Abstract
C48H200N8O104Si32, monoclinic, C2/m (no. 12), a = 16.2532(14) Å, b = 13.3020(7) Å, c = 16.7771(14) Å, β = 96.476(10)°, V = 3604.07(3) Å3, Z = 1, R(F) = 0.031, χ 2 = 2.44, Rgt (F) = , wRref (F 2) = , T = 293 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless grains |
| Size: | 1 × 1 × 0.05 μm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54059 Å) |
| μ: | not determined |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Siemens D5000, Debye–Scherrer |
| 2θ range used: | 2.96°–89.77° |
| N(hkl)measured | 1822 |
| N(param)refined: | 78 |
| Programs: | Fullprof 2K [1], VESTA [2] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso */U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si1 | −0.0848 (2) | 0.7313 (3) | 0.0322 (2) | 0.0162 (6)* |
| Si2 | 0.8537 (2) | 0.8814 (3) | 0.1592 (2) | 0.0162 (6)* |
| Si3 | 0.4920 (2) | 0.8827 (3) | 0.1872 (2) | 0.0162 (6)* |
| Si4 | 0.1630 (2) | 0.6159 (3) | 0.1206 (2) | 0.0162 (6)* |
| O1 | −0.1270 (7) | 0.8248 (6) | 0.0763 (4) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O2 | −0.0602 (7) | 0.6489 (6) | 0.1025 (4) | 0.021 (3)* |
| OH3 | 0.9106 (7) | 0.8530 (8) | 0.2419 (5) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O4 | 0.8708 (10) | 0.00000 | 0.1449 (10) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O5 | 0.00000 | 0.7743 (8) | 0.00000 | 0.021 (3)* |
| OH6 | 0.4697 (8) | 0.8107 (7) | 0.2598 (5) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O10 | 0.3556 (6) | 0.8127 (8) | −0.0425 (5) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O12 | 0.2544 (2) | 0.6365 (8) | 0.1672 (5) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O13 | 0.9689 (10) | 0.50000 | 0.2023 (10) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O15 | 1.0909 (3) | 0.6330 (9) | 0.1782 (6) | 0.021 (3)* |
| O16 | 0.3453 (12) | 0.00000 | −0.0918 (8) | 0.021 (3)* |
| N1 | 0.1769 (5) | 0.00000 | 0.1364 (6) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C1 | 0.2189 (15) | 0.9090 (11) | 0.1758 (6) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C2 | 0.2047 (18) | 0.00000 | 0.0546 (9) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C3 | 0.0837 (6) | 0.00000 | 0.1243 (17) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C4 | 0.2335 (14) | 0.1119 (15) | 0.2668 (5) | 0.411 (6)* |
| N2 | 0.2418 (5) | 0.50000 | 0.4157 (6) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C5 | 0.1509 (6) | 0.50000 | 0.3899 (16) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C6 | 0.2669 (19) | 0.50000 | 0.5045 (6) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C7 | 0.2874 (12) | 0.5873 (9) | 0.3851 (7) | 0.411 (6)* |
| C8 | 0.3201 (16) | 0.6596 (13) | 0.4549 (10) | 0.411 (6)* |
| O17(water) | 0.4985 (13) | 0.50000 | 0.6430 (12) | 0.098 (3)* |
| O18(water) | −0.0780 (9) | 0.7807 (8) | 0.6470 (9) | 0.098 (3)* |
| O19(water) | 0.50000 | 0.7838 (12) | 0.50000 | 0.098 (3)* |
| O20(water) | 0.0803 (7) | 0.5964 (8) | 0.6004 (7) | 0.098 (3)* |
1 Source of material
RUB-56 samples were hydrothermally synthesized in Teflon-lined autoclaves at 140 °C for 2–7 days using diethyldimethylammonium hydroxide (Sigma-Aldrich, 20 % in water) as the structure directing agent (SDA). Reaction mixtures of composition 0.9–1 SiO2 : 0.5 SDA : 6–10 H2O were used. Lab-made silica gel (11 wt% H2O) served as the silica source. A more detailed view on the synthesis of RUB-56 is presented in a patent application [3]. The sample of highest crystallinity with respect to purity and (small) halfwidths of the reflections was used for the structure analysis.
