous amide]}-bis[μ-(phenylmethanethiolato)]diiron (Fe–Fe), C48H39Fe2NO4P2S2
- Crystal structure of baryte from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of [(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3 N,N,O)-(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)copper(II)] monohydrate, C23H17N3O5Cu
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(μ-[N-benzyl-N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide])-tetracarbonyl diiron (Fe–Fe), C47H37Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of diaqua-methanol-κ1 O- (3-thiophenecarboxylato-κO)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2 N,N′)manganese(II) 3-thiophenecarboxylate, C21H22N2O7S2Mn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(butyl)-μ2-2-((oxido(phenyl)methylene)hydrazineylidene)propanoato-κ4 O:O,O′,N-μ2-2-((oxido(phenyl)methylene)hydrazineylidene)propanoato-κ4 O,N,O′:N′-ditin(IV)], C34H50N6O6Sn2
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(2-nitrophenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide, C14H10ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1′-deoxy-3′,5′-O-dibenzy-β-d-ribosyl)adenine dichloromethane solvate, C49H52Cl2N10O6
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H17N3O
- The co-crystal structure of etoricoxib–phthalic acid (1/1), C18H15ClN2O2S·C8H6O4
- Crystal structure of (glycinto-κ 2 O,N ′)-[5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ 4 N,N ′,N ″,N ‴]nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate C18H42ClN5NiO7
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(1-ethylimidazole-k1 N)-(μ 2-benzene-1-carboxyl-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)zinc(II)], C19H20N4O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 3-(thiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C11H12N2O4S
- Rietveld structure analysis of keatite, a rare, metastable SiO2 polymorph
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-isophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)(4-(4-pyridyl)-2,5-dipyrazylpyridine-k3 N,N′,N″)cobalt(II)] trihydrate C26H22N6O7Co1
- Crystal structure of 3,5–di-O-benzoyl-1,2-O-isopropylidene-α–D-ribose, C22H22O7
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(6-bromo-2,2-bipyridine-κ2 N,N)-(nitrato-κO)rhenium(I), C13H7BrN3O6Re
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-2-naphthohydrazide monohydrate, C19H18N2O4
- The crystal structure of 5,5′-diselanediyl-bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde), C14H10O4Se2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-m2-dicyanido-κ2 C:N-dicyanido-κ1 C-bis(4-(pyridin-4-yl)benzaldehyde-κ1N)iron(II)-platinum(II), C28H22N6O4PtFe
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 5,14-dihydro-6,17-dimethyl-8,15-diphenyldibenzo(b,i)(1,4,8,11)tetra-azacyclotetradecine, C32H28N4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl) benzimidazole-6-carboxylato-κ4O:O:O′:O″)lead(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N2O7Pb
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(2-pyridin-2-yl-quinoline-κ2 N,N′)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I)nitrate, C20H14N4O3ReNO3
- Crystal structure of dibromo-dicarbonyl-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)-osmium(II) dichloromethane solvate, C38H66Br2O2OsP2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ 2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ 2 N:N′)copper(II)] diperchlorate dihydrate, C22H22Cl2CuN10O10
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(N-benzoyl-N,N-cyclohexylmethylcarbamimidothioato-κ2 S,O)-(pyridine-κN)rhenium(I), C23H24N3O4ReS
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S, 17S)-3-((2-methoxyphenyl)amino)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl((pyridin-2-yl)methanamino-κ2 N,N′)-((pyridin-2-yl)methanamino-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C15H16O3N4Re
- The crystal structure of (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-N-((1-(4-vinylbenzyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)methanamine-κ 4 N,N′,N″,N‴)tris(nitrato-kO,O′)-erbium(III), C29H27ErN8O9
