Abstract
C20H38CdN4O4P2S4, triclinic, P1̄ (no. 2), a = 9.6352(2) Å, b = 11.3986(2) Å, c = 14.8017(3) Å, α = 85.713(2)°, β = 89.877(2)°, γ = 86.048(2)°, V = 1617.23(6) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0285, wRref(F2) = 0.0829, T = 100 K.
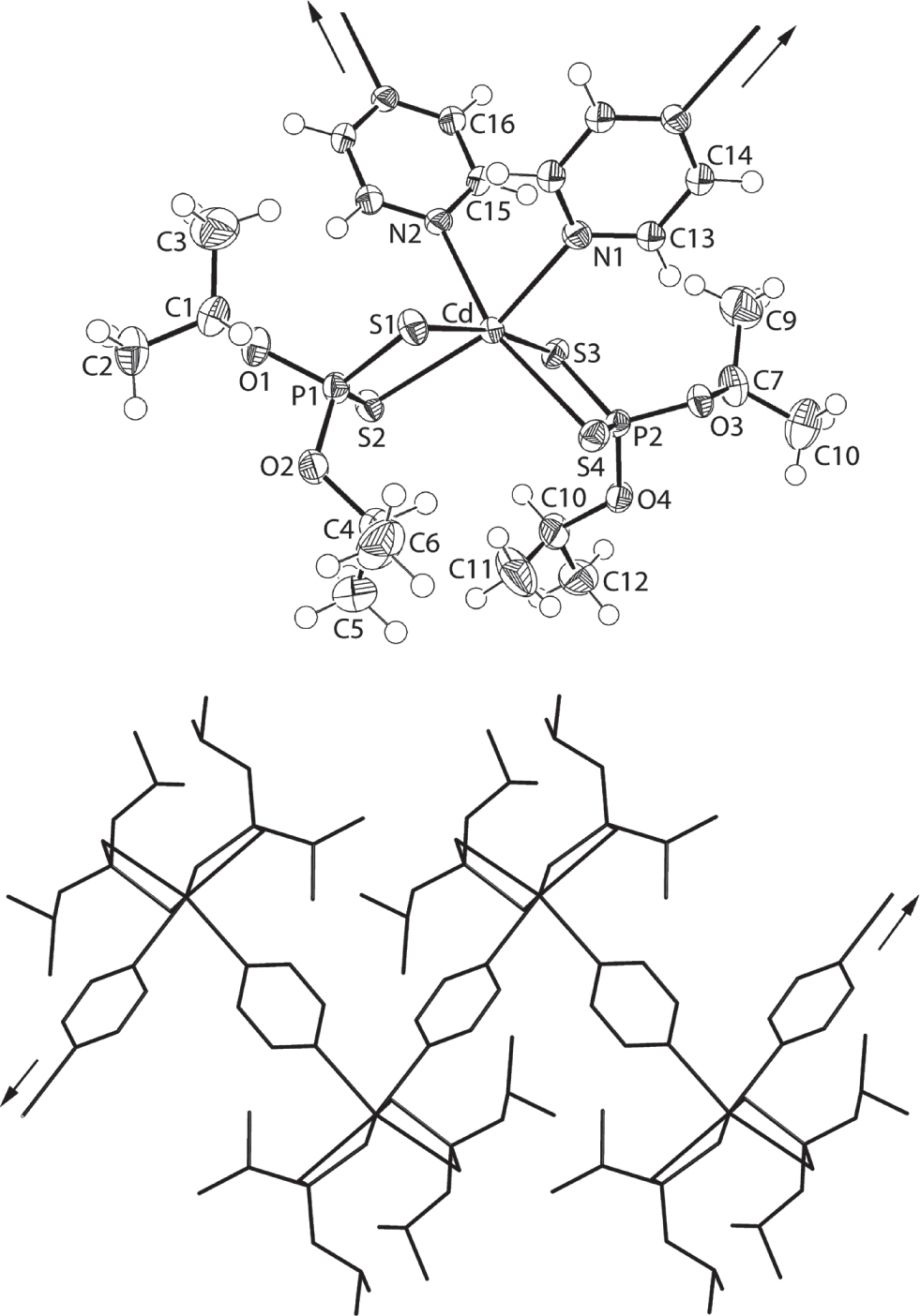
A part of the coordination polymer is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow prism |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.16 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 9.01 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB Synergy, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 67.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 35021, 5774, 0.026 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 5699 |
| N(param)refined: | 326 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.24881(2) | 0.01263(2) | 0.30020(2) | 0.01594(8) |
| S1 | 0.20107(8) | 0.24528(7) | 0.28202(6) | 0.02164(18) |
| S2 | 0.44987(8) | 0.08041(7) | 0.18577(5) | 0.02047(17) |
| S3 | 0.30923(8) | −0.21808(7) | 0.29062(6) | 0.02071(17) |
| S4 | 0.04659(8) | −0.04897(7) | 0.19308(6) | 0.02090(17) |
| P1 | 0.13777(8) | −0.21045(7) | 0.21454(5) | 0.01741(17) |
| P2 | 0.36493(8) | 0.24181(7) | 0.19914(6) | 0.01782(17) |
| O1 | 0.4831(2) | 0.3179(2) | 0.23202(17) | 0.0221(5) |
| O2 | 0.3252(2) | 0.3087(2) | 0.10350(16) | 0.0237(5) |
| O3 | 0.0227(2) | −0.2885(2) | 0.25895(16) | 0.0209(5) |
| O4 | 0.1688(2) | −0.2733(2) | 0.12354(16) | 0.0232(5) |
| N1 | 0.0902(3) | 0.0030(2) | 0.42669(18) | 0.0184(6) |
| N2 | 0.4108(3) | 0.0061(2) | 0.42553(18) | 0.0180(6) |
| N3 | 0.6923(5) | 0.7159(4) | 0.4335(3) | 0.0584(11) |
| N4 | 0.8120(5) | 0.2285(5) | 0.3963(3) | 0.0743(17) |
| C1 | 0.4530(4) | 0.4409(3) | 0.2569(3) | 0.0233(7) |
