Abstract
C9H7F3I3NO, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 7.5581(4) Å, b = 20.9303(11) Å, c = 9.3548(5) Å, β = 92.208(5)°, V = 1478.78(13) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0336, wRref(F2) = 0.0610, T = 290 K.
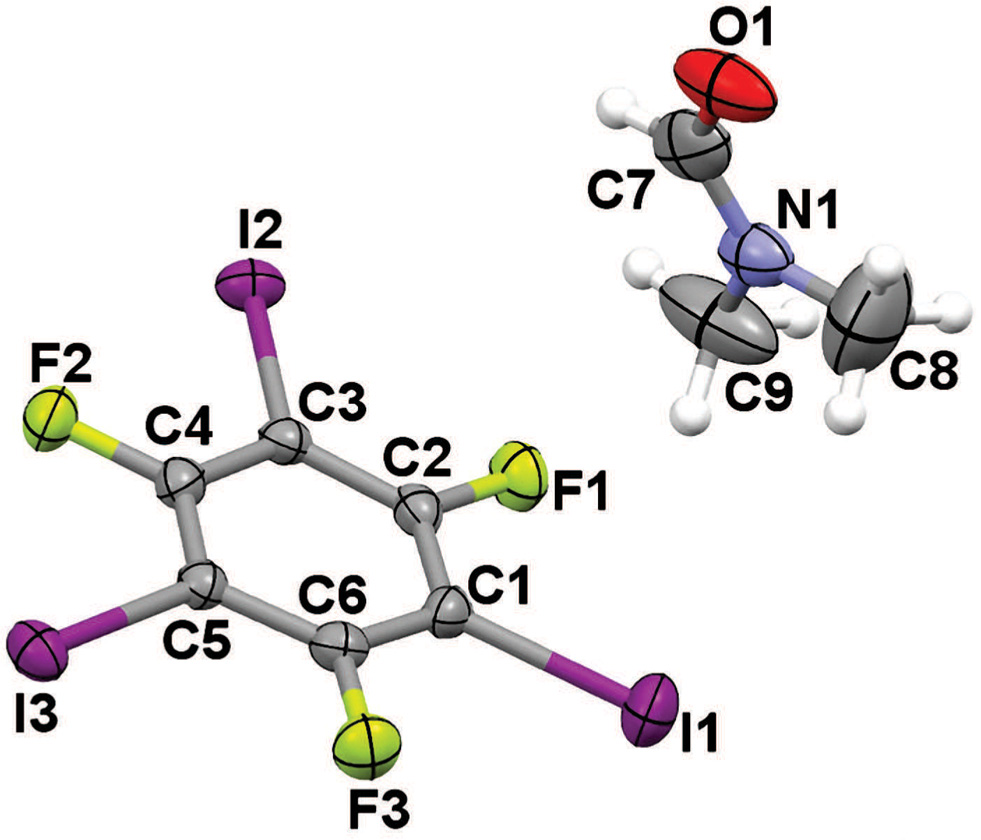
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, clear, colourless |
| Size: | 0.29 × 0.14 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 6.36 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω-scans |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 26.2°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 7946, 2695, 0.034 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2324 |
| N(param)refined: | 157 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2, 3] , OLEX2 [4] |
Source of material
The 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene and N,N-dimethylformamide were purchased from Aldrich Chemical Co., and used as received. The 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene (51.0 mg, 0.1 mmol) was dissolved in approximately 10 mL of N,N-dimethylformamide with gentle stirring at 50–60 °C. The undissolved materials were removed by filtration. The filtrate was set aside for crystallization by slow evaporation at room temperature. After a few days, colourless crystals of title compound were obtained.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 0.75542(6) | 0.54578(2) | 0.91796(4) | 0.07562(18) |
| I2 | 0.62380(5) | 0.35271(2) | 0.44873(4) | 0.05582(15) |
| I3 | 0.86979(5) | 0.62061(2) | 0.30805(4) | 0.05378(15) |
| F1 | 0.6449(4) | 0.41963(16) | 0.7510(3) | 0.0635(9) |
| F2 | 0.7455(4) | 0.47525(15) | 0.2763(3) | 0.0612(9) |
| F3 | 0.8575(5) | 0.62321(15) | 0.6439(4) | 0.0643(9) |
| C1 | 0.7510(7) | 0.5220(3) | 0.7017(5) | 0.0454(13) |
| C2 | 0.6981(7) | 0.4625(3) | 0.6550(5) | 0.0438(13) |
| C3 | 0.6973(6) | 0.4448(2) | 0.5121(6) | 0.0414(12) |
| C4 | 0.7471(6) | 0.4911(3) | 0.4161(5) | 0.0446(13) |
| C5 | 0.7998(6) | 0.5512(2) | 0.4553(5) | 0.0391(12) |
| C6 | 0.8026(6) | 0.5650(2) | 0.6003(6) | 0.0431(13) |
| O1 | 0.9966(8) | 0.2729(3) | 0.8581(7) | 0.112(2) |
| N1 | 0.7267(8) | 0.2921(3) | 0.9394(7) | 0.0774(17) |
| C7 | 0.8320(14) | 0.2689(4) | 0.8478(9) | 0.095(3) |
| H7 | 0.7820 | 0.2477 | 0.7686 | 0.113* |
| C8 | 0.7941(19) | 0.3249(7) | 1.0568(12) | 0.195(6) |
| H8A | 0.7475 | 0.3676 | 1.0559 | 0.292* |
| H8B | 0.9208 | 0.3265 | 1.0538 | 0.292* |
| H8C | 0.7609 | 0.3035 | 1.1425 | 0.292* |
| C9 | 0.5371(12) | 0.2862(5) | 0.9276(13) | 0.157(5) |
| H9A | 0.4956 | 0.2647 | 1.0106 | 0.236* |
| H9B | 0.5042 | 0.2621 | 0.8435 | 0.236* |
