Abstract
C19H14ClFN2O2, triclinic, P
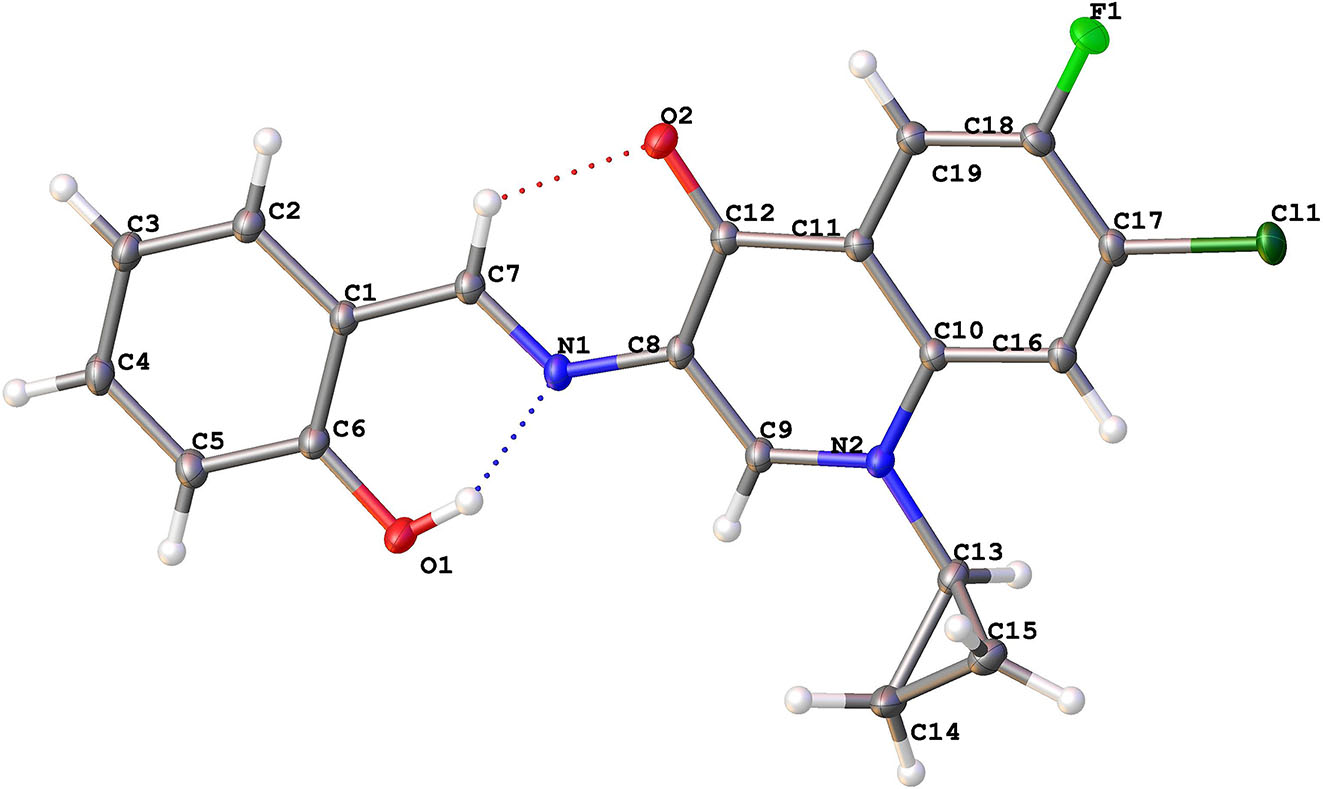
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data. The list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters can be found in the cif-file attached to this article.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.23 × 0.22 × 0.09 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.28 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Apex2, φ and ω scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 32.0°, 100 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 39,310, 5,348, 0.025 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 4,787 |
| N(param)refined: | 229 |
| Programs: | Bruker, 1 Olex2, 2 SHELX 3 , 4 |
1 Source of materials
The preparation of the target compound was performed under the Schiff base typical conditions: To a solution of 3-amino-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoroquinolin-4(1H)-one (0.4 mmol, 1.0 eq.) in EtOH (4 mL) was added salicylaldehyde (0.436, 1.05 eq.) at room temperature. The reaction was stirred at reflux temperature overnight where no more amine was being observed through TLC. The solution was evaporated to dryness and the obtained crude residue was triturated in diethyl ether and pentane. The target compound was produced in 89 % yield. Crystals were obtained through recrystallization from methanol. The structure of the compound was firstly determined by 1H and 13C NMR and further verified by XRD analyses. 1 H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, 298 K): δ 13.45 (s, 1H), 10.23 (s, 1H), 8.22 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 8.03 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 7.41 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (ddd, J = 8.8, 7.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (td, J = 7.5, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 3.56–3.43 (m, 1H), 1.39 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 1.17 (q, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H). 13 C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, 298 K); δ 172.5, 165.3, 161.1, 155.3 (d, JC–F = 249.6 Hz), 142.3, 136.3, 132.7, 132.5, 127.8 (d, JC–F = 5.9 Hz), 126.9 (d, JC–F = 20.5 Hz), 126.2, 120.2, 119.3, 118.7, 117.0, 113.3 (d, JC–F = 22.7 Hz), 34.6, 8.6.
