Abstract
C8H18NCl, orthorhombic, P212121 (no. 19), a = 5.5244(3) Å, b = 11.0915(6) Å, c = 16.0339(12) Å, V = 982.46(11) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0295, wRref(F2) = 0.0785, T = 233(2) K.
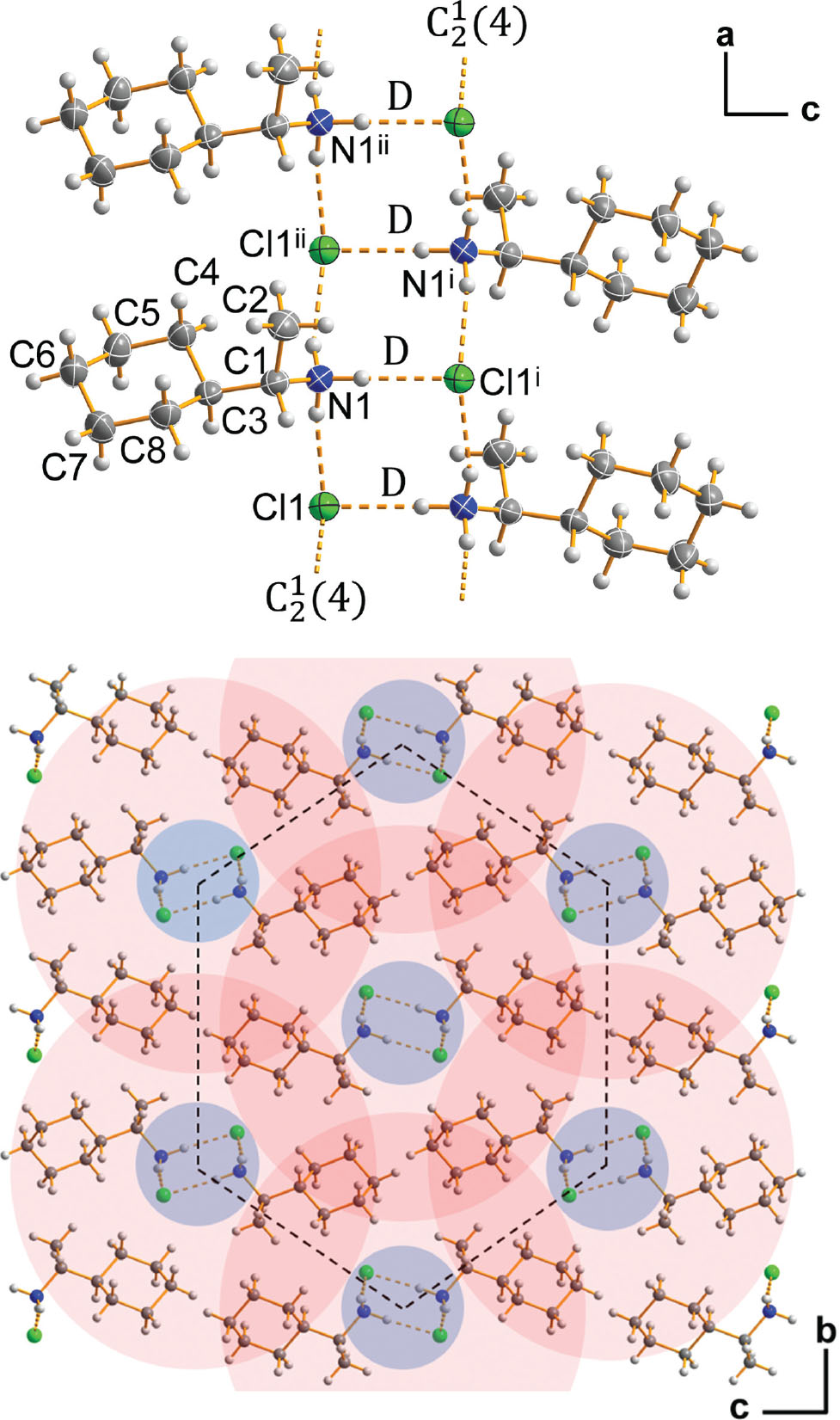
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless needle |
| Size: | 0.90 × 0.30 × 0.22 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.33 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | STOE IPDS 2T, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 17396, 2248, 0.130 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2242 |
| N(param)refined: | 104 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], [2], Diamond [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl1 | 0.09050(8) | 0.13794(4) | 0.90935(3) | 0.04724(14) |
| N1 | 0.5898(3) | 0.27635(16) | 0.90315(9) | 0.0444(3) |
| H1 | 0.591(6) | 0.306(3) | 0.9595(19) | 0.083(9)* |
| H2 | 0.718(5) | 0.233(2) | 0.8945(15) | 0.051(6)* |
| H3 | 0.454(5) | 0.234(2) | 0.8988(16) | 0.060(7)* |
| C1 | 0.5740(3) | 0.37912(16) | 0.84298(10) | 0.0419(4) |
| H11 | 0.430457 | 0.427885 | 0.858132 | 0.050* |
| C2 | 0.7976(4) | 0.4579(2) | 0.85491(14) | 0.0553(5) |
| H21 | 0.942117 | 0.409722 | 0.846500 | 0.083* |
| H22 | 0.798134 | 0.490713 | 0.910996 | 0.083* |
| H23 | 0.794914 | 0.523408 | 0.814835 | 0.083* |
| C3 | 0.5348(3) | 0.33088(15) | 0.75430(11) | 0.0386(4) |
| H31 | 0.403387 | 0.270368 | 0.757415 | 0.046* |
| C4 | 0.7574(4) | 0.26687(19) | 0.71782(11) | 0.0462(4) |
| H41 | 0.892637 | 0.323819 | 0.714409 | 0.055* |
| H42 | 0.805469 | 0.200627 | 0.754716 | 0.055* |
| C5 | 0.7024(4) | 0.21738(19) | 0.63133(12) | 0.0511(5) |
| H51 | 0.848055 | 0.179046 | 0.608637 | 0.061* |
| H52 | 0.575879 | 0.155761 | 0.635539 | 0.061* |
| C6 | 0.6196(4) | 0.3160(2) | 0.57266(11) | 0.0521(4) |
