Abstract
C16H14N2OS, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 13.8369(4) Å, b = 15.8967(4) Å, c = 13.8600(4) Å, β = 109.983(1)°, V = 2865.11(14) Å3, Z = 8, R gt(F) = 0.0439, wR ref(F 2) = 0.1091, T = 296.15 K.
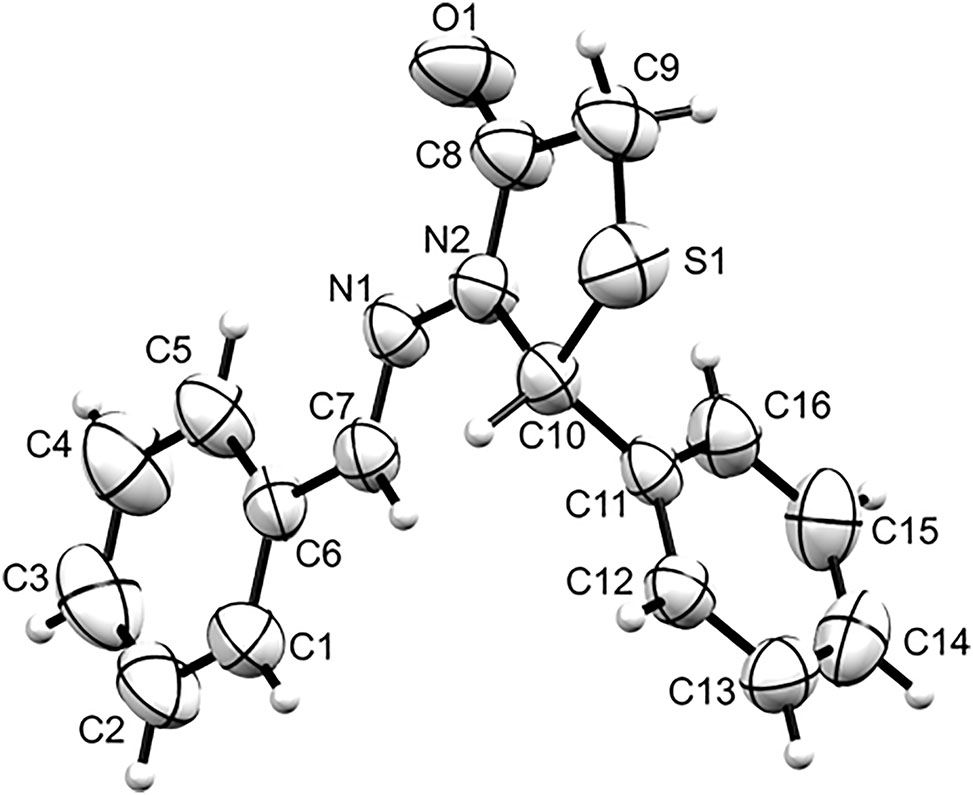
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.21 × 0.18 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | MoKα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.22 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.5°, 99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 43,056, 6440, 0.029 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 5007 |
| N(param) refined: | 411 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], Shelx [3], Olex2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.80113 (11) | 0.48262 (8) | 0.52504 (12) | 0.0746 (5) |
| O1 | 0.59821 (13) | 0.60062 (10) | 0.60184 (16) | 0.0893 (6) |
| N1 | 0.73209 (13) | 0.71535 (9) | 0.57983 (12) | 0.0505 (4) |
| N2 | 0.74721 (12) | 0.63002 (9) | 0.57233 (12) | 0.0502 (4) |
| C1 | 0.85699 (19) | 0.91160 (14) | 0.56051 (18) | 0.0721 (6) |
| H1 | 0.91369 (19) | 0.89048 (14) | 0.54690 (18) | 0.0865 (8)* |
| C2 | 0.8448 (2) | 0.99829 (16) | 0.5677 (2) | 0.0886 (8) |
| H2 | 0.8940 (2) | 1.03494 (16) | 0.5600 (2) | 0.1064 (10)* |
| C3 | 0.7604 (3) | 1.02951 (15) | 0.5861 (2) | 0.0928 (9) |
| H3 | 0.7521 (3) | 1.08731 (15) | 0.5900 (2) | 0.1114 (10)* |
| C4 | 0.6885 (3) | 0.97586 (15) | 0.5985 (2) | 0.0913 (8) |
| H4 | 0.6313 (3) | 0.99744 (15) | 0.6109 (2) | 0.1095 (10)* |
| C5 | 0.69976 (19) | 0.89009 (13) | 0.59293 (18) | 0.0680 (6) |
| H5 | 0.65059 (19) | 0.85410 (13) | 0.60205 (18) | 0.0816 (7)* |
| C6 | 0.78443 (16) | 0.85726 (12) | 0.57371 (14) | 0.0521 (5) |
| C7 | 0.79769 (16) | 0.76613 (12) | 0.56561 (14) | 0.0518 (5) |
| H7 | 0.85358 (16) | 0.74544 (12) | 0.55020 (14) | 0.0621 (5)* |
| C8 | 0.67520 (18) | 0.57766 (13) | 0.58712 (18) | 0.0620 (5) |
| C9 | 0.70427 (19) | 0.48644 (13) | 0.5843 (2) | 0.0711 (6) |
| H9a | 0.64470 (19) | 0.45370 (13) | 0.5449 (2) | 0.0853 (8)* |
| H9b | 0.73087 (19) | 0.46369 (13) | 0.6533 (2) | 0.0853 (8)* |
| C10 | 0.83518 (15) | 0.59357 (11) | 0.55153 (14) | 0.0493 (4) |
| H10 | 0.84076 (15) | 0.61969 (11) | 0.48961 (14) | 0.0592 (5)* |
| C11 | 0.93671 (14) | 0.60321 (10) | 0.63844 (14) | 0.0458 (4) |
| C12 | 1.02737 (16) | 0.60309 (12) | 0.61672 (16) | 0.0546 (5) |
