Abstract
H10N3O14Y, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 6.5965(12) Å, b = 9.5374(17) Å, c = 10.5249(19) Å, α = 63.809(13)°, β = 84.677(15)°, γ = 76.397(19)°, V = 577.46(18) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0330, wRref(F2) = 0.0697, T = 223 K.
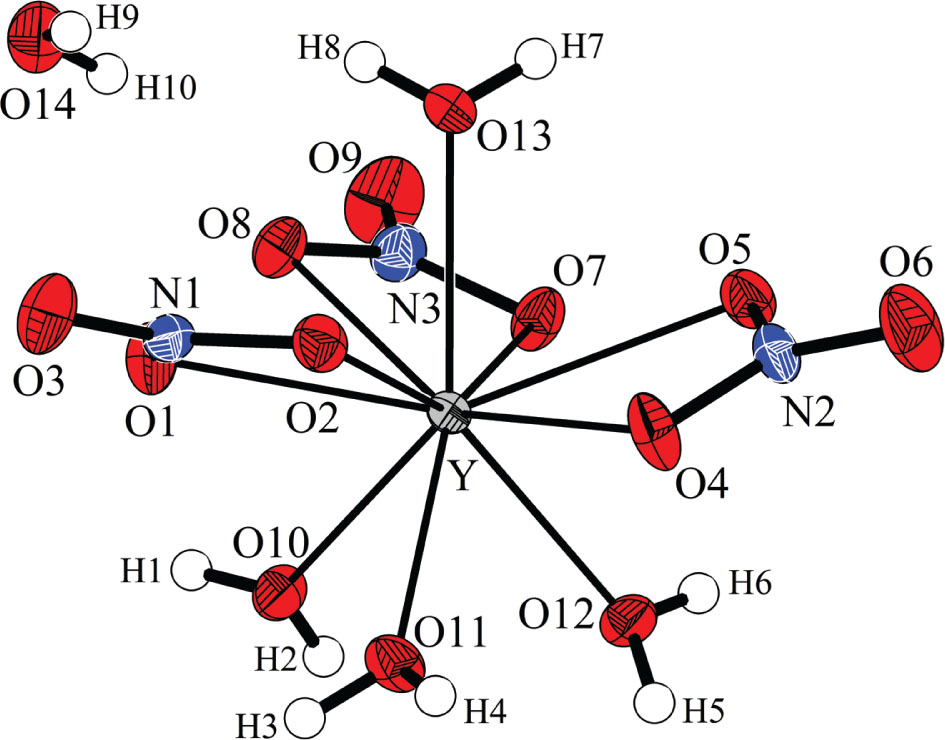
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.35 × 0.28 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 5.13 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | STOE StadiVari, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 26.0°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 7245, 2228, 0.039 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1863 |
| N(param)refined: | 203 |
| Programs: | X-Area [1], SHELX [2], [3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 0.24426(5) | 0.34906(4) | 0.29472(4) | 0.01196(11) |
| N1 | 0.4689(5) | 0.2818(3) | 0.5548(3) | 0.0169(6) |
| O1 | 0.2952(4) | 0.3817(3) | 0.5087(3) | 0.0220(6) |
| O2 | 0.5519(4) | 0.2135(3) | 0.4782(3) | 0.0204(6) |
| O3 | 0.5483(5) | 0.2561(3) | 0.6655(3) | 0.0296(7) |
| N2 | 0.5201(5) | 0.2133(4) | 0.1251(3) | 0.0210(7) |
| O4 | 0.5028(4) | 0.1400(3) | 0.2579(3) | 0.0261(6) |
| O5 | 0.4065(4) | 0.3559(3) | 0.0667(3) | 0.0219(6) |
| O6 | 0.6383(5) | 0.1555(4) | 0.0566(3) | 0.0383(8) |
| N3 | 0.0243(5) | 0.6860(4) | 0.1459(3) | 0.0205(7) |
| O7 | 0.0616(4) | 0.5816(3) | 0.0955(3) | 0.0215(6) |
| O8 | 0.1053(4) | 0.6380(3) | 0.2660(3) | 0.0210(6) |
| O9 | −0.0809(5) | 0.8197(3) | 0.0813(3) | 0.0365(8) |
| O10 | −0.0906(4) | 0.3855(3) | 0.3938(3) | 0.0210(6) |
| H1 | −0.153(7) | 0.457(6) | 0.421(5) | 0.028(12)* |
| H2 | −0.177(9) | 0.372(6) | 0.363(6) | 0.046(17)* |
| O11 | 0.1966(5) | 0.1000(3) | 0.4680(3) | 0.0212(6) |
| H3 | 0.140(7) | 0.080(5) | 0.547(5) | 0.016(11)* |
| H4 | 0.261(7) | 0.017(5) | 0.483(5) | 0.017(12)* |
| O12 | 0.0258(5) | 0.2634(3) | 0.1944(3) | 0.0212(6) |
| H5 | 0.034(7) | 0.164(6) | 0.228(5) | 0.023(11)* |
| H6 | 0.006(8) | 0.306(6) | 0.116(6) | 0.036(15)* |
| O13 | 0.5142(4) | 0.5024(3) | 0.2219(3) | 0.0188(6) |
| H7 | 0.544(7) | 0.536(6) | 0.139(6) | 0.031(14)* |
| H8 | 0.493(7) | 0.571(6) | 0.250(5) | 0.030(13)* |
| O14 | 0.0031(6) | 0.9537(4) | 0.2799(3) | 0.0291(7) |
| H9 | 0.112(11) | 0.882(8) | 0.296(7) | 0.07(2)* |
| H10 | −0.062(10) | 0.957(7) | 0.223(7) | 0.055(19)* |
Source of material
Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O was prepared by dissolving Y2O3 (Chempur, 99.9%) in hot aqueous nitric acid. From concentrated solutions single crystals were grown at room temperature within one day. The compound is highly hygroscopic, so out of the mother liquor crystals deliquesce within few minutes. Thus, for the X-ray data collection crystals have been immersed into perfluoroalkylether, which also acts as glue on a glass tip during the measurement.
