Abstract
C36H30AsBrOSn, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 9.8316(1) Å, b = 10.8781(2) Å, c = 14.9388(2) Å, α = 102.367(1)°, β = 93.369(1)°, γ = 103.134(1)°, V = 1510.07(4) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0175, wRref(F2) = 0.0469, T = 100 K.
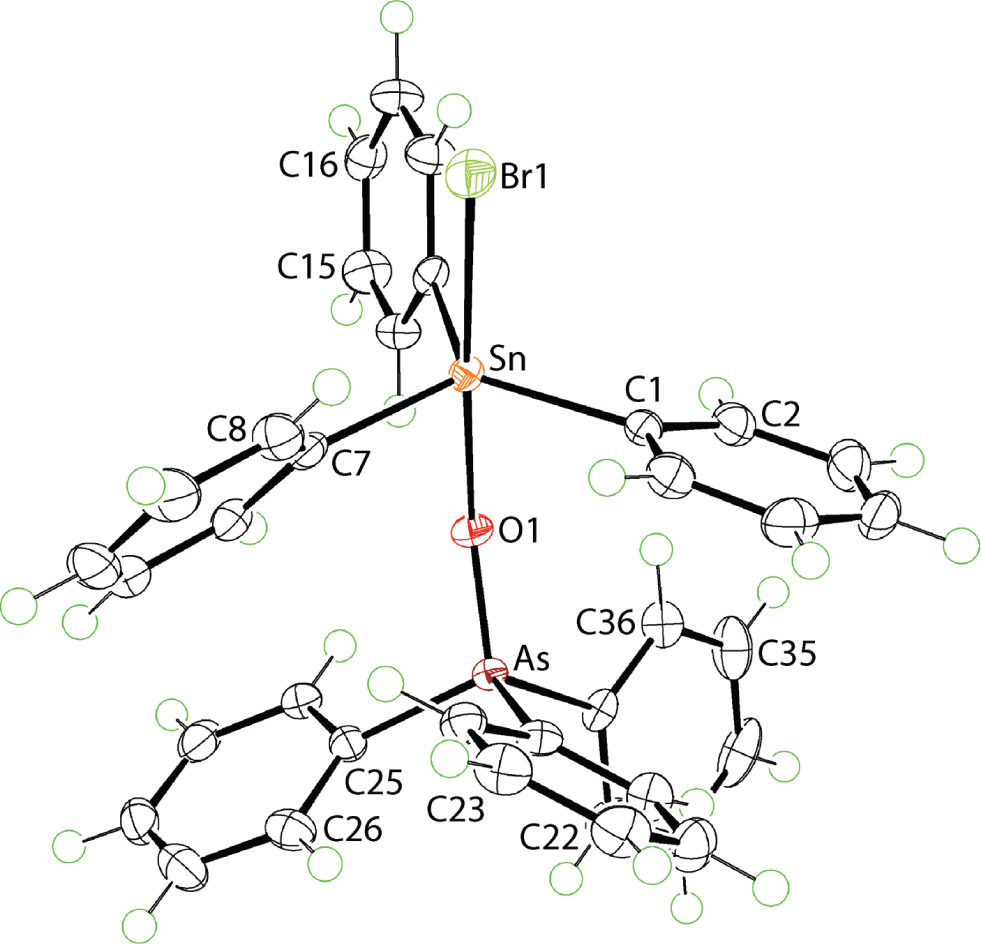
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 9.70 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 67.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 35879, 5393, 0.029 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 5331 |
| N(param)refined: | 361 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sn | 0.78069(2) | 0.55247(2) | 0.73706(2) | 0.01062(5) |
| As | 0.69267(2) | 0.21868(2) | 0.76382(2) | 0.00971(6) |
| Br1 | 0.87976(2) | 0.75872(2) | 0.66552(2) | 0.01932(6) |
| O1 | 0.69163(14) | 0.37567(13) | 0.79001(9) | 0.0131(3) |
| C1 | 0.6651(2) | 0.44394(18) | 0.60825(13) | 0.0128(4) |
| C2 | 0.5188(2) | 0.4096(2) | 0.59939(14) | 0.0170(4) |
| H2 | 0.470875 | 0.439276 | 0.649927 | 0.020* |
| C3 | 0.4420(2) | 0.3326(2) | 0.51763(15) | 0.0223(5) |
| H3 | 0.342152 | 0.311435 | 0.511968 | 0.027* |
| C4 | 0.5110(3) | 0.2870(2) | 0.44464(15) | 0.0231(5) |
| H4 | 0.458781 | 0.233455 | 0.388917 | 0.028* |
| C5 | 0.6570(3) | 0.3195(2) | 0.45267(15) | 0.0222(5) |
| H5 | 0.704572 | 0.287004 | 0.402748 | 0.027* |
| C6 | 0.7335(2) | 0.3993(2) | 0.53358(14) | 0.0174(4) |
| H6 | 0.833255 | 0.423715 | 0.538001 | 0.021* |
| C7 | 0.9875(2) | 0.53195(18) | 0.77377(13) | 0.0138(4) |
| C8 | 1.0990(2) | 0.5641(2) | 0.72234(15) | 0.0181(4) |
| H8 | 1.084950 | 0.598993 | 0.670421 | 0.022* |
| C9 | 1.2304(2) | 0.5454(2) | 0.74644(17) | 0.0241(5) |
| H9 | 1.305319 | 0.567521 | 0.710944 | 0.029* |
| C10 | 1.2523(2) | 0.4945(2) | 0.82198(17) | 0.0245(5) |
| H10 | 1.342130 | 0.481936 | 0.838326 | 0.029* |
| C11 | 1.1424(2) | 0.4620(2) | 0.87383(15) | 0.0207(4) |
| H11 | 1.156961 | 0.426572 | 0.925439 | 0.025* |
| C12 | 1.0119(2) | 0.48123(19) | 0.85021(14) | 0.0162(4) |
| H12 | 0.937707 | 0.459715 | 0.886401 | 0.019* |
| C13 | 0.6917(2) | 0.65907(19) | 0.84714(13) | 0.0127(4) |
| C14 | 0.6474(2) | 0.60513(19) | 0.92056(14) | 0.0159(4) |
| H14 | 0.646868 | 0.517112 | 0.918440 | 0.019* |
| C15 | 0.6040(2) | 0.6784(2) | 0.99664(14) | 0.0198(4) |
| H15 | 0.574648 | 0.640148 | 1.046027 | 0.024* |
| C16 | 0.6034(2) | 0.8065(2) | 1.00092(14) | 0.0181(4) |
| H16 | 0.574089 | 0.856503 | 1.053098 | 0.022* |
| C17 | 0.6460(2) | 0.8614(2) | 0.92854(15) | 0.0205(4) |
| H17 | 0.645558 | 0.949286 | 0.930939 | 0.025* |
