Abstract
C17H23ClN4RhF6P, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 10.6954(2) Å, b = 15.3868(3) Å, c = 12.6130(2) Å, β = 90.5590(10)°, V = 2075.60(7) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0296, wRref(F2) = 0.0727, T = 100(2) K.
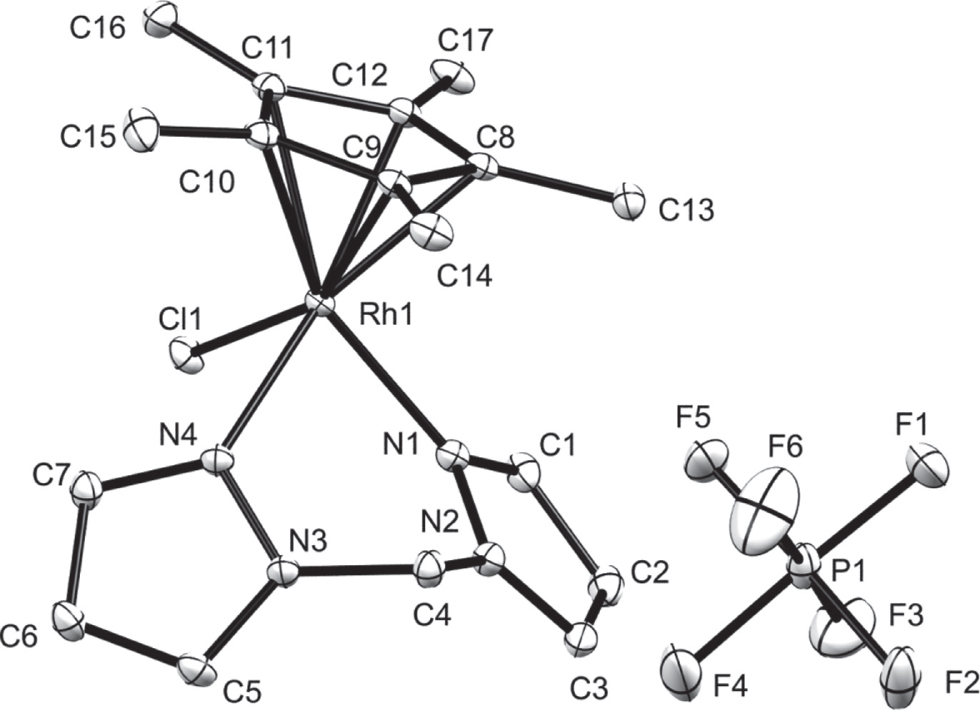
The asymmetric unit of the salt title structure is shown in the figure (hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity). Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Orange block |
| Size: | 0.35 × 0.31 × 0.23 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.09 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 31369, 5166, 0.017 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 4994 |
| N(param)refined: | 276 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], [3], Mercury [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rh1 | 0.69970(2) | 0.11853(2) | 0.33986(2) | 0.01016(6) |
| Cl1 | 0.67376(5) | 0.10711(4) | 0.52789(4) | 0.01562(10) |
| N1 | 0.70574(17) | −0.01726(12) | 0.33402(14) | 0.0138(4) |
| N2 | 0.80103(18) | −0.06209(12) | 0.28963(15) | 0.0148(4) |
| N3 | 0.96207(17) | 0.03978(12) | 0.32904(15) | 0.0141(3) |
| N4 | 0.89583(17) | 0.10842(12) | 0.36637(15) | 0.0135(3) |
| C1 | 0.6225(2) | −0.07659(15) | 0.36404(18) | 0.0177(4) |
| H1 | 0.5459 | −0.0641 | 0.3983 | 0.021* |
| C2 | 0.6641(2) | −0.15980(16) | 0.33783(19) | 0.0202(5) |
| H2 | 0.6222 | −0.2133 | 0.3499 | 0.024* |
| C3 | 0.7783(2) | −0.14813(15) | 0.29097(18) | 0.0187(4) |
| H3 | 0.8313 | −0.1925 | 0.2645 | 0.022* |
| C4 | 0.9074(2) | −0.01508(15) | 0.24775(18) | 0.0158(4) |
| H4A | 0.9708 | −0.0569 | 0.2223 | 0.019* |
| H4B | 0.8801 | 0.0211 | 0.1869 | 0.019* |
| C5 | 1.0774(2) | 0.03702(16) | 0.37305(19) | 0.0178(4) |
| H5 | 1.1401 | −0.0052 | 0.3594 | 0.021* |
| C6 | 1.0876(2) | 0.10634(16) | 0.44118(19) | 0.0184(4) |
| H6 | 1.1580 | 0.1221 | 0.4835 | 0.022* |
| C7 | 0.9719(2) | 0.14879(15) | 0.43480(18) | 0.0164(4) |
| H7 | 0.9505 | 0.1994 | 0.4738 | 0.020* |
| C8 | 0.5812(2) | 0.12664(14) | 0.20087(17) | 0.0125(4) |
| C9 | 0.6921(2) | 0.17742(14) | 0.18605(17) | 0.0133(4) |
| C10 | 0.6934(2) | 0.24515(14) | 0.26632(17) | 0.0151(4) |
| C11 | 0.5842(2) | 0.23564(14) | 0.32890(17) | 0.0150(4) |
| C12 | 0.5168(2) | 0.15966(14) | 0.29214(17) | 0.0134(4) |
