Abstract
C12H15N7O3, P21/c (no. 14), a = 7.1782(3) Å, b = 16.6800(6) Å, c = 12.1070(5) Å, β = 92.030(2)°, V = 1448.69(10) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt (F) = 0.0449, wRref (F 2) = 0.1220, T = 296(2) K.
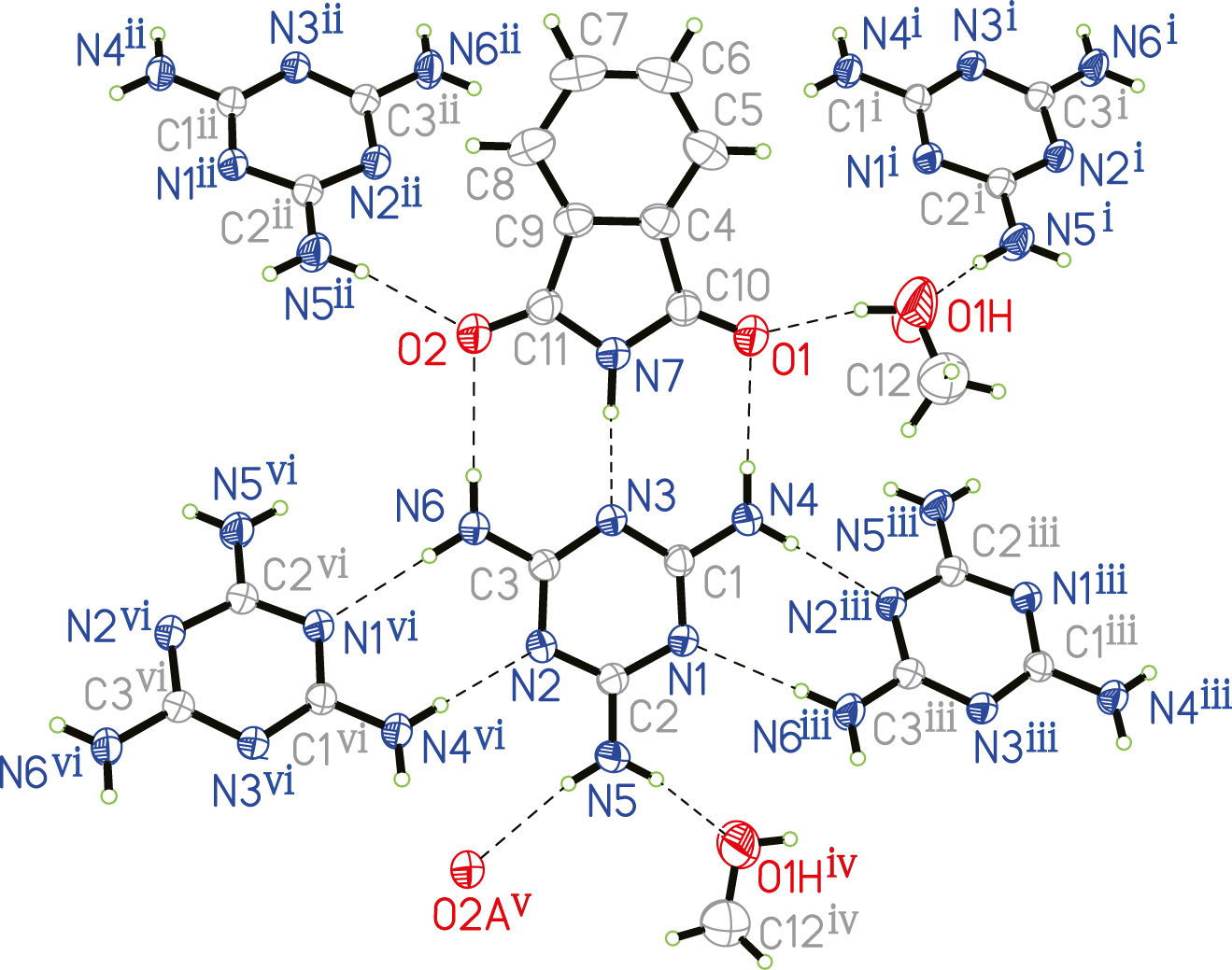
The molecular structure is shown in the figure (symmetry code i) −x + 1, y − 0.5, −z + 1.5; ii) −x + 1, y − 0.5, −z + 0.5; iii) x, −y + 1.5, z + 0.5; iv) −x + 1, y + 0.5, −z + 1.5; v) −x + 1, y + 0.5, −z + 0.5; vi) x, −y + 1.5, z − 0.5). Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.89 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX3, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 72.2°, 98% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 12,956, 2788, 0.044 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2451 |
| N(param)refined: | 215 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Shelx [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.77763 (18) | 0.48446 (7) | 0.63688 (9) | 0.0495 (3) |
| O2 | 0.73763 (17) | 0.47187 (7) | 0.26140 (9) | 0.0472 (3) |
| N1 | 0.48553 (16) | 0.76466 (7) | 0.54272 (9) | 0.0316 (3) |
| N2 | 0.48105 (17) | 0.76418 (7) | 0.34500 (9) | 0.0347 (3) |
| N3 | 0.57738 (16) | 0.64749 (7) | 0.44564 (9) | 0.0308 (3) |
| N4 | 0.58375 (17) | 0.65188 (7) | 0.63506 (9) | 0.0359 (3) |
| H4A | 0.565381 | 0.676383 | 0.696222 | 0.043* |
| H4B | 0.624555 | 0.603403 | 0.635834 | 0.043* |
| N5 | 0.3781 (2) | 0.87190 (8) | 0.44225 (11) | 0.0452 (4) |
| H5B | 0.357019 | 0.895889 | 0.503428 | 0.054* |
| H5C | 0.353090 | 0.895498 | 0.380335 | 0.054* |
| N6 | 0.5735 (2) | 0.65050 (8) | 0.25636 (10) | 0.0473 (4) |
| H6B | 0.613390 | 0.601880 | 0.257049 | 0.057* |
| H6C | 0.553089 | 0.674837 | 0.194484 | 0.057* |
| N7 | 0.74011 (18) | 0.49566 (8) | 0.44844 (10) | 0.0378 (3) |
| H7N | 0.685 (3) | 0.5476 (14) | 0.4445 (17) | 0.062 (6)* |