| H1 | 0.3547 | 0.4674 | 0.2402 | 0.028* |
| C2 | 0.5500(4) | 0.5153(3) | 0.2020(3) | 0.0322(9) |
| H2A | 0.6464 | 0.4865 | 0.2155 | 0.048* |
| H2B | 0.5354 | 0.5974 | 0.2172 | 0.048* |
| H2C | 0.5313 | 0.5105 | 0.1373 | 0.048* |
| C3 | 0.4715(5) | 0.4427(4) | 0.3571(3) | 0.0420(10) |
| H3A | 0.4036 | 0.3940 | 0.3884 | 0.063* |
| H3B | 0.4571 | 0.5239 | 0.3744 | 0.063* |
| H3C | 0.5658 | 0.4113 | 0.3741 | 0.063* |
| C4 | 0.2183(4) | 0.2609(3) | 0.0481(2) | 0.0277(8) |
| H4 | 0.1800 | 0.1916 | 0.0825 | 0.033* |
| C5 | 0.2872(5) | 0.2217(4) | −0.0371(3) | 0.0447(11) |
| H5A | 0.3220 | 0.2900 | −0.0719 | 0.067* |
| H5B | 0.2194 | 0.1856 | −0.0737 | 0.067* |
| H5C | 0.3649 | 0.1639 | −0.0211 | 0.067* |
| C6 | 0.1039(5) | 0.3572(4) | 0.0312(3) | 0.0450(11) |
| H6A | 0.0647 | 0.3791 | 0.0892 | 0.068* |
| H6B | 0.0307 | 0.3289 | −0.0058 | 0.068* |
| H6C | 0.1419 | 0.4262 | −0.0008 | 0.068* |
| C7 | 0.0543(4) | −0.4154(3) | 0.2875(3) | 0.0272(8) |
| H7 | 0.1431 | −0.4443 | 0.2590 | 0.033* |
| C8 | −0.0643(5) | −0.4782(4) | 0.2530(3) | 0.0418(11) |
| H8A | −0.1504 | −0.4523 | 0.2832 | 0.063* |
| H8B | −0.0458 | −0.5634 | 0.2657 | 0.063* |
| H8C | −0.0741 | −0.4598 | 0.1875 | 0.063* |
| C9 | 0.0687(5) | −0.4289(4) | 0.3893(3) | 0.0451(11) |
| H9A | 0.1419 | −0.3802 | 0.4081 | 0.068* |
| H9B | 0.0934 | −0.5117 | 0.4088 | 0.068* |
| H9C | −0.0197 | −0.4034 | 0.4170 | 0.068* |
| C10 | 0.2906(4) | −0.2496(4) | 0.0664(3) | 0.0353(10) |
| H10 | 0.3737 | −0.2450 | 0.1060 | 0.042* |
| C11 | 0.2644(6) | −0.1347(4) | 0.0106(3) | 0.0527(13) |
| H11A | 0.1777 | −0.1359 | −0.0237 | 0.079* |
| H11B | 0.3418 | −0.1234 | −0.0315 | 0.079* |
| H11C | 0.2567 | −0.0699 | 0.0506 | 0.079* |
| C12 | 0.3134(4) | −0.3540(4) | 0.0101(3) | 0.0359(9) |
| H12A | 0.3236 | −0.4266 | 0.0501 | 0.054* |
