Abstract
Vergence and accommodation responses of human vision are very important factors when a 3D image is observed, and a vergence-accommodation conflict (VAC) causes perceptual distortion, visual discomfort, and fatigue for an observer. Theoretically, a hologram is expected to provide a 3D image without such a conflict. In this article, natural focusing was verified by human accommodation response (A-R) measurement during on-axis analog reflection Denisyuk hologram observation. The A-R of a group of participants were measured for a real marker and its Denisyuk hologram at various visualization distances using an Nvision K5001 autorefractor. The experimental results statistically confirmed the equivalence of the responses to the Denisyuk hologram and its real counterpart, as well as the absence of a VAC.
1 Introduction
Most of the current approaches to creating three-dimensional (3D) images use a single-eye mechanism, the binocular-stereoscopic-depth perception principle that shows the plasticity of objects well but dissociates the natural coupling between vergence and accommodation [18]. Some well-known examples of 3D displays using this principle are polarized 3D glasses to watch 3D films on a computer or movie screen, virtual reality (VR) headsets, or Microsoft Hololens smart glasses (Figure 1). This vergence-accommodation conflict causes perceptual distortions, and visual discomfort and fatigue when these stereoscopic displays are used for too long [19,20].

3D displays using the stereoscopic principle: polarized 3D glasses (a), VR headsets (b), and Microsoft hololens (c) (public domain).
Accommodation refers to the muscle tension used to adjust the eye’s focal distance. The convergence is the angular difference in the viewing directions between a person’s left and right eye when they look at the same fixing point. Figure 2(a) shows the change in the thickness of a crystalline lens to focus the image on the retina when a human observes an object at either a far or near distance. When looking at the object at a near distance, the thickness of the crystalline lens becomes thicker because of the contraction of the ciliary muscle and relaxation of the ciliary zonule. When observing an object at a far distance, the thickness of the crystalline lens becomes thin as a result of the relaxation of the ciliary muscle and contraction of the ciliary zonule. When accommodation occurs, an adjustment of the thickness of the crystalline lens occurs. And, when the accommodation contracts, the radius of curvature decreases and the refractive power increases. On the other hand, when the accommodation is relaxed, the radius of curvature increases and the refractive power decreases. Figure 2(b) shows the change in convergence angle that occurs when a human observes an object at either a far or near distance. The convergence angle is the intersection of the left and right eye when a human looks at the convergence point.

Accommodation and convergence: (a) accommodation and (b) convergence.
Accommodation and convergence function together. When we look at an object at a near distance, the crystalline lens becomes thick. At the same time, the convergence angle becomes large. Conversely, when we look at an object at a far distance, the crystalline lens becomes thin, while the convergence angle becomes small.
Additionally, because both eyes are separated by approximately 60 mm, a difference occurs in the relative positional relationship between images formed on the right and the left retina. This is called binocular disparity [13]. Accommodation, convergence, binocular disparity, and other factors enable humans to see objects in three dimensions.
A hologram-theorized in 1948 by the British-Hungarian physicist Gabor [1] – is a recording in a medium of the interference pattern formed when a light reference beam of fixed wavelength encounters light arriving from the object beam. When the hologram is illuminated by the reference beam alone, the diffraction pattern recreates the wave fronts of light from the original object and a viewer sees a 3D image indistinguishable from the original object. For this reason, a hologram is expected to provide a 3D image that does not cause visual fatigue, which is a result of the conflict between accommodation and vergence.
Studies related to the visual perception of holograms have suggested that holography provides natural parallax and focusing, but these studies have been conducted mostly on the view angle of observers [2,3,4]. The study of the accommodation of the human eye using some types of holograms has been an area of research for the past 10 years. Several studies with quantitative measurements of the accommodation of the human eye using computer-generated holograms (CGHs) [5,6] and off-axis Leith and Upatnieks holograms [7,8] have been conducted. CGHs of these studies use electronic devices such as liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and spatial lighting modulator (SLM) instead of silver halide plates to display holograms, while off-axis Leith and Upatnieks holograms are monochrome analog transmission holograms [9] visible only with laser light illumination. These studies confirmed that there was no problem of accommodation-vergence for these two types of holograms.