| C18 | 0.6893(2) | 0.7883(2) | 0.85240(14) | 0.0187(4) |
| H18 | 0.717795 | 0.826951 | 0.803028 | 0.022* |
| C19 | 0.7680(2) | 0.16074(19) | 0.65139(13) | 0.0133(4) |
| C20 | 0.6827(2) | 0.0670(2) | 0.57993(14) | 0.0170(4) |
| H20 | 0.588107 | 0.029310 | 0.587122 | 0.020* |
| C21 | 0.7374(2) | 0.0287(2) | 0.49753(14) | 0.0208(4) |
| H21 | 0.680067 | −0.036182 | 0.448434 | 0.025* |
| C22 | 0.8749(2) | 0.0847(2) | 0.48676(14) | 0.0201(4) |
| H22 | 0.911131 | 0.059244 | 0.429995 | 0.024* |
| C23 | 0.9601(2) | 0.1783(2) | 0.55919(15) | 0.0190(4) |
| H23 | 1.054520 | 0.216347 | 0.551712 | 0.023* |
| C24 | 0.9078(2) | 0.21616(19) | 0.64194(14) | 0.0157(4) |
| H24 | 0.966066 | 0.278993 | 0.691694 | 0.019* |
| C25 | 0.7981(2) | 0.18617(18) | 0.86439(13) | 0.0128(4) |
| C26 | 0.9084(2) | 0.1262(2) | 0.85161(15) | 0.0179(4) |
| H26 | 0.928468 | 0.091814 | 0.791238 | 0.021* |
| C27 | 0.9891(2) | 0.1175(2) | 0.92865(16) | 0.0228(5) |
| H27 | 1.066662 | 0.079195 | 0.920912 | 0.027* |
| C28 | 0.9568(2) | 0.1643(2) | 1.01673(16) | 0.0224(5) |
| H28 | 1.012568 | 0.158006 | 1.068909 | 0.027* |
| C29 | 0.8436(2) | 0.2201(2) | 1.02907(15) | 0.0203(4) |
| H29 | 0.820044 | 0.249387 | 1.089398 | 0.024* |
| C30 | 0.7647(2) | 0.23313(19) | 0.95272(14) | 0.0154(4) |
| H30 | 0.688841 | 0.273633 | 0.960667 | 0.018* |
| C31 | 0.5021(2) | 0.12307(19) | 0.75776(13) | 0.0125(4) |
| C32 | 0.4716(2) | −0.0060(2) | 0.76344(14) | 0.0175(4) |
| H32 | 0.544719 | −0.049488 | 0.766518 | 0.021* |
| C33 | 0.3328(3) | −0.0705(2) | 0.76455(15) | 0.0250(5) |
| H33 | 0.310563 | −0.158785 | 0.768413 | 0.030* |
| C34 | 0.2268(2) | −0.0068(2) | 0.76006(15) | 0.0272(5) |
| H34 | 0.132132 | −0.051425 | 0.761224 | 0.033* |
| C35 | 0.2574(2) | 0.1212(2) | 0.75388(14) | 0.0244(5) |
| H35 | 0.183873 | 0.164171 | 0.750373 | 0.029* |
| C36 | 0.3961(2) | 0.1872(2) | 0.75281(14) | 0.0173(4) |
| H36 | 0.417873 | 0.275403 | 0.748731 | 0.021* |
Source of material
Tetraphenyltin (0.85 g, 2 mmol) and 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine hydrobromide perbromide (Sigma-Aldrich; 0.72 g, 2 mmol) were dissolved in ethanol (50 mL). The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature until a colourless solution was obtained. Next, triphenylarsine oxide (Sigma Aldrich; 0.64 g, 2 mmol) in ethanol (10 mL) was added to the mixture which was then refluxed for 3 h. After filtration, the filtrate was evaporated slowly until colourless crystals formed. The crystals were filtered, washed with a minimum amount of hexane and air-dried. Yield: 0.88 g (59.1%). M.pt (Mel-temp II digital melting point apparatus): 447–449 K. IR (Bruker Vertex 70v FTIR Spectrophotometer; cm−1): 1085 (m) ν(C—C), 997 (m) ν(As—O), 476 (w) ν(Sn—O). 1H NMR (Bruker Ascend 400 MHz NMR spectrometer, chemical shifts relative to Me4Si, CDCl3 solution at 40 °C; ppm): δ 7.47–7.66 (m, 30H, Phenyl-H). 13C{1H} NMR (as for 1H NMR): δ 128.0, 129.3, 131.5, 131.9, 132.5, 136.4 (Phenyl—C).