| H12B | 0.3979 | −0.3461 | −0.0261 | 0.054* |
| H12C | 0.2335 | −0.3574 | −0.0302 | 0.054* |
| C13 | 0.0030(3) | −0.0832(3) | 0.4409(2) | 0.0204(7) |
| H13 | 0.0028 | −0.1437 | 0.4001 | 0.025* |
| C14 | 0.0868(3) | 0.0856(3) | 0.4857(2) | 0.0208(7) |
| H14 | 0.1475 | 0.1478 | 0.4774 | 0.025* |
| C15 | 0.4142(3) | −0.0842(3) | 0.4887(2) | 0.0205(7) |
| H15 | 0.3540 | −0.1458 | 0.4826 | 0.025* |
| C16 | 0.4973(3) | 0.0906(3) | 0.4372(2) | 0.0207(7) |
| H16 | 0.4981 | 0.1563 | 0.3939 | 0.025* |
| C17 | 0.6917(4) | 0.7703(4) | 0.3664(3) | 0.0351(9) |
| C18 | 0.6907(4) | 0.8379(4) | 0.2804(3) | 0.0455(11) |
| H18A | 0.7792 | 0.8218 | 0.2494 | 0.068* |
| H18B | 0.6782 | 0.9221 | 0.2900 | 0.068* |
| H18C | 0.6140 | 0.8158 | 0.2432 | 0.068* |
| C19 | 0.8125(4) | 0.2179(4) | 0.3205(4) | 0.0476(13) |
| C20 | 0.8130(4) | 0.2061(4) | 0.2239(3) | 0.0412(10) |
| H20A | 0.7463 | 0.2656 | 0.1943 | 0.062* |
| H20B | 0.7867 | 0.1272 | 0.2120 | 0.062* |
| H20C | 0.9064 | 0.2177 | 0.2000 | 0.062* |
Source of material
The Cd[S2P(OiPr)2]2 precursor was prepared in high yield from the in situ reaction of Cd(NO3)2⋅4 H2O (Acros Organic; 15.42 g, 0.05 mol), iPrOH (Merck; 16.05 mL, 0.21 mol), P2S5 (Sigma-Aldrich; 11.11 g, 0.05 mol) and 50% w/w NaOH solution (Merck; 8.80 mL, 0.11 mol). The anticipated title compound was obtained by mixing a suspension of Cd[S2P(OiPr)2]2 (0.50 g, 0.93 mmol) and pyrazine (Merck, 0.08 g, 1.00 mmol) in dimethylformamide (Merck; 5 mL), followed by stirring for 30 min. at 373 K. The solution was filtered and the filtrate collected in a sample vial containing acetonitrile (Merck; 1 mL). Yellow crystals formed after three days. An isolated crystal was harvested and examined directly by X-ray crystallography without further characterization.