There is another kind of hologram, introduced in 1965 by the Russian scientist Yuri Denisyuk [10] with the single-beam reflection holographic technique, for which the accommodation of the human eye has not been verified. The most recent generation of full-color on-axis analog reflection Denisyuk holograms is categorized as ultra-realistic because it is difficult for a spectator to discriminate between these holograms and their real counterparts [11,12]; furthermore, unlike transmission holograms, Denisyuk holograms can be observed using a white light source on the same side of the hologram as the spectator. Quantitative measurement of the accommodation reaction of eyes has been conducted in this article to verify the natural parallax and focusing when observing a Denisyuk hologram of a marker (a cardboard card representing a drawing), with a group of participants and an autorefractor, and a statistical test has been performed to analyze the results.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials for recording and developing the hologram
The hologram was recorded on iso-panchromatic silver-halide holographic material
2.2 Method to obtain a reflection analog hologram of the marker
A two-color reflection analog hologram of the marker was recorded with the on-axis single-beam Denisyuk technique. The recording setup used two different laser beamsŰred and greenŰcombined with an X-cube prism to give a yellow laser beam. As the marker is yellow and black, it was not necessary to add a blue laser to obtain a realistic hologram of the original. After passing through a spatial filter, the divergent yellow beam illuminated both the holographic plate and the marker (Figure 3) at an angle of 45 degrees. The marker was positioned exactly 67 mm below the holographic plate.

Two-color single-beam reflection setup to record Denisyuk hologram.
2.3 Method to illuminate a reflection analog hologram
To illuminate and reconstruct the hologram of the marker, the lamp has to be placed facing the holographic plate at the correct angle and position. The choice of the illumination source is important in full-color reflection holography because the light must be a source point and match the wavelengths of the original recording lasers. RGB LEDs currently offer the best solution because their wavelengths are centered on the lasers’ wavelengths, with no unwanted colors, which usually create diffusion [15]. To illuminate the hologram, a 3 W RGB LED was chosen and placed 50 cm from the center of the hologram at a 45-degree angle. The spectrum and the color gamut in CIE 1931 color space of our RGB LED are shown in Figure 4(a) and (b).

RGB LED spectrum (a) and color gamut in CIE 1931 color space (b).
2.4 Materials to measure the accommodative response
In this article, an open automatic refractometer was used as an accommodative response measurement method. The accommodative response under binocular viewing conditions was measured using an N-vision K5001 [16] autorefractor from Shin-Nippon. An autorefractor [17] is a computer-controlled machine commonly used during an eye examination to provide an objective measurement of a patient’s refractive error. This experiment is to observe the accommodative response of the crystalline lens when the ocular is subjected to an external near stimulus. The N-vision K5001 wide-view window allows the subject to naturally look with both eyes and relax during measurement (Figure 5(a)). Tests can be performed with an attached near marker (Figure 5(b)).
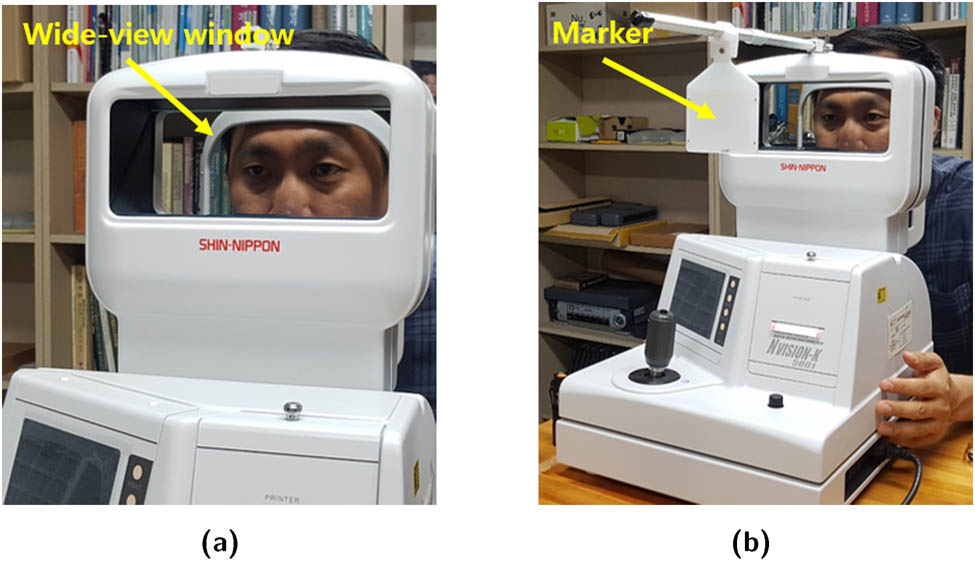
N-vision K5001 autorefractor: (a) wide-view window and (b) attached near marker.
2.5 Method to verify the accommodative response
The accommodative response of the eye was measured with an N-vision K5001 for a group of participants with a real marker and its hologram placed at various positions.
2.5.1 Hypothesis
The hypothesis is that the accommodative response for the holographic marker was not made on the plane of the holographic plate but, on the contrary, 67 mm behind this position, where the virtual holographic image of the marker is reconstructed by the RGB illumination.