- Crystal structure of tetracene-5,12-dione, C18H10O2
- Crystal structure of (3R,3aS,6R,6aR)-6-hexyl-3-methyltetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]furan-2,4-dione, C13H20O4
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-bis((E)-thiophen-2-ylmethylene)isophthalohydrazide monohydrate, C18H16N4O3S2
- Crystal structure of methyl ((4-aminobenzyl)sulfonyl)-L-prolinate, C13H18N2O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-methoxybenzylidene)benzofuran-2(3H)-one, C16H12O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure (E)-1-(4-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C11H12BrNO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (S,E)-4-hydroxy-3-(2-((4aR,6aS,7R,10aS,10bR)-3,3,6a,10b-tetramethyl-8-methylenedecahydro-1H-naphtho[2,1-d][1,3]dioxin-7-yl)ethylidene)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one, C23H34O5
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(1,2-phenylene)bis (2-((2-oxopropyl)selanyl)benzamide), C26H24N2O4Se2
- The crystal structure of 1-ethyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C5H7N3O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluorophenyl)naphtho[2,1-d]thiazole, C17H10FNS
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-di-tert-butyl-6-(((2-fluorophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C21H26FNO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-(methylthio)-4H-chromen-4-one, C12H12O2S
- Crystal structure of dithieno[2,3-d:2′,3′-d′]benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]dithiophene-5,10-dione, C14H4O2S4
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2ʹ-((adamantane-1,3-diylbis(4,1-phenylene)) bis(oxy))diacetate, C28H32O6
- The crystal structure of N-(6-chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-yl)acetamide, C10H10ClN3O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-(5-bromoisophthalato-κ1 O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N:N′)nickel(II) hydrate, C18H19BrN2NiO8
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-4-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[5-aminonicotinic acid-k1 N-m2-bromido-copper(I)], Cu(C6N2H6O2)Br
- The crystal structure of 2,2-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro- 2λ4,3λ4 -[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline - dichloromethane (1/1)
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridne-κ2 N:N)cadmium(II)], C34H24N4O4Cd
- The crystal structure of 5,7-dinitropyrazolo[5,1-b]quinazolin-9(4H)-one, C10H5N5O5
- Crystal structure of rac-1,8-bis(2-carbamoylethyl)-5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane, C22H46N6O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N ′-(2-bromobenzylidene)-2-naphthohydrazide, C36H26Br2N4O2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitronaphthoquinone, C10H5NO4
- The crystal structure of (S, R p )-4–benzhydrylideneamino-12-(4-tert-butyl oxazolin-2-yl)[2.2]paracyclophane, C36H36N2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-(o-tolyl)ethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C18H14O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(thiazol-2-yl)hexahydro-1H-4,7-epoxyisoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C11H10N2O3S
- Crystal structure of N-(diaminomethylene)-1-(dimethylamino)-1-iminiomethanaminium dichloride, C4H13Cl2N5
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-3, 5-dichloro-2-hydroxy-benzoato-κ4 Cl,O:O′:O″) silver(I)], C7H3AgCl2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropylimidazole-κ1 N)-[μ2- imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,N′)]- trioxido-divanadium, C29H41N10O7V2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ3-bromido)-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ1 N)copper(I)], C9H7BrCuN3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of a polymorph of potassium picrate, C6H2KN3O7
- The crystal structure of (1E,2E)-1,2-bis(quinolin-2-ylmethylene)hydrazine, C20H14N4
- 5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluoro-N-(N-isopropyl-N-methylsulfamoyl) benzamide, C11H15O3ClFN3S
- Crystal structure of trans-N 1,N 8-bis(2-cyanoethyl)-5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane, C22H42N6