| C1 | 0.54889 (17) | 0.68916 (8) | 0.53879 (10) | 0.0280 (3) |
| C2 | 0.44947 (19) | 0.79830 (8) | 0.44339 (11) | 0.0313 (3) |
| C3 | 0.54331 (19) | 0.68818 (8) | 0.35128 (11) | 0.0313 (3) |
| C4 | 0.87601 (19) | 0.37945 (9) | 0.51090 (12) | 0.0364 (3) |
| C5 | 0.9523 (2) | 0.31777 (10) | 0.57374 (16) | 0.0479 (4) |
| H5A | 0.961700 | 0.320866 | 0.650429 | 0.057* |
| C6 | 1.0140 (2) | 0.25114 (11) | 0.51753 (19) | 0.0561 (5) |
| H6A | 1.066654 | 0.208632 | 0.557333 | 0.067* |
| C7 | 0.9991 (3) | 0.24635 (11) | 0.40369 (19) | 0.0578 (5) |
| H7A | 1.040814 | 0.200497 | 0.368521 | 0.069* |
| C8 | 0.9231 (2) | 0.30867 (10) | 0.34058 (16) | 0.0490 (4) |
| H8A | 0.913054 | 0.305583 | 0.263902 | 0.059* |
| C9 | 0.8635 (2) | 0.37513 (9) | 0.39665 (13) | 0.0367 (3) |
| C10 | 0.7951 (2) | 0.45710 (9) | 0.54442 (12) | 0.0360 (3) |
| C11 | 0.7750 (2) | 0.45069 (9) | 0.35583 (12) | 0.0359 (3) |
| O1H | 0.7746 (4) | 0.46085 (12) | 0.87128 (14) | 0.1113 (8) |
| H1H | 0.764 (5) | 0.457 (2) | 0.797 (4) | 0.134* |
| C12 | 0.8271 (4) | 0.53823 (16) | 0.8936 (2) | 0.0783 (7) |
| H12A | 0.811 (5) | 0.549 (2) | 0.973 (3) | 0.117* |
| H12B | 0.752 (5) | 0.579 (2) | 0.850 (3) | 0.117* |
| H12C | 0.965 (5) | 0.5445 (19) | 0.883 (3) | 0.117* |
Source of material
2,4,6-Triamino-1,3,5-triazine (melamine) mono(dimethyl sulfoxide) solvate (MA-DMSO) was prepared by following the literature procedures [4]. MA-DMSO (25 mg, 0.198 mmol) was dissolved in methanol (12 mL) under reflux at 70 °C under N2 atmosphere to obtain a clear solution. To 4.0 mL of the solution, 29.2 mg (0.198 mmol) of 1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione (phthalimide) was added. The mixture was kept at 50 °C to get a clear solution and was then cooled down naturally. Crystals of the title compound suitable for single crystal analysis were obtained in 2–3 days, with a yield of 12.5 mg or 50%.