| H9C | 0.4849 | 0.3280 | 0.9209 | 0.236* |
Experimental details
H atom H7 was placed in at calculated position with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C). The H atoms of the methyl group were allowed to rotate with a fixed angle around the C—C bond to best fit the experimental electron density, with Uiso(H) set to 1.5Ueq(C).
Discussion
The crystal packing is a consequence of a delicate balance between many weak non-covalent intermolecular forces. Hence, different types of non-covalent interactions should be considered jointly in crystal structure analysis. These intermolecular interactions include: hydrogen bond [5], halogen bond [6], [7], [8], chalcogen bond [9], π⋯π stacking interaction [10], etc. Evidently, it is important to study the cooperation and competition between the directional or non-directional non-covalent interactions of different nature and strength in crystal engineering. In recent years, the key role of the halogen bond in crystal growth and design has been revealed both experimentally and theoretically [6], [7], [8]. The π⋯π stacking interaction is another one of the most important non-covalent driving forces for supramolecular assembly [10]. The structural competition between the C—I⋯N halogen bond and the π–π stacking interaction was investigated [11]. 1,3,5-Trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene and N,N-dimethylformamide are good candidates for the formation of the C—I⋯O halogen bond and the π⋯π stacking interaction, allowing to explore the cooperation and competition between the C—I⋯O halogen bond and the π⋯π stacking interaction.
All bond lengths and angles in the title crystal structure are in normal ranges. One N,N-dimethylformamide molecule and two 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene molecules are linked by two asymmetric bifurcated halogen bonds with d(I2⋯O1) = 2.913 Å, d(I3⋯O1) = 2.923 Å, <(C3—I2⋯O1) = 176.13° and <(C5—I3⋯O1) = 170.49°. At the same time, the π⋯π stacking interactions between two 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene molecules are present. All these non covalent bonds cooperate to construct a 2D network. According to the quantum chemical calculations [12, 13] , the π⋯π stacking interaction between two 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene molecules is much stronger than the halogen bond with the type of C—I⋯N, and the C—I⋯N halogen bond is much stronger than the C—I⋯O halogen bond.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21173113) and the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (Grant No. 13HASTIT015).