- The crystal structure of [N-{[2-(oxy)-4-methoxyphenyl](phenyl)methylidene}alaninato]-diphenyl-silicon(IV) – chloroform (1/1), C29H25NO4Si·CHCl3
- Crystal structure of tetracarbonyl-{μ-[N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-N,P,P-triphenylphosphinous amide]}-bis[μ-(phenylmethanethiolato)]diiron (Fe–Fe), C48H39Fe2NO4P2S2
- Crystal structure of baryte from Mine du Pradet (France)
- The crystal structure of [(2,2′-bipyridine-6-carboxylato-κ3 N,N,O)-(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)copper(II)] monohydrate, C23H17N3O5Cu
- Crystal structure of bis(μ-benzeneselenolato)-(μ-[N-benzyl-N-(diphenylphosphanyl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinous amide])-tetracarbonyl diiron (Fe–Fe), C47H37Fe2NO4P2Se2
- The crystal structure of diaqua-methanol-κ1 O- (3-thiophenecarboxylato-κO)-(2,2′-dipyridyl-κ2 N,N′)manganese(II) 3-thiophenecarboxylate, C21H22N2O7S2Mn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(butyl)-μ2-2-((oxido(phenyl)methylene)hydrazineylidene)propanoato-κ4 O:O,O′,N-μ2-2-((oxido(phenyl)methylene)hydrazineylidene)propanoato-κ4 O,N,O′:N′-ditin(IV)], C34H50N6O6Sn2
- Crystal structure of 4-chloro-N′-[(1E)-(2-nitrophenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide, C14H10ClN3O3
- The crystal structure of 3-(1′-deoxy-3′,5′-O-dibenzy-β-d-ribosyl)adenine dichloromethane solvate, C49H52Cl2N10O6
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-amino-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H17N3O
- The co-crystal structure of etoricoxib–phthalic acid (1/1), C18H15ClN2O2S·C8H6O4
- Crystal structure of (glycinto-κ 2 O,N ′)-[5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-κ 4 N,N ′,N ″,N ‴]nickel(II) perchlorate monohydrate C18H42ClN5NiO7
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(1-ethylimidazole-k1 N)-(μ 2-benzene-1-carboxyl-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ 2 O, O′)zinc(II)], C19H20N4O6Zn
- Crystal structure of 3-(thiazol-2-ylcarbamoyl)-7-oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, C11H12N2O4S
- Rietveld structure analysis of keatite, a rare, metastable SiO2 polymorph
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-isophthalato-k3 O,O′:O″)(4-(4-pyridyl)-2,5-dipyrazylpyridine-k3 N,N′,N″)cobalt(II)] trihydrate C26H22N6O7Co1
- Crystal structure of 3,5–di-O-benzoyl-1,2-O-isopropylidene-α–D-ribose, C22H22O7
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(6-bromo-2,2-bipyridine-κ2 N,N)-(nitrato-κO)rhenium(I), C13H7BrN3O6Re
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-2-naphthohydrazide monohydrate, C19H18N2O4
- The crystal structure of 5,5′-diselanediyl-bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde), C14H10O4Se2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-m2-dicyanido-κ2 C:N-dicyanido-κ1 C-bis(4-(pyridin-4-yl)benzaldehyde-κ1N)iron(II)-platinum(II), C28H22N6O4PtFe
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 5,14-dihydro-6,17-dimethyl-8,15-diphenyldibenzo(b,i)(1,4,8,11)tetra-azacyclotetradecine, C32H28N4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-2-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl) benzimidazole-6-carboxylato-κ4O:O:O′:O″)lead(II)] monohydrate, C16H10N2O7Pb
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(2-pyridin-2-yl-quinoline-κ2 N,N′)-(pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I)nitrate, C20H14N4O3ReNO3
- Crystal structure of dibromo-dicarbonyl-bis(tricyclohexylphosphine)-osmium(II) dichloromethane solvate, C38H66Br2O2OsP2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ 2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ 2 N:N′)copper(II)] diperchlorate dihydrate, C22H22Cl2CuN10O10
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(N-benzoyl-N,N-cyclohexylmethylcarbamimidothioato-κ2 S,O)-(pyridine-κN)rhenium(I), C23H24N3O4ReS
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(4-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13S, 17S)-3-((2-methoxyphenyl)amino)-10,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO2