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Comment
Recently, the X-ray crystal structure determinations of two new triorganoarsine oxide adduct of organotin species were described, namely six-coordinate, trans-(4-MeC6H4CH2)2SnCl2(O=AsPh3)2 [5] and five-coordinate (4-MeC6H4CH2)3SnCl(O=AsPh3) [6]. The rest of the known, comparatively rare mononuclear species are also five-coordinate, that is, (4-ClC6H4CH2)3SnCl(O=AsPh3) [7], Ph3SnCl(O=AsPh3) [8] and (4-ClC6H4)3SnCl(O=AsPh3) [8]. In continuation of previous structural studies in this area [5], [6], [8], the crystal and molecular structures of the title triphenylarsine oxide adduct of tri(4-methylbenzyl)tin bromide, Ph3SnBr(O=AsPh3), (I), are described.
The molecular structure of (I) is shown in the figure (70% displacement ellipsoids) and features a distorted trigonal bipyramidal geometry with the three phenyl rings occupying equatorial positions, and with the bromido [Sn—Br1 = 2.6983(2) Å] and As-oxido [Sn—O1 = 2.2493(13) Å] atoms occupying axial positions; Br1—Sn—O1 = 177.18(3)°. The Sn atom lies 0.119(1) Å out of the trigonal plane in the direction of the Br1 atom. The Sn—C bond lengths span an experimentally distinct range, that is, from short Sn—C1 = 2.1326(19), Sn—C7 = 2.147(2) to longer Sn—C13 = 2.1514(19) Å. Similarly, there is a disparity in the C—Sn—C angles with the widest angles of C1—Sn—C7 = 120.16(7)° and C1—Sn—C13 = 124.06(7)° involving the C1-phenyl ring which forms the smallest dihedral angle with the C3 plane, that is, 21.95(7)° and the shortest Sn—C1 bond. The comparable dihedral angles for the C7- and C13-phenyl rings are 57.64(5) and 79.388(7)°, respectively, with the greater dihedral angle correlating with the longest Sn—C13 bond. When the molecule of (I) is viewed down the Sn⋯As axis, the phenyl rings bound to the Sn and As atoms are close to being staggered. The Sn—O1—As angle is bent, presenting an angle of 136.77(7)°. The C3O donor set around the As atom is based on a tetrahedron with the range of angles subtended at the As atom being a narrow 106.45(8)° for O1—As—C31 to a wide 115.55(7)° for O1—As—C19, indicating relatively minor distortions from the ideal geometry.