| H61 | 0.577808 | 0.280803 | 0.518493 | 0.063* |
| H62 | 0.751747 | 0.373628 | 0.564026 | 0.063* |
| C7 | 0.3998(4) | 0.3819(2) | 0.60811(13) | 0.0585(5) |
| H71 | 0.357207 | 0.449187 | 0.571326 | 0.070* |
| H72 | 0.261602 | 0.326532 | 0.609972 | 0.070* |
| C8 | 0.4496(4) | 0.42975(18) | 0.69545(12) | 0.0487(4) |
| H81 | 0.573596 | 0.492782 | 0.692381 | 0.058* |
| H82 | 0.301558 | 0.466201 | 0.717775 | 0.058* |
Source of material
For the synthesis of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride 0.057 g (0.45 mmol) (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylamine (Sigma-Aldrich) were mixed with 2 mL concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 mL methanol. Colourless crystals (m.p. 521 K) suitable for X-ray crystal structure determination grew in the course of evaporating this solution to dryness under isothermal conditions (T = 293 K). Note that the compound crystallizes acicular with a strong tendency of the needles to break into thinner segments. Raman spectra were measured with a Bruker MultiRAM spectrometer equipped with a Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm) and an InGaAs detector. Raman 4000-70 cm−1: ν(C—H): 3050 cm−1 (w); ν(N—H): 2972 cm−1 (m); ν(C—H): 2928 cm−1 (vs), 2860 cm−1 (s); δas(C—H): 1444 cm−1 (m). IR spectroscopic data were obtained with a Perkin-Elmer Spektrum Two FT-IR spectrometer equipped with a LiTaO3 detector and universal ATR equipment. IR 4000-350 cm−1: ν(N—H): 2969 cm−1 (m); ν(C—H): 2924 cm−1 (vs), 2883 cm−1 (s), 2854 cm−1 (s), δ(N—H): 1606 cm−1 (m), 1518 cm−1 (m), δ(C—H): 1455 cm−1 (w), 1395 cm−1 (w). The band assignments are based on [4]. A CHN analysis was performed with a Elementar Analysensysteme vario Micro CUBE. EA C8H18NCl (163.688 g/mol): C 58.42, H 10.98, N 8.51; calc. C 58.70, H 11.08, N 8.56.
