Abstract
C22H8N6O6, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 15.3939(6) Å, b = 7.3053(3) Å, c = 16.8282(6) Å, β = 91.567(3)°, V = 1891.74(13) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0510, wRref(F2) = 0.0867, T = 140(2) K.
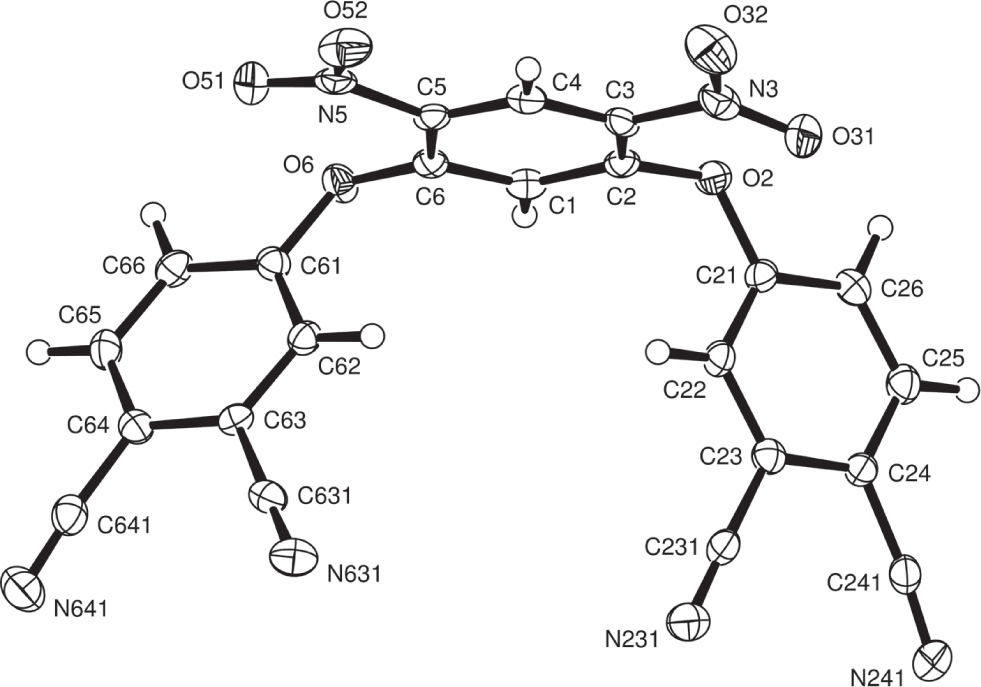
Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Plate, pale yellow |
| Size: | 0.08 × 0.03 × 0.01 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.12 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur 3/Sapphire3, Thin |
| slice φ and ω-scans | |
| θmax, completeness: | 25°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 23318, 3333, 0.085 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2315 |
| N(param)refined: | 339 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2, 3] , WinGX and ORTEP [4, 5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.57921(15) | 0.8096(3) | 0.20185(14) | 0.0199(6) |
| C2 | 0.53242(14) | 0.7043(3) | 0.14712(13) | 0.0193(5) |
| C3 | 0.53716(15) | 0.5142(3) | 0.15288(13) | 0.0190(6) |
| C4 | 0.59101(15) | 0.4339(3) | 0.20993(14) | 0.0212(6) |
| C5 | 0.63902(15) | 0.5404(3) | 0.26216(13) | 0.0189(6) |
| C6 | 0.63195(14) | 0.7311(3) | 0.26008(13) | 0.0182(5) |
| O2 | 0.48760(10) | 0.7927(2) | 0.08682(9) | 0.0232(4) |
| C21 | 0.40277(15) | 0.8442(3) | 0.09919(14) | 0.0196(6) |
| C22 | 0.36351(16) | 0.8123(3) | 0.17038(15) | 0.0200(6) |
| C23 | 0.27956(15) | 0.8749(3) | 0.18027(13) | 0.0198(6) |
| C24 | 0.23554(15) | 0.9672(3) | 0.11806(14) | 0.0202(6) |
| C25 | 0.27591(17) | 0.9935(3) | 0.04637(15) | 0.0241(6) |
| C26 | 0.35984(16) | 0.9330(3) | 0.03719(15) | 0.0220(6) |
| C231 | 0.23842(15) | 0.8575(3) | 0.25549(14) | 0.0227(6) |
| N231 | 0.20400(14) | 0.8493(3) | 0.31519(13) | 0.0314(5) |
| C241 | 0.15022(17) | 1.0347(3) | 0.13437(14) | 0.0237(6) |
| N241 | 0.08405(14) | 1.0852(3) | 0.15378(13) | 0.0352(6) |
| N3 | 0.48709(13) | 0.3912(3) | 0.09940(12) | 0.0267(5) |
| O31 | 0.42934(11) | 0.4568(2) | 0.05668(10) | 0.0315(4) |