Experimental details
The C-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C). Owing to poor agreement, three reflections, i.e. (1 −5 2), (0 5 4) and (3 −5 5), were omitted from the final cycles of refinement. The maximum and minimum residual electron density peaks of 1.27 and 0.55 eÅ−3, respectively, were located 0.91 and 0.83 Å from the S3 and Cd atoms, respectively.
Comment
In a recent report, the first example of a cadmium(II) 1,1-dithiolate compound complexed with pyrazine (pyr) was described, namely, {Cd[S2P(OEt)2]2(pyr)}n, (I) [5]. In its crystal, this is a one-dimensional coordination polymer with a linear topology, analogous to that found in the zinc xanthate analogue [Zn(S2COEt)2(pyr)]n [6]. The only other related examples were found to be binuclear, i.e. {Zn[S2CN(CH2CH2OH)2]2}2(pyr), isolated in solvent-free form and as a dioxane solvate [7], and {Zn[S2P(O-iPr)2]2}2(pyr) [8]. In continuation of systematic studies in this area [7], [8], [9], [10], herein, the crystal and molecular structures of {Cd[S2P(O-iPr)2]2(pyr)}n, (II), i.e. the isopropyl analogue of (I), isolated as a di-acetonitrile solvate, are described.
The immediate coordination environment for the cadmium atom in (II) is shown in the figure (70% probablility displacement ellipsoids; solvent molecules are omitted). The cadmium atom and dithiophosphate ligands lie in general positions whereas each of the independent pyr molecules is disposed about a centre of inversion (referring to the figure, the complete N1-pyr molecule is completed by the application of symmetry operation (i) − x, −y, 1 − z while (ii) 1 − x, −y, 1 − z is required to generate the full N2-pyr molecule). The cadmium atom is octahedrally coordinated within a cis-N2S4 donor set defined by two chelating dithiophosphate ligands and two pyr-nitrogen atoms. The dithiophosphate ligands are chelating in a symmetric mode [Cd—S1, S2 = 2.6537(8) and 2.6861(8) Å; Cd—S3, S4 = 2.6681(8) and 2.6780(8) Å]. The differences between Cd—S(long) and Cd—S(short) = Δ(Cd—S) are quite small, i.e. values of 0.03 and 0.01 Å are noted for the S1- and S3-dithiophosphate ligands, respectively. The difference in Δ(Cd—S) is also reflected in the P—S bond lengths. Thus, Δ(P—S) is greater, i.e. 0.013 Å for the S1-dithiophosphate (P1—S1, S2 = 1.9974(12) and 1.9849(12) Å] than 0.007 for the S3-dithiophosphate ligand [P2—S3, S4 = 1.9946(11) and 1.9879(12) Å]. The Cd—N bond lengths are experimentally equivalent [Cd—N1, N2 = 2.416(3) and 2.420(3) Å]. In the N2S4 octahedron, the more tightly bound S1 and S3 atoms occupy mutually trans-positions [170.78(3)°] and the pyrazine-nitrogen atoms are each trans to a less-tightly bound S2 or S4 atom [N1—Cd—S2 = 162.22(7)° and N2—Cd—S4 = 160.15(7)°]. The maximum distortion in terms of cis-angles is seen in S2—Cd—S4 angle of 104.75(3)°.
As shown in the lower view of the figure, the resultant one-dimensional coordination polymer in the crystal of (II) is a zigzag chain. This contrasts the linear chain noted in the crystal of (I) [5]. An obvious difference between the molecular structures of (II) and (I) relates to the relative positions of the nitrogen atoms within the N2S4 donor set, i.e. cis- and trans-, respectively. As to why one disposition occurs preferentially in (I) and (II) is not yet clear.
In the packing, each of the acetonitrile molecules is loosely associated with the one-dimensional chain, i.e. via pyrazinyl-C—H⋯N(acetonitrile) [C15—H15⋯N4ii: H15⋯N4ii = 2.57 Å, C15⋯N4ii = 3.227(6) Å with angle at H15 = 127°] and methyl-C—H⋯O(alkoxy) interactions [C18—H18a⋯O3iii: H18a⋯O3iii = 2.58 Å, C18⋯O3iii = 3.441(4) Å with angle at H18a = 146° for (iii) 1 + x, 1 + y, z]. The resultant aggregates pack without directional interactions between them.