| H12 | 1.02459 (16) | 0.60108 (12) | 0.54876 (16) | 0.0655 (6)* |
| C13 | 1.12151 (17) | 0.60589 (13) | 0.69432 (19) | 0.0658 (6) |
| H13 | 1.18173 (17) | 0.60487 (13) | 0.67868 (19) | 0.0789 (7)* |
| C14 | 1.1263 (2) | 0.61021 (14) | 0.7951 (2) | 0.0761 (7) |
| H14 | 1.1897 (2) | 0.61224 (14) | 0.8477 (2) | 0.0913 (8)* |
| C15 | 1.0364 (2) | 0.61152 (16) | 0.81768 (17) | 0.0758 (7) |
| H15 | 1.0394 (2) | 0.61480 (16) | 0.88566 (17) | 0.0910 (8)* |
| C16 | 0.94206 (18) | 0.60798 (13) | 0.73990 (16) | 0.0624 (5) |
| H16 | 0.88194 (18) | 0.60882 (13) | 0.75571 (16) | 0.0749 (6)* |
| S2 | 0.47471 (14) | 0.87662 (8) | 0.67313 (12) | 0.0869 (6) |
| O2 | 0.39559 (15) | 0.78070 (11) | 0.88800 (13) | 0.0852 (5) |
| N3 | 0.40935 (13) | 0.65434 (9) | 0.76625 (12) | 0.0512 (4) |
| N4 | 0.42559 (13) | 0.73714 (9) | 0.74434 (12) | 0.0508 (4) |
| C17 | 0.36990 (18) | 0.48535 (13) | 0.80700 (18) | 0.0647 (6) |
| H17 | 0.35290 (18) | 0.52688 (13) | 0.84569 (18) | 0.0776 (7)* |
| C18 | 0.3519 (2) | 0.40260 (15) | 0.8223 (2) | 0.0884 (8) |
| H18 | 0.3230 (2) | 0.38827 (15) | 0.8715 (2) | 0.1060 (10)* |
| C19 | 0.3762 (2) | 0.34048 (15) | 0.7655 (2) | 0.0934 (9) |
| H19 | 0.3622 (2) | 0.28452 (15) | 0.7751 (2) | 0.1120 (10)* |
| C20 | 0.4213 (2) | 0.36117 (15) | 0.6944 (2) | 0.0854 (8) |
| H20 | 0.4391 (2) | 0.31918 (15) | 0.6568 (2) | 0.1025 (9)* |
| C21 | 0.44020 (18) | 0.44434 (13) | 0.67901 (17) | 0.0661 (6) |
| H21 | 0.47118 (18) | 0.45824 (13) | 0.63125 (17) | 0.0794 (7)* |
| C22 | 0.41333 (15) | 0.50752 (11) | 0.73417 (15) | 0.0516 (4) |
| C23 | 0.43125 (15) | 0.59615 (11) | 0.71380 (14) | 0.0495 (4) |
| H23 | 0.45840 (15) | 0.60956 (11) | 0.66292 (14) | 0.0594 (5)* |
| C24 | 0.41574 (16) | 0.79630 (13) | 0.81165 (16) | 0.0559 (5) |
| C25 | 0.4356 (2) | 0.88308 (13) | 0.78137 (19) | 0.0707 (6) |
| H25a | 0.4890 (2) | 0.90979 (13) | 0.83772 (19) | 0.0848 (7)* |
| H25b | 0.3736 (2) | 0.91672 (13) | 0.76524 (19) | 0.0848 (7)* |
| C26 | 0.45345 (15) | 0.76256 (11) | 0.65598 (14) | 0.0466 (4) |
| H26 | 0.51791 (15) | 0.73500 (11) | 0.65947 (14) | 0.0559 (5)* |
| C27 | 0.37313 (14) | 0.74560 (10) | 0.55294 (14) | 0.0461 (4) |
| C28 | 0.40457 (19) | 0.73730 (13) | 0.46840 (15) | 0.0616 (5) |
| H28 | 0.47430 (19) | 0.73688 (13) | 0.47728 (15) | 0.0739 (6)* |
| C29 | 0.3324 (2) | 0.72966 (15) | 0.37109 (18) | 0.0839 (7) |