2.5.2 Participants
A total of 30 participants ranging from 20 to 30 years old (mean:
2.5.3 Experimental design
Three experimental setups were used to verify the hypothesis. In the first setup, a real marker was attached in front of the N-vision K5001 autorefractor at a distance of 3.00 diopters (D), as shown in Figure 6(a). The accommodative response of the eye was then measured for each participant. In the second setup, the same real marker was this time attached at a distance of 2.50 D, as shown in Figure 6(b). At 2.50 D parallel rays of light focus at 40.0 cm. The accommodative response of the eye was then measured for each participant. In the third setup, the hologram of the marker-illuminated with a RGB LED lamp at a 45-degree angle-was attached at a distance of 3.00 D (Figure 6(c)). The accommodative response of the eye was then measured for each participant. In the experiment, we measured by setting Auto-Refractor (NVision-K5001, Shin-Nippon) in 0.125 D units. In optometry, it was determined that the difference in the diopter (0.25 D) was in the range of the error of measurement. In this experiment, the measurement distances were set to 2.50 and 3.00 D to set the difference (0.50 D) between the two-stage diopters. Accordingly, when the hologram target was set at a distance of 3.00 D, the hologram image was reconstructed at 2.50 D. In this experiment, the illumination conditions were set to maintain brightness that does not interfere with the measurement of refractive power. The wall was set to be a uniform white color, and there were no objects obstructing the visual field around the target. The subjects measured three times at each location (real marker 3.00 D, real marker 2.50 D, and hologram marker 3.00 D) and used the average value for statistics.

Experimental environment: (a) a real marker is placed 3.00 D from the viewer; (b) a real marker is placed 2.50 D from the viewer; and (c) a holographic marker, illuminated with a white LED lamp, is placed 3.00 D from the viewer.
2.5.4 Data analysis
For data analysis, a paired sample t-test was performed using SPSS software, Ver. 18.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The paired sample t-test is a statistical procedure used to determine whether the mean difference between two sets of observations is zero. In a t-test, each entity is measured twice, resulting in pairs of observations. Statistical significance is determined by looking at the
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Holographic marker
A Denisyuk hologram of the marker was recorded on a U04 glass plate according to the Denisyuk method (Figure 7(a)) and developed in two chemical baths. After processing, a blur-free, two-color, transparent 1:1 scale image was obtained. When illuminated at the proper distance with an RGB LED lamp, a sharp holographic reconstruction of the marker appeared completely behind the glass plate surface with a

Recording (a) and reconstruction (b) of the marker hologram.
3.2 Accommodative responses
The accommodative response of the eye was measured for each participant, with a real marker attached at a distance of 2.50 and 3.00 D and a holographic marker attached at 3.00 D. The experimental results found with the N-vision K5001 autorefractor are shown in Figure 8.

Accommodative response to each distance stimulus
3.2.1 Comparison between a 3.00 and 2.50 D stimulus of a real marker
A t-test was performed to compare the accommodative response in the observation of a real marker between a 3.00 D stimulus and a 2.50 D stimulus. The accommodative response to the 3.00 D stimulus was significantly
Comparison of accommodative response for a real marker at 2.50 and 3.00 D
|
|
MD | t | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.00 D | 2.50 D | −0.49 | −11.188 |
|
| (
|
(
|
|||
SD: standard deviation.
MD: mean difference.
These results confirm that the accommodative response of the eyes of an observer measured with the N-vision K5001 is different, if the real marker is placed at 3.00 or 2.50 D.
3.2.2 Comparison between a 3.00 D stimulus of a real marker and a 3.00 D stimulus of a holographic marker
Table 2 presents a comparison of the accommodative response between a 3.00 D stimulus of a real marker and a 3.00 D stimulus of a holographic marker.
Comparison of accommodative response for real and holographic markers at 3.00 D
|
|
MD | t | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.00 D | Hologram | −0.46 | −9.020 |
|
| (
|
(
|
|||
SD: standard deviation.
MD: mean difference.
The results show that the accommodative response to a stimulus of a real marker was significantly
3.2.3 Comparison between a 2.50 D stimulus of a real marker and a 3.00 D stimulus of a holographic marker
Table 3 shows results of comparison of accommodative response of the viewers eyes between a 2.50 D stimulus of a real marker and a 3.00 D stimulus of an holographic marker.
Comparison of accommodative response for a real marker at 2.50 D and a holographic marker at 3.00 D
|
|
MD | t | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.50 D | Hologram | 0.03 | 1.111 | 0.274 |
| (
|
(
|
|||
SD: standard deviation.