References
Agilent Technologies: CrysAlisPRO Software system, version 1.171.38.41r, Agilent Technologies UK Ltd, Oxford, UK (2015).Suche in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Suche in Google Scholar
Arunan, E.; Desiraju, G. R.; Klein, R. A.; Sadlej, J.; Scheiner, S.; Alkorta, I.; Clary, D. C.; Crabtree, R. H.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Hobza, P.; Kjaergaard, H. G.; Legon, A. C.; Mennucci, B.; Nesbitt, D. J.: Definition of the hydrogen bond. Pure Appl. Chem. 83 (2011) 1637–1641.10.1351/PAC-REC-10-01-02Suche in Google Scholar
Desiraju, G. R.; Ho, P. S.; Kloo, L.; Legon, A. C.; Marquardt, R.; Metrangolo, P.; Politzer, P.; Resnati, G.; Rissanen, K.: Definition of the halogen bond. Pure Appl. Chem. 85 (2013) 1711–1713.10.1351/PAC-REC-12-05-10Suche in Google Scholar
Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G.: The halogen bond. Chem. Rev. 116 (2016) 2478–2601.10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00484Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Jin, W. J.: σ–hole bond vs π–hole bond: A comparison based on halogen bond. Chem. Rev. 116 (2016) 5072–5104.10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00527Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
Wang, W.; Ji, B.; Zhang, Y.: Chalcogen bond: a sister noncovalent bond to halogen bond. J. Phys. Chem. A 113 (2009) 8132–8135.10.1021/jp904128bSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Kim, K. S.; Tarakeshwar, P.; Lee, J. Y.: Molecular clusters of π–systems: Theoretical studies of structures, spectra, and origin of interaction energies. Chem. Rev. 100 (2000) 4145–4186.10.1021/cr990051iSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Ji, B.; Wang, W.; Deng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhou, L.; Ruan, C.; Li, T.: Structural competition between π⋯π interactions and halogen bonds: a crystallographic study. CrystEngComm 15 (2013) 769–774.10.1039/C2CE26520FSuche in Google Scholar
Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-B.: The π⋯π stacking interactions between homogeneous dimers of C6FxI(6-x) (x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5): A comparative study with the halogen bond. J. Phys. Chem. A 116 (2012) 12486–12491.10.1021/jp308019kSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-B.: Unexpected strong stacking interactions between the homogeneous dimers of C6FxI(6-x) (x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5). Comput. Theor. Chem. 1023 (2013) 88–94.10.1016/j.comptc.2013.09.014Suche in Google Scholar
©2017 Limin Dang et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of potassium 1-methyl-1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole-5-thiolate, C2H3N4SK
- Crystal structure of bis(3-(3-ethylureido)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-aminium) bis (μ3-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(oxidomethyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato))-(μ6-oxo)-hexakis(μ2-oxo)-hexaoxo-hexavanadium(V) – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H60Cl2N6O23V6
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-methanolato-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-dimethanol-bis{6,6′-(1,3-dihydroxyl-2-acetylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(2-chloro-4-bromophenolato)}tetramanganese(III) C40H40Br4Cl4Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dibromo-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5)tetramanganese(III), C40H40Br8Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dichloro-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5), tetramanganese(III), C40H40Cl8Mn4O16
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)}copper(II), C34H34CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-hydroxy-3-{[2-hydroxybenzylidene]amino}phenyl)ethan-1-one, C15H13NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′′:O′′}tricobalt(II), C44H49Cl2Co3N6O12
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-2,4-dichloro-6-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ5O:O,N,N′,O′}dicobalt(II) acetone solvate, C43H48Br4Co2N6O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′:O′}trizinc(II), C44H49Cl2N6O12Zn3
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(N,N′-diethylamine)-5′-methoxy -2,2′-[ethylenediyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenolato}-bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)trizinc(II), C46H56Zn3N6O14
- Crystal structure of tris(cyano-(hydrogen tris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate))-iron(III) 4-methoxypyridinium monohydrate, C24H32BN10O2Fe
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{1-(((4-(1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)naphthalen-2-olato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C38H30CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-{[(E)-2-Hydroxy-1-naphthalenylmethylene] amino}phenyl)ethanone oxime, C19H16N2O2
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 2-(2-naphthalenyl)-3-nitro-2H-1-benzopyran, C38H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C19H14N2O2
- N′-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethyl-pyrrol-2-yl-methylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide monohydrate, C17H21N3O5
- The crystal structure of carbonyl-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenylamino)pent-3-en-2-onato-κ2N,O]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), RhC30H25Cl2NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-5-(diethylamino)-2-(((1,1,2-trihydroxyethyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C15H24N2O4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,4-bis((2-ethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)(μ2-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C34H30N4O4Cd