| C13 | 0.5399(2) | 0.05056(15) | 0.13573(18) | 0.0170(4) |
| H13A | 0.6129 | 0.0235 | 0.1028 | 0.026* |
| H13B | 0.4816 | 0.0702 | 0.0803 | 0.026* |
| H13C | 0.4983 | 0.0081 | 0.1813 | 0.026* |
| C14 | 0.7856(2) | 0.16944(16) | 0.09947(18) | 0.0181(4) |
| H14A | 0.8701 | 0.1746 | 0.1294 | 0.027* |
| H14B | 0.7717 | 0.2158 | 0.0473 | 0.027* |
| H14C | 0.7762 | 0.1128 | 0.0648 | 0.027* |
| C15 | 0.7914(2) | 0.31409(16) | 0.2772(2) | 0.0224(5) |
| H15A | 0.7962 | 0.3335 | 0.3511 | 0.034* |
| H15B | 0.7697 | 0.3634 | 0.2314 | 0.034* |
| H15C | 0.8726 | 0.2904 | 0.2561 | 0.034* |
| C16 | 0.5413(2) | 0.29392(16) | 0.41568(19) | 0.0214(5) |
| H16A | 0.5349 | 0.2606 | 0.4816 | 0.032* |
| H16B | 0.4593 | 0.3181 | 0.3970 | 0.032* |
| H16C | 0.6015 | 0.3413 | 0.4255 | 0.032* |
| C17 | 0.3963(2) | 0.12866(17) | 0.33710(19) | 0.0190(4) |
| H17A | 0.3269 | 0.1616 | 0.3055 | 0.029* |
| H17B | 0.3972 | 0.1373 | 0.4141 | 0.029* |
| H17C | 0.3856 | 0.0667 | 0.3213 | 0.029* |
| P1 | 0.84478(6) | −0.13070(4) | −0.03400(5) | 0.02066(13) |
| F1 | 0.72533(18) | −0.13738(13) | −0.10906(16) | 0.0413(5) |
| F2 | 0.91255(16) | −0.20669(13) | −0.10006(16) | 0.0412(5) |
| F3 | 0.7831(2) | −0.20471(13) | 0.03929(17) | 0.0485(5) |
| F4 | 0.96244(18) | −0.12937(15) | 0.04689(18) | 0.0502(6) |
| F5 | 0.77755(16) | −0.05845(11) | 0.03655(14) | 0.0324(4) |
| F6 | 0.9090(3) | −0.06062(15) | −0.10376(19) | 0.0627(7) |
Source of material
The title compound was synthesized using a mixture of the rhodium dimer pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium(III) dichloride (0.055 mmol), bis(pyrazol-1-yl)methane (0.110 mmol) and NH4PF6 (0.110 mmol) which were stirred in methanol (10 mL) for six hours, where upon the orange yellow product separated out. The product was filtered, washed with diethyl ether and dried under vacuum. X-ray quality, orange block crystals were grown by vapour diffusion of diethyl ether into an acetone solution. m.p = >300 °C (decomposition); IRv(cm−1): 1519, 1429, 1401 (C=N), 832 (PF6); 1H NMR (400 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ(ppm) = 8.23 (d, 2H, J = 2.40 Hz, Pyrazole), 7.90 (s, 2H, Pyrazole), 7.09 (s, 1H, Pyrazole), 7.05 (s, 1H, Pyrazole), 6.63 (t, 2H, J = 2.12 Hz, –CH2), 13C NMR (400 MHz, d6-DMSO): δ(ppm) = 146.39, 145.27, 135.47, 108.81, 106.69, 97.26, 9.24.