Experimental details
A crystal of a size 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm was mounted on a glass fiber with expoxy glue. Data collection was performed on a Bruker D8 VENTURE Photon II diffractometer at room temperature, operating at 50 kV and 30 mA. Data were processed on a PC using the Bruker AXS Crystal Structure Analysis Package [1]. Data collection: Bruker APEX3; cell refinement: Bruker SAINT; Data reduction: Bruker SAINT; Structure solution: Shelxt 2014/5 [2]; Structure refinement: Shelxl-2018/3 [3]; Molecular graphics: Bruker Shelxtl [2]; Publication materials: Bruker Shelxtl [2].
The H-atoms on N7 and O1H were located from the difference-Fourier maps. All other H-atoms were placed geometrically and refined using a riding model with common isotropic displacement factors U iso(H) = 1.2 U eq (parent C-atom).
Comment
The development of multipoint hydrogen bonding motifs that form complexes or cocrystals with high stability and selectivity is important both for the understanding of biological processes and in the design of new materials [5]. In the study of organic semiconductors, the key materials of today’s organic electronics, hydrogen bonding have received surprisingly limited, but quickly growing attentions [6, 7]. Efficient charge transport in hydrogen-bonded materials has been realized in organic field-effect transistor (OFET) devices, where the organic complex or cocrystal serves as an active layer across extraordinary charge pathways, ensuring the efficient transport of induced charges [8], [9], [10], [11]. Naphthalenetetracarboxydiimide and its derivatives (NDIs) and related arylenetetracarboxydiimides are among the most promising candidates of next generation n-type organic semiconductors, with their electronic properties being easily tailored through π- and/or N-substitutions [12], [13], [14]. For examples, not only they show record-high electron mobilities in organic field electric transistors (OFETs), but also they are only second to fullerene derivatives when used in OPV as the acceptor. Meanwhile, the electronic properties of NDIs can be tuned through strong H-bonding interactions [15, 16].
With an Acceptor–Donor–Acceptor (ADA) structure, naphthalenetetracarboxydiimide (NDI) can triply hydrogen-bond to a compound with a complimentary structure, i.e. Donor–Acceptor–Donor (DAD) structure, such as 2,4-diaminopyridine or 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine (melamine). However, since the structure of NDI is quite rigid, it has limited solubility in most of the solvents, which makes co-crystal production in solution very challenging. We therefore use 1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione (phthalimide) as a model compound to study its co-crystallization reaction with melamine and the ADA…DAD triply hydrogen bonding. It is worth noting that, by reacting phthalimide (PI) and melamine (MA) via a gaseous phase reaction, a co-crystal compound, (MA)(PI)3 had been obtained [17].
The asymmetric unit contains one 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine molecule (melamine: MA), one 1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione molecule and one methanol solvent molecule (see the figure). All moieties are connected by hydrogen bonds to form the title cocrystal. The structure demonstrates a polymeric feature with each MA hydrogen-bonded to two neighboring MA molecules, two isoindoles and two methanol molecules. All bond lengths are in the expected ranges.