Experimental details
Positions of the H atoms bound to N1 and the majority of the hydrogen atoms bound to carbon atoms were identified by difference-Fourier synthesis. Coordinates and isotropic displacement parameters of the N-bonded H atoms were refined. For the C-bonded hydrogen atoms in the refinement a riding model was applied using idealized C—H bond lengths (0.97–0.99 Å) and H—C—H and C—C—H angles. In addition, the H atoms of the CH3-group were allowed to rotate around the adjacent C—C bond. The Uiso(C) values were set to 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl) and 1.2Ueq(Cmethylene and Cmethine). Absolute structure parameters were refined to 0.01(2) (Flack [5]) and 0.002(17) (Hooft [6]).
Comment
Enantiomers do not differ in their physical and chemical properties, but could differ in their physiological mode of action [7]. Therefore crystal structures of chiral amines or hydrochlorides thereof are almost exclusively related to investigations prior to pharmacological use. However, enantiomeric pure chiral amines or the related aminium ions may also serve as chiral building blocks for the construction of chiral supramolecular hydrogen-bonded networks in crystal engineering. Surprisingly, only very few crystal structures of carbon-based chiral primary amine hydrochlorides [R*–NH3]Cl are known so far, namely (S)-(–)-1-(4-methylphenyl)ethylammonium chloride [8], (S)-α-methylbenzylammonium chloride [9] and rimantadine hydrochloride [10]. Herein we present the crystal structure of the ‘chiral salt’ (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride that exhibits a ladder-shaped hydrogen-bonded double chain combined with a ‘ladder in the tube’ structure motif based on the surrounding organic substituents.
The title compound crystallizes in the noncentrosymmetric space group P212121. The absolute structure is given by synthesis based on the corresponding amine, (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylamine. The asymmetric unit of the crystal structure is defined by one (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium cation and one chloride anion. In the protonated amine moiety the bond lengths N1—C1 1.496(2) Å, C1—C2 1.526(3) Å, and C1—C3 1.535(2) Å as well as the angles at C1 are as expected [11]. The cyclohexyl group of the cation is present in the energetically most favourable conformation, the chair conformation [12]. The C—C bonds in the group have bond lengths of 1.514(3) Å to 1.536(3) Å with an average length of 1.524(3) Å, which is close to the reference value of 1.535(16) Å for C(sp3)–C(sp3) bonds in cyclohexyl groups [11]. In correspondence with the values given by Bastiansen et al. (gas phase ED of C6H12, [13]) and Kahn et al. (crystal structure analysis of C6H12-II [14]), the C—C—C bond angles in the six-membered ring vary from 110.17(15)° to 112.02(16)°, averaging to 111.10(16)° ([13]: 111.4°; [14]: 111.34°). The torsion angles in the cyclohexyl group range from 54.6(3)° to 57.4(2)° with an average value of 55.8(2)°, which is in good agreement with the calculated value of 55.7° [15]. Taking a closer look at the cation’s structure, it is obvious that C5—C6 is shorter and C3—C4 is longer than the average bond length in the cyclohexyl moiety. This is the only feature that might be attributed to the asymmetry of the chiral ethylaminium ‘substituent’ in equatorial postion. However, the difference is at the border of significance and the torsion angles C1—C3—C4—C5 [177.85(15)°] and C1—C3—C8—C7 [177.56(16)°] do not seem to be different, in both cases indicating a nearly staggered conformation. The NH3 group of the cation is engaged in N—H⋯Cl type hydrogen bonds to the neighbouring Cl− ions and each anion serves as an acceptor for two further hydrogen bonds. The N⋯Cl distances range from 3.1529(16) to 3.1650(17) Å and the hydrogen bond angles from 163(2) to 176(3)°. According to the bond valence method [16] these hydrogen bonds have to be characterized as moderately strong. As shown in the upper part of the figure, altogether the hydrogen bonds form a double-chain hydrogen bond system propagating along the a axis of the unit cell that is similar to the system found in (S)-(–)-1-(4-methylphenyl) ethylammonium chloride [8]. Note the graph set symbols [17] of the two hydrogen bond motifs defining this ladder-like structure. Projected along the chain propagation direction the lower part of the figure shows a packing diagram indicating the arrangement of the double-chains (blue) according to a moderately distorted hexagonal pattern. Around each of the double-chains a closed surrounding of organyl groups can be recognized that reminds of a tube (red). Each organyl group is part of three neighbouring tubes, giving a pattern of interpenetrating tubular ‘organic’ sections visualized by the different red areas in the figure. We suppose that this ‘ladder in the tube’-structure with its tightly interlocking organic groups is responsible for the unexpected high thermal stability (m. p. 521 K) in comparison to other classes of organylammonium chlorides.