- Crystal structure of 5,6-Dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-a]chinolizinium 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate - methanol - water (1/1/1), C36H33NO10
- A single crystal study on 2-(methylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid, C9H9NO3
- Crystal structure of the salt 1,1′-(ethane-1,2-diyl)bis(1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium) diperchlorate, C14H28N4(ClO4)2
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis((E)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)cyclopentan-1-one, C21H14F6O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-benzene-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)] 1.25 hydrate, C25H26.5N3O8.25FZn
- Crystal structure of 1-methyl-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium poly[aqua-bis(μ2-perchlorato-κ3O,O′:O′′)sodium], C7H17Cl2N2NaO9
- Crystal structure of trimethyammonium 2,6-dicarboxyisonicotinate monohydrate, C11H16N2O7
- Crystal structure of dodecaguanidinium bis(tetrapropylammonium) heptacarbonate, C43H128N38O21
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ6-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)nickel(II)diyttrium(III)]dihydrate, C20H16NiO22Y2
- Halogen bonds and π–π interactions in the crystal structure of 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene–N,N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C9H7F3I3NO
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetraethylammonium carbonate dihydrate, C10H30N4O5
- The crystal structure of oxonium chlorido-ethylenediaminetetraactetotin(IV) hydrate, C10H17ClN2O10Sn
- Crystal structure of 8-((E)-((4-((E)-1-((benzyloxy)imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C26H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(diethylamino)-2-(((2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C40H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(tri(p-tolyl)phosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C29H28O5PRe
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(benzyldiphenylphosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C27H24O5PRe
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium bis{3-(((3-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N,O′}manganese(III), C46H38MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-ethyldimethylethanaminium) bis(heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II), C12H32N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of bis(4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2-(2-((2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetate-κO)cadmium(II), C44H34N8CdCl4O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(pyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′] dihydrate, C48H42O22N2Ca
- The crystal structure of (S)-2-benzylsuccinic acid, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-4-(pyridin-4-yl)isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′)yttrium(III)], C26H17N2O9Y
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C14H17N3O2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(methanol-κO)-bis{μ2-3-((4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olate-κ4O,N;O′:O′}dizinc(II), C38H38Zn2N2O14
- Crystal structure of bromido(4,4′-dimethoxy-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)(isopropyl(diphenyl)phosphane-κP)copper(I), C27H29BrCuN2O2P
- Crystal structure of bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane)-9,9-dioctylfluorene, C41H64B2O4
- Crystal structure of 11-oxo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H,5H,11H-pyrano[2,3-f]pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-10-carbaldehyde - a julolidine derivative, C16H15NO3
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-5,5-dibenzylbarbituric acid, C20H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium) poly[bis(μ2-heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II)], C10H28N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of 1-{4-[(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl} ethanone O-ethyl-oxime, C17H17ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of methyl N-(4-bromophenyl)carbamate, C8H8BrNO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-{4-[(2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone oxime, C15H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-butanebis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(hexafluorophosphate), C12H20F12N4P2
- (E)-N-benzylidene-3-(benzylthio)-5-p-tolyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-amine, C23H20N4S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-1-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C11H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,5-difluoro-10-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-4l4,5l4-dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine - a Z′ = 3 structure, C19H18B2F3N2
- The crystal structure of the Matrine derivative: 12-(1H-indol-1-yl)dodecahydro-1H,5H,10H-dipyrido[2,1-f:3′,2′,1′-ij][1,6]naphthyridin-10-one hydrate, C23H29N3O
- The crystal structure of tris(μ2-1,3-bis(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxido-1-(oxo)but-2-en-1-yl)phenyl-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(1,2-dimethoxyethane-κ2O,O′)dilutetium(III), C50H38F18Lu2O16
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(3-(2-(4-chlorobenzoyl)hydrazono)-2-oxoindolin-1-yl) acetic acid, C17H12ClN3O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraqua-bis(2-(((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)ammonio)acetato-κO)cobalt(II) hexahydrate, C36H48CoN2O28S2
