Abstract
[C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3, orthorhombic, Fdd2 (no. 43), a = 30.3986(6) Å, b = 40.4094(13) Å, c = 7.0603(2) Å, V = 8672.8(4) Å3, Z = 16, R gt (F) = 0.0324, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0828, T = 153 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.48 × 0.45 × 0.40 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.08 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | STOE IPDS 2, rotation method |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.1°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 26,188, 4629, 0.039 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 4497 |
| N(param)refined: | 288 |
| Programs: | X-RED/X-AREA [1], SHELX [2, 3], ORTEP-3 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0.68493 (6) | 0.39062 (5) | 0.4898 (3) | 0.0224 (4) |
| O1 | 0.66234 (4) | 0.41465 (3) | 0.6114 (2) | 0.0267 (3) |
| O2 | 0.72643 (4) | 0.40745 (3) | 0.43799 (19) | 0.0240 (3) |
| C1 | 0.66995 (7) | 0.47085 (5) | 0.7228 (4) | 0.0398 (5) |
| H1A | 0.653757 | 0.478198 | 0.610441 | 0.060* |
| H1B | 0.691437 | 0.487798 | 0.758898 | 0.060* |
| H1C | 0.649311 | 0.467293 | 0.827501 | 0.060* |
| C2 | 0.69384 (6) | 0.43859 (5) | 0.6788 (3) | 0.0283 (4) |
| C3 | 0.71512 (8) | 0.42566 (6) | 0.8593 (3) | 0.0383 (5) |
| H3A | 0.692233 | 0.420462 | 0.952431 | 0.058* |
| H3B | 0.734842 | 0.442574 | 0.911155 | 0.058* |
| H3C | 0.732006 | 0.405614 | 0.830649 | 0.058* |
| C4 | 0.71070 (9) | 0.46363 (5) | 0.3528 (3) | 0.0403 (5) |
| H4A | 0.730342 | 0.461735 | 0.243282 | 0.061* |
| H4B | 0.710741 | 0.486518 | 0.398640 | 0.061* |
| H4C | 0.680782 | 0.457369 | 0.315535 | 0.061* |
| C5 | 0.72660 (6) | 0.44073 (5) | 0.5096 (3) | 0.0272 (4) |
| C6 | 0.77344 (7) | 0.45010 (6) | 0.5647 (4) | 0.0405 (5) |
| H6A | 0.784932 | 0.433878 | 0.655194 | 0.061* |
| H6B | 0.773463 | 0.472116 | 0.622913 | 0.061* |
| H6C | 0.792040 | 0.450339 | 0.451319 | 0.061* |
| O3 | 0.65527 (4) | 0.38154 (3) | 0.33421 (18) | 0.0252 (3) |
| O4 | 0.69718 (4) | 0.35858 (3) | 0.57469 (19) | 0.0244 (3) |
| C7 | 0.69660 (7) | 0.34397 (5) | 0.1413 (3) | 0.0337 (4) |
| H7A | 0.688444 | 0.356892 | 0.029193 | 0.051* |
| H7B | 0.700152 | 0.320677 | 0.105837 | 0.051* |
| H7C | 0.724360 | 0.352385 | 0.192900 | 0.051* |
| C8 | 0.66052 (6) | 0.34703 (5) | 0.2908 (3) | 0.0256 (4) |
| C9 | 0.61739 (7) | 0.33396 (5) | 0.2093 (4) | 0.0366 (5) |
| H9A | 0.593626 | 0.337578 | 0.300812 | 0.055* |
| H9B | 0.620220 | 0.310233 | 0.183459 | 0.055* |
| H9C | 0.610622 | 0.345693 | 0.091371 | 0.055* |
| C10 | 0.70329 (7) | 0.30175 (5) | 0.4757 (4) | 0.0357 (5) |
| H10A | 0.730239 | 0.307483 | 0.406921 | 0.054* |
| H10B | 0.687942 | 0.283906 | 0.408860 | 0.054* |
| H10C | 0.710842 | 0.294409 | 0.603907 | 0.054* |
| C11 | 0.67350 (6) | 0.33203 (4) | 0.4871 (3) | 0.0250 (4) |
| C12 | 0.63385 (7) | 0.32407 (5) | 0.6111 (3) | 0.0342 (4) |
| H12A | 0.643792 | 0.318998 | 0.739913 | 0.051* |
| H12B | 0.618253 | 0.304903 | 0.558863 | 0.051* |
| H12C | 0.614013 | 0.343173 | 0.614239 | 0.051* |