MD: mean difference.
The accommodative response to the 3.00 D holographic marker stimulus was slightly higher
4 Conclusions
Experimental results verify that an on-axis analog reflection Denisyuk hologram provides a complete 3D image and can be naturally observed because the accommodative response and the convergence response are generated in accordance with the position where the image is reconstructed. So there is no vergence-accommodation conflict in a Denisyuk hologram. This study can be applied to human ocular physiological viewpoints of quantitative evaluation indices of analog reflection holographic images. In the case of a subject wearing spectacles, measurement with an Auto-Refractor may cause an error in the measured value due to light reflex. As a result, it is judged that the standard deviation was relatively high. However, the final mean value of the experimental result data is calculated by including the accommodative lag in ocular physiology.
Acknowledgement
The work reported in this article was conducted during the sabbatical year of Kwangwoon University in 2017. This research was supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2021-0-01846) supervised by the IITP (Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation). This research was supported by Institute of Information communications Technology Planning Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021-0-00922, Development of holographic stereogram printing technology based on multi-view imaging).
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Gabor D. A new microscopic principle. Nature 1948;161:777–8. 10.1038/161777a0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Reichelt S, Häussler R, Fütterer G, Leister N. Depth cues in human visual perception and their realization in 3D displays. Three dimensional imaging, visualization, and display, Proc. SPIE 7690; 2010.10.1117/12.850094Search in Google Scholar
[3] Barabas J, Bove VM. Visual perception and holographic displays. J Phys. 2013;415:25–9.10.1088/1742-6596/415/1/012056Search in Google Scholar
[4] Park MC, Mun SC. Overview of measurement methods for factors affecting the human visual system in 3D displays. J Display Technol. 2015;11:877–88. 10.1109/JDT.2015.2389212Search in Google Scholar
[5] Ohara R, Kurita M, Yoneyama T, Okuyama F, Sakamoto Y. Response of accommodation and vergence to electro-holographic images. Appl Opt. 2015;54(4):615–21. 10.1364/AO.54.000615Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Takaki Y, Yokouchi M. Accommodation measurements of horizontally scanning holographic display. Opt Express. 2012;20:3918–31. 10.1117/12.907574Search in Google Scholar
[7] Avudainayagam KV, Avudainayagam CS, Nguyen N, Chiam KW, Truong C. Performance of the holographic multivergence target in the subjective measurement of spherical refractive error and amplitude of accommodation of the human eye. J Opt Soc Am A. 2007;24(10):3037–44. 10.1364/JOSAA.24.003037Search in Google Scholar
[8] Avudainayagam KV, Avudainayagam CS. Holographic multivergence target for subjective measurement of the astigmatic error of the human eye. Opt Lett. 2007;32:1926–8. 10.1364/OL.32.001926Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Leith EN, Upatnieks J. Reconstructed wavefronts and communication theory. J Opt Soc Am. 1962;52:1123–30. 10.1364/JOSA.52.001123Search in Google Scholar
[10] Denisyuk YN. On the reproduction of the optical properties of an object by the wave field of its scattered radiation. Opt Spectrosc. 1963;14:279–84. Search in Google Scholar
[11] Gentet P, Gentet Y, Choi PH, Lee SH. Evaluation of the realism of a full-color reflection H2 analog hologram recorded on ultra-fine-grain silver-halide material. Open Phys. 2019;17(1):449–57. 10.1515/phys-2019-0046Search in Google Scholar
[12] Bjelkhagen H, Brotherton-Ratcliffe D. Ultra-realistic imaging: advanced techniques in analogue and digital colour holography. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2013. Search in Google Scholar
[13] Fiorentini A, Maffei L. Electrophysiological evidence for binocular disparity detectors in human visual system. Science. 1970;1699:208–9. 10.1126/science.169.3941.208Search in Google Scholar
[14] Gentet P, Gentet Y, Lee SH. Ultimate 04 the new reference for ultra-realistic color holography. In Emerging Trends Innovation in ICT(ICEI) 2017 International Conference on IEEE; 2017. p. 162–6. 10.1109/ETIICT.2017.7977030Search in Google Scholar
[15] Gentet P, Gentet Y, Lee SH. New LEDas wavelengths improve drastically the quality of illumination of pulsed digital holograms. In digital holography and three-dimensional imaging. OSA (Optical Society of America) Publishing; 2017 May. p. M3A-4. 10.1364/DH.2017.M3A.4Search in Google Scholar
[16] Davies LN, Mallen EA, Wolffsohn JS, Gilmartin B. Clinical evaluation of the Shin-Nippon NVision-K 5001/Grand Seiko WR-5100K autorefractor. Optom Vis Sci. 2003;80:320–4. 10.1097/00006324-200304000-00011Search in Google Scholar
[17] Han GA, Hwang JH, Mah KC. Objective measurement of accommodative responses with open-field autorefractor. Korean J Vis Sci. 2009;11:35–44. Search in Google Scholar
[18] Wann JP, Rushton S, Mon-Williams M. Natural problems for stereoscopic depth perception in virtual environments. Vis Res. 1995;35(19):33. 10.1016/0042-6989(95)00018-USearch in Google Scholar