| O32 | 0.50654(12) | 0.2285(2) | 0.10111(10) | 0.0379(5) |
| N5 | 0.70039(13) | 0.4432(3) | 0.31619(12) | 0.0261(5) |
| O51 | 0.75237(12) | 0.5349(2) | 0.35598(10) | 0.0360(5) |
| O52 | 0.69727(11) | 0.2753(2) | 0.31646(10) | 0.0344(5) |
| O6 | 0.67834(10) | 0.8492(2) | 0.30921(9) | 0.0239(4) |
| C61 | 0.65818(15) | 0.8576(3) | 0.38875(13) | 0.0195(6) |
| C62 | 0.58248(15) | 0.7833(3) | 0.41665(14) | 0.0196(6) |
| C63 | 0.56391(14) | 0.8028(3) | 0.49640(13) | 0.0178(5) |
| C64 | 0.62098(15) | 0.8988(3) | 0.54776(13) | 0.0197(6) |
| C65 | 0.69742(16) | 0.9701(3) | 0.51824(15) | 0.0224(6) |
| C66 | 0.71587(16) | 0.9497(3) | 0.43899(14) | 0.0217(6) |
| C631 | 0.48516(16) | 0.7239(3) | 0.52597(13) | 0.0215(6) |
| N631 | 0.42304(14) | 0.6595(3) | 0.54914(12) | 0.0308(5) |
| C641 | 0.59660(16) | 0.9205(3) | 0.62918(16) | 0.0250(6) |
| N641 | 0.57146(15) | 0.9336(3) | 0.69278(13) | 0.0365(6) |
| H1 | 0.5752(13) | 0.941(3) | 0.2002(11) | 0.016(6)* |
| H22 | 0.3917(13) | 0.754(3) | 0.2123(12) | 0.022(6)* |
| H25 | 0.2473(14) | 1.055(3) | 0.0023(13) | 0.023(6)* |
| H26 | 0.3892(14) | 0.952(3) | −0.0117(13) | 0.017(6)* |
| H4 | 0.5943(15) | 0.304(3) | 0.2118(13) | 0.035(7)* |
| H62 | 0.5419(14) | 0.719(3) | 0.3833(12) | 0.023(6)* |
| H65 | 0.7371(14) | 1.032(3) | 0.5518(12) | 0.017(6)* |
| H66 | 0.7688(13) | 0.995(2) | 0.4190(11) | 0.010(6)* |
Short intermolecular contacts, ‘weak hydrogen bonds’, in Ångstroms and degrees.
| D–H⋯A | d(D–H) | d(H⋯A) | d(D⋯A) | <(DHA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(22)–H(22)⋯N(241)#1 | 0.92(2) | 2.59(2) | 3.468(3) | 160.1(17) |
| C(26)–H(26)⋯O(32)#2 | 0.96(2) | 2.59(2) | 3.362(3) | 137.7(15) |
| C(62)–H(62)⋯N(241)#1 | 0.95(2) | 2.24(2) | 3.147(3) | 157.9(17) |
| C(65)–H(65)⋯N(231)#3 | 0.94(2) | 2.54(2) | 3.416(3) | 154.8(17) |
| C(25)–H(25)⋯O(51)#4 | 0.96(2) | 2.55(2) | 3.221(3) | 126.8(16) |
Symmetry transformations used to generate equivalent atoms:#1: ½ − x, y − ½, ½ − z; #2: 1 − x, 1 − y, −z; #3: 1 − x, 2 − y, 1 − z; #4: x − ½, 1½ − y, z − ½.
