Abstract
C10H14N6O2Ni2, monoclinic, I2/m (no. 12), a = 6.7377(1) Å, b = 7.3500(1) Å, c = 14.8647(2) Å, β = 96.051(1)°, V = 732.030(18) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt(F) = 0.0314, wRref(F2) = 0.0996, T = 150.01(10) K.
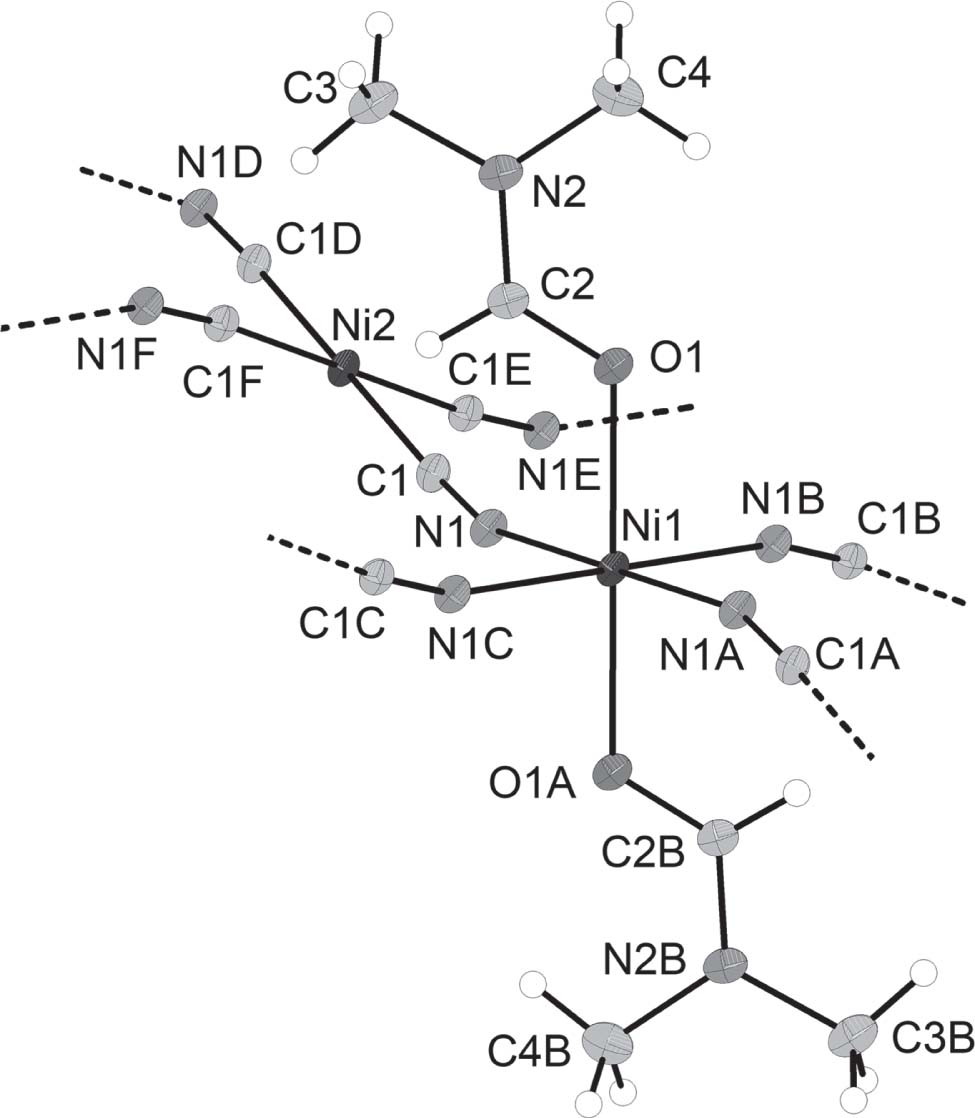
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Brown block |
| Size: | 0.2 × 0.08 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 3.30 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | XtaLAB AFC12, ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 73.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 2748, 783, 0.027 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 713 |
| N(param)refined: | 71 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], OLEX2 [2], SHELX [3], [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni1 | 1.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.0171(3) |
| Ni2 | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.0178(3) |
| O1 | 0.8655(3) | 0.5000 | 0.36693(15) | 0.0253(5) |
| N1 | 0.8040(3) | 0.2983(3) | 0.53023(13) | 0.0218(4) |
| N2 | 0.5848(4) | 0.5000 | 0.2681(2) | 0.0272(6) |
| C1 | 0.6917(3) | 0.1821(3) | 0.52274(15) | 0.0206(5) |
| C2 | 0.6801(5) | 0.5000 | 0.3500(2) | 0.0233(7) |
| H2 | 0.6040 | 0.5000 | 0.3987 | 0.028* |
| C3 | 0.3670(6) | 0.5000 | 0.2541(3) | 0.0405(10) |
| H3A | 0.315(6) | 0.5000 | 0.320(3) | 0.030(11)* |
| H3B | 0.329(5) | 0.396(5) | 0.217(3) | 0.059(10)* |
| C4 | 0.6906(7) | 0.5000 | 0.1877(3) | 0.0408(10) |
| H4A | 0.654(5) | 0.397(5) | 0.153(2) | 0.055(10)* |
| H4B | 0.828(8) | 0.5000 | 0.202(4) | 0.055(15)* |
Source of materials
A mixture of Ni(NO3)2 ⋅ 6H2O (0.1 mmol, 0.030 g), 5,15-bis(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin (0.05 mmol, 0.023 g), N,N-dimethylformamide (4 mL), acetonitrile (2 mL) and water (1 mL) was sonicated for 30 min. Then the reaction mixture was transferred to Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor and placed in the oven. Subsequently, the temperature was kept 393 K for 3 days. After cooling to room temperature at a rate of 6 K⋅h−1, brown block crystals of the title compound were obtained as a side product. Yield: 5 mg (27%, based on Ni). Anal. Calcd. for C2.5H3.5N1.5O0.5Ni0.5 (%): C, 32.67; H, 3.84; N, 22.86. Found: C, 32.25.; H, 3.26; N, 22.43.
Experimental details
Crystallographic data collection and reduction were performed using the program CrysAlisPRO [1]. Using Olex2 [2], the structure was solved with the ShelXT [3] structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL [4] refinement package. Coordinates of some hydrogen atoms were refined without any constraints or restraints others were included using a riding model (see Suppl. Material). The Uiso values were set to be 1.5Ueq of the carrier atom for methyl hydrogen atoms and 1.2Ueq for formyl hydrogen atom.