Acknowledgements
Sunway University Sdn Bhd is thanked for financial support of this work through Grant no. STR-RCTR-RCCM-001-2019.
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction: CrysAlisPRO. Rigaku Corporation, Oxford, UK (2018).Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
5. Tan, Y. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-pyrazine-N,N′)-bis(O,O′-di-ethyldithiophosphato-S,S′)cadmium(II)], [C12H24CdN2O4P2S4]n. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 235 (2020) 319–321.10.1515/ncrs-2019-0648Search in Google Scholar
6. Ara, I.; El Bahij, F.; Lachkar, M.: Synthesis, characterization and X-ray crystal structures of new ethylxanthato complexes of zinc(II) with N-donor ligands. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met. Chem. 36 (2006) 399–406.10.1080/15533170600732569Search in Google Scholar
7. Jotani, M. M.; Poplaukhin, P.; Arman, H. D.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Supramolecular association in (μ2-pyrazine)-tetrakis(N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)dithiocarbamato)dizinc(II) and its di-dioxane solvate. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 232 (2017) 287–298.10.1515/zkri-2016-2014Search in Google Scholar
8. Chen, D.; Lai, C. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Supramolecular aggregation in diimine adducts of zinc(II) dithiophosphates: controlling the formation of monomeric, dimeric, polymeric (zig-zag and helical), and 2-D motifs. CrystEngComm 8 (2006) 51–58.10.1039/B513393ASearch in Google Scholar
9. Lai, C. S.; Tiekink, E. R. T.: Engineering polymers with variable topology – bipyridine adducts of cadmium dithiophosphates. CrystEngComm 6 (2004) 593–605.10.1039/b414847aSearch in Google Scholar
10. Tiekink, E. R. T.: Perplexing coordination behaviour of potentially bridging bipyridyl-type ligands in the coordination chemistry of zinc and cadmium 1,1-dithiolate compounds. Crystals 8 (2018) 18.10.3390/cryst8010018Search in Google Scholar
©2019 Yee Seng Tan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{5-fluorine-2-(((4-(1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C32H28CuF2N4O4
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of N′-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazide monohydrate, C16H17FN2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl) ethylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H12ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-[4-(1H)-imidazolyl phenyl]-(2-methylphenyl)methanimine, C17H15N3
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-4-(2-(phenylethynyl)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C23H17N3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[{μ2-1,5-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)pentane-κ2P:P′}dichloridocadmium(II)], C29H30CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-N2-((3-methylquinolin-8-yl)sulfonyl)-Nω′-nitro-L-argininate - ethanol (1/1), C19H28N6O7S
- The crystal structure of trans-carbonyl-(diphenylcyclohexyl-phosphine-κP)iodidomethyl-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)rhodium(III), C25H28INO3PRh
- Crystal structure of N-(amino(pyrazin-2-yl)methylene)-6-methylpyridin-1-ium-3-carbohydrazonate-κ3O,N,N′)-(dinitrato-κ1O)zinc(II), C12H12N8O7Zn
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)chromium(III) chloride — methanol (1/3), CrC27H33Cl3N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ4-piperazine-1,4-bis(2-hydroxypropanesulfonato-κ8O,O′:O′,N:N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))silver(I)], C10H24Ag2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2–2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κO)-oktakis(3-chlorobenzyl-κC)tetratin(IV), C84H52Cl8F16O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-methyl oxime, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)zinc(II)], {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-iodopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H12IN3O2
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-(μ2-methanoato-k2O:O′)-(μ2–bis(di-p-tolylphosphino)cyclohexylamine-κ2P:P′)dirhenium(I), C42H45NO8P2Re2
- The cocrystal structure of 1′-hydroxy-1H,1′H-[5,5′-bitetrazol]-1-olate and 1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium, C14H10N10O2
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-2-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)ethynyl)pyridin-1-ium bromide,C24H24BrN
- Crystal structure of (5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline)-copper(II), C26H16CuN12O2
- Crystal structure of bis(ammonium) diaqua-tetrakis(4-hydroxybenzoato)-manganese(II) tetrahydrate, [NH4]2[C28H24MnO14] ⋅ 4(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 3-chloro-1-hydrazino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, C6H4ClN5O6
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ2-pyrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-ethyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C12H24CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-pyrazine-N,N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-S,S′)cadmium(II) acetonitrile di-solvate], [C16H32CdN2O4P2S4⋅2(C2H3N)]n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{(μ2-N1,N2-bis[(pyridin-4-yl)methyl]ethanediamide-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)} — acetonitrile (1/1), C26H42N4O6P2S4Zn⋅C2H3N
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)cobalt(II), C16H22O10Co