2 Experimental details
All chemicals and solvent were used as purchased without further purification. The starting material 3-amino-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoroquinolin-4(1H)-one was prepared as described earlier 1 and used directly without crystallization. NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker Avance III 500 spectrometer. All NMR spectra were reported in parts per million (ppm, δ) relative to tetramethylsilane for 1H and 13C NMR spectra, with the residual solvent proton and carbon resonances were used as internal standards. Coupling constants (J) were reported in Hertz (Hz), and integrations were reported as number of protons. The following abbreviations were used to describe peak patterns: s = singlet, d = doublet, m = multiplet, bs = broad singlet. All H atoms that were bonded to C atoms were refined as riding, with C–H distances of 0.93 Å (for aromatic rings).
3 Discussion
The fluoroquinolone scaffolds are among the most promising chemical agents to fight the bacterial infections world wide. 5 , 6 Structural modification of this scaffold is still an expanding area to generate new entities, which can be used to treat bacterial and fungal strains and mainly to overcome the bacterial resistance. 7 Current trends in this area are based on structural modifications of all position available while keeping the fluorine atom and the carboxylic acid moiety untouched at position 6 and 7, respectively. 5 , 6 , 7 Few approaches tackle the carboxylic acid replacements with heterocyclic rings and their derivatives. 8 In a continuation of our contribution on the fluoroquinolone to produce biologically active agents to combat bacterial infections as well as cancer, 9 , 10 , 11 we envision the introduction of the Schiff base components for their recognized activities. 12 , 13 In this regard the carboxylic acid moiety at position three in the compound 1-cyclopropyl-7-chloro-7-fluoro-quinolone-3-carboxylic acid is converted to nitro and thereafter reduced to get the 3-amine derivative, which herein reacts with salicylaldehyde to produce the desired compound. Eventually, the target compound has been isolated in high percentage yield and recrystallized into triclinic crystal system. The hydroxyl group in the salicylaldehyde shows a clear H-bonding with the imine nitrogen that forms an E isomer, which encouraged us to synthesize the target compound that features the salicylaldehyde and the fluoroquinolone moieties. The amine at position three of the quinolone compounds has been produced via successive decarboxylation-nitration and thereafter reduction to produce an amino group at that position as described in Ref. 14].
In the C19H14ClFN2O2 molecules all bond lengths are in normal ranges. The normal plane of the phenyl ring is almost coplanar with the normal plane of benzoquinolone ring with an angle of 4.46(3)°. This can be attributed to the strong intramolecular hydrogen bonding between H1⋯N1 with distance = 1.795(19) Å and weaker hydrogen bonding between H7⋯O2 with distance = 2.2234(7) Å. These interactions are accompanied by elongation of the O1–H1 to be 1.299(18) Å.
The crystal is stabilized by intramolecular interactions with halogen atom with the following distances: F⋯H (F1⋯H5, +x, −1 + y, 1 + z) = 2.4601(7) Å and Cl⋯H interactions (Cl1⋯H15b, 2 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z) = 2.9534(2) Å. These interactions build up a two-dimensional arrangement of the molecules. These layers are connected to each other by O⋯H hydrogen bonding between O1⋯H14A (−1x, −1 + y, +z) with distance equal 2.4792(7) Å.
Funding source: University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates
Award Identifier / Grant number: competitive grant number 23021440137
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank the Research Institute of Science and Engineering (RISE), University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, competitive grant number 23021440137. Part of this work has been carried out during sabbatical leave granted to MAK from the University of Jordan during the academic year 2021–2022.