Comment
Hofmann type complexes, as one of the longest-known cyano-bridged coordination compounds, are still extensively investigated in recent years due to their unique structures and properties [5], [6], [7], [8], [9]. Up to now, a number of Hofmann complexes, varying from two-dimensional to three-dimensional structures, have been synthesized by mediating metal ions, coordinated small molecules and guest molecules [10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15], [16], [17], [18], [19]. However, the preparation method remains the classic solution chemistry method. To the best of our knowledge, the effective solvothermal method for preparing Hofmann complexes has not been reported so far. Fortunately, a Hofmann-DMF-type compound, [Ni(DMF)2Ni(CN)4]n (where DMF = N,N-dimethyl formamide), was unexpectedly synthesized by solvothermal method when the porphyrin-based Ni-MOFs were attempted to synthesize by assembling 5,15-bis(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin ligand and Ni(NO3)2. Although two isomorphous compounds have been reported [5], [6], their central metal ions and preparation method are different from those of the title compound.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains two Ni(II) ions with occupancies of 0.25, one cyanide ion (CN−), a half DMF molecule. It is particularly worth mentioning that the coordinated CN− ions derive not from the addition of the cyano compounds, but from the thermal decomposition of the solvent acetonitrile. Each Ni1 center is coordinated by four cyanide ligands in the equatorial positions and two oxygen atoms from two coordinated DMF molecules at the axial positions to form an approximately regular octahedron geometry (NiO2N4; A = −x + 2, −y + 1, −z + 1; B = −x + 2, y, −z + 1; C = x, −y + 1, z; cf. the figure). Ni1 and four coordinated nitrogen atoms are in the same plane (p1). Each Ni2 center exhibits a four-coordinated square geometry (NiC4; D = −x + 1, −y, −z + 1; E = x, −y, z; F = −x + 1, y, −z + 1; cf. the figure) by four carbon atoms from four cyanide ligands. Ni2 and four coordinated carbon atoms are also coplanar (p2). The dihedral angle between the two planes (p1 and p2) is 146.9(9)° (cf. the figure). The Ni—C, Ni—N and Ni—O bond lengths are 1.866(2), 2.0663(19) and 2.088(2) Å, respectively. The neighbouring Ni1 and Ni2 centers are connected by cyanide ligands to furnish a two-dimensional layered structure. The adjacent layers are further assembled by van-der-Waals forces to extend into a three-dimensional network structure. All bond lengths and bond angles within the title structure are in the typical ranges [20], [21].