| H29 | 0.3539 (2) | 0.72466 (15) | 0.31467 (18) | 0.1007 (8)* |
| C30 | 0.2304 (3) | 0.72940 (16) | 0.3572 (2) | 0.0958 (9) |
| H30 | 0.1824 (3) | 0.72499 (16) | 0.2914 (2) | 0.1150 (11)* |
| C31 | 0.1980 (2) | 0.73564 (15) | 0.4404 (2) | 0.0857 (8) |
| H31 | 0.1281 (2) | 0.73437 (15) | 0.4308 (2) | 0.1028 (10)* |
| C32 | 0.26924 (16) | 0.74381 (12) | 0.53869 (18) | 0.0617 (5) |
| H32 | 0.24719 (16) | 0.74807 (12) | 0.59481 (18) | 0.0740 (6)* |
1 Source of material
All reagents were purchased from Merck and used as obtained. The target compound was synthesized in two synthetic steps where the intermediate (1E,2E)-1,2-dibenzylidenehydrazine was obtained according to Brown with slight modification [5]. In the first step, benzaldehyde (19.6 mmol) and acetic acid (0.5 mL) were added to a round bottom flask containing 10 mL of absolute ethanol. To this mixture, 2 mol equivalence of hydrazine monohydrate was added dropwise and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. Thereafter, the precipitate was filtered and dried under vacuum. To synthesize (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, a procedure by Ravichandran [6] was employed with slight modification. A mixture of (1E,2E)-1,2-dibenzylidenehydrazine (1 mmol), thioglycolic acid (1 mmol) and a catalytic amount of ZnCl2 was refluxed at 100 °C overnight. After the completion of the reaction, as monitored by TLC, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the remaining residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate. The organic layer was then successively washed with water, 10 % NaHCO3 and brine solution. Subsequently, the organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure to afford the crude product. Slow evaporation of an ethanolic solution of the crude afforded colourless block crystals of the target compound. The crystals were collected by vacuum filtration and dried in vacuo. Yield = 67 %, 1 H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO‑d 6) δ (ppm): 8.26 (s, 1H, N=CH), 7.63 (d, 2H, Ar–H) 7.46–7.36 (m, 8H, Ar–H), 6.56 (s, 1H, thiazolidine-4-one-CH), 4.07 (d, J = 16.08 Hz, 1H, thiazolidine-4-one-CH2), 4.03 (d, J = 16.06 Hz, 1H, thiazolidine-4-one-CH2). 13 C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO‑d 6) δ (ppm): 168.08, 151.11, 140.07, 134.10, 131.18, 129.51, 129.33, 128.95, 127.77, 126,47, 60.90, 30.52.