Funding source: Key Program Special Fund of XJTLU
Award Identifier / Grant number: Research Project No. KSF-E-06
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work is supported by Key Program Special Fund of XJTLU (Research Project No. KSF-E-06).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Apex3, saint; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with Shelxl. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Shelxtl – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Vella-Zarb, L., Braga, D., Orpen, A. G., Baisch, U. The influence of hydrogen bonding on the planar arrangement of melamine in crystal structures of its solvates, cocrystals and salts. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 8147–8159.10.1039/C4CE00748DSearch in Google Scholar
5. Tayi, A. S., Shveyd, A. K., Sue, A. C. H., Szarko, J. M., Rolczynski, B. S., Cao, D., Kennedy, T. J., Sarjeant, A. A., Stern, C. L., Paxton, W. F., Wu, W., Dey, S. K., Fahrenbach, A. C., Guest, J. R., Mohseni, H., Chen, L. X., Wang, K. L., Stoddart, J. F., Stupp, S. I. Room-temperature ferroelectricity in supramolecular networks of charge-transfer complexes. Nature 2012, 488, 485–489; https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11395.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Wang, Y., Zhu, W., Dong, H., Zhang, X., Li, R., Hu, W. Organic cocrystals: new strategy for molecular collaborative innovation. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 83; https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-016-0081-8.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Zhu, W., Dong, H., Zhen, Y., Hu, W. Challenges of organic “cocrystals”. Sci. China Mater. 2015, 58, 854–859; https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-015-0099-1.Search in Google Scholar
8. Hayashi, S., Yamamoto, S. Y., Takeuchi, D., Ie, Y., Takagi, K. Creating elastic organic crystals of pi-conjugated molecules with bending mechanofluorochromism and flexible optical waveguide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 17002–17008; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201810422.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Sun, L., Zhu, W., Zhang, X., Li, L., Dong, H., Hu, W. Creating organic functional materials beyond chemical bond synthesis by organic cocrystal engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 19243–19256; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c07678.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Peng, B., Wu, R., Li, H. Crystallization from a droplet: single-crystalline arrays and heterojunctions for organic electronics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 4498–4507; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00537.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Kukhta, N. A., Marks, A., Luscombe, C. K. Molecular design strategies toward improvement of charge injection and ionic conduction in organic mixed ionic-electronic conductors for organic electrochemical transistors. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 4325–4355; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00266.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
12. Hecht, M., Würthner, F. Supramolecularly engineered J-aggregates based on perylene bisimide dyes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 642–653; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00590.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Kumagai, S., Ishii, H., Watanabe, G., Yu, C. P., Watanabe, S., Takeya, J., Okamoto, T. Nitrogen-containing perylene diimides: molecular design, robust aggregated structures, and advances in n-type organic semiconductors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 660–672; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00548.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Schmidt, R., Oh, J. H., Sun, Y.-S., Deppisch, M., Krause, A.-M., Radacki, K., Braunschweig, H., Könemann, M., Erk, P., Bao, Z., Würthner, F. High-performance air-stable n-channel organic thin film transistors based on halogenated perylene bisimide semiconductors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6215–6228; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja901077a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Zhao, Y., Di, C.-A., Gao, X., Hu, Y., Guo, Y., Zhang, L., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Hu, W., Zhu, D. All-solution-processed, high-performance n-channel organic transistors and circuits: toward low-cost ambient electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2448–2453; https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201004588.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
16. Zhang, Y., Chen, A., Kim, M.-W., Alaei, A., Lee, S. S. Nanoconfining solution-processed organic semiconductors for emerging optoelectronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 9375–9390; https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cs00430a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