Experimental details
The H atoms have been located from the difference Fourier map and refined with unrestrained atomic coordinates and isotropic displacement parameters.
Comment
Yttrium nitrate forms several crystalline hydrates. While Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 6H2O is commercially available and its crystal structure was determined first [5], the existence of most of the other hydrates has been deduced from DSC experiments investigating the thermal decomposition of the hexahydrate. Pure phases have been found after recrystallisation from remains of the hexahydrate at enhanced temperature, [Y(NO3)2(H2O)5][Y(NO3)4(H2O)2] at 361 K [6], [7], Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 3H2O at 382 K [8], and Y(NO3)3 ⋅ H2O at 443 K [9]. As an exception, the pentahydrate was not obtained after temperature dependent transformation from the hexahydrate, but was crystallized at room temperature directly from aqueous solution. [10] The crystal structure of Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5H2O was redetermined from single crystal data. Improving the results of the previous structure determination [10] lattice parameters, atomic coordinates and anisotropic displacement parameters of the non-H atoms have been obtained with a higher precision, and H atom positions have been located for the first time. During the final refinement cycles the H atoms were refined with unrestrained atomic coordinates and isotropic displacement parameters. The crystal structure of Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5H2O is formed by a [Y(NO3)3(H2O)4] complex and an additional free water molecule. The three crystallographically independent nitrate anions are almost perfectly planar and act as bidentate ligands of the Y atom, exhibiting N—O bond lengths between 1.260(4) Å to 1.289(4) Å as well as 1.216(4) Å to 1.221(4) Å when including the coordinating and non-coordinating O atoms, respectively. The water molecules show O—H bond lengths from 0.74(6) Å to 0.86(5) Å and angles between 99(3)° and 114(5)°. The Y atoms are in a tenfold coordination of O atoms, provided by three bidentately coordinating nitrate anions and by four water molecules. The nitrate ligands are arranged in an equatorial plane separating one water ligand from the other three, as seen in the figure. The NO3 molecule planes are slightly tilted with respect to the main complex axis as defined by the Y-O13 bond forming a propeller-like shape. The shortest Y-O bonds between 2.336(3) Å to 2.370(3) Å are formed by the three H2O ligands at one side of the Y(NO3)3 plane while the remaining Y-O(H2) bond is in the same range as the shortest Y-O(NO2) bonds. The nitrate ligands are slightly unsymmetrically coordinating with one shorter and one longer Y-O distance for each independent NO3 anion. These molecular building units, i. e. metal complex and free water molecules, are connected by almost linear hydrogen bonds; more specifically, eight of the ten independent H atoms form hydrogen bonds shorter than 2.30 Å with O—H⋯O angles above 164°, while atoms H2 and H10 from bifurcated and slightly longer hydrogen bonds.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Technische Universität München within the funding programme Open Access Publishing.
References
1. Stoe & Cie GmbH: X-Area Version 1.76. Stoe & Cie GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany (2017).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Version 3.2i. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany (2012).Suche in Google Scholar
5. Ribár, B.; Milinski, N.; Budovalcev, Z.; Krstanović, I.: Tetraaquatri(nitrato)yttrium(III) dihydrate, Y(H2O)4(NO3)3 ⋅ 2 H2O. Cryst. Struct. Commun. 9 (1980) 203–206.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Radivojević, P.; Milinski, N.; Ribár, B.; Lazar, D.: The crystal structure of the complex [Y(H2O)5(NO3)2] [Y(H2O)2(NO3)4]. Croat. Chem. Acta 57 (1984) 451–455.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Ribár, B.; Kapor, A.; Scott, B.; Willett, R. D.: Reinvestigation of the Structure of [Y(H2O)5(NO3)2][Y(H2O)2(NO3)4]. Acta Crystallogr. C49 (1993) 314–316.10.1107/S0108270192005687Suche in Google Scholar
8. Ribár, B.; Radivojević, P.; Argay, G.; Kálmán, A.: Structure of yttrium nitrate trihydrate. Acta Crystallogr. C44 (1988) 595–597.10.1107/S0108270187012095Suche in Google Scholar
9. Ribár, B.; Radivojević, P.; Argay, G.; Kálmán, A.: Structure of yttrium nitrate monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. C46 (1990) 525–527.10.1107/S0108270189008711Suche in Google Scholar
10. Eriksson, B.: Crystal and molecular structure of tetraaquatrinitratoyttrium(III) hydrate. Acta Chem. Scand. Ser. A 36 (1982) 186–188. [ICSD code 31872; https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/Search?Ccdcid=31872].Suche in Google Scholar
©2020 Wilhelm Klein, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4