Experimental details
The structure was solved by the direct method using the SHELXS [2] program and refined. The visual crystal structure information was performed using Mercury [4] system software. All C—Haromatic, C—Hmethyl and C—Hmethylene bond distances were restrained to 0.95 Å, 0.98 Å and 0.99 Å with Uiso(Haromatic and Hmethylene) = 1.2Ueq and Uiso(Hmethyl) = 1.5Ueq of parent atom, respectively. Some larger electron density peaks are located near the PF6− anion. These peaks may be the result of a minor disorder of this anion.
Comment
The pyrazole nucleus has been widely used as core motif for a large number of compounds with various applications and especially in coordination chemistry [5], [6]. Bis(pyrazolyl)alkanes are one of the most fascinating family of stable and flexible ligands and they are isoelectronic and isosteric with the well-known bis(pyrazolyl)borates. The coordinating properties of bis(pyrazol-1-yl)alkanes can be varied over wide range by introduction of various substituents into the pyrazole rings which are able to modify steric and electronic properties [7]. The bis(pyrazol-1-yl)alkanes are neutral ligands containing two pyrazole cycles linked by an aliphatic spacer and are related in concept to the heteroscorpionate ligands. The coordination properties of bis(pyrazol-1-yl)alkanes may be varied in wide range by introducing substituents into the pyrazole rings. Generally, two major coordination modes can be expected for bis(pyrazol-1-yl)alkanes, namely bidentate chelating and bidentate bridging. Bis(pyrazol1-yl)methanes and 1,2-bis (pyrazol-1-yl)ethanes usually act as bidentate chelating ligands forming boat-shaped six- and seven-membered rings, respectively. 1,3-Bis(pyrazol-1-yl)propane forms eight-membered metallocycles or acts as a bidentate bridging ligand, whereas bis(pyrazol-1-yl)alkanes with four and more methylene groups in the spacer coordinate in a bridging mode to give coordination compounds of intriguing architectures and topologies [8], [9], [10]. We have prepared the title compound as part of our ongoing studies of Rh complexes with bidentate ligands [11], [12].
The asymmetric unit of the title compound consists of an cationic Rh(III) complex with a PF6− anion. The Rh complex exists in the piano-stool conformation with a six-membered metallocycle (Rh1–N1–N2–C4–N3–N4) formed by coordination of the bidentate ligand. Furthermore, the metallocycle adopts a distorted boat conformation with a dihedral angle of 27.4(1)° between the N1–N2–N3–N4 and N1–Rh1–N4 planes. Upon coordination of the ligand, the dihedral angle between the pyrazolyl rings significantly decreased from 72.8(2)–73.06(9)° (observed in the free ligand [13], [14]) to 56.85(9)°. All bond distances and angles were found to be in agreement with closely related complexes reported in the literature [15], [16], [17]. Intermolecular, very weak π⋯π interactions between pyrazolyl rings N3—N4—C5—C6—C7 of neighbouring molecules were observed in the crystal packing of the title compound (π⋯π = 3.899(1) Å; symmetry code: 2 − x, −y, 1 − z). C—H⋯π intermolecular interactions were also observed between the H6 atom and the center of gravity of the N1—N2—C1—C2—C3 ring (H6⋯π = 2.82 Å; C6⋯π = 3.638(2) Å; C6—H6⋯π = 145°; symmetry code: 2 − x, −y, 1 − z).
Acknowledgements
We wish to extend our sincere thanks to the NRF, THRIP (Grant no. Tp 1208035643) and UKZN (URF) for their financial support. Joel Gichumbi thanks Chuka University for its support.