17. Perpetuo, G. J., Janczak, J. 2,4,6-Triamino-1,3,5-triazine-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione (1/3). Acta Crystallogr. 2007, C63, o301–o302; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108270107015880.Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-(2-((5-methylthiophen-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene)chroman-2,4-dione, C17H14N2O3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η 6-toluene)(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluoridophosphate(V) ─ acetone (1/1) C22H26ClN2ORuPF6
- Crystal structure of 4-(((2-(3-(1-(3-(3-cyanophenyl)-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)ethyl)phenyl) pyrimidin-5-yl)oxy)methyl)-1-methylpiperidin-1-ium chloride monohydrate, C30H33N6O2Cl
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-N-((2-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl)nicotinamide, C13H9Cl2N3O2
- Crystal structure of 9-(t-butyl)-3,11-dihydro-6H-pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrrolo[3′,2′:5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-6-one hemihydrate, C30H32N10O3
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-hydroxido-tetrakis(6-methylpyridine-2-carboxylato-k2 N,O) diiron(III) trihydrate C28H32Fe2N4O13
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[qua-(μ2-2-aminoisophthalat-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)manganese(II)] C20H15MnN3O5
- Crystal structure of poly[(bis(isothiocyano)-bis(μ 2-(E)-N′-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide))iron(II) – methanol – 1,4-dioxane (1/2/2), C36H44FeN10O8S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-benzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(μ2-benzoato-k3O,O′:O′)dinitrato-k2O,O′-bis(phenanthroline-k2 N,N′)dierbium(III), C52H36Er2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-2-{[(4-nitrophenyl)methyl]sulfanyl}-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C14H12N4O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3- (phenylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C27H39NO
- Crystal structre of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,3,5,6-tetramethylbenzene, C12H16Br2
- Crystal structure of 2-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(3,5-dinitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C18H18N4O5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-benzylidene-4-nitrobenzohydrazide – methanol (1/1), C15H15N3O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-bromophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23BrO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoato-κ1 O)zinc(II)], C24H16Br2N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,2-ethanediyl)bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S)zinc(II), C20H14N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of pentacarbonyl-(μ2-propane-1,3-dithiolato-κ4 S:S,S′:S′)-(diphenyl(o-tolyl)phosphine-κ1 P)diiron (Fe-Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid–pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C14H15N3O6
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((RS)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile-κ1 N)zinc(II), C30H34Cl4N8Zn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine – 1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione – methanol (1/1/1), C12H15N7O3
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-((3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methyl) benzoate, C23H28O3
- Crystal structure of (poly[µ2-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ 2 N:N)-(nitrato-κ 2 O:O′) silver(I), C9H8AgN7O3
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1 N]cadmium(II), C18H20CdN6O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)nickel(II) dihydrate, C14H16N6O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-aqua-aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)-(μ2-4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-(μ4-4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ5 O,O′:O″:O′″:O′″)dicobalt(II)] – water – dimethylformamide (1/1/1) C44H43N11O12Co2
- Crystal structure of N-((Z)-amino(((E)-amino(phenylamino)methylene) amino)methylene)benzenaminium chloride – benzo[f]isoquinolino[3,4-b][1,8]naphthyridine – tetrahydrofurane (1/2/2), C60H54ClN11O2
- The crystal structure of Chrysosplenol D, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of poly[deca aqua-bis(μ 4-2-(triazol-1-yl)-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)- bis(μ 5-2-(triazol-1-yl)-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-5-carboxyl acid) pentamanganese(II)] dihydrate, C44H42Mn5N12O36
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-dichloro-6,6′-dimethoxy-2,2′,3,3′,5,5′- hexanitroazobenzene, C14H6N8O14Cl2
- Crystal structure of N 2,N 4-dimesitylpentane-2,4-diamine, C23H34N2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ 6O6)potassium(2-methylphenylamino)ethyl-2-methylphenylamide ammoniate (1/3.5), [K(18-crown-6)](o-CH3C6H4)NH(CH2)2N(o-CH3C6H4) 3.5 NH3, C28H53.5KN5.5O6
- The crystal structure of N′,N″,2-tris((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide hydrochloride – methanol (1/3), C25H30Cl4N6O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(3,5-dimethoxybenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H17BrO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl) ethylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O3