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyl dithiophosphato-κ2-S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C16H22CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(E)-2-(((5-((trimethylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol], C12H15N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(N-o-tolyl-1,1-di-p-tolylphosphanamine–κ1P)-(methoxydi-p-tolylphosphane-κ1P)palladium(II), C36H39Cl2NOP2Pd
- The crystal structure of the triclinic polymorph of hexameric (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, C24H66Li6Si6
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′O)cobalt(III) 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane, C34H22CoN8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of benzyl 5-oxo-5-phenyl-2-(quinolin-2-yl)pentanoate, C27H23NO3
- Crystal structure of 5,5-dimethyl-3-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl 4-(2,2-dichloroacetyl)-3,4-dihydro-2 H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-7-carboxylate, C19H19Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of dipentyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C18H28O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)], C30H18Cd2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of 2,7-diiodo-1,3,6,8-tetramethyl-bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine, C14H14B2F4I2N4
- A dinuclear Eu(III) complex in the crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′) bis(5-(4-carboxylatophenyl)tetrazol-1-ide) tetrahydrate, C32H50Eu2N16O24
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one, C24H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one-methanol-hydrate (2/1/1), C53H50F2N6O10S2
- Crystal structure of 4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium uracil-1-acetate, C13H16N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium 5-fluorouracil-1-acetate, C8H12N3O4F
- Crystal structure of bis(N′-((5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-N-ethylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2N,O)nickel(II), C22H30N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-((bis-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexafluorophosphate. (C17H23ClN4RhF6P)
- The crystal structure of 5-(benzofuran-2-carbonyl)-N-cyclohexyl-5,6-dihydrophenanthridine-6-carboxamide, C29H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl acetate, C11H8O4
- The crystal structure of 2-nitroisophthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-9-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino [2′,1′:1,6]pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H17FN4O
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl-κC)(bis(2-hydroxyethyl) carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)(2,2′-imino-diethanolato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C16H25FN2O4S2Sn
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18BrF3N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18ClF3N2O3S
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridomanganate(II), C10H16Cl4MnN2
- The crystal structure of 3-carboxy-5-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-carboxylate, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methoxy-N-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato κ3O,N,N′)zinc(II), C30H28N6O4Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(4,4′-dichloro-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) — acetone (1/1), C13H12Cl4N2PtO
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2,10-dimethoxy-3,9-diphenyl-3,9-diazatetracyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C42H42F2N2O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,3E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylisophthalaldehyde O,O-di(2-((((E)-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)oxy)ethyl) dioxime, C35H32N4O7
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazine, C15H11N3O2
- Crystal structure of 7-(2-{4-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C22H23BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(3-ethyl-1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-3-bromo-benzoic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-cadmium(II), C30H28N8O2Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H9FO3
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)butanoic acid, C14H18O4
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyridine, C13H19BBrNO3
- The crystal structure of 6-methyl-3,20-dioxo-19-norpregna-4,6-dien-17-yl acetate–2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (1/1), C30H36O8
- The crystal structure of (5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-(pyridine-κ1N)copper(II), C20H16ClCuN3O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-cyano-N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)acetohydrazide, C11H3N5O
- Crystal structure of (2,7-dihexyl-9,9-dimethyl-9H-xanthene-4,5-diyl)bis(diphenylphosphane), C51H56OP2
- Crystal structure of 5-((bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)methyl)quinolin-8-ol, C22H20N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C28H20FN3O2S
- The crystal structure of [(tetra-μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′)]dierbium(III) C66H34N4O12F12Er2
- Crystal structure of bis(3-chloro-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C26H20N8O2Cl2Ni
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C27H21N5O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)-N,N-dimethylformimidamide, C9H13N3O2S