References
1. Bruker. APEX-II. Bruker AXS Inc, Madison, WI, USA (2009).Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Macrae, C. F.; Bruno, I. J.; Chisholm, J. A.; Edgington, P. R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P. A.: Mercury CSD 2.0 – new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41 (2008) 466–470.10.1107/S0021889807067908Suche in Google Scholar
5. Di Nicola, C.; Marchetti, F.; Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.; Brisdelli, F.; Crucianelli, M.; Lelii, C.; Crispini, A.: Synthesis and characterization of a new alkyne functionalized bis(pyrazolyl)methane ligand and of its Pd(II) complexes: evaluation of their in vitro cytotoxic activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta 455 (2017) 677–682.10.1016/j.ica.2016.04.032Suche in Google Scholar
6. Fujisawa, K.; Kanda, R.; Miyashita, Y.; Okamoto, K.-I.: Copper(II) complexes with neutral bis(pyrazolyl)methane ligands: the influence of steric hindrance on their structures and properties. Polyhedron 27 (2008) 1432–1446.10.1016/j.poly.2008.01.019Suche in Google Scholar
7. Marchetti, F.; Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.; Cerquetella, A.; Di Nicola, C.; Macchioni, A.; Zuccaccia, D.; Monari, M.; Piccinelli, F.: Synthesis and intramolecular and interionic structural characterization of half-sandwich (arene)ruthenium(II) derivatives of bis(pyrazolyl)alkanes. Inorg. Chem. 47 (2008) 11593–11603.10.1021/ic801150cSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Machura, B.; Palion, J.; Penkala, M.; Gron, T.; Duda, H.; Kruszynski, R.: Thiocyanate manganese(II) and cobalt(II) complexes of bis(pyrazol-1-yl)methane and bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)methane: syntheses, spectroscopic characterization, X-ray structure and magnetic properties. Polyhedron 56 (2013) 189–199.10.1016/j.poly.2013.03.052Suche in Google Scholar
9. Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.: Metal derivatives of poly(pyrazolyl)alkanes: II. bis(pyrazolyl)alkanes and related systems. Coord. Chem. Rev. 249 (2005) 663–691.10.1016/j.ccr.2004.08.017Suche in Google Scholar
10. Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.; Marchetti, F.; Macchioni, A.; Zuccaccia, D.; Skelton, B. W.; White, A. H.: Synthesis, reactivity, spectroscopic characterization, X-ray structures, PGSE, and NOE NMR studies of (η5-C5Me5)-rhodium and -iridium derivatives containing bis(pyrazolyl)alkane ligands. Inorg. Chem. 46 (2007) 896–906.10.1021/ic061928gSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Thangaval, S.; Paulpandi, M.; Friedrich, H. B.; Murugan, K.; Kalva, S.; Skelton, A. A.: Synthesis, characterization, antiproliferative and molecular docking study of new half sandwich Ir(III), Rh(III) and Ru(II) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 159 (2016) 50–61.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.02.006Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Gallicano, K. D.; Paddock, N. L.; Rettig, S. J.; Trotter, J.: The molecular and electronic structure of 1-pyrazolylphosphazenes. Can. J. Chem. 70 (1992) 1855–1868.10.1139/v92-231Suche in Google Scholar
13. Churchill, M. R.; Churchill, D. G.; Huynh, M. H. V.; Takeuchi, K. J.; Castellano, R. K.; Jameson, D. L.: Crystal and molecular structure of di(1-pyrazolyl)methane, CH2(C3N2H3)2. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 26 (1996) 93–97.10.1007/BF01669723Suche in Google Scholar
14. Fink, C.; Laurenczy, G.: A precious catalyst: rhodium–catalyzed formic acid dehydrogenation in water. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019 (2019) 2381–2387.10.1002/ejic.201900344Suche in Google Scholar
15. Kennedy, D. F.; Messerle, B. A.; Smith, M. K.: Synthesis of Cp* iridium and rhodium complexes containing bidentate sp2 – N-donor ligands and counter-anions [Cp*MCl3]. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007 (2007) 80–89.10.1002/ejic.200600735Suche in Google Scholar
16. Wong, C. M.; Vuong, K. Q.; Gatus, M. R. D.; Hua, C.; Bhadbhade, M.; Messerle, B. A.: Catalyzed tandem C—N/C—C bond formation for the synthesis of tricyclic indoles using Ir(III) pyrazolyl-1,2,3-triazolyl complexes. Organometallics 31 (2012) 7500–7510.10.1021/om300792bSuche in Google Scholar
17. Fink, C.; Laurenczy, G.: A precious catalyst: rhodium-catalyzed formic acid dehydrogenation in water. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019 (2019) 2381–2387.10.1002/ejic.201900344Suche in Google Scholar
©2019 Joel M. Gichumbi et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{5-fluorine-2-(((4-(1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C32H28CuF2N4O4
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of N′-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazide monohydrate, C16H17FN2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl) ethylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H12ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-[4-(1H)-imidazolyl phenyl]-(2-methylphenyl)methanimine, C17H15N3