- {2-(((2-aminoethyl)imino)methyl)-6-bromophenolato-κ3 N,N′,O}iron(III) nitrate, C18H20Br2FeN5O5
- Crystal structure of 2-(tert-pentyl)anthracene-9,10-dione, C19H18O2
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(2-(2-(carboxymethyl)phenyl)acetate), C32H30N4O8
- Crystal structure of N 2,N 6-bis(2-(((E)-naphthalen-1-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C41H29N5O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazolium 2,4,5-trinitroimidazolate, C5H5O6N9
- Hydrogen bonded dimers in the crystal structure of 2-chloro-N-(phenylcarbamoyl)nicotinamide, C26H20Cl2N6O4
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridine-5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one-water(1/2/2), C40H32N2O12
- Crystal structure of N,N'-bis(4-fluoro-salicylaldehyde)-3,6-dioxa-1,8-diaminooctane, C20H22F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(1,3-dinitropropan-2-yl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C12H10N2O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(2-bromoethoxy)-phenyl)(phenyl)methanone, C15H13BrO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H15BrO2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)cadmium(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Cd
- Crystal structure of diaqua-diphenanthroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3 O,O′:O′)didysprosium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Dy2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-oxido-2-phenylacetato-κ3 O,O′:O′)-bis(N-oxido-benzamide-κ2 O,O′)-bis(propan-2-olato-κ1 O)dititanium(IV), C36H38N2O12Ti2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-5-carboxylato-κ2 O:O′)(μ2-oxalato-κ4O,O:O″,O′″)europium(III)] monohydrate, C9H10N3O9Eu
- Crystal structure of bis((N-methyl-2-oxyethyl)amine)-bis(μ 2-N,N,N-tris(2-oxoethyl)amine)-bis(isopropoxy)-bis(μ 3-oxo)tetratitanium(IV)– isopropanol (1/2), C34H76N4O16Ti4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-iodobenzyl)amino)benzoate, C16H16INO2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-5-((5-(tert- butyl)-2H-pyrrol-2-ylidene)(mesityl)methyl)-1H-pyrrole, C26H34N2
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium poly[μ4-1,1′-(1,4- phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ6 N,O:O′:N′,O″:O‴) manganese(II)], C22H26MnN6O8
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-(1-(2-((5-methylthiophen-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl)ethylidene)chroman-2,4-dione, C17H14N2O3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η 6-toluene)(5,5′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluoridophosphate(V) ─ acetone (1/1) C22H26ClN2ORuPF6
- Crystal structure of 4-(((2-(3-(1-(3-(3-cyanophenyl)-6-oxopyridazin-1(6H)-yl)ethyl)phenyl) pyrimidin-5-yl)oxy)methyl)-1-methylpiperidin-1-ium chloride monohydrate, C30H33N6O2Cl
- The crystal structure of 2-chloro-N-((2-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl)nicotinamide, C13H9Cl2N3O2
- Crystal structure of 9-(t-butyl)-3,11-dihydro-6H-pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrrolo[3′,2′:5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-6-one hemihydrate, C30H32N10O3
- Crystal structure of di-μ2-hydroxido-tetrakis(6-methylpyridine-2-carboxylato-k2 N,O) diiron(III) trihydrate C28H32Fe2N4O13
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[qua-(μ2-2-aminoisophthalat-κ3 O,O′:O′′)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)manganese(II)] C20H15MnN3O5
- Crystal structure of poly[(bis(isothiocyano)-bis(μ 2-(E)-N′-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)isonicotinohydrazide))iron(II) – methanol – 1,4-dioxane (1/2/2), C36H44FeN10O8S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)propylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C16H15ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-benzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(μ2-benzoato-k3O,O′:O′)dinitrato-k2O,O′-bis(phenanthroline-k2 N,N′)dierbium(III), C52H36Er2N6O14
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-2-{[(4-nitrophenyl)methyl]sulfanyl}-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-5-carbonitrile, C14H12N4O3S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3- (phenylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[α] phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C27H39NO
- Crystal structre of 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)-2,3,5,6-tetramethylbenzene, C12H16Br2
- Crystal structure of 2-(adamantan-1-yl)-5-(3,5-dinitrophenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C18H18N4O5
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-benzylidene-4-nitrobenzohydrazide – methanol (1/1), C15H15N3O4
- The crystal structure of 3-(2-bromophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23BrO2
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ 2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2 N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoato-κ1 O)zinc(II)], C24H16Br2N2O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,2-ethanediyl)bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S)zinc(II), C20H14N6ZnS4