2 Experimental details
Powder diffraction data were collected using a Siemens D5000 diffractometer equipped with a Braun linear position-sensitive detector (2θ coverage = 6°) and a curved germanium (111) primary monochromator. The powder was kept in a sealed glass capillary (0.3 mm in diameter) to avoid preferred orientation of the crystals. No absorption correction was necessary. The powder pattern contains a weak additional peak at 5.75°. Since no other reflections could be detected that do not belong to the pattern of RUB-56, this peak was not assigned to an impurity phase. Instead, the peak at 5.75° was included in the background. Soft distance restraints were applied to d(Si–O) = 1.620(5) Å, d(Si⋯Si) = 3.08(4) Å, d(O⋯O) = 2.63(3) Å, d(C–C) = 1.54(1) Å, d(C–N) = 1.48(1) Å, d(N⋯C, next–next neighbour) = 2.45(4) Å and d(C⋯C, next–next neighbour) = 2.50(4) Å. Common isotropic displacement parameters B (iso) were refined for all Si, all O (layer), all O (water molecules) and all C and N atoms. The occupancy factors of carbon atoms and those oxygen atoms representing water molecules were increased to include the scattering power of the hydrogen atoms which could not be located. This procedure was chosen because the highly diffuse electron density at the position of the carbon and (water) oxygen atoms includes also the electrons of the hydrogen atoms.
3 Comment
Hydrous layer silicates (HLSs) – sometimes also called 2-dimensional zeolites (2D-zeolites) – are materials consisting of (i) pure silica layers (seldom traces of other elements are present such as Al, B, Ga, Fe), (ii) intercalated cations of low charge density like [Na(H2O)6] complexes or organic cations such as tetramethylammonium, and (iii) in most cases water molecules. Overviews on HLSs have for example been published by Marler et al. [4], Ramos et al. [5] and Roth et al. [6]. HLSs are mainly used as precursors to form expanded silica frameworks by techniques of pillaring, mesoporous silicas by delamination of the structures, and high silica zeolites by topotactic condensation of the layers.
RUB-56 forms very small and thin, quadrangular, plate-like crystals (approx. size: 1 × 1 × 0.05 μm3). Because of the small size of the crystals only powder data were available for structure analysis. The powder XRD pattern of RUB-56 was indexed in the monoclinic system with approx. lattice parameters a = 16.22 Å, b = 13.28 Å, c = 16.76 Å and β = 96.45°. The analysis of systematically extincted reflections led to possible space group symmetries C2, Cm or C2/m. In addition, RUB-56 had been characterized by thermal analysis, SEM, FTIR spectroscopy as well as 29Si MAS and 1H–29Si CP MAS NMR spectroscopy [7].
The structure was solved by model building taking into account the close correspondence of the structures of RUB-56 and ITQ-8 [8, 9] which became obvious from the comparison of lattice parameters, FTIR and NMR spectra. Based on the known structure of ITQ-8 [9] a rough model of the structure of RUB-56 was built to start the Rietveld refinement. While the atoms of the silicate layer were, at the very beginning of the refinement, already close to the finally refined positions, the sites of the water molecules and the coordinates of the carbon and nitrogen atoms were derived from successively calculated difference Fourier maps. All atomic coordinates (ignoring protons) were subsequently refined by the Rietveld method using FullProf [1] in space group no. 12 (C2/m). The structure refinement of the title compound gave T–O, T–T and O–O distances in the range of 1.606–1.652 Å, 3.072–3.163 Å, and 2.385–2.802 Å, respectively, which are typical values for layer silicates possessing only Si at T sites of the [TO4]-tetrahedra.
RUB-56 contains levyne-type silicate layers (lev layer) as the main structural constituents. In contrast to most HLSs [10], which possess dense silicate layers with 6-rings as largest pores (free diameter ca. 2.5 Å), the lev layer of RUB-56 contains slightly elliptical 8-rings pores with free diameters of 4.0 Å × 3.3 Å (see Figure 1). These pores are large enough to let small organic molecules pass, rendering the lev layer a microporous silicate layer. The lev layers in the structure of RUB-56, are interconnected to neighboring ones by bands of water molecules being hydrogen bonded to each other and to the terminal Si–OH-/Si–O- groups of the layers (see Figure 2). The diethyldimethylammonium cations which are intercalated between water bands and lev layers compensate their negative charge. Like ITQ-8, RUB-56 is also an interesting material to act as a precursor for the synthesis of microporous framework silicates by interlayer expansion reactions. Intercalating suitable metal-linker units like Si(CH3)2Cl2, Fe(III)Cl3 or Fe(III) acetylacetonate and docking these linkers to two neighboring lev layers would lead to framework structures with three-dimensional pore systems.