References
1. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd., CrysAlisPRO, Version 1.171.39.28b, England (2015).Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H.: OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42 (2009) 339–341.10.1107/S0021889808042726Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Lu, R.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Yuan, A.: Syntheses, crystal structures, and thermal stabilities of the first Hofmann-DMF-type complexes Zn(DMF)2M(CN)4 (M = Ni, Pd, Pt). J. Coord. Chem. 63 (2010) 794–800.10.1080/00958971003646514Search in Google Scholar
6. Zhang, M.; Li, B. B.; Sun, J.; Kong, X. P.; Gu, P. P.; Chen, Y. Y.; Yuan, A. H.: Series of two-dimensional Hofmann-DMF-type compounds M(DMF)2M′(CN)4 (M = Cd, Fe; M′ = Ni, Pd, Pt): syntheses, structures, and thermal stabilities. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 640 (2014) 1174–1184.10.1002/zaac.201300352Search in Google Scholar
7. González, M. M.; Osiry, H.; Martínez, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Lemus-Santana, A. A.; Reguera, E.: Magnetic interaction in a 2D solid through hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471 (2019) 70–76.10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.058Search in Google Scholar
8. González, M.; Lemus-Santana, A. A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Aguirre-Velez, C. I.; Knobel, M.; Reguera, E.: Intermolecular interactions between imidazole derivatives intercalated in layered solids. Substituent group effect. J. Solid State Chem. 204 (2013) 128–135.10.1016/j.jssc.2013.05.029Search in Google Scholar
9. González, M.; Lemus-Santana, A. A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Knobel, M.; Reguera, E.: π-π Interactions and magnetic properties in a series of hybrid inorganic-organic crystals. J. Solid State Chem. 197 (2013) 317–322.10.1016/j.jssc.2012.08.026Search in Google Scholar
10. Nakano, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Sasaki, Y.: New Clathrate Compounds, Diamminemetal (Mn, Fe, Co or Zn) Tetracyanoniccolate Dibenzene and Dianiline. B. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 40 (1967) 1297.10.1246/bcsj.40.1297Search in Google Scholar
11. Iwamoto, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Fujiwara, S.: The metal ammine cyanide aromatics clathrates. I. The preparation and stoichiometry of the diamminemetal(II) tetracyano-niccolate(II) dibenzene and dianiline. B. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 40 (1967) 1174–1178.10.1246/bcsj.40.1174Search in Google Scholar
12. Iwamoto, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Sasaki, Y.: The metal ammine cyanide aromatic clathrates. XIII. The crystal structure of the Hofmann-type biphenyl clathrate, diamminenickel(II) tetracyanonickelate(II) di-biphenyl: Ni(NH3)2Ni(CN)4⋅C12H10. Acta Crystallogr. B30 (1974) 292–295.10.1107/S056774087400269XSearch in Google Scholar
13. Iwamoto, T.; Ohtsu, Y.: The thiophene and pyrrole clathrates of Cd(en)Ni(CN)4 host lattice Cd(en)Ni(CN)4⋅C4H4S and Cd(en)Ni(CN)4⋅C4H4NH. Chem. Lett. 1 (1972) 463–468.10.1246/cl.1972.463Search in Google Scholar
14. Morehouse, R. L.; Ayta c, K.; Ülkü, D.: Unit-cell dimensions of hofmann pyridine complexes. Z. Krist.-Cryst. Mater. 145 (1977) 157–160.10.1524/zkri.1977.145.1-2.157Search in Google Scholar
15. Echevarría, F.; Lemus-Santana, A. A.; González, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Reguera, E.: Intercalation of thiazole in layered solids. A 3D framework supported in dipolar and quadrupolar intermolecular interactions. Polyhedron 95 (2015) 75–80.10.1016/j.poly.2015.04.016Search in Google Scholar
16. Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Lemus-Santana, A. A.; Ortiz-López, J.; Jiménez-Sandoval, S.; Reguera, E.: Low temperature structural transformation in T[Ni(CN)4]⋅xpyz with x=1, 2; T=Mn, Co, Ni, Zn, Cd; pyz = pyrazine. J. Solid State Chem. 183 (2010) 105–113.10.1016/j.jssc.2009.11.004Search in Google Scholar
17. Lemus-Santana, A. A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; González, M.; Demeshko, S.; Ávila, M.; Knobel, M.; Reguera, E.: Synthesis and characterization of T[Ni(CN)4]⋅2pyz with T=Fe, Ni; pyz = pyrazine: Formation of T-pyz-Ni bridges. J. Solid State Chem. 184 (2011) 2124–2130.10.1016/j.jssc.2011.06.011Search in Google Scholar