- Crystal structure of pentacarbonyl-(μ2-propane-1,3-dithiolato-κ4 S:S,S′:S′)-(diphenyl(o-tolyl)phosphine-κ1 P)diiron (Fe-Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid–pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C14H15N3O6
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis((RS)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)hexanenitrile-κ1 N)zinc(II), C30H34Cl4N8Zn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine – 1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione – methanol (1/1/1), C12H15N7O3
- The crystal structure of methyl 4-((3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methyl) benzoate, C23H28O3
- Crystal structure of (poly[µ2-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-benzotriazole-κ 2 N:N)-(nitrato-κ 2 O:O′) silver(I), C9H8AgN7O3
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzoato-k1 N]cadmium(II), C18H20CdN6O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)nickel(II) dihydrate, C14H16N6O8Ni
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-aqua-aqua-(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2 N:N′)-(μ2-4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-(μ4-4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ5 O,O′:O″:O′″:O′″)dicobalt(II)] – water – dimethylformamide (1/1/1) C44H43N11O12Co2
- Crystal structure of N-((Z)-amino(((E)-amino(phenylamino)methylene) amino)methylene)benzenaminium chloride – benzo[f]isoquinolino[3,4-b][1,8]naphthyridine – tetrahydrofurane (1/2/2), C60H54ClN11O2
- The crystal structure of Chrysosplenol D, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of poly[deca aqua-bis(μ 4-2-(triazol-1-yl)-benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylato)- bis(μ 5-2-(triazol-1-yl)-benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-5-carboxyl acid) pentamanganese(II)] dihydrate, C44H42Mn5N12O36
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C20H24N2O2
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-dichloro-6,6′-dimethoxy-2,2′,3,3′,5,5′- hexanitroazobenzene, C14H6N8O14Cl2
- Crystal structure of N 2,N 4-dimesitylpentane-2,4-diamine, C23H34N2
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ 6O6)potassium(2-methylphenylamino)ethyl-2-methylphenylamide ammoniate (1/3.5), [K(18-crown-6)](o-CH3C6H4)NH(CH2)2N(o-CH3C6H4) 3.5 NH3, C28H53.5KN5.5O6
- The crystal structure of N′,N″,2-tris((E)-5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonhydrazide hydrochloride – methanol (1/3), C25H30Cl4N6O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(3,5-dimethoxybenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H17BrO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl) ethylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H13ClN2O3
- {2-(((2-aminoethyl)imino)methyl)-6-bromophenolato-κ3 N,N′,O}iron(III) nitrate, C18H20Br2FeN5O5
- Crystal structure of 2-(tert-pentyl)anthracene-9,10-dione, C19H18O2
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(2-(2-(carboxymethyl)phenyl)acetate), C32H30N4O8
- Crystal structure of N 2,N 6-bis(2-(((E)-naphthalen-1-ylmethylene)amino)phenyl)pyridine-2,6-dicarboxamide, C41H29N5O2
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-1,2,4-triazolium 2,4,5-trinitroimidazolate, C5H5O6N9
- Hydrogen bonded dimers in the crystal structure of 2-chloro-N-(phenylcarbamoyl)nicotinamide, C26H20Cl2N6O4
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridine-5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one-water(1/2/2), C40H32N2O12
- Crystal structure of N,N'-bis(4-fluoro-salicylaldehyde)-3,6-dioxa-1,8-diaminooctane, C20H22F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of 3-(1,3-dinitropropan-2-yl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C12H10N2O6
- The crystal structure of (4-(2-bromoethoxy)-phenyl)(phenyl)methanone, C15H13BrO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-bromo-2-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C18H15BrO2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-tetrakis((E)-(RS)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)pent-1-en-3-ol-κ 1 N)cadmium(II), C60H68O4N12Cl10Cd
- Crystal structure of diaqua-diphenanthroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3 O,O′:O′)didysprosium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C80H38Dy2F16N8O18
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-2-oxido-2-phenylacetato-κ3 O,O′:O′)-bis(N-oxido-benzamide-κ2 O,O′)-bis(propan-2-olato-κ1 O)dititanium(IV), C36H38N2O12Ti2
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(μ2-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole-5-carboxylato-κ2 O:O′)(μ2-oxalato-κ4O,O:O″,O′″)europium(III)] monohydrate, C9H10N3O9Eu
- Crystal structure of bis((N-methyl-2-oxyethyl)amine)-bis(μ 2-N,N,N-tris(2-oxoethyl)amine)-bis(isopropoxy)-bis(μ 3-oxo)tetratitanium(IV)– isopropanol (1/2), C34H76N4O16Ti4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-iodobenzyl)amino)benzoate, C16H16INO2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-5-((5-(tert- butyl)-2H-pyrrol-2-ylidene)(mesityl)methyl)-1H-pyrrole, C26H34N2
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium poly[μ4-1,1′-(1,4- phenylenebis(methylene))bis(1H-pyrazole-3,5-dicarboxylato-κ6 N,O:O′:N′,O″:O‴) manganese(II)], C22H26MnN6O8