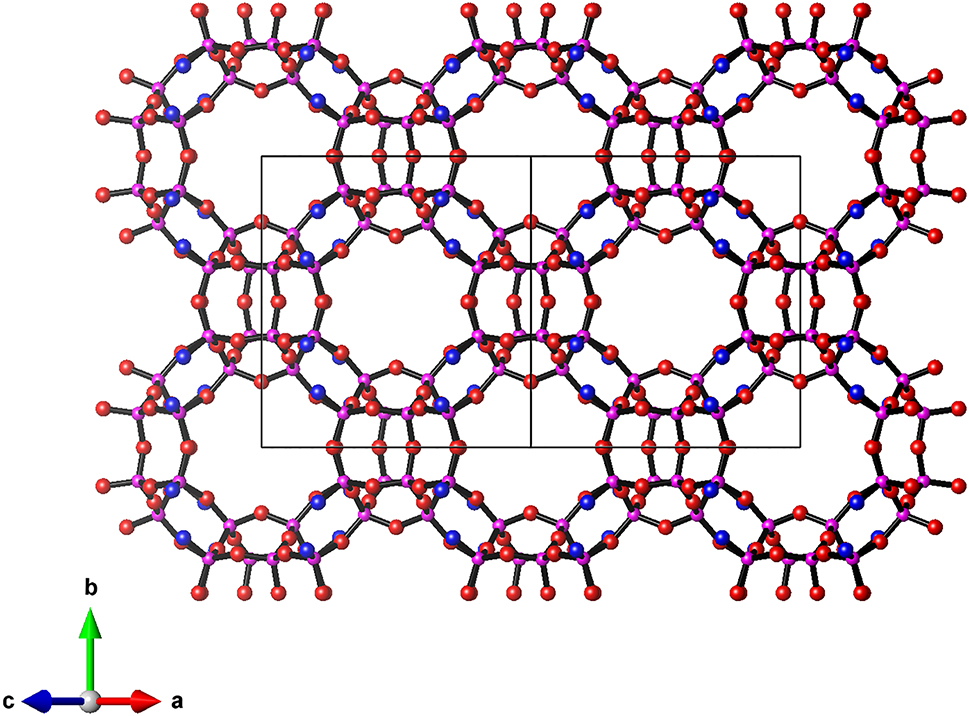
The lev layer projected on (010) to show the 8-ring pores. Si: purple, O: red, O–/OH groups: blue.
![Figure 2:
The structure of RUB-56 constructed from silicate layers ([SiO4] = blue tetrahedra with terminal O–/OH groups as blue spheres), bands of hydrogen bonded water molecules (light blue) and diethyldimethylammonium cations (C: brown, N: green).](/document/doi/10.1515/ncrs-2024-0067/asset/graphic/j_ncrs-2024-0067_fig_002.jpg)
The structure of RUB-56 constructed from silicate layers ([SiO4] = blue tetrahedra with terminal O–/OH groups as blue spheres), bands of hydrogen bonded water molecules (light blue) and diethyldimethylammonium cations (C: brown, N: green).
Funding source: International Network of Centers of Excellence (INCOE) project coordinated by BASF SE, Germany
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: International Network of Centers of Excellence (INCOE) project coordinated by BASF SE, Germany.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rodriguez-Carvajal, J. FullProf: A Program for Rietveld Refinementand Profile Matching Analysis of Complex Powder Diffraction Patterns Version 7.30; ILL: Grenoble, France, 2020. http://www.ill.eu/sites/fullprof/index.html.Search in Google Scholar
2. Momma, K., Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889811038970.Search in Google Scholar
3. Feyen, M., Mueller, U., Bao, X., Zhang, W., De Vos, D., Gies, H., Xiao, F.-S., Yokoi, T., Kolb, U., Marler, B., Wang, Y., De Baerdemaeker, T., Shi, C., Pan, X., Meng, X., Gruenewald-Lueke, A. A layered silicate. US Patent Application 2021/0101800 A1, 2021.Search in Google Scholar
4. Marler, B., Gies, H. Hydrous layer silicates as precursors for zeolites obtained through topotactic condensation a review. Eur. J. Mineral. 2012, 24, 405–428; https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2012/0024-2187.Search in Google Scholar
5. Ramos, F. S. O., de Pietre, M. K., Pastore, H. O. Lamellar zeolites: an oxymoron? RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2084–2111; https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra21573j.Search in Google Scholar
6. Roth, W. J., Gil, B., Marszalek, B. Comprehensive system integrating 3D and 2D zeolite structures with recent new types of layered geometries. Catal. Today 2014, 227, 9–14; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2013.09.032.Search in Google Scholar
7. Diaz-Cabañas, M. J., Camblor, M. A., Liu, Z., Ohsuna, T., Terasaki, O. Zeolite syntheses using linear diquats of varying length in fluoride media. The synthesis of ITQ-8, ITQ-10, ITQ-14 and high silica Nu-87. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 249–257; https://doi.org/10.1039/b105273j.Search in Google Scholar
8. Marler, B., Müller, M., Gies, H. Structure and properties of ITQ-8: a hydrous layer silicate with microporous silicate layers. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 10155–10164; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6dt00713a.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Zhang, L., Gruenewald-Lueke, A., Marler, B., Wei, Y., Gies, H. Two new hydrous layer silicates – RUB-56 and RUB-57. In Book of Abstracts, IV Int. Workshop on Layered Materials: Campinas, Brazil, 2012; pp. 139–140.Search in Google Scholar
10. Marler, B., Gruenewald-Lueke, A., Ikeda, T., Zuber, P., Gies, H. Database of hydrous layer silicates. https://hls-database.com/.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3