References
1. Bruker. APEX4, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2021.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – Integrated Space-Group and Crystal-Structure Determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Nowakowska, J.; Radomska, D.; Czarnomysy, R.; Marciniec, K. Recent Development of Fluoroquinolone Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2024, 29, 3538; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153538.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
6. Suaifan, G. A.; Mohammed, A. A. M.; Alkhawaja, B. A. Fluoroquinolones’ Biological Activities against Laboratory Microbes and Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2024, 27, 1658; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051658.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Mohammed, H. H.; Abuo-Rahma, G. E.-D. A.; Abbas, S.; Abdelhafez, E.-S. M. Current Trends and Future Directions of Fluoroquinolones. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 3132–3149; https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867325666180214122944.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Hryhoriv, H.; Kovalenko, S. M.; Georgiyants, M.; Sidorenko, L.; Georgiyants, V. A Comprehensive Review on Chemical Synthesis and Chemotherapeutic Potential of 3-Heteroaryl Fluoroquinolone Hybrids. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 625; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030625.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Al-Qawasmeh, R. A.; Zahra, J. A.; Zani, F.; Vicini, P.; Boese, R.; El-Abadelah, M. M. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of 9-cyclopropyl-4-fluoro-6-oxo-6, 9-dihydro-[1, 2, 5] thiadiazolo [3, 4-h] quinoline-7-Carboxylic Acid and its Ethyl Ester. Arkivoc: Online J. Org. Chem. 2009, 12, 322–336; https://doi.org/10.3998/ark.5550190.0010.c28.Search in Google Scholar
10. Al-Qawasmeh, R. A.; Huthail, B. B.; Sinnokrot, M. O.; Semreen, M. H.; Odeh, R. A.; Abu-Zarga, M. H.; Tarazi, H.; Yousef, I. A.; Al-Tel, T. H. Design, Synthesis and Qualitative Structure Activity Relationship Evaluations of Quinoline-Based Bisarylimidazoles as Antibacterial Motifs. Med. Chem. 2016, 12l, 563–573; https://doi.org/10.2174/1573406412666160518142441.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Al-Qawasmeh, R. A.; Abadleh, M. M.; Zahra, J. A.; El-Abadelah, M. M.; Albashiti, R.; Zani, F.; Incerti, M.; Vicini, P. Design Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity Studies of New Thiadiazoloquinolone Compounds. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 777–785; https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2013.855925.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Younus, H. A.; Saleem, F.; Hameed, A.; Al-Rashida, M.; Al-Qawasmeh, R. A.; El-Naggar, M.; Khan, K. M.; Saeed, M. Part-II: An Update of Schiff Bases Synthesis and Applications in Medicinal Chemistry-A Patent Review (2016–2023). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2023, 33, 841–864; https://doi.org/10.1080/13543776.2023.2297729.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Tomisic, Z. B.; Kujundzic, N.; Krajacic, M. B.; Visnjevac, A.; Kojic-Prodic, B. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 611, 73; https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2860(02)00062-5.Search in Google Scholar
14. Al-Qawasmeh, R. A.; Zahra, J. A.; Khanfar, M. A.; Al-Hiari, Y. M.; El-Abadelah, M. M.; Voelter, W. A Convenient Synthesis of 1-Alkyl-7-chloro-6- fluoro-3-nitro-4-quinolones. Lett. Org. Chem. 2009, 6, 511–514; https://doi.org/10.2174/157017809789124812.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-bis(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)-2,2′-bi(1,3,4-oxadiazole), C16H4N10O14
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-4,4′-oxydibenzoato- κ5 O,O′: O″,O‴:O‴)-bis(2,4,6-tri(3-pyridine)-1,3,5-triazine-κ1 N)cadmium(II)], C50H32CdN12O5
- The crystal structure of 1,4-diazepane-1,4-diium potassium trinitrate, C5H14KN5O9
- The crystal structure of benzyl 2,2,5,5-tetramethylthiazolidine-4-carboxylate, C15H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxyethyl-triphenylphosphonium tetracyanidoborate, C24H20BN4OP
- The crystal structure of 1-methyl-3-(N-methylnitrous amide–N-methylene) imidazolidine-2,4,5-trione
- Crystal structure of N-((3-cyano-1-(2,6-dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide, C20H7Cl2F8N5O3S
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a] isoquinolin-6(5H)-one, C20H18F2N2O
- The crystal structure of N′,N″-[1,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane-1,2-diylidene]bis(furan-2- carbohydrazide), C24H16Cl2N4O4
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromoantimony(III), [C25H21BrP]+[SbBr4]−
- Crystal structure of [(4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] tetrabromidoindium(III), [C25H21BrP]+[InBr4]−
- The crystal structure of 4-carboxy-2-oxobutan-1-aminium chloride, C5H10ClNO3
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of dichlorido(η6-p-cymene)(triphenylarsine)ruthenium(II), C28H29AsCl2Ru
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-hydroxy-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H16N2O2