18. Wong-Ng, W.; Culp, J. T.; Chen, Y. S.; Deschamps, J. R.; Marti, A.: Synthesis and structural characterization of a flexible metal organic framework {[Ni(dpbz)][Ni(CN)4]}n, dpbz = 1,4-bis(4-pyridyl)benzene) with an unusual Ni-N bond. Solid State Sci. 52 (2016) 1–9.10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2015.11.010Search in Google Scholar
19. Lemus-Santana, A. A.; González, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Knobel, M.; Reguera, E.: 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone: from exfoliating solvent to a paramagnetic ligand. J. Phys. Chem. A 117 (2013) 2400–2407.10.1021/jp4007813Search in Google Scholar PubMed
20. Orpen, A. G.; Brammer, L.; Allen, F. H.; Kennard, O.; Watson, D. G.; Taylor, R.: Supplement. Tables of bond lengths determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Part 2. Organometallic compounds and co-ordination complexes of the d- and f-block metals. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 12 (1989) S1–S83.10.1039/dt98900000s1Search in Google Scholar
21. Allen, F. H.; Bruno, I. J.: Bond lengths in organic and metal-organic compounds revisited: X-H bond lengths from neutron diffraction data. Acta Crystallogr. B66 (2010) 380–386.10.1107/S0108768110012048Search in Google Scholar PubMed
©2020 Shuang-Hua Yang, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of bis [1-(phenylsulfonyl)-2-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)hydrazin-1-ido-κ3N,N′,O]cobalt(II), C24H22N8O4S2Co
- The crystal structure of 1,3-bis(4-(methoxycarbonyl)benzyl)-2-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium bromide, C26H25BrN2O4
- Crystal structure of {tris((1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)methyl)amine-κ4N,N′,N′′,N′′′}-(nitrito-κ2O,O′)nickel(II) perchlorate – ethanol (1/1), C26H27ClN8NiO7
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,O′:N′)](μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7
- Crystal structure of chlorido-tris(4-methylbenzyl-κC)-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C42H42AsClOSn
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis(3-carboxy-2-nitrobenzoate) tetrahydrate, C13H13N2O8
- Crystal structure of 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-(((2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy)methyl)phenethyl)piperazine, C28H31ClN2O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-5,5′-(1H-imidazole-4,5-diyl)bis(tetrazol-2-ido)-κ4N,N′:N′′,N′′′)magnesium], C10H8N20O2Mg
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzylidene)amino)-2-methylpropane-1,3-diol monohydrate, C13H21NO5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(3,5-dichloroisonicotinato-κO)cadmium(II)] dihydrate, C22H20CdCl4N4O8
- The crystal structure of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, C13H15ClO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of yttrium(III) trinitrate(V) pentahydrate, Y(NO3)3 ⋅ 5 H2O, H10N3O14Y
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[di-μ2-chlorido-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′-cadmium(II)], C12H8Cl2CdN2
- Crystal structure of 4-((2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)benzoic acid, C13H9F3N2O3
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid, C18H16O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,2-bis(4-ethoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonothioato-κ2N,S)nickel(II) — N,N-dimethylformamide (1/2), C44H56N10S2O6Ni
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-amine, C6H8ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ4O,O′,O′′,O′′′)bis(μ2-1-(4-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-κ2N:N)dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5O5
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(5-dimethylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonato-κ2N:O)(μ2-4,4′-bipyridyl -κ2N:N′)silver(I)], C44H44Ag2N6O8S2
