Abstract
Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48, cubic,
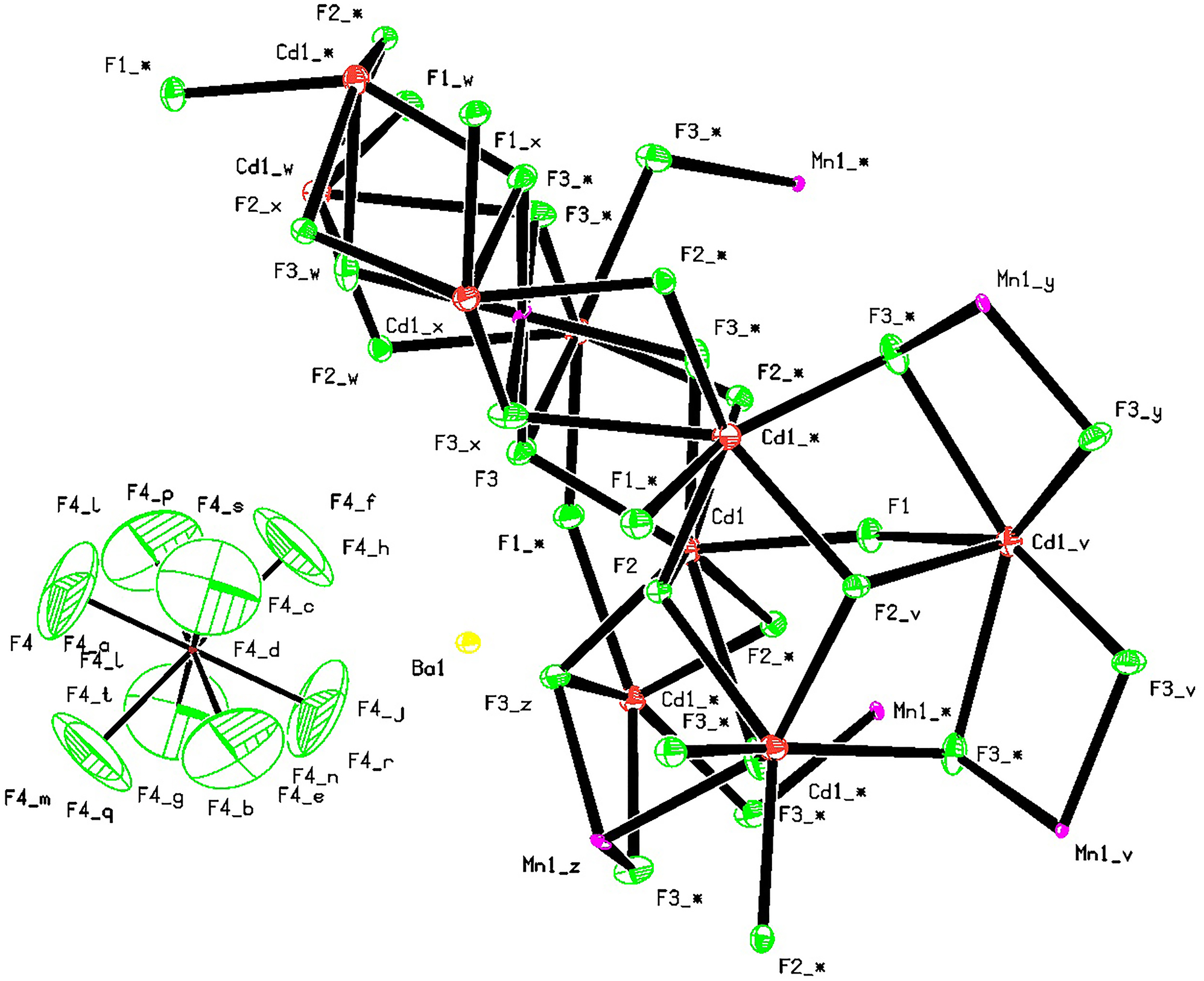
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Pink block |
| Size: | 0.21 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 13.6 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 28.2°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 18,964, 472, 0.093 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 472 |
| N(param)refined: | 38 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], WinGX/ORTEP [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba1 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.20122 (6) | 0.0066 (3) |
| Cd1 | 0.14763 (6) | 0.500000 | 0.17432 (6) | 0.0100 (3) |
| Mn1 | 0.250000 | 0.750000 | 0.250000 | 0.0036 (4) |
| Si1 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.0008 (14) |
| F1 | 0.1083 (7) | 0.500000 | 0.000000 | 0.0121 (16) |
| F2 | 0.3119 (4) | 0.500000 | 0.1070 (4) | 0.0089 (11) |
| F3 | 0.1896 (4) | 0.6070 (3) | 0.3111 (3) | 0.0142 (9) |
| F4a | 0.5765 (8) | 0.5765 (8) | 0.5765 (8) | 0.109 (9) |
-
aOccupancy: 0.75.