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-4-(2-(phenylethynyl)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C23H17N3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[{μ2-1,5-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)pentane-κ2P:P′}dichloridocadmium(II)], C29H30CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-N2-((3-methylquinolin-8-yl)sulfonyl)-Nω′-nitro-L-argininate - ethanol (1/1), C19H28N6O7S
- The crystal structure of trans-carbonyl-(diphenylcyclohexyl-phosphine-κP)iodidomethyl-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)rhodium(III), C25H28INO3PRh
- Crystal structure of N-(amino(pyrazin-2-yl)methylene)-6-methylpyridin-1-ium-3-carbohydrazonate-κ3O,N,N′)-(dinitrato-κ1O)zinc(II), C12H12N8O7Zn
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)chromium(III) chloride — methanol (1/3), CrC27H33Cl3N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ4-piperazine-1,4-bis(2-hydroxypropanesulfonato-κ8O,O′:O′,N:N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))silver(I)], C10H24Ag2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2–2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κO)-oktakis(3-chlorobenzyl-κC)tetratin(IV), C84H52Cl8F16O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-methyl oxime, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)zinc(II)], {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-iodopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H12IN3O2
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-(μ2-methanoato-k2O:O′)-(μ2–bis(di-p-tolylphosphino)cyclohexylamine-κ2P:P′)dirhenium(I), C42H45NO8P2Re2
- The cocrystal structure of 1′-hydroxy-1H,1′H-[5,5′-bitetrazol]-1-olate and 1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium, C14H10N10O2
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-2-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)ethynyl)pyridin-1-ium bromide,C24H24BrN
- Crystal structure of (5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline)-copper(II), C26H16CuN12O2
- Crystal structure of bis(ammonium) diaqua-tetrakis(4-hydroxybenzoato)-manganese(II) tetrahydrate, [NH4]2[C28H24MnO14] ⋅ 4(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 3-chloro-1-hydrazino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, C6H4ClN5O6
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ2-pyrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-ethyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C12H24CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-pyrazine-N,N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-S,S′)cadmium(II) acetonitrile di-solvate], [C16H32CdN2O4P2S4⋅2(C2H3N)]n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{(μ2-N1,N2-bis[(pyridin-4-yl)methyl]ethanediamide-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)} — acetonitrile (1/1), C26H42N4O6P2S4Zn⋅C2H3N
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)cobalt(II), C16H22O10Co
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyl dithiophosphato-κ2-S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C16H22CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(E)-2-(((5-((trimethylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol], C12H15N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(N-o-tolyl-1,1-di-p-tolylphosphanamine–κ1P)-(methoxydi-p-tolylphosphane-κ1P)palladium(II), C36H39Cl2NOP2Pd
- The crystal structure of the triclinic polymorph of hexameric (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, C24H66Li6Si6
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′O)cobalt(III) 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane, C34H22CoN8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of benzyl 5-oxo-5-phenyl-2-(quinolin-2-yl)pentanoate, C27H23NO3
- Crystal structure of 5,5-dimethyl-3-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl 4-(2,2-dichloroacetyl)-3,4-dihydro-2 H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-7-carboxylate, C19H19Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of dipentyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C18H28O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)], C30H18Cd2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of 2,7-diiodo-1,3,6,8-tetramethyl-bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine, C14H14B2F4I2N4
- A dinuclear Eu(III) complex in the crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′) bis(5-(4-carboxylatophenyl)tetrazol-1-ide) tetrahydrate, C32H50Eu2N16O24
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one, C24H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one-methanol-hydrate (2/1/1), C53H50F2N6O10S2
- Crystal structure of 4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium uracil-1-acetate, C13H16N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium 5-fluorouracil-1-acetate, C8H12N3O4F
- Crystal structure of bis(N′-((5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-N-ethylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2N,O)nickel(II), C22H30N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-((bis-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexafluorophosphate. (C17H23ClN4RhF6P)