- Crystal structure of 1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)cinnamoyl]-3-(pyridin-2-yl-κN)pyrazole-κ2N-bis(2-phenylpyridinato-k2C,N)iridium(III) hexafluorophosphate complex, [C40H28F3IrN5O]PF6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua(μ6-piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonato-κ6N:N′:O:O′:O′′:O′′′)(μ2-pyrazinyl-κ2N:N′)disilver(I)sesquihydrate], C12H30Ag2N4O11S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-nitrophenyl)-N-(o-tolyl)methanimine, C14H12N2O2
- Crystal structure of 4′-amino-3′,5′-diisopropyl-(1,1′-biphenyl)-4-carbonitrile, C19H22N2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(N,N-dimethylformamide-κ1O)-tetrakis(μ2-cyanido-κ2C:N)dinickel(II)], C10H14N6O2Ni2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3-bromo-5-chlorosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br2Cl2N2O2
- Crystal structure of rac-trans-N,N′-bis(3,5-dibromosalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine, C20H18Br4N2O2
- The crystal structure of (dichromato-κ2O,O′)bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)nickel(II), C12H16N4O7Cr2Ni
- The crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetrachloridozincate(II) monohydrate, C10H18Cl4ZnN2O
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-azido-k2N,N)-bis(2-amino-1-(N-(3-bromosalicylaldiminato))ethane)-dicopper(II), C20H18Br4N2O2
- Crystal structure of (η6-1-methyl-4-isopropylbenzene)-[5-bromo-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl-κ2C,N]-chloro-ruthenium(II), C21H21BrClNRu
- Crystal structure of N-(methyl(oxo)(1-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)ethyl)-λ6-sulfanylidene)cyanamide, C10H10F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((cyclohexane-1,2-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-bromo-4-chlorophenolato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel(II), C20H16Br2Cl2NiN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ2-tetraoxidomolybdato(VI)-κ2O:O′)manganese(II) monohydrate, C12H12N2O6MoMn
- The crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-o-chlorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(methanol-κ1O)dirhodium(II), C30H24Cl4O10Rh2
- Crystal structure of bis(2,3-diphenyltetrazolidine-5-thione-κ1S)-(nitrato-κ1O)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)lead(II), C26H20N10O6S2Pb
- Crystal structure of bis(3-bromo-N-(1-(3-methylpyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ3O,N,N′)cadmium(II) hemihydrate, C28H25N8O2.5Br2Cd
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-trifluoroacetato-κ2O:O′)(μ2-2,5-dimethylpyrazine-κ2N,N′)dicopper(II)], C7H4CuF6NO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[bis[3-azoniapentane-1,5-diammonium][bis(μ4-oxo)-tetrakis(μ3-oxo)-heptakis(μ2-oxo)-tetradecaoxo-octa-molybdenum] dihydrate], (C8H36N6O29Mo8)n
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-κO)-nickel(II)—diaqua-bis(2-((3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl)oxy)acetato-nickel(II), C28H24Cl12N4Ni2O18
- The crystal structure of bis(2-hydroxypyrimidinium) pentachloridobismuthate(III), (C4N2H5O)2BiCl5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-4,4′-dipyridine-κ2N,N′)-bis(3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-oxyacetato-κO)-bis(ethanol-κO)nickel(II)], C28H26Cl6N4NiO8
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-1-((4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl3F2NO3S
- The crystal structure of 5-bromopicolinic acid monohydrate, C6H6BrNO3
- The crystal structure of 2-(3-(4-bromophenyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]thiazole, C25H17BrFN3S
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-2-((3-bromo-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)acetato-κ4O,N,O′:O′′)-(dimethylformamide-κ1O)]zinc(II), C12H13N2O4BrZn
- Crystal structure of aqua-azido-κ1N-(6,6′-((propane-1,3-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(3-bromophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′iron(III), C17H16Br2FeN5O3
- The crystal structure of tris(1-ethylimidazole-κ1N)-(sulfato-κ2O,O′)vanadium(IV), C15H24N6O5SV
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-methoxy-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, C15H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of dichloro-bis-(1-butyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole)-nickel(II), C22H28Cl2N4Ni