The most closely related literature precedent to (I) is the chlorido analogue, Ph3SnCl(O=AsPh3), (II) [8]; the structures are not isostructural. As would be expected, very similar coordination geometries are noted. The Cl1—Sn—O1 angles in (II) are 139.3(2) and 139.4(2)° for the two independent molecules comprising the asymmetric unit and are over two degrees wider compared with (I). The As—O bond lengths, that is 1.6709(13) Å in (I), and 1.672(4) and 1.663(4) Å in (II), are equal within experimental errors suggesting little influence exerted by the Sn-bound halide atom upon the mode of coordination of O=AsPh3. Such invariance in the As=O bond lengths is consistent with that noted previously for analogous P=O bonds in phosphineoxide adducts of organotin species [9].
In the molecular packing of (I), As-phenyl-C—H⋯Br contacts [C34—H34⋯Br1i: H34⋯Br1i = 2.91 Å, C34⋯Br1i = 3.752(2) Å with angle at H34 = 149° for symmetry operation (i) −1 + x, −1 + y, z] lead to supramolecular chains aproximately parallel to [3 5 −13]. The connections between the chains are of the type phenyl-C—H⋯π(phenyl). Thus, Sn—phenyl-C—H⋯π(As-phenyl) [C16—H16⋯Cg(C31—C36)ii: H16⋯Cg = 2.75 Å with angle at H16 = 142° and C17—H17⋯Cg(C24—C30)iii: H17⋯Cg = 2.91 Å with angle at H17 = 130° for (ii) 1 – x, 1 – y, 2 – z and (iii) x, 1 + y, z] and As—phenyl-C—H⋯π(Sn-phenyl) [C29—H29⋯Cg(C7—C12)iv: H29⋯Cg = 2.68 Å with angle at H29 = 131° for (iv) 2 – x, 1 – y, 2 – z] are apparent. The layers interdigitate along the c-axis allowing for π-stacking interactions between centrosymmetrically-related Sn-bound phenyl rings [Cg(C1—C6)⋯Cg(C1—C6)v = 3.9112(13) Å for (v) 1 – x, 1 – y, 1 – z]. It is noted that the phenyl rings are off-set with a slippage of 1.75 Å [10].
The lack of directional interactions in the crystal of (I) is reflected in the analysis of the calculated Hirshfeld surfaces and two-dimensional fingerprint plots (overall and decomposed). The calculations were performed with Crystal Explorer 17 [11] following standard protocols [12]. The specified H⋯Br contacts leading to the supramolecular chain contribute 7.5% to the overall surface whereas the C⋯H/H⋯C contacts, largely corresponding to the C—H⋯π(phenyl) and π⋯π interactions, contribute 30.7% of all contacts. Small contributions of 1.5%, due to C⋯C contacts, and 0.3%, due to C⋯Br/Br⋯C contacts, are also noted. However, the most significant contribution, that is, 60.0%, arise from H⋯H surface contacts.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant No. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: CrysAlisPRO. Rigaku Corporation, Oxford, UK (2018).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Suche in Google Scholar
5. Lo, K. M.; Lee, S. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C50H44As2Cl2O2Sn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 235 (2020) 183–185.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0564Suche in Google Scholar
6. Lee, S. M.; Lo, K. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 235 (2020) 775–777.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0888Suche in Google Scholar
7. Johari, N. H.; Lo, K. M.; Ng, S. W.: Chloridotris(4-chlorobenzyl-κC)(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV). Acta Crystallogr. E65 (2009) m815.10.1107/S1600536809022247Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Lo, K. M.; Niu, J.-Y.; Wang, J.-P.: Synthesis and structures of coordination compounds of triphenylarsine with triorganotin and triorganolead chlorides Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 16 (2000) 763–768.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Gielen, M.; Pan, H.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structures of CH2=CHCH2OC(O)CH2CH2SnCl3⋅OPPh3 and BuOC(O)CH(CH3)CH2SnCl3⋅OPPh3. Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 102 (1993) 447–453.10.1002/bscb.19931020703Suche in Google Scholar
10. Spek, A. L.: checkCIF validation ALERTS: what they mean and how to respond. Acta Crystallogr. E76 (2020) 1–11.10.1107/S2056989019016244Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Turner, M. J.; Mckinnon, J. J.; Wolff, S. K.; Grimwood, D. J.; Spackman, P. R.; Jayatilaka, D.; Spackman, M. A.: Crystal Explorer v17. The University of Western Australia, Australia (2017).Suche in Google Scholar
12. Tan, S. L.; Jotani, M. M.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Utilizing Hirshfeld surface calculations, non-covalent interaction (NCI) plots and the calculation of interaction energies in the analysis of molecular packing. Acta Crystallogr. E75 (2019) 308–318.10.1107/S2056989019001129Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
©2020 Kong Mun Lo et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4