- The crystal structure of 5-(benzofuran-2-carbonyl)-N-cyclohexyl-5,6-dihydrophenanthridine-6-carboxamide, C29H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl acetate, C11H8O4
- The crystal structure of 2-nitroisophthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-9-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino [2′,1′:1,6]pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H17FN4O
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl-κC)(bis(2-hydroxyethyl) carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)(2,2′-imino-diethanolato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C16H25FN2O4S2Sn
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18BrF3N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18ClF3N2O3S
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridomanganate(II), C10H16Cl4MnN2
- The crystal structure of 3-carboxy-5-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-carboxylate, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methoxy-N-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato κ3O,N,N′)zinc(II), C30H28N6O4Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(4,4′-dichloro-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) — acetone (1/1), C13H12Cl4N2PtO
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2,10-dimethoxy-3,9-diphenyl-3,9-diazatetracyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C42H42F2N2O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,3E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylisophthalaldehyde O,O-di(2-((((E)-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)oxy)ethyl) dioxime, C35H32N4O7
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazine, C15H11N3O2
- Crystal structure of 7-(2-{4-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C22H23BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(3-ethyl-1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-3-bromo-benzoic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-cadmium(II), C30H28N8O2Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H9FO3
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)butanoic acid, C14H18O4
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyridine, C13H19BBrNO3
- The crystal structure of 6-methyl-3,20-dioxo-19-norpregna-4,6-dien-17-yl acetate–2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (1/1), C30H36O8
- The crystal structure of (5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-(pyridine-κ1N)copper(II), C20H16ClCuN3O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-cyano-N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)acetohydrazide, C11H3N5O
- Crystal structure of (2,7-dihexyl-9,9-dimethyl-9H-xanthene-4,5-diyl)bis(diphenylphosphane), C51H56OP2
- Crystal structure of 5-((bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)methyl)quinolin-8-ol, C22H20N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C28H20FN3O2S
- The crystal structure of [(tetra-μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′)]dierbium(III) C66H34N4O12F12Er2
- Crystal structure of bis(3-chloro-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C26H20N8O2Cl2Ni
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C27H21N5O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)-N,N-dimethylformimidamide, C9H13N3O2S
- Crystal structure of η6-p-cymene-iodido-(N-isopropyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C19H26IN2F6Ru
- Crystal structure of 6-iodo-3-phenyl-2-propylquinazolin-4(3H)-one, C17H15IN2O
- Low temperature redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tri-4-fluorobenzyltin(IV)]μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O], {C27H22F3NO2Sn}n
- Crystal structure of bis(2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrachloridozincate(II), C10H13Cl4N2Zn
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydrazono-5-nitroindolin-2-one – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C8H6N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-cyanoacetic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-zinc(II), C18H16N10O2Zn
- Crystal structure and photochromism of 1-(2,5-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(benzaldoxime)-3-thienyl] perfluorocyclopentene, C23H17F6NOS2
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{5-fluorine-2-(((4-(1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl) imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}copper(II), C32H28CuF2N4O4
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of N′-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-fluorobenzohydrazide monohydrate, C16H17FN2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl) ethylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C15H12ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-[4-(1H)-imidazolyl phenyl]-(2-methylphenyl)methanimine, C17H15N3
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-4-(2-(phenylethynyl)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole, C23H17N3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[{μ2-1,5-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)pentane-κ2P:P′}dichloridocadmium(II)], C29H30CdCl2P2