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl((pyridin-2-yl)methanamino-κ2 N,N′)-((pyridin-2-yl)methanamino-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C15H16O3N4Re
- The crystal structure of (1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-N-((1-(4-vinylbenzyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)methanamine-κ 4 N,N′,N″,N‴)tris(nitrato-kO,O′)-erbium(III), C29H27ErN8O9
- Crystal structure of tetracene-5,12-dione, C18H10O2
- Crystal structure of (3R,3aS,6R,6aR)-6-hexyl-3-methyltetrahydrofuro[3,4-b]furan-2,4-dione, C13H20O4
- The crystal structure of N′1,N′3-bis((E)-thiophen-2-ylmethylene)isophthalohydrazide monohydrate, C18H16N4O3S2
- Crystal structure of methyl ((4-aminobenzyl)sulfonyl)-L-prolinate, C13H18N2O4S
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-methoxybenzylidene)benzofuran-2(3H)-one, C16H12O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure (E)-1-(4-bromo-2-hydroxyphenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)prop-2-en-1-one, C11H12BrNO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (S,E)-4-hydroxy-3-(2-((4aR,6aS,7R,10aS,10bR)-3,3,6a,10b-tetramethyl-8-methylenedecahydro-1H-naphtho[2,1-d][1,3]dioxin-7-yl)ethylidene)dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one, C23H34O5
- The crystal structure of N,N′-(1,2-phenylene)bis (2-((2-oxopropyl)selanyl)benzamide), C26H24N2O4Se2
- The crystal structure of 1-ethyl-2-nitro-imidazole oxide, C5H7N3O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-fluorophenyl)naphtho[2,1-d]thiazole, C17H10FNS
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-di-tert-butyl-6-(((2-fluorophenyl)imino) methyl)phenol, C21H26FNO
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 3-methyl-2-(methylthio)-4H-chromen-4-one, C12H12O2S
- Crystal structure of dithieno[2,3-d:2′,3′-d′]benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]dithiophene-5,10-dione, C14H4O2S4
- The crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2ʹ-((adamantane-1,3-diylbis(4,1-phenylene)) bis(oxy))diacetate, C28H32O6
- The crystal structure of N-(6-chloro-2-methyl-2H-indazol-5-yl)acetamide, C10H10ClN3O
- Crystal structure of triaqua-(5-bromoisophthalato-κ1 O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N:N′)nickel(II) hydrate, C18H19BrN2NiO8
- The crystal structure of 2-amino-4-carboxypyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C6H7ClN2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[5-aminonicotinic acid-k1 N-m2-bromido-copper(I)], Cu(C6N2H6O2)Br
- The crystal structure of 2,2-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-tosyl-1,2-dihydro- 2λ4,3λ4 -[1,3,2]diazaborolo[4,5,1-ij]quinoline - dichloromethane (1/1)
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridne-κ2 N:N)cadmium(II)], C34H24N4O4Cd
- The crystal structure of 5,7-dinitropyrazolo[5,1-b]quinazolin-9(4H)-one, C10H5N5O5
- Crystal structure of rac-1,8-bis(2-carbamoylethyl)-5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane, C22H46N6O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-N ′-(2-bromobenzylidene)-2-naphthohydrazide, C36H26Br2N4O2
- The crystal structure of 5-nitronaphthoquinone, C10H5NO4
- The crystal structure of (S, R p )-4–benzhydrylideneamino-12-(4-tert-butyl oxazolin-2-yl)[2.2]paracyclophane, C36H36N2O
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-(o-tolyl)ethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C18H14O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(thiazol-2-yl)hexahydro-1H-4,7-epoxyisoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C11H10N2O3S
- Crystal structure of N-(diaminomethylene)-1-(dimethylamino)-1-iminiomethanaminium dichloride, C4H13Cl2N5
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ3-3, 5-dichloro-2-hydroxy-benzoato-κ4 Cl,O:O′:O″) silver(I)], C7H3AgCl2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(1-isopropylimidazole-κ1 N)-[μ2- imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylato-κ4 O,N,O′,N′)]- trioxido-divanadium, C29H41N10O7V2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ3-bromido)-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-κ1 N)copper(I)], C9H7BrCuN3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O2