2 Experimental details
Using Olex2 [2], the structure was solved with the Shelxt [3] structure solution program using intrinsic phasing and refined with the olex2.refine [4] refinement package.
3 Comment
Thiazolidinones are widely recognized for their remarkable biological properties, including anticancer [7] and antidiabetic effects [8, 9]. The electron-rich thiazole component of the pharmacophore makes it an ideal ligand for binding to enzymes and receptors [10]. As a result, medicinal chemists find thiazolidinones to be an intriguing subject of study [11]. In this work, we report a crystal structure of a novel thiazolidinone derivative.
The crystal structure of the title compound consists of two symmetrically independent molecules in the asymmetric unit. Each molecular unit has a thiazolidinone core with benzylideneamino and phenyl moieties bonded to the alpha nitrogen (N2 and N4) and beta carbon (C10 and C26) atoms, respectively. Despite the thiazolidinone core having two sp 3 hybridized carbons, the five-membered heterocycle is almost planar with N2–C8–C9–S1–C10 and N4–C24–C25–S2–C26 root mean squared deviation (RMSD) values of 0.111 and 0.030 Å, respectively. On one hand, the phenyl moiety is almost orthogonal with respect to the thiazolidinone core (dihedral angle = 98.42–100.43°) which is similar to the previously reported 3-anilino-5-methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one and 3-anilino-5-methyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives [12]. On the other hand, the benzylideneamino group is relatively coplanar with the thiazolidinone core (dihedral angle = 6.87(7)–10.23(8)°) which is different from other substituted thiazolidinone derivatives [13, 14]. Intermolecular C23–H23⋯O1 (C23⋯O1 = 3.194(2) Å; C23–H23⋯O1 = 148°; symmetry code: x, y, z) and C7–H7⋯O2 (C7⋯O2 = 3.275(3) Å; C7–H7⋯O2 = 136°; symmetry code: 1/2 + x, 3/2 − y, −1/2 − z) hydrogen bonding patterns were observed in the crystal packing of the title compound. These C–H⋯O interactions join neighbouring molecules to form a chain structure that extends diagonally with respect to the crystallographic ac plane.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: National Research Foundation (South Africa) for a Competitive grant for rated researchers (Grant Number: SRUG2204092857).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Brown, M. J. Synthesis, Structure and Functionalisation of 1, 2-Diazetidines. Doctoral dissertation, University of Warwick, 2011.Search in Google Scholar
2. Ravichandran, V., Jain, A., Kumar, K. S., Rajak, H., Agrawal, R. K. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of thiazolidinone derivatives as antimicrobial and anti-viral agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 464–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747–0285.2011.01149.x.10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01149.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Bruker. Apex II; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
5. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
6. Bourhis, L. J., Dolomanov, O. V., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. The anatomy of a comprehensive constrained, restrained refinement program for the modern computing environment-Olex2 dissected. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 59–75; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314022207.Search in Google Scholar
7. Finiuk, N., Kryshchyshyn-Dylevych, A., Holota, S., Klyuchivska, O., Kozytskiy, A., Karpenko, O., Manko, N., Ivasechko, I., Stoika, R., Lesyk, R. Novel hybrid pyrrolidinedione-thiazolidinones as potential anticancer agents: synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114422.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Gummidi, L., Kerru, N., Ebenezer, O., Awolade, P., Sanni, O., Islam, M. S., Singh, P. Multicomponent reaction for the synthesis of new 1, 3, 4-thiadiazole-thiazolidine-4-one molecular hybrids as promising antidiabetic agents through α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105210.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Khan, S. A., Ali, M., Latif, A., Ahmad, M., Khan, A., Al-Harrasi, A. Mercaptobenzimidazole-based 1, 3-thaizolidin-4-ones as antidiabetic agents: synthesis, in vitro α-glucosidase inhibition activity, and molecular docking studies. ACS Omega 2021, 7, 28041–28051. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c01969.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
10. Yang, X. C., Zhang, P. L., Kumar, K. V., Li, S., Geng, R. X., Zhou, C. H. Discovery of unique thiazolidinone-conjugated coumarins as novel broad spectrum antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 232, 114192. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202200618.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