- The crystal structure of N,N-dimethyl-2,6-di-p-tolylpyrimidin-4-amine, C20H21N3
- The crystal structure (E)-4-methyl-N′-(2-nitrobenzylidene)benzenesulfonohydrazide, C14H13N3O4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane κ2N:N′)-(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] hydrate, C26H24ZnN4O6
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(quinolin-2-ylmethylene)furan-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C15H13N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2,8-diphenyl-3,7,9-trioxa-1-azaspiro[4.5]dec-1-ene, C18H17N1O3
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxane-5,5-dicarboxylate, C16H19ClO6
- Crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole 3-oxide, C8H7N3O3
- Crystal structure of (acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(2-amino-6-chlorobenzoato-κO)-oxido(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)vanadium(IV) – trichloromethane (1/1)
- Crystal structure of (1E,4E)-1,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one, C17H12Cl2O
- The crystal structure of trans-dibromido-bis(pyridine-κN)platinum(II), C10H10Br2N2Pt
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of potassium 1-methyl-1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole-5-thiolate, C2H3N4SK
- Crystal structure of bis(3-(3-ethylureido)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-aminium) bis (μ3-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(oxidomethyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato))-(μ6-oxo)-hexakis(μ2-oxo)-hexaoxo-hexavanadium(V) – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H60Cl2N6O23V6
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-methanolato-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-dimethanol-bis{6,6′-(1,3-dihydroxyl-2-acetylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(2-chloro-4-bromophenolato)}tetramanganese(III) C40H40Br4Cl4Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dibromo-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5)tetramanganese(III), C40H40Br8Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dichloro-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5), tetramanganese(III), C40H40Cl8Mn4O16
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)}copper(II), C34H34CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-hydroxy-3-{[2-hydroxybenzylidene]amino}phenyl)ethan-1-one, C15H13NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′′:O′′}tricobalt(II), C44H49Cl2Co3N6O12
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-2,4-dichloro-6-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ5O:O,N,N′,O′}dicobalt(II) acetone solvate, C43H48Br4Co2N6O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′:O′}trizinc(II), C44H49Cl2N6O12Zn3
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(N,N′-diethylamine)-5′-methoxy -2,2′-[ethylenediyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenolato}-bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)trizinc(II), C46H56Zn3N6O14
- Crystal structure of tris(cyano-(hydrogen tris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate))-iron(III) 4-methoxypyridinium monohydrate, C24H32BN10O2Fe
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{1-(((4-(1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)naphthalen-2-olato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C38H30CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-{[(E)-2-Hydroxy-1-naphthalenylmethylene] amino}phenyl)ethanone oxime, C19H16N2O2
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 2-(2-naphthalenyl)-3-nitro-2H-1-benzopyran, C38H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C19H14N2O2
- N′-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethyl-pyrrol-2-yl-methylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide monohydrate, C17H21N3O5
- The crystal structure of carbonyl-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenylamino)pent-3-en-2-onato-κ2N,O]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), RhC30H25Cl2NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-5-(diethylamino)-2-(((1,1,2-trihydroxyethyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C15H24N2O4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,4-bis((2-ethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)(μ2-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C34H30N4O4Cd
- Crystal structure of 5,6-Dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-a]chinolizinium 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate - methanol - water (1/1/1), C36H33NO10
- A single crystal study on 2-(methylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid, C9H9NO3
- Crystal structure of the salt 1,1′-(ethane-1,2-diyl)bis(1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium) diperchlorate, C14H28N4(ClO4)2
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis((E)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)cyclopentan-1-one, C21H14F6O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-benzene-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)] 1.25 hydrate, C25H26.5N3O8.25FZn
- Crystal structure of 1-methyl-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium poly[aqua-bis(μ2-perchlorato-κ3O,O′:O′′)sodium], C7H17Cl2N2NaO9
- Crystal structure of trimethyammonium 2,6-dicarboxyisonicotinate monohydrate, C11H16N2O7
- Crystal structure of dodecaguanidinium bis(tetrapropylammonium) heptacarbonate, C43H128N38O21