- The crystal structure of 10-(1-bromoethyl)-14-(bromomethyl)dibenzo[a, c]acridine, C24H17NBr2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-methoxy-7-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methoxy]-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one, C18H16O5
- Synthesis and crystal structure of ethyl 4-((4-trifluoromethylbenzyl)amino)benzo, C17H16F3NO2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-(7-(tert-butyl)-5-methylbenzo[d][1,3]oxathiol-2-ylidene)-4-methylcyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C23H28O2S
- The crystal structure of (R)-2-aminobutanamide hydrochloride, C4H11ClN2O
- Crystal structure of bromido[hydridotris(3-tert-butyl-5-isopropylpyrazolyl)borato-κ3 N,N′,N″]copper(II), C30H52BBrCuN6
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-mesityl-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}-copper(II) dichloromethane monosolvate
- Crystal structure of 4-[3,5-bis(propan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridine, C14H19N3
- Crystal structure of ((4-(4-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)methyl)ferrocene, C21H16BrFeNO
- Crystal structure of [(4-chlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] dichloridocopper(I), {[C25H21ClP]+[CuCl2]−}n
- The crystal structure of {Cu(2,9-diisopropyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline)[4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene]}+ PF6−·1.5(EtOAC)
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(t-butyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-amine, C11H21N3
- Crystal structure of [(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium] trichloridocopper(II), [C25H20Cl2P]+[CuCl3]−
- The crystal structure of dipotassium sulfide, K2S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonyl)ferrocene, C22H19FeNO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H23F3N2O
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-morpholino-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C22H20F3NO2
- Crystal structure of Ce9Ir37Ge25
- The crystal structure of ethyl 6-(2-nitrophenyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole-3-carboxylate, C14H11N3O4S
- Crystal structure of (4-(4-isopropylphenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl)methanone, C24H23FeNO
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) tetrathiotungstate(VI), (CH3NH3)2[WS4]
- Crystal structure of 6,11-dihydro-12H-benzo[e]indeno[1,2-b]oxepin-12-one, C17H12O2
- Crystal structure of 3-[(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)methyl]-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4- oxadiazole-2-thione, C18H19N3OS2
- Crystal structure of N-isopropyl-1,8-naphthalimide C15H13NO2
- TiNiSi-type EuPdBi
- Crystal structure of 1-(p-tolylphenyl)-4-(2-thienoyl)-3-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C16H14N2O2S
- The crystal structure of 3-(3-carboxypropyl)-2-nitro-1H-pyrrole 1-oxide, C7H9N3O5
- The crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k2O:N)-tetrakis(2-(2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetato-k1N)trizinc(II) hexahydrate C36H52N18O32Zn3
- The crystal structure of 4-(3-carboxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinolin-7-yl)piperazin-1-ium 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate monohydrate, C25H30FN3O9
- Crystal structure of bis(DL-1-carboxy-2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium) oxalate — acetic acid (1/2)
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-4-((4-methylphenyl)sulfonamido)but-2-enoate, C12H15NO4S
- The crystal structure of actarit, C10H11NO3
- The crystal structure of bicyclol, C19H18O9
- The crystal structure of topiroxostat, C13H8N6
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(4-p-tolylthiazol-2-yl)acetamide, C13H12Cl2N2OS
- Crystal structure of 4-(trifluoromethyl)-7-coumarinyl trifluoromethanesulfonate C11H4F6O5S
- Crystal structure of (1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane-κ6O6)-((Z)-N,N′-bis(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)carbamimidato-κ1N)potassium(I)
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(5-((4-(dimethylamino)naphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid, C18H16N2O3S2
- Crystal structure of (4-fluorobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide, C25H21BrFP
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-[6-(pyridin-2-yl)phenanthridine-κ2N, N′]zinc(II)-chloroform (1/1), C19H13N2ZnCl5
- Crystal structure of (E)-(3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)acryloyl)ferrocene, C19H14Cl2FeO
- The crystal structure of (E)-7-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-3-((2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)quinolin-4(1H)-one, C19H14ClFN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2-bromo-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13BrFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-11-(((fluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-6-methyl-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[c,f][1,2]thiazepine 5,5-dioxide, C16H13ClFNO4S2
- Crystal structure of 5-(2,2-difluoropropyl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydrobenzo[4,5]imidazo[2,1-a]isoquinoline-3-carbonitrile, C20H15F2N3O