1 Source of materials
BaF2 (Alfa Asear, 99 %), CdF2 (Alfa Asear, 99.9 %), MnF3 (Alfa Asear, 98 %), SiO2 (Alfa Asear, 99.0 %) and CF3COOH (Alfa Aesar, 99 %) were used without any further purification. Crystals of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48 were obtained by hydrothermal method using a diluted CF3COOH aqueous solution. 0.100 g of BaF2 (0.570 mmol), 0.0860 g of CdF2 (0.570 mmol), 0.1276 g of MnF3 (1.14 mmol), 0.0180 g of SiO2 (0.300 mmol), 3 ml of CF3COOH (39 mmol) and 5 ml of H2O were combined in a 23-ml Teflon-lined stainless autoclave. The autoclave was subsequently closed, gradually heated to 230 °C, held for 24 h, and cooled slowly to room temperature at a rate of 6 °C/h. The mother liquor was decanted from the products, and products were recovered by filtration and washed with distilled water and ethanol. Pink colored block shaped crystals of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48 were isolated by hand sorting. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis of the crystal indicated a chemical composition of Ba6.12Cd11.8Mn3.94Si1.01F47.78.
2 Experimental details
The structure was solved by Direct Methods with SHELXS and further refined with the SHELXL program [5]. The crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48 was refined as merohedral twin.
3 Comment
Mixed metal fluoride materials have been investigated thoroughly attributable to their diverse crystal structures and significant magnetic, electric, multiferroic, optical, and luminescent properties [6, 7]. A search for barium cadmium manganese silicon fluorides in the Inorganic Structure Database (ICSD, web version 5.1.0) [8] yielded no relevant results. In fact, only six crystal structures could be found in barium manganese fluorides, cadmium manganese fluorides and barium silicon fluorides, for example, BaMnF4 [9], BaMnF5 [10], BaMnF5(H2O) [11], Ba5Mn3F19 [12], CdMnF5 [13], and BaSiF6 [14].
The crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48 belongs to the cubic
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research fund from Chosun University.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The author declares no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contributions: The author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Research fund from Chosun University.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M., Dittrich, B. ShelXle: a Qt graphical user interface for SHELXL. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1281–1284; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889811043202.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Hagenmuller, P. INORGANIC SOLID FLUORIDES: Chemistry and Physics; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, 1985.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Leblanc, M., Maisonneuve, V., Tressaud, A. Crystal chemistry and selected physical properties of inorganic fluorides and oxide-fluorides. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1191–1254; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500173c.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Zagorac, D., Müller, H., Ruehl, S., Zagorac, J., Rehme, S. Recent developments in the inorganic crystal structure database: theoretical crystal structure data and related features. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2019, 52, 918–925; https://doi.org/10.1107/s160057671900997x.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Kim, S. W., Chang, H. Y., Halasyamani, P. S. Selective pure-phase synthesis of the multiferroic BaMF4 (M = Mg, Mn, Co, Ni, and Zn) family. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17684–17685; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja108965s.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Bukovec, P., Hoppe, R. Zur Kenntnis von BaMnF5: Eine Jahn–Teller–verzerrte Variante von BaGaF5. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1984, 509, 138–144; https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19845090214.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Massa, W., Burck, V. Erdalkali-fluoromanganate(III): BaMnF5·H2O und SrMnF5·H2O. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1984, 516, 119–126; https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19845160916.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Dahlke, P., Graulich, J., Welsch, M., Pebler, J., Babel, D. Struktur- und magnetochemische Untersuchungen an Ba5Mn5F19 und verwandten Verbindungen A5II M3III F19. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2000, 626, 1255–1263; https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1521-3749(200005)626:5<1255::aid-zaac1255>3.0.co;2-j.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3749(200005)626:5<1255::AID-ZAAC1255>3.3.CO;2-ASuche in Google Scholar
13. Mueller, U., Hoppe, R. Korrektur zu den Kristallstrukturen von CaMnF5 und CdMnF5. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1990, 583, 205–208; https://doi.org/10.1002/zaac.19905830125.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Hoskins, B. F., Linden, A., Mulvaney, P. C., O’Donnell, T. A. The structures of barium hexafluorosilicate and cesium hexafluororhenate(V). Inorg. Chim. Acta 1984, 88, 217–222; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-1693(00)83600-2.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Brown, I. D. The Chemical Bond in Inorganic Chemistry: The Bond Valence Model; Oxford University Press: New York, 2002.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3