[19] Hoffman DM, Girshick AR, Akeley K, Banks MS. Vergence-accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue. J Vision. 2008;8(3):2731–6. 10.1167/8.3.33Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Lambooij M, Fortuin M, Heynderickx I, IJsselsteijn W. Visual discomfort and visual fatigue of stereoscopic displays: A review. J Imag Sci Technol. 2009;53(3):30201-1. 10.2352/J.ImagingSci.Technol.2009.53.3.030201Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Seunghyun Lee et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Circular Rydberg states of helium atoms or helium-like ions in a high-frequency laser field
- Closed-form solutions and conservation laws of a generalized Hirota–Satsuma coupled KdV system of fluid mechanics
- W-Chirped optical solitons and modulation instability analysis of Chen–Lee–Liu equation in optical monomode fibres
- The problem of a hydrogen atom in a cavity: Oscillator representation solution versus analytic solution
- An analytical model for the Maxwell radiation field in an axially symmetric galaxy
- Utilization of updated version of heat flux model for the radiative flow of a non-Newtonian material under Joule heating: OHAM application
- Verification of the accommodative responses in viewing an on-axis analog reflection hologram
- Irreversibility as thermodynamic time
- A self-adaptive prescription dose optimization algorithm for radiotherapy
- Algebraic computational methods for solving three nonlinear vital models fractional in mathematical physics
- The diffusion mechanism of the application of intelligent manufacturing in SMEs model based on cellular automata
- Numerical analysis of free convection from a spinning cone with variable wall temperature and pressure work effect using MD-BSQLM
- Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic oscillation of side-by-side double-floating-system with a narrow gap in waves
- Closed-form solutions for the Schrödinger wave equation with non-solvable potentials: A perturbation approach
- Study of dynamic pressure on the packer for deep-water perforation
- Ultrafast dephasing in hydrogen-bonded pyridine–water mixtures
- Crystallization law of karst water in tunnel drainage system based on DBL theory
- Position-dependent finite symmetric mass harmonic like oscillator: Classical and quantum mechanical study
- Application of Fibonacci heap to fast marching method
- An analytical investigation of the mixed convective Casson fluid flow past a yawed cylinder with heat transfer analysis
- Considering the effect of optical attenuation on photon-enhanced thermionic emission converter of the practical structure
- Fractal calculation method of friction parameters: Surface morphology and load of galvanized sheet
- Charge identification of fragments with the emulsion spectrometer of the FOOT experiment
- Quantization of fractional harmonic oscillator using creation and annihilation operators
- Scaling law for velocity of domino toppling motion in curved paths
- Frequency synchronization detection method based on adaptive frequency standard tracking
- Application of common reflection surface (CRS) to velocity variation with azimuth (VVAz) inversion of the relatively narrow azimuth 3D seismic land data
- Study on the adaptability of binary flooding in a certain oil field
- CompVision: An open-source five-compartmental software for biokinetic simulations
- An electrically switchable wideband metamaterial absorber based on graphene at P band
- Effect of annealing temperature on the interface state density of n-ZnO nanorod/p-Si heterojunction diodes
- A facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic adsorption material 5A zeolite for oil–water separation with potential use in floating oil
- Shannon entropy for Feinberg–Horodecki equation and thermal properties of improved Wei potential model
- Hopf bifurcation analysis for liquid-filled Gyrostat chaotic system and design of a novel technique to control slosh in spacecrafts
- Optical properties of two-dimensional two-electron quantum dot in parabolic confinement
- Optical solitons via the collective variable method for the classical and perturbed Chen–Lee–Liu equations
- Stratified heat transfer of magneto-tangent hyperbolic bio-nanofluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms: Keller-Box solution technique
- Analysis of the structure and properties of triangular composite light-screen targets
- Magnetic charged particles of optical spherical antiferromagnetic model with fractional system
- Study on acoustic radiation response characteristics of sound barriers
- The tribological properties of single-layer hybrid PTFE/Nomex fabric/phenolic resin composites underwater
- Research on maintenance spare parts requirement prediction based on LSTM recurrent neural network
- Quantum computing simulation of the hydrogen molecular ground-state energies with limited resources
- A DFT study on the molecular properties of synthetic ester under the electric field
- Construction of abundant novel analytical solutions of the space–time fractional nonlinear generalized equal width model via Riemann–Liouville derivative with application of mathematical methods
- Some common and dynamic properties of logarithmic Pareto distribution with applications
- Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model
- Fractional modeling of COVID-19 epidemic model with harmonic mean type incidence rate
- Liquid metal-based metamaterial with high-temperature sensitivity: Design and computational study
- Biosynthesis and characterization of Saudi propolis-mediated silver nanoparticles and their biological properties
- New trigonometric B-spline approximation for numerical investigation of the regularized long-wave equation
- Modal characteristics of harmonic gear transmission flexspline based on orthogonal design method
- Revisiting the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations
- Time-periodic pulse electroosmotic flow of Jeffreys fluids through a microannulus
- Exact wave solutions of the nonlinear Rosenau equation using an analytical method
- Computational examination of Jeffrey nanofluid through a stretchable surface employing Tiwari and Das model
- Numerical analysis of a single-mode microring resonator on a YAG-on-insulator
- Review Articles
- Double-layer coating using MHD flow of third-grade fluid with Hall current and heat source/sink
- Analysis of aeromagnetic filtering techniques in locating the primary target in sedimentary terrain: A review
- Rapid Communications
- Nonlinear fitting of multi-compartmental data using Hooke and Jeeves direct search method
- Effect of buried depth on thermal performance of a vertical U-tube underground heat exchanger
- Knocking characteristics of a high pressure direct injection natural gas engine operating in stratified combustion mode
- What dominates heat transfer performance of a double-pipe heat exchanger
- Special Issue on Future challenges of advanced computational modeling on nonlinear physical phenomena - Part II
- Lump, lump-one stripe, multiwave and breather solutions for the Hunter–Saxton equation
- New quantum integral inequalities for some new classes of generalized ψ-convex functions and their scope in physical systems
- Computational fluid dynamic simulations and heat transfer characteristic comparisons of various arc-baffled channels
- Gaussian radial basis functions method for linear and nonlinear convection–diffusion models in physical phenomena
- Investigation of interactional phenomena and multi wave solutions of the quantum hydrodynamic Zakharov–Kuznetsov model
- On the optical solutions to nonlinear Schrödinger equation with second-order spatiotemporal dispersion
- Analysis of couple stress fluid flow with variable viscosity using two homotopy-based methods
- Quantum estimates in two variable forms for Simpson-type inequalities considering generalized Ψ-convex functions with applications
- Series solution to fractional contact problem using Caputo’s derivative
- Solitary wave solutions of the ionic currents along microtubule dynamical equations via analytical mathematical method
- Thermo-viscoelastic orthotropic constraint cylindrical cavity with variable thermal properties heated by laser pulse via the MGT thermoelasticity model
- Theoretical and experimental clues to a flux of Doppler transformation energies during processes with energy conservation
- On solitons: Propagation of shallow water waves for the fifth-order KdV hierarchy integrable equation
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part II
- Numerical study on heat transfer and flow characteristics of nanofluids in a circular tube with trapezoid ribs
- Experimental and numerical study of heat transfer and flow characteristics with different placement of the multi-deck display cabinet in supermarket
- Thermal-hydraulic performance prediction of two new heat exchangers using RBF based on different DOE
- Diesel engine waste heat recovery system comprehensive optimization based on system and heat exchanger simulation
- Load forecasting of refrigerated display cabinet based on CEEMD–IPSO–LSTM combined model
- Investigation on subcooled flow boiling heat transfer characteristics in ICE-like conditions
- Research on materials of solar selective absorption coating based on the first principle
- Experimental study on enhancement characteristics of steam/nitrogen condensation inside horizontal multi-start helical channels
- Special Issue on Novel Numerical and Analytical Techniques for Fractional Nonlinear Schrodinger Type - Part I
- Numerical exploration of thin film flow of MHD pseudo-plastic fluid in fractional space: Utilization of fractional calculus approach
- A Haar wavelet-based scheme for finding the control parameter in nonlinear inverse heat conduction equation
- Stable novel and accurate solitary wave solutions of an integrable equation: Qiao model
- Novel soliton solutions to the Atangana–Baleanu fractional system of equations for the ISALWs
- On the oscillation of nonlinear delay differential equations and their applications
- Abundant stable novel solutions of fractional-order epidemic model along with saturated treatment and disease transmission
- Fully Legendre spectral collocation technique for stochastic heat equations
- Special Issue on 5th International Conference on Mechanics, Mathematics and Applied Physics (2021)
- Residual service life of erbium-modified AM50 magnesium alloy under corrosion and stress environment
- Special Issue on Advanced Topics on the Modelling and Assessment of Complicated Physical Phenomena - Part I