- Crystal structure of η6-p-cymene-iodido-(N-isopropyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C19H26IN2F6Ru
- Crystal structure of 6-iodo-3-phenyl-2-propylquinazolin-4(3H)-one, C17H15IN2O
- Low temperature redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tri-4-fluorobenzyltin(IV)]μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O], {C27H22F3NO2Sn}n
- Crystal structure of bis(2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrachloridozincate(II), C10H13Cl4N2Zn
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydrazono-5-nitroindolin-2-one – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C8H6N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-cyanoacetic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-zinc(II), C18H16N10O2Zn
- Crystal structure and photochromism of 1-(2,5-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(benzaldoxime)-3-thienyl] perfluorocyclopentene, C23H17F6NOS2
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{5-fluorine-2-(((4-(1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C32H28CuF2N4O4
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of N′-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazide monohydrate, C16H17FN2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl) ethylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H12ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-[4-(1H)-imidazolyl phenyl]-(2-methylphenyl)methanimine, C17H15N3
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-4-(2-(phenylethynyl)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C23H17N3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[{μ2-1,5-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)pentane-κ2P:P′}dichloridocadmium(II)], C29H30CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-N2-((3-methylquinolin-8-yl)sulfonyl)-Nω′-nitro-L-argininate - ethanol (1/1), C19H28N6O7S
- The crystal structure of trans-carbonyl-(diphenylcyclohexyl-phosphine-κP)iodidomethyl-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)rhodium(III), C25H28INO3PRh
- Crystal structure of N-(amino(pyrazin-2-yl)methylene)-6-methylpyridin-1-ium-3-carbohydrazonate-κ3O,N,N′)-(dinitrato-κ1O)zinc(II), C12H12N8O7Zn
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)chromium(III) chloride — methanol (1/3), CrC27H33Cl3N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ4-piperazine-1,4-bis(2-hydroxypropanesulfonato-κ8O,O′:O′,N:N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))silver(I)], C10H24Ag2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2–2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κO)-oktakis(3-chlorobenzyl-κC)tetratin(IV), C84H52Cl8F16O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-methyl oxime, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)zinc(II)], {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-iodopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H12IN3O2
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-(μ2-methanoato-k2O:O′)-(μ2–bis(di-p-tolylphosphino)cyclohexylamine-κ2P:P′)dirhenium(I), C42H45NO8P2Re2
- The cocrystal structure of 1′-hydroxy-1H,1′H-[5,5′-bitetrazol]-1-olate and 1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium, C14H10N10O2
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-2-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)ethynyl)pyridin-1-ium bromide,C24H24BrN
- Crystal structure of (5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline)-copper(II), C26H16CuN12O2
- Crystal structure of bis(ammonium) diaqua-tetrakis(4-hydroxybenzoato)-manganese(II) tetrahydrate, [NH4]2[C28H24MnO14] ⋅ 4(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 3-chloro-1-hydrazino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, C6H4ClN5O6
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ2-pyrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-ethyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C12H24CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-pyrazine-N,N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-S,S′)cadmium(II) acetonitrile di-solvate], [C16H32CdN2O4P2S4⋅2(C2H3N)]n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{(μ2-N1,N2-bis[(pyridin-4-yl)methyl]ethanediamide-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)} — acetonitrile (1/1), C26H42N4O6P2S4Zn⋅C2H3N
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)cobalt(II), C16H22O10Co
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyl dithiophosphato-κ2-S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C16H22CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(E)-2-(((5-((trimethylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol], C12H15N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(N-o-tolyl-1,1-di-p-tolylphosphanamine–κ1P)-(methoxydi-p-tolylphosphane-κ1P)palladium(II), C36H39Cl2NOP2Pd
- The crystal structure of the triclinic polymorph of hexameric (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, C24H66Li6Si6
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′O)cobalt(III) 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane, C34H22CoN8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of benzyl 5-oxo-5-phenyl-2-(quinolin-2-yl)pentanoate, C27H23NO3