- The crystal structure of 2-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H14O5
- The crystal structure of 5-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)hydrazono)-4-methyl-2-((3-(5-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylene) hydrazono)-2,5-dihydrothiazole dimethylformamide monosolvate, C30H25FN10S⋅C3H7NO
- The crystal structure of 1,8-bis(pyridin-4-ylethynyl)anthracene-1,2,4,5-tetrafluoro-3,6-diiodobenzene (2/1), C62H32F4I2N4
- The crystal structure of 3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9-methyl-9H-carbazole, C21H25I2N
- The crystal structure of 8-((4-chlorophenylamino)methylene)-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione, C15H14ClNO4
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[oktaaqua-bis(μ2-4,4′-ethene-1,2-diyldipyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3,3′-(1-oxidodiazene-1,2-diyl)diphthalato-κ2O:O′)dicobalt(II)] dihydrate, C28H36N4O19Co2
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-cyano-3-oxo-1-phenylprop-1-en-1-yl)-3,7-diphenylindolizine-6-carbonitrile, C31H19N3O
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-(1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene-κ2P,P′)-(O-isobutyl sulfurodithioito-κ2S,S′)copper(I), C39H37CuFeOP2S2
- Crystal structure of poly[(5-bimethylamino-1-naphthalenesulfonato-κO)-(μ3-hexamethylenetetramino-κ3N:N′:N′′)silver(I)] dihydrate, C36H52Ag2N10O8S2
- Crystal structure of poly[μ2-diaqua-(μ2-2-amino-4,5-dicyano-κ2N:N′-imidazol-1-ide)sodium(I)], C5H6N5O2Na
- Crystal structure of (1,3-propanediamine-κ2N,N′)(N-(3-aminopropyl)-α-methyl aspartato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)cobalt(III) chloride, C11H24ClCoN4O4
- Crystal structure and anti-inflammatory activity of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C26H20Cl2F3NO3S
- Crystal structure of (S)-(+)-1-cyclohexylethylaminium chloride, C8H18NCl
- The crystal structure of tris(nitrato-κ2O,O′)-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(o-pyridyl)imidazoline-1-oxyl 3-oxide-κ2N,O)yttrium(III), C24H32N9O13Y
- Hydrogen bonding versus packing effects in the crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium tetraiodidozincate(II), C10H16I4ZnN2
- Dimerization of 2-[(2-((2-aminophenyl)thio)phenyl)amino]-cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one through hydrogen bonding, C19H16N2OS
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-ethoxyl-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H12ClF2NO4
- Crystal structure of 7-ethoxy-6,8-difluoro-4-oxo-1-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid, C18H14F2N2O4
- Crystal structure of octahydro-7aR,8′R-dimethylspiro[isobenzofuran-4(1H), 4′ (3′H)-[1H-7,9a]methanocyclohepta[c]pyran]-1′,3, 9′ (3aH,4′aH)-trione, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of bis(5-ethoxy-2-(((1-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxidopropan-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ3N,O,O’)manganese(IV) – methanol (1/1), C27H38MnN2O9
- Crystal structure of 8a,8a′′-oxybis(8aH-8,9-dioxa-3a1λ4-aza-8aλ4-borabenzo[fg]tetracene), C34H22B2N2O5
- Crystal structure of bromido-triphenyl-(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C36H30AsBrOSn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-formato-κ2O:O′)-(1,10-phenathroline-κ2N,N′)copper(II)], C26H18Cl2Cu2N4O4
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ10-5-carboxyisophthalato-κ10O)disodium], C9H4Na2O6
- The crystal structure of 3,5-difluoroisonicotinic acid, C6H3F2NO2
- The crystal structure of ethyl-1-(N-(adamantan-1-yl)-carbamothioyl)piperidine-4-carboxylate, C19H30N2O2S
- Crystal structure of 5-methyl-3-phenyl-1-tosyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, C19H21NO2S
- Crystal structure of bis((3-chlorosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)nickel (II), C16H12Cl2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide — dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1/1), C18H17ClN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis((3-bromosalicylidene)-ethylenediaminato-κ4N,N′,O,O′) nickel (II), C16H12Br2NiN2O2
- Crystal structure of trimethylsulfoxonium tetrachloridocobaltate(II) [(CH3)3SO]2CoCl4