- Diverse wave propagation in shallow water waves with the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili–Benjamin–Bona–Mahony and Benney–Luke integrable models
- Intensification of thermal stratification on dissipative chemically heating fluid with cross-diffusion and magnetic field over a wedge
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Circular Rydberg states of helium atoms or helium-like ions in a high-frequency laser field
- Closed-form solutions and conservation laws of a generalized Hirota–Satsuma coupled KdV system of fluid mechanics
- W-Chirped optical solitons and modulation instability analysis of Chen–Lee–Liu equation in optical monomode fibres
- The problem of a hydrogen atom in a cavity: Oscillator representation solution versus analytic solution
- An analytical model for the Maxwell radiation field in an axially symmetric galaxy
- Utilization of updated version of heat flux model for the radiative flow of a non-Newtonian material under Joule heating: OHAM application
- Verification of the accommodative responses in viewing an on-axis analog reflection hologram
- Irreversibility as thermodynamic time
- A self-adaptive prescription dose optimization algorithm for radiotherapy
- Algebraic computational methods for solving three nonlinear vital models fractional in mathematical physics
- The diffusion mechanism of the application of intelligent manufacturing in SMEs model based on cellular automata
- Numerical analysis of free convection from a spinning cone with variable wall temperature and pressure work effect using MD-BSQLM
- Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic oscillation of side-by-side double-floating-system with a narrow gap in waves
- Closed-form solutions for the Schrödinger wave equation with non-solvable potentials: A perturbation approach
- Study of dynamic pressure on the packer for deep-water perforation
- Ultrafast dephasing in hydrogen-bonded pyridine–water mixtures
- Crystallization law of karst water in tunnel drainage system based on DBL theory
- Position-dependent finite symmetric mass harmonic like oscillator: Classical and quantum mechanical study
- Application of Fibonacci heap to fast marching method
- An analytical investigation of the mixed convective Casson fluid flow past a yawed cylinder with heat transfer analysis
- Considering the effect of optical attenuation on photon-enhanced thermionic emission converter of the practical structure
- Fractal calculation method of friction parameters: Surface morphology and load of galvanized sheet
- Charge identification of fragments with the emulsion spectrometer of the FOOT experiment
- Quantization of fractional harmonic oscillator using creation and annihilation operators
- Scaling law for velocity of domino toppling motion in curved paths
- Frequency synchronization detection method based on adaptive frequency standard tracking
- Application of common reflection surface (CRS) to velocity variation with azimuth (VVAz) inversion of the relatively narrow azimuth 3D seismic land data
- Study on the adaptability of binary flooding in a certain oil field
- CompVision: An open-source five-compartmental software for biokinetic simulations
- An electrically switchable wideband metamaterial absorber based on graphene at P band
- Effect of annealing temperature on the interface state density of n-ZnO nanorod/p-Si heterojunction diodes
- A facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic adsorption material 5A zeolite for oil–water separation with potential use in floating oil
- Shannon entropy for Feinberg–Horodecki equation and thermal properties of improved Wei potential model
- Hopf bifurcation analysis for liquid-filled Gyrostat chaotic system and design of a novel technique to control slosh in spacecrafts
- Optical properties of two-dimensional two-electron quantum dot in parabolic confinement
- Optical solitons via the collective variable method for the classical and perturbed Chen–Lee–Liu equations
- Stratified heat transfer of magneto-tangent hyperbolic bio-nanofluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms: Keller-Box solution technique
- Analysis of the structure and properties of triangular composite light-screen targets
- Magnetic charged particles of optical spherical antiferromagnetic model with fractional system
- Study on acoustic radiation response characteristics of sound barriers
- The tribological properties of single-layer hybrid PTFE/Nomex fabric/phenolic resin composites underwater
- Research on maintenance spare parts requirement prediction based on LSTM recurrent neural network
- Quantum computing simulation of the hydrogen molecular ground-state energies with limited resources
- A DFT study on the molecular properties of synthetic ester under the electric field
- Construction of abundant novel analytical solutions of the space–time fractional nonlinear generalized equal width model via Riemann–Liouville derivative with application of mathematical methods
- Some common and dynamic properties of logarithmic Pareto distribution with applications
- Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model
- Fractional modeling of COVID-19 epidemic model with harmonic mean type incidence rate
- Liquid metal-based metamaterial with high-temperature sensitivity: Design and computational study