- Crystal structure of 5,5-dimethyl-3-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl 4-(2,2-dichloroacetyl)-3,4-dihydro-2 H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-7-carboxylate, C19H19Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of dipentyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C18H28O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)], C30H18Cd2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of 2,7-diiodo-1,3,6,8-tetramethyl-bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine, C14H14B2F4I2N4
- A dinuclear Eu(III) complex in the crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′) bis(5-(4-carboxylatophenyl)tetrazol-1-ide) tetrahydrate, C32H50Eu2N16O24
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one, C24H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one-methanol-hydrate (2/1/1), C53H50F2N6O10S2
- Crystal structure of 4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium uracil-1-acetate, C13H16N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium 5-fluorouracil-1-acetate, C8H12N3O4F
- Crystal structure of bis(N′-((5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-N-ethylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2N,O)nickel(II), C22H30N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-((bis-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexafluorophosphate. (C17H23ClN4RhF6P)
- The crystal structure of 5-(benzofuran-2-carbonyl)-N-cyclohexyl-5,6-dihydrophenanthridine-6-carboxamide, C29H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl acetate, C11H8O4
- The crystal structure of 2-nitroisophthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-9-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino [2′,1′:1,6]pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H17FN4O
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl-κC)(bis(2-hydroxyethyl) carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)(2,2′-imino-diethanolato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C16H25FN2O4S2Sn
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18BrF3N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18ClF3N2O3S
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridomanganate(II), C10H16Cl4MnN2
- The crystal structure of 3-carboxy-5-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-carboxylate, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methoxy-N-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato κ3O,N,N′)zinc(II), C30H28N6O4Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(4,4′-dichloro-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) — acetone (1/1), C13H12Cl4N2PtO
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2,10-dimethoxy-3,9-diphenyl-3,9-diazatetracyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C42H42F2N2O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,3E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylisophthalaldehyde O,O-di(2-((((E)-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)oxy)ethyl) dioxime, C35H32N4O7
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazine, C15H11N3O2
- Crystal structure of 7-(2-{4-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C22H23BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(3-ethyl-1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-3-bromo-benzoic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-cadmium(II), C30H28N8O2Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H9FO3
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)butanoic acid, C14H18O4
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyridine, C13H19BBrNO3
- The crystal structure of 6-methyl-3,20-dioxo-19-norpregna-4,6-dien-17-yl acetate–2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (1/1), C30H36O8
- The crystal structure of (5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-(pyridine-κ1N)copper(II), C20H16ClCuN3O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-cyano-N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)acetohydrazide, C11H3N5O
- Crystal structure of (2,7-dihexyl-9,9-dimethyl-9H-xanthene-4,5-diyl)bis(diphenylphosphane), C51H56OP2
- Crystal structure of 5-((bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)methyl)quinolin-8-ol, C22H20N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C28H20FN3O2S
- The crystal structure of [(tetra-μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′)]dierbium(III) C66H34N4O12F12Er2
- Crystal structure of bis(3-chloro-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C26H20N8O2Cl2Ni
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C27H21N5O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)-N,N-dimethylformimidamide, C9H13N3O2S
- Crystal structure of η6-p-cymene-iodido-(N-isopropyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C19H26IN2F6Ru
- Crystal structure of 6-iodo-3-phenyl-2-propylquinazolin-4(3H)-one, C17H15IN2O
- Low temperature redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tri-4-fluorobenzyltin(IV)]μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O], {C27H22F3NO2Sn}n
- Crystal structure of bis(2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrachloridozincate(II), C10H13Cl4N2Zn
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydrazono-5-nitroindolin-2-one – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C8H6N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-cyanoacetic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-zinc(II), C18H16N10O2Zn
- Crystal structure and photochromism of 1-(2,5-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(benzaldoxime)-3-thienyl] perfluorocyclopentene, C23H17F6NOS2