Acknowledgements
We thank E. Hammes and P. Roloff for technical support.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar
3. Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.0. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany (2014).Search in Google Scholar
4. Hesse, M.; Meier, H.; Zeeh, B.: Spektroskopische Methoden in der organischen Chemie. 7th ed. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York (2005).10.1055/b-002-46985Search in Google Scholar
5. Flack, H. D.: On enantiomorph-polarity estimation. Acta Crystallogr. A39 (1983) 876–881.10.1107/S0108767383001762Search in Google Scholar
6. Hooft, R. W. W.; Straver, L. H.; Spek, A. L.: Determination of absolute structure using Bayesian statistics on Bijvoet differences. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41 (2008) 96–103.10.1107/S0021889807059870Search in Google Scholar
7. Fassihi, A. R.: Racemates and enantiomers in drug development. Int. J. Pharm. 92 (1993) 1–14.10.1016/0378-5173(93)90257-GSearch in Google Scholar
8. Hernández, G.; Bernès, S.; Portillo, R.; Gutiérrez, R.: (S)-(–)-1-(4-Methylphenyl)ethylammonium chloride. Acta Crystallogr. E63 (2007) o1053–o1055.10.1107/S1600536807003753Search in Google Scholar
9. Ben Salah, A. M.; Naïli, H.; Mhiri, T.; Bataille, T.: Synthesis and crystal structure of a chiral aromatic amine chloride salt (C8H12N)Cl. Crystallogr. Rep. 60 (2015) 1053–1057.10.1134/S1063774515070032Search in Google Scholar
10. Mishnev, A.; Stepanovs, D.: Crystal structure explains crystal habit for the antiviral drug rimantadine hydrochloride. Z. Naturforsch. B 69 (2014) 823–828.10.5560/znb.2014-4075Search in Google Scholar
11. Allen, F. H.; Kennard, O.; Watson, D. G.; Brammer, L.; Orpen, A. G.; Taylor, R.: Tables of bond lengths determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. part 1. bond lengths in organic compounds. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 12 (1987) 1–19.10.1039/p298700000s1Search in Google Scholar
12. Johnson, W. S.; Bauer, V. J.; Margrave, J. L.; Frisch, M. A.; Dreger, L. H.; Hubbard, W. N.: The energy difference between the chair and boat forms of cyclohexane. the twist conformation of cyclohexane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83 (1961) 606–614.10.1021/ja01464a027Search in Google Scholar
13. Bastiansen, O.; Fernholt, L.; Seip, H. M.; Kambara, H.; Kuchitsu, K.: Structure of cyclohexane determined by two independent gas electron-diffraction investigations. J. Mol. Struct. 18 (1973) 163–168.10.1016/0022-2860(73)85218-4Search in Google Scholar
14. Kahn, R.; Fourme, R.; André, D.; Renaud, M.: Crystal structures of cyclohexane I and II. Acta Crystallogr. B29 (1973) 131–138.10.1107/S0567740873002074Search in Google Scholar
15. Geise, H. J.; Buys, H. R.; Mijlhoff, F. C.: Conformation of non-aromatic ring compounds: part 72. an electron diffraction study of gaseous cyclohexane and methylcyclohexane. J. Mol. Struct. 9 (1971) 447–454.10.1016/0022-2860(71)87034-5Search in Google Scholar
16. Brown, I. D.: Recent developments in the methods and applications of the bond valence model. Chem. Rev. 109 (2009) 6858–6919.10.1021/cr900053kSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
17. Etter, M. C.; MacDonald, J. C.; Bernstein, J.: Graph-set analysis of hydrogen-bond patterns in organic crystals. Acta Crystallogr. B46 (1990) 256–262.10.1107/S0108768189012929Search in Google Scholar PubMed
©2020 Ann-Kathrin Scherer et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4