- Biosynthesis and characterization of Saudi propolis-mediated silver nanoparticles and their biological properties
- New trigonometric B-spline approximation for numerical investigation of the regularized long-wave equation
- Modal characteristics of harmonic gear transmission flexspline based on orthogonal design method
- Revisiting the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations
- Time-periodic pulse electroosmotic flow of Jeffreys fluids through a microannulus
- Exact wave solutions of the nonlinear Rosenau equation using an analytical method
- Computational examination of Jeffrey nanofluid through a stretchable surface employing Tiwari and Das model
- Numerical analysis of a single-mode microring resonator on a YAG-on-insulator
- Review Articles
- Double-layer coating using MHD flow of third-grade fluid with Hall current and heat source/sink
- Analysis of aeromagnetic filtering techniques in locating the primary target in sedimentary terrain: A review
- Rapid Communications
- Nonlinear fitting of multi-compartmental data using Hooke and Jeeves direct search method
- Effect of buried depth on thermal performance of a vertical U-tube underground heat exchanger
- Knocking characteristics of a high pressure direct injection natural gas engine operating in stratified combustion mode
- What dominates heat transfer performance of a double-pipe heat exchanger
- Special Issue on Future challenges of advanced computational modeling on nonlinear physical phenomena - Part II
- Lump, lump-one stripe, multiwave and breather solutions for the Hunter–Saxton equation
- New quantum integral inequalities for some new classes of generalized ψ-convex functions and their scope in physical systems
- Computational fluid dynamic simulations and heat transfer characteristic comparisons of various arc-baffled channels
- Gaussian radial basis functions method for linear and nonlinear convection–diffusion models in physical phenomena
- Investigation of interactional phenomena and multi wave solutions of the quantum hydrodynamic Zakharov–Kuznetsov model
- On the optical solutions to nonlinear Schrödinger equation with second-order spatiotemporal dispersion
- Analysis of couple stress fluid flow with variable viscosity using two homotopy-based methods
- Quantum estimates in two variable forms for Simpson-type inequalities considering generalized Ψ-convex functions with applications
- Series solution to fractional contact problem using Caputo’s derivative
- Solitary wave solutions of the ionic currents along microtubule dynamical equations via analytical mathematical method
- Thermo-viscoelastic orthotropic constraint cylindrical cavity with variable thermal properties heated by laser pulse via the MGT thermoelasticity model
- Theoretical and experimental clues to a flux of Doppler transformation energies during processes with energy conservation
- On solitons: Propagation of shallow water waves for the fifth-order KdV hierarchy integrable equation
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part II
- Numerical study on heat transfer and flow characteristics of nanofluids in a circular tube with trapezoid ribs
- Experimental and numerical study of heat transfer and flow characteristics with different placement of the multi-deck display cabinet in supermarket
- Thermal-hydraulic performance prediction of two new heat exchangers using RBF based on different DOE
- Diesel engine waste heat recovery system comprehensive optimization based on system and heat exchanger simulation
- Load forecasting of refrigerated display cabinet based on CEEMD–IPSO–LSTM combined model
- Investigation on subcooled flow boiling heat transfer characteristics in ICE-like conditions
- Research on materials of solar selective absorption coating based on the first principle
- Experimental study on enhancement characteristics of steam/nitrogen condensation inside horizontal multi-start helical channels
- Special Issue on Novel Numerical and Analytical Techniques for Fractional Nonlinear Schrodinger Type - Part I
- Numerical exploration of thin film flow of MHD pseudo-plastic fluid in fractional space: Utilization of fractional calculus approach
- A Haar wavelet-based scheme for finding the control parameter in nonlinear inverse heat conduction equation
- Stable novel and accurate solitary wave solutions of an integrable equation: Qiao model
- Novel soliton solutions to the Atangana–Baleanu fractional system of equations for the ISALWs
- On the oscillation of nonlinear delay differential equations and their applications
- Abundant stable novel solutions of fractional-order epidemic model along with saturated treatment and disease transmission
- Fully Legendre spectral collocation technique for stochastic heat equations
- Special Issue on 5th International Conference on Mechanics, Mathematics and Applied Physics (2021)
- Residual service life of erbium-modified AM50 magnesium alloy under corrosion and stress environment
- Special Issue on Advanced Topics on the Modelling and Assessment of Complicated Physical Phenomena - Part I
- Diverse wave propagation in shallow water waves with the Kadomtsev–Petviashvili–Benjamin–Bona–Mahony and Benney–Luke integrable models
- Intensification of thermal stratification on dissipative chemically heating fluid with cross-diffusion and magnetic field over a wedge