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ6-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)nickel(II)diyttrium(III)]dihydrate, C20H16NiO22Y2
- Halogen bonds and π–π interactions in the crystal structure of 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene–N,N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C9H7F3I3NO
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetraethylammonium carbonate dihydrate, C10H30N4O5
- The crystal structure of oxonium chlorido-ethylenediaminetetraactetotin(IV) hydrate, C10H17ClN2O10Sn
- Crystal structure of 8-((E)-((4-((E)-1-((benzyloxy)imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C26H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(diethylamino)-2-(((2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C40H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(tri(p-tolyl)phosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C29H28O5PRe
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(benzyldiphenylphosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C27H24O5PRe
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium bis{3-(((3-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N,O′}manganese(III), C46H38MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-ethyldimethylethanaminium) bis(heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II), C12H32N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of bis(4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2-(2-((2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetate-κO)cadmium(II), C44H34N8CdCl4O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(pyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′] dihydrate, C48H42O22N2Ca
- The crystal structure of (S)-2-benzylsuccinic acid, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-4-(pyridin-4-yl)isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′)yttrium(III)], C26H17N2O9Y
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C14H17N3O2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(methanol-κO)-bis{μ2-3-((4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olate-κ4O,N;O′:O′}dizinc(II), C38H38Zn2N2O14
- Crystal structure of bromido(4,4′-dimethoxy-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)(isopropyl(diphenyl)phosphane-κP)copper(I), C27H29BrCuN2O2P
- Crystal structure of bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane)-9,9-dioctylfluorene, C41H64B2O4
- Crystal structure of 11-oxo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H,5H,11H-pyrano[2,3-f]pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-10-carbaldehyde - a julolidine derivative, C16H15NO3
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-5,5-dibenzylbarbituric acid, C20H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium) poly[bis(μ2-heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II)], C10H28N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of 1-{4-[(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl} ethanone O-ethyl-oxime, C17H17ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of methyl N-(4-bromophenyl)carbamate, C8H8BrNO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-{4-[(2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone oxime, C15H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-butanebis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(hexafluorophosphate), C12H20F12N4P2
- (E)-N-benzylidene-3-(benzylthio)-5-p-tolyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-amine, C23H20N4S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-1-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C11H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,5-difluoro-10-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-4l4,5l4-dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine - a Z′ = 3 structure, C19H18B2F3N2
- The crystal structure of the Matrine derivative: 12-(1H-indol-1-yl)dodecahydro-1H,5H,10H-dipyrido[2,1-f:3′,2′,1′-ij][1,6]naphthyridin-10-one hydrate, C23H29N3O
- The crystal structure of tris(μ2-1,3-bis(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxido-1-(oxo)but-2-en-1-yl)phenyl-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(1,2-dimethoxyethane-κ2O,O′)dilutetium(III), C50H38F18Lu2O16
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(3-(2-(4-chlorobenzoyl)hydrazono)-2-oxoindolin-1-yl) acetic acid, C17H12ClN3O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraqua-bis(2-(((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)ammonio)acetato-κO)cobalt(II) hexahydrate, C36H48CoN2O28S2
- The crystal structure of N,N-dimethyl-2,6-di-p-tolylpyrimidin-4-amine, C20H21N3
- The crystal structure (E)-4-methyl-N′-(2-nitrobenzylidene)benzenesulfonohydrazide, C14H13N3O4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane κ2N:N′)-(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] hydrate, C26H24ZnN4O6
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(quinolin-2-ylmethylene)furan-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C15H13N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2,8-diphenyl-3,7,9-trioxa-1-azaspiro[4.5]dec-1-ene, C18H17N1O3
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxane-5,5-dicarboxylate, C16H19ClO6
- Crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole 3-oxide, C8H7N3O3
- Crystal structure of (acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(2-amino-6-chlorobenzoato-κO)-oxido(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)vanadium(IV) – trichloromethane (1/1)
- Crystal structure of (1E,4E)-1,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one, C17H12Cl2O
- The crystal structure of trans-dibromido-bis(pyridine-κN)platinum(II), C10H10Br2N2Pt