Source of material
1,5-Difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (0.2 g, 1 mmol), 4-hydroxyphthalonitrile (0.3 g, 2.1 mmol) and potassium carbonate (0.274 g, 2.0 mmol) were added to acetone (7 mL) and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The solvent was removed and the residue redissolved in DCM. This was washed with water and the washings were extracted with DCM three times. The combined organic extracts were dried over MgSO4 and the solvent removed under reduced pressure. The product was purified by column chromatography (eluting with DCM). Recrystallization from acetone gave the title compound as a yellow crystalline solid (0.3 g, 66%). Mp. 197 °C; 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone) δ 9.04 (s, 1H), 8.14 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 2H), 7.80 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.5 Hz, 2H), 7.73 (s, 1H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, Acetone) δ 160.10, 153.48, 139.12, 137.36, 126.49, 124.56, 124.31, 118.82, 117.81, 116.11, 115.74, 112.56; IR (KBr, cm−1): 3047, 2240, 1630, 1536.
Experimental details
The structure was determined by the intrinsic phasing routines in the SHELXT program [2] and refined by full-matrix least-squares methods, in SHELXL [3]. Hydrogen atoms were included in idealized positions, but then allowed to refine freely. The figure was drawn with ORTEP [4, 5] .
Discussion
1,2-Cyano-containing benzene compounds or phthalonitriles are important precursors for phthalocyanine molecules [6] and have potential uses in composite matrices, adhesives, sensitizers and pigments [7], [8], [9], [10], [11]. As part of our ongoing work on the synthesis and study of phthalocyanine dimers, we targeted the title novel compound as a linker unit.
The synthesis of the bis-phthalonitrile is a straightforward procedure which can be achieved by the substitution reaction method, mixing 4-hydroxyphthalonitrile with 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene in acetone in the presence of freshly ground potassium carbonate. After workup, purification over silica gel gave the target compound as the second fraction. The 1H-NMR spectrum shows singlets at ca 9.05 and 7.75 p.p.m. assigned to the two protons of the bridging benzene ring. This easily prepared bis-phthalonitrile is a potential candidate for making a variety of dimers of phthalocyanines which are unique in their electronic and optical properties [12].
The crystal structure of the title compound shows an approximately planar central C6H2(NO2)2(O)2 group. The two nitro groups are rotated about the C—N bonds by 10.93(14) and 9.05(14)°. The phthalonitrile groups are turned out of the central plane by rotation about the C(2)—O(2) and C(6)—O(6) bonds (by 88.05(14) and 68.16(11)°, respectively) and aligned so that the normals to these C6 rings are approximately perpendicular (85.82(7) and 77.29(7)°, respectively) to the normal to the central ring plane. The bond lengths and angles are within normal ranges and are comparable to those observed in similar structures [13]. Molecules are connected through ‘weak hydrogen bonds’, the shortest of which is for C(62)—H(62)⋯N(2411) where the H⋯N distance is 2.24(4) Å Table 3. The dicyanophenyl rings form a short-range stack and are close to parallel (the angles between their normals are zero or 10.53(11)°), but with, in some cases, limited overlap of the rings; shorter interactions within this stack include C(24)⋯C(644) at 3.40 Å.