| B2 | 0.80650 (7) | 0.35419 (5) | 0.5795 (3) | 0.0262 (4) |
| O5 | 0.77645 (4) | 0.35143 (4) | 0.7230 (2) | 0.0308 (3) |
| H5O | 0.7483 (11) | 0.3563 (8) | 0.683 (5) | 0.060 (9)* |
| O6 | 0.79634 (4) | 0.36891 (4) | 0.40959 (19) | 0.0273 (3) |
| H6O | 0.7721 (12) | 0.3822 (8) | 0.419 (5) | 0.071 (10)* |
| O7 | 0.84689 (5) | 0.34168 (4) | 0.6151 (2) | 0.0357 (3) |
| H7O | 0.8649 (10) | 0.3436 (8) | 0.524 (5) | 0.057 (9)* |
| N1 | 0.57369 (6) | 0.40936 (4) | 0.3146 (2) | 0.0281 (3) |
| H1D | 0.5572 (8) | 0.4029 (6) | 0.211 (4) | 0.044 (7)* |
| H1E | 0.5609 (10) | 0.4004 (8) | 0.424 (4) | 0.062 (9)* |
| H1F | 0.6024 (8) | 0.4014 (8) | 0.300 (5) | 0.061 (9)* |
| C13Aa | 0.57046 (14) | 0.44498 (9) | 0.3624 (6) | 0.0322 (8) |
| H13Aa | 0.590060 | 0.450179 | 0.470368 | 0.039* |
| H13Ba | 0.539904 | 0.450520 | 0.399172 | 0.039* |
| C14Aa | 0.58394 (14) | 0.46510 (8) | 0.1895 (5) | 0.0436 (10) |
| H14Aa | 0.613155 | 0.457566 | 0.144900 | 0.052* |
| H14Ba | 0.562506 | 0.461345 | 0.086097 | 0.052* |
| C15Aa | 0.5859 (3) | 0.50146 (10) | 0.2347 (9) | 0.0752 (19) |
| H15Aa | 0.556772 | 0.509103 | 0.274946 | 0.113* |
| H15Ba | 0.595073 | 0.513752 | 0.121730 | 0.113* |
| H15Ca | 0.607149 | 0.505213 | 0.336870 | 0.113* |
| C13Bb | 0.5834 (3) | 0.44626 (17) | 0.2849 (14) | 0.0324 (18) |
| H13Cb | 0.600660 | 0.454693 | 0.393698 | 0.039* |
| H13Db | 0.601471 | 0.449049 | 0.169233 | 0.039* |
| C14Bb | 0.5425 (2) | 0.46587 (17) | 0.2660 (12) | 0.045 (2) |
| H14Cb | 0.525586 | 0.464445 | 0.385632 | 0.054* |
| H14Db | 0.524170 | 0.456250 | 0.163936 | 0.054* |
| C15Bb | 0.5514 (4) | 0.5014 (2) | 0.2219 (19) | 0.068 (3) |
| H15Db | 0.568414 | 0.511319 | 0.325299 | 0.103* |
| H15Eb | 0.523469 | 0.513261 | 0.207801 | 0.103* |
| H15Fb | 0.568188 | 0.502960 | 0.103741 | 0.103* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.663 (6), bOccupancy: 0.337 (6).
1 Source of materials
All experiments were carried out under a dry argon atmosphere using standard Schlenk technique [5].
In a representative experiment 2.223 g pinacolborane (0.0174 mol, TCI – Tokyo Chemical Industry) were placed in a 50 mL round bottom flask. About 10 mL 1,2-dimethoxyethane (Acros Organics, distilled from CaH2) were added. The resulting solution was stirred at room temperature and cooled in an ice bath (ice/NaCl) to −20 °C. O-Triethylsilyl-N-n-propylcarbamate (0.855 g, 0.0039 mol, synthesized according to [6]) was slowly added into this solution within 5 min while a gas evolution was visible. The dropping funnel was flushed with about 5 mL of 1,2-dimethoxyethane. The clear solution was stirred at room temperature for a week. Then, the solution was heated under reflux for about 1 h. Afterwards, the solution was stirred at room temperature until a white precipitate was formed. After standing an additional night at room temperature, the viscosity of the solution had increased. Crystals suitable for single crystal X-ray diffraction were obtained from this suspension after standing 6 months at room temperature. Colourless prisms, m.p. 130 °C.