11. Chawla, P. A., Wahan, S. K., Negi, M., Faruk, A., Chawla, V. Synthetic strategies and medicinal perspectives of 4 -thiazolidinones: recent developments and structure -activity relationship studies. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2023, 60, 1248–1286. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.4596.Search in Google Scholar
12. Ekinci, A. S., Moncol, J., Krishna, V. S., Sriram, D., Ozadali-Sari, K. 5-methyl-4-thiazolidinones: synthesis and evaluation as antitubercular agents. J. Res. Pharm. 2020, 24, 1–8; https://doi.org/10.35333/jrp.2020.110.Search in Google Scholar
13. Akkurt, M., Celik, I., Demir, H., Ozkirimli, S., Buyukgungor, O. N-[5-Methyl-2-(2-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl]pyridine-3-carboxamide monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. 2011, E67, o293; https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536811000481.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
14. Akkurt, M., Celik, I., Demir, H., Ozkirimli, S., Buyukgungor, O. N[2-(4-Chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-oxo-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl]pyridine-3-carboxamide. Acta Crystallogr. 2011, E67, o745; https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536811007136.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of tris((Z)-2-hydroxy-N-((E)-pyridin-2-ylmethylene)benzohydrazonato-k2O,N)europium(III), C39H30N9O6Eu
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(benzylideneamino)-2-phenylthiazolidin-4-one, C16H14N2OS
- The crystal structure of (E)-4-fluoro-N′-(1-(o-tolyl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C16H15FN2O
- Crystal structure of (6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-methoxy-4-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethoxy)benzoate, C12H14O6
- The crystal structure of bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)(picolinoyl)amido-κ2 N:N′]copper(II), C26H22CuN4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[di(μ2-aqua)-diaqua-bis(3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-tetra(μ2-3-aminopyridine-4-carboxylate-κ2 O: O′)-dineodymium(III), [Nd2(C6H5N2O2)6(H2O)4] n
- The crystal structure of t-butyl 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(propan-2-yl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate, C28H34FNO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(benzylamine-κ1 N)-(sorbato-κ1 O)-(μ2-sorbato-κ2 O,O′)-copper(II), C19H23CuNO4
- Crystal structure of (4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)(ferrocenyl) methanone, C21H16ClFeNO
- The crystal structure of N-[4-(4-bromophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-3-(2-methylphenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enamide hydrate, C19H17BrN2O2S2
- The crystal structure of N′-{5-[2-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy) acetamido]-4-hydroxy-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl}-3-methyl-2-(2-oxo-1,3-diazinan-1-yl)butanamide hydrate
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C26H24O3
- Crystal structure of naphthalen-1-ylmethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C25H22O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua- (μ4-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5N:O,O’:O’’:O’’’)calcium(II), C10H9CaN3O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-((E)-3-(dimethylamino)acryloyl)-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N, N-dimethylformimidamide, C14H19N3O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one, C13H17NO4
- Crystal structure of (2-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C20H18ClNO3
- The crystal structure of diethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate, C21H27NO4
- Crystal structure of (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-17-((4-(2-phenylpropyl)phenyl)ethynyl)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C36H42O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione, C15H13N3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(2,6-di-(2-pyridyl)-pyridine-κ3 N,N′, N″)(μ2-1,4-naphthalene dicarboxylato-κ2 O,O′)nickel(II)], C27H19NiN3O5
- Crystal structure of 3-(diphenylphosphoryl)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylpropan-1-one, C21H19O3P
- The crystal structure of R,S-{N-[(2-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylidene]phenylglycinato}divinylsilicon, C23H19NO3Si
- The crystal structure of 1,2,4-tris(bromomethyl)benzene, C9H9Br3
- Crystal structure of chlorido-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)benzaldehyde-κ2 N,C]-(diethylamine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C16H18ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of 3-(methoxycarbonyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2,3,4,9- tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-ium chloride hydrate, C40H48Cl2N4O9
- The crystal structure of 1-(2-chlorobenzyl)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)urea, C14H12Cl2N2O
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of aqua-tris(4-acetamidobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)terbium(III) hydrate C39H36N5O11Tb