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-N2-((3-methylquinolin-8-yl)sulfonyl)-Nω′-nitro-L-argininate - ethanol (1/1), C19H28N6O7S
- The crystal structure of trans-carbonyl-(diphenylcyclohexyl-phosphine-κP)iodidomethyl-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-κ2O,O′)rhodium(III), C25H28INO3PRh
- Crystal structure of N-(amino(pyrazin-2-yl)methylene)-6-methylpyridin-1-ium-3-carbohydrazonate-κ3O,N,N′)-(dinitrato-κ1O)zinc(II), C12H12N8O7Zn
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′)chromium(III) chloride — methanol (1/3), CrC27H33Cl3N7O3
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ4-piperazine-1,4-bis(2-hydroxypropanesulfonato-κ8O,O′:O′,N:N′,O′′:O′′,O′′′))silver(I)], C10H24Ag2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2–2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κO)-oktakis(3-chlorobenzyl-κC)tetratin(IV), C84H52Cl8F16O10Sn4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-{4-[(4-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-methyl oxime, C16H15FN2O2
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)zinc(II)], {C20H30N4O4P2S4Zn}n
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(4-(3-iodopyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)phenyl)acetate, C15H12IN3O2
- Crystal structure of hexacarbonyl-(μ2-methanoato-k2O:O′)-(μ2–bis(di-p-tolylphosphino)cyclohexylamine-κ2P:P′)dirhenium(I), C42H45NO8P2Re2
- The cocrystal structure of 1′-hydroxy-1H,1′H-[5,5′-bitetrazol]-1-olate and 1,10-phenanthrolin-1-ium, C14H10N10O2
- The crystal structure of 1-benzyl-2-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)ethynyl)pyridin-1-ium bromide,C24H24BrN
- Crystal structure of (5,5′-bitetrazole-1,1′-diolate)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline)-copper(II), C26H16CuN12O2
- Crystal structure of bis(ammonium) diaqua-tetrakis(4-hydroxybenzoato)-manganese(II) tetrahydrate, [NH4]2[C28H24MnO14] ⋅ 4(H2O)
- The crystal structure of 3-chloro-1-hydrazino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, C6H4ClN5O6
- Crystal structure of catena-[(μ2-pyrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-ethyldithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C12H24CdN2O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-pyrazine-N,N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-S,S′)cadmium(II) acetonitrile di-solvate], [C16H32CdN2O4P2S4⋅2(C2H3N)]n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly{(μ2-N1,N2-bis[(pyridin-4-yl)methyl]ethanediamide-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-di-isopropyldithiophosphato-κ1S)zinc(II)} — acetonitrile (1/1), C26H42N4O6P2S4Zn⋅C2H3N
- Crystal structure of tetraqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)benzoato-κO)cobalt(II), C16H22O10Co
- Crystal structure of catena-[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-N,N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)-bis(O,O′-dimethyl dithiophosphato-κ2-S,S′)cadmium(II)], {C16H22CdN4O4P2S4}n
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(bis(O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphato-κ2S,S′)-μ2-1,2-bis(3-pyridylmethylene)hydrazine-κ2N:N′)cadmium(II)], {C20H30CdN4O4P2S4}n
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(E)-2-(((5-((trimethylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol], C12H15N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido(N-o-tolyl-1,1-di-p-tolylphosphanamine–κ1P)-(methoxydi-p-tolylphosphane-κ1P)palladium(II), C36H39Cl2NOP2Pd
- The crystal structure of the triclinic polymorph of hexameric (trimethylsilyl)methyllithium, C24H66Li6Si6
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxydi(pyridin-2-yl)methanolato-κ3N,N′O)cobalt(III) 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane, C34H22CoN8O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of benzyl 5-oxo-5-phenyl-2-(quinolin-2-yl)pentanoate, C27H23NO3
- Crystal structure of 5,5-dimethyl-3-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl 4-(2,2-dichloroacetyl)-3,4-dihydro-2 H-benzo[b][1,4]oxazine-7-carboxylate, C19H19Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of dipentyl 2,5-dihydroxycyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,4-dicarboxylate, C18H28O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ4-5-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylate-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)dicadmium(II)], C30H18Cd2N2O10S2
- Crystal structure of 2,7-diiodo-1,3,6,8-tetramethyl-bis(difluoroboron)-1,2-bis((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)hydrazine, C14H14B2F4I2N4
- A dinuclear Eu(III) complex in the crystal structure of dodecaaqua-bis(μ2-4-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′) bis(5-(4-carboxylatophenyl)tetrazol-1-ide) tetrahydrate, C32H50Eu2N16O24
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one, C24H18F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3-(2-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-acetamidophenyl)sulfonyl)-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethylene)piperidin-4-one-methanol-hydrate (2/1/1), C53H50F2N6O10S2