2 Comment
Pinacolborane is utilized for a variety of transformations like iron-catalysed alkene hydroboration, catalytic enantioselective hydroboration of ketones and imines, and other types of hydroborations [7], [8], [9]. Herein we describe the crystal structure of an ionic borate complex formed out of pinacolborane and a silylcarbamate. The crystal structure was obtained as side product during our work about the hydrogenation of carbamates of aluminium and silicon [10], [11], [12], [13].
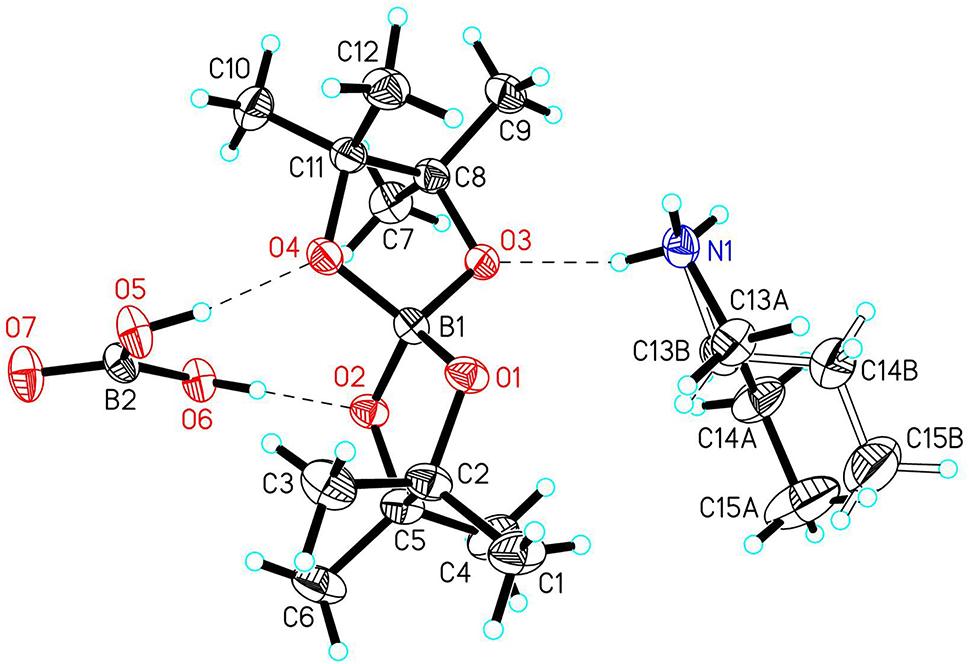
The asymmetric unit contains one molecule boric acid, B(OH)3, a bispinacolylborate anion, [Bpin2]−, and an n-propylammonium cation, CH3–CH2–NH+ 3. These are linked to each other by hydrogen bonds as shown in the figure. The boron atom B2 in boric acid is planar coordinated by the three oxygen atoms O5, O6, O7 (sum of O–B–O angles is 360°). The hydrogen atoms at O5 and O6 are orientated towards the neighbouring oxygen atoms O4 and O2, forming hydrogen bonds to the [Bpin2]− anion. The boron atom B1 is distorted tetrahedrally coordinated by the four oxygen atoms of the pinacolyl groups. The angles O1–B1–O2 and O3–B1–O4 are smaller with values of 103.8(1)° and 103.9(1)°, respectively. This can be explained with the coordination of the pinacolyl units, which form five membered rings with the boron atom. These small inner-cyclic angles are compensated by larger angles between both pinacolyl units which spread up to a value of 117.5(2)° for O1–B1–O4. The B–O bond lengths are similar as in comparable compounds [14], [15], [16]. The [Bpin2]− anion is linked to the n-propylammonium cation via a hydrogen bond N1–H1F⋯O3. Further hydrogen bonds from the n-propylammonium cation to symmetry equivalent oxygen atoms from neighbouring boronic acid molecules form an infinite network of molecules parallel to the crystallographic a axis.