- The crystal structure of zwitterionic 3-aminoisonicotinic acid, C6H6N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis{[monoaqua-μ2-4-[(pyridine-4-carbonyl)-amino]-phthalato-κ3 N:O,O′-(2,2′-bipyridine κ2 N,N′)copper(II)]}decahydrate, C48H56N8O22Cu2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ10-4,4′-methylene-bis(oxy)benzoatodipotassium], C15H10K2O6
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[[tetraaqua[(μ2-1,4-di(4-methyl-1-imidazolyl)benzene] cobalt(II)]bis(formate)], C16H24CoN4O8
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-chloro-5-((2-(nitromethylene)imidazolidin-1-yl)methyl)pyridine, C10H11ClN4O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-1-(((2-amino-4,5-dimethylphenyl)iminio)methyl)naphthalen-2-olate, C19H18N2O
- Crystal structure of N-(acridin-9-yl)-2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl) acetamide monohydrate, C21H25N3O2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(3-methyl-3-imidazolium-1-ylpropionato-κ2 O,O′)-zinc(II), C14H20Cl2N4O4Zn
- The crystal structure of 2,8-diethyl-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-4λ4,5λ4-spiro[dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine-5,2′-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinine], C25H29BN2O2
- The crystal structure of 5-tert-butyl-2-(5-tert-butyl-3-iodo-benzofuran-2-yl)-3-iodobenzofuran, C24H24I2O2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of methyl 2-{[4-(4-cyclopropyl-1-naphthyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-yl]thio} acetate, C18H17N3O2S
- The crystal structure of n-propylammonium bis(2,3-dimethylbutane-2,3-diolato)borate-boric acid (1/1), [C3H10N][C12H24BO4]·B(OH)3
- Crystal structure of methyl 1-(2-bromophenyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C19H17BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of (4-bromobenzyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide ethanol solvate, C52H48Br4OP2
- The crystal structure of unsymmetrical BOPHY C26H27BN4
- The crystal structure of Tb3B5O11(OH)2
- The crystal structure of (Z)-4-ethyl-2-((4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2H-pyrrol-1-ium 2,2'-spirobi[naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]dioxaborinin]-2-uide, C37H37BN2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(methylammonium) hexadecaselenidopalladate(II), (CH3NH3)2PdSe16
- The crystal structure of (2-diphenylphosphanylphenyl) 2-[7-(dimethylamino)-2-oxochromen-4-yl]acetate, C31H26NO4P
- Crystal structure of (E)-6-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C23H25FN2O
- The structure of RUB-56, (C6H16N)8 [Si32O64(OH)8]·32 H2O, a hydrous layer silicate (2D-zeolite) that contains microporous levyne-type silicate layers
- Crystal structure of 4-amino-3,5-dibromobenzonitrile, C7H4Br2N2
- Crystal structure of 2-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl 2-acetoxybenzoate, C21H18O4
- Single-crystal structure determination of Tm3B12O19(OH)7
- Crystal structure determination of NdB3.6O7
- The crystal structure of NdB6O8(OH)5·H3BO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H25NO3
- Crystal structure of N-(1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropyl)aniline, C18H23NO2
- Crystal structure of Ba6Cd12Mn4SiF48
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-fluoro-1-methyl-2-oxo-3-(2-oxochroman-4-yl)indolin-3-yl acetate, C20H16FNO5
- The crystal structure of 6-methacryloylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4-nitrobenzenesulfonate, C17H13NO8S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazin-1-yl)- 2,2-difluoroacetate, C19H16F2N2O3
- The crystal structure of tetrakis(μ 2-(1H-benzimidazole-2-methoxo-κ2 N,O:O:O)-(n-butanol-κO)-chlorido)-tetranickel(II), C48H68Cl4N8O8Ni4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis((1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)piperidin-1-ium-4-carbonyl)oxy-κO)zinc(II)hexahydrate, C46H64N2O28S2Zn
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-carboxybutyl)-3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium hexafluoridophosphate, C9H15F6N2O2P
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(2-furoyl)-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-ol, C20H13ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of dimethyl (R)-2-(3-(1-phenylethyl)thioureido)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylate, C25H24N2O4S
- The crystal structure of 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-1H-imidazole-3-oxide, C7H10N2O3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 4,4′-(propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy))dibenzoate, C19H20O6
- Crystal structure of methyl-1-(p-tolyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate, C20H20N2O2
- The crystal structure of 1-(1-adamantan-1-yl)ethyl-3-(3-methoxyphenyl)thiourea, C20H28N2OS
- The crystal structure of N,N′-carbonylbis(2,6-difluorobenzamide), C15H8F4N2O3