- Crystal structure of 4-dimethylamino-pyridin-1-ium uracil-1-acetate, C13H16N4O4
- Crystal structure of dimethylammonium 5-fluorouracil-1-acetate, C8H12N3O4F
- Crystal structure of bis(N′-((5-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-N-ethylcarbamohydrazonothioato-κ2N,O)nickel(II), C22H30N8O4S2Ni
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)-((bis-pyrazol-1-yl)methane-κ2N,N′) rhodium(III) hexafluorophosphate. (C17H23ClN4RhF6P)
- The crystal structure of 5-(benzofuran-2-carbonyl)-N-cyclohexyl-5,6-dihydrophenanthridine-6-carboxamide, C29H26N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl acetate, C11H8O4
- The crystal structure of 2-nitroisophthalic acid, C8H5NO6
- Crystal structure of 3-fluoro-9-methoxy-4b,5,14,15-tetrahydro-6H-isoquinolino [2′,1′:1,6]pyrazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline, C19H17FN4O
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl-κC)(bis(2-hydroxyethyl) carbamodithioato-κ2S,S′)(2,2′-imino-diethanolato-κ3N,O,O′)tin(IV), C16H25FN2O4S2Sn
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18BrF3N2O3S
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(pyridin-4-ylmethylene)-5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)piperidin-4-one, C25H18ClF3N2O3S
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridomanganate(II), C10H16Cl4MnN2
- The crystal structure of 3-carboxy-5-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-carboxylate, C8H7NO4
- Crystal structure of bis(3-methoxy-N-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato κ3O,N,N′)zinc(II), C30H28N6O4Zn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-(4,4′-dichloro-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)platinum(II) — acetone (1/1), C13H12Cl4N2PtO
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2,10-dimethoxy-3,9-diphenyl-3,9-diazatetracyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C42H42F2N2O6
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (1E,3E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylisophthalaldehyde O,O-di(2-((((E)-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)oxy)ethyl) dioxime, C35H32N4O7
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)-1,3,5-triazine, C15H11N3O2
- Crystal structure of 7-(2-{4-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl}ethoxy)-2H-chromen-2-one, C22H23BrN2O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(3-ethyl-1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-3-bromo-benzoic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-cadmium(II), C30H28N8O2Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one, C12H9FO3
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-3-(2,4,5-trimethyl-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)butanoic acid, C14H18O4
- The crystal structure of 3-bromo-6-methoxy-2-methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyridine, C13H19BBrNO3
- The crystal structure of 6-methyl-3,20-dioxo-19-norpregna-4,6-dien-17-yl acetate–2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (1/1), C30H36O8
- The crystal structure of (5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-(4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3N,O,O′)-(pyridine-κ1N)copper(II), C20H16ClCuN3O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-cyano-N′-(1-(3-ethylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)acetohydrazide, C11H3N5O
- Crystal structure of (2,7-dihexyl-9,9-dimethyl-9H-xanthene-4,5-diyl)bis(diphenylphosphane), C51H56OP2
- Crystal structure of 5-((bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)methyl)quinolin-8-ol, C22H20N4O
- Crystal structure of 3-(2-(5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one, C28H20FN3O2S
- The crystal structure of [(tetra-μ2-2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(2,6-difluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N′)]dierbium(III) C66H34N4O12F12Er2
- Crystal structure of bis(3-chloro-N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)nickel(II), C26H20N8O2Cl2Ni
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C27H21N5O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)-N,N-dimethylformimidamide, C9H13N3O2S
- Crystal structure of η6-p-cymene-iodido-(N-isopropyl-1-(pyridin-2-yl)methanimine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate(V), C19H26IN2F6Ru
- Crystal structure of 6-iodo-3-phenyl-2-propylquinazolin-4(3H)-one, C17H15IN2O
- Low temperature redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[[tri-4-fluorobenzyltin(IV)]μ2-pyridine-4-carboxylato-κ2N:O], {C27H22F3NO2Sn}n
- Crystal structure of bis(2-propyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium) tetrachloridozincate(II), C10H13Cl4N2Zn
- The crystal structure of (Z)-3-hydrazono-5-nitroindolin-2-one – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1), C8H6N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis-[N-(1-pyrazin-2-yl-ethylidene)-cyanoacetic acid-hydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)]-zinc(II), C18H16N10O2Zn
- Crystal structure and photochromism of 1-(2,5-dimethyl-3-thienyl)-2-[2-methyl-5-(benzaldoxime)-3-thienyl] perfluorocyclopentene, C23H17F6NOS2