There are three related crystal structures in the literature. These contain boric acid, B(OH)3, the bispinacolylborate anion, [Bpin2]−, and different ammonium ions to compensate the negative charge of the [Bpin2]− unit. These cations are tetra-n-butylammonium [14], dibenzylammonium [15], and 2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10-octahydropyrimido[1,2-a]azepin-1-ium (protonated DBU) [16]. The combination of boric acid with [Bpin2]− and alkylammonium ions results in complicated patterns of intermolecular interactions in these crystal structures; similar as in the structure which is presented here. As can be seen from the available structural analyses, the combination of these three structural elements allows the formation of unique networks of hydrogen bonds.
3 Experimental details
The carbon-bound H atoms were geometrically placed (C–H = 0.98–0.99 Å) and refined as riding atoms with U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C). The disordered n-propyl group was refined with a split atom model. Site occupation factors for parts A and B were refined to 0.66/0.34, respectively. Restraints were applied to keep the bond lengths of the disordered propyl group to sensible values.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank TU Bergakademie Freiberg (Freiberg, Germany) for financial support. Open Access Funding by the Publication Fund of the TU Bergakademie Freiberg.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: TU Bergakademie Freiberg (Freiberg, Germany).
References
1. Stoe & Cie. X-RED (Version 1.53) and X-AREA (Version 1.55); STOE & Cie GmbH: Darmstadt, Germany, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Farrugia, L. J. ORTEP-3 for Windows – a version of ORTEP-III with a Graphical User Interface (GUI). J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1997, 30, 565; https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889897003117.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Böhme, U. Inertgastechnik – Arbeiten unter Schutzgas in der Chemie, 1. Auflage; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin/Boston, 2020.10.1515/9783110627046Suche in Google Scholar
6. Knausz, D., Meszticzky, A., Szak’acs, L., Cs’akv’ari, B., Ujsz’aszy, K. Trimethylsilylated N- alkyl-substituted carbamates I. preparation and some reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 1983, 256, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022–328X(00)99291–X.10.1016/S0022-328X(00)99291-XSuche in Google Scholar
7. Zhang, L., Huang, Z. Iron-catalyzed alkene hydroboration with pinacolborane. Synlett 2013, 24, 1745–1747; https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033–1339645.10.1055/s-0033-1339645Suche in Google Scholar
8. Wenbo, L., Zhan, L. Application of pinacolborane in catalytic enantioselective hydroboration of ketones and imines. Youji Huaxue (Chin. J. Org. Chem.) 2020, 40, 3596–3604; https://doi.org/10.6023/cjoc202008039.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Bage, A. D., Nicholson, K., Hunt, T. A., Langer, T., Thomas, S. P. The hidden role of boranes and borohydrides in hydroboration catalysis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 13479–13486; https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c04051.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Herbig, M., Gevorgyan, L., Pflug, M., Wagler, J., Schwarzer, S., Kroke, E. CO2 capture with silylated ethanolamines and piperazines. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 894. https://doi.org/10.1002/open.201900269.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Schumann, E., Brendler, E., Böhme, U., Mertens, F. Synthesis of aluminum N,N-dialkylcarbamates by insertion of CO2 into Al–N bonds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 26, e202200568. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.202200568.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Herbig, M., Böhme, U. 9-(Pyrrolidinium-1-yl)-9-boranuidabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane. IUCrData 2023, 8, x230332. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2414314623003322.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
13. Herbig, M., Böhme, U. The crystal structure of 4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)morpholine, C10H20BNO3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2023, 238, 449–450. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2023–0030.10.1515/ncrs-2023-0030Suche in Google Scholar
14. Pietsch, S., Neeve, E. C., Apperley, D. C., Bertermann, R., Mo, F., Qiu, D., Cheung, M. S., Dang, L., Wang, J., Radius, U., Lin, Z., Kleeberg, C., Marder, T. B. Synthesis, structure, and reactivity of anionic sp2–sp3 diboron compounds: readily accessible boryl nucleophiles. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 7082–7098. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201500235.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Li, X., Chen, Z., Chen, W., Xie, X., Zhou, H., Liao, Y., Yu, F., Huang, J. B2pin2–mediated cascade cyclization/aromatization reaction: facial access to functionalized indolizines. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 7372–7377; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.2c02905.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
16. Hao, W., Garcia, J. M., Haeffner, F., Radomkit, S., Zhugralin, A. R., Hoveyda, A. H. Mechanism of NHC-catalyzed conjugate additions of diboron and borosilane reagents to α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10585–10602; https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b06745.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3