References
Oxford Diffraction. CrysAlisPRO. Oxford Diffraction Ltd., Yarnton, England (2011).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: SHELXT – Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053273314026370Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Sheldrick, G. M.: Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C71 (2015) 3–8.10.1107/S2053229614024218Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
Johnson, C. K.: ORTEPII. Report ORNL-5138. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, TN, USA (1976).Search in Google Scholar
Cammidge, A. N.; Gopee, H.: Synthesis and properties of macrodiscotic triphenylenophthalocyanines. J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 13 (2009) 235–246.10.1142/S1088424609000267Search in Google Scholar
Shoji, M.; Nishide, H.: Fluorophilic cobalt phthalocyanine-containing Nafion membrane: high oxygen permeability and proton conductivity in the membrane. Polym. Adv. Technol. 21 (2010) 646–650.10.1002/pat.1480Search in Google Scholar
Laskoski, M.; Dominguez, D. D.; Keller, T. M.: Synthesis and properties of aromatic ether phosphine oxide containing oligomeric phthalonitrile resins with improved oxidative stability. Polymer 48 (2007) 6234–6240.10.1016/j.polymer.2007.08.028Search in Google Scholar
Löbbert, G.: Phthalocyanines. In: Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany (2000).10.1002/14356007.a20_213Search in Google Scholar
Oliver, S. W.; Smith, T. D.: Oligomeric cyclization of dinitriles in the synthesis of phthalocyanines and related compounds: the role of the alkoxide anion. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 (1987) 1579–1582.10.1039/p29870001579Search in Google Scholar
Uchida, H.; Tanaka, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Reddy, P. Y.; Nakamura, S.; Toru, T.: Novel synthesis of phthalocyanines from phthalonitriles under mild conditions. Synlett. (2002) 1649–1652.10.1055/s-2002-34237Search in Google Scholar
De la Torre, G.; Bottari, G.; Hahn, U.; Torres, T.: Functional phthalocyanines: synthesis, nanostructuration, and electro-optical applications. Struct. Bond. 135 (2010) 1–44.10.1007/978-3-642-04752-7_1Search in Google Scholar
Özdemir, L.; Yılmaz, Y.; Sönmez, M.; Akkurt, M.; Tahir, M. N.: Synthesis and crystal structure of a new phthalonitrile and its phthalocyanines bearing diamagnetic metals. Synth. React. Inorganic, Met. Nano-Metal Chem. 46 (2016) 110–117.10.1080/15533174.2014.900790Search in Google Scholar
©2018 Ateyatallah Aljuhani et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo-pyran, C18H16N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ5O,O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], C100H60N12O16Cd4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C19H18N2O6
- Crystal structure of 1-{4-[(2-hydroxy-5-methyl benzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-ethyl-oxime, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis{4-methyl-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)}copper(II), C36H38CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}nickel(II), C34H34N4NiO6
- Crystal structure of poly[μ8-3-carboxyphthalat-κ8-O:O1,O1,O1:O2:O3,O3:O4)silver(I)], C9H4Ag2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)iminio)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolate, C16H16N2O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one oxime, C16H16N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(tert-butyl)-4-chloro-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine, C13H14Cl1N3
- Crystal structure of (6,6′-(((((2-aminoethyl)azanediyl)bis(ethane-2,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato)-κ6N,N′,N′′,N′′′,O,O′)cadmium(II) – ethanol – water (1/1/1), C22H28CdCl4N4O4
- Crystal structure of 6-chloro-N-methylpyrimidin-4-amine, C5H6ClN3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-2-naphtholato-κ2N,O}nickel(II), C40H34N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-bromophenyl)ethenesulfonyl fluoride (C8H6BrFO2S)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2,2′-ethylenedioxybis(benzimide)-2,2′-bis[O-(1-propyloxyamide)]oxime-4,4′,6,6′-tetrachlorodiphenol, C36H34Cl4N4O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II) – methanol (1/1), C26H28N10O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)samarium(III), C12H14N7O9Sm
- Crystal structure of hexaaqua-{(E)-N′-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O}praseodym(III) trichloride monohydrate, C12H25Cl3N5O8Pr
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(3-cyanophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C21H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carboxylate, C22H19NO6
- Crystal structure of 2,12-dibromo-5,15-dihexyl-5,15-dihydrobenzo [1,2-b:5,6-c′]dicarbazole, C38H38Br2N2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carboxylate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c] chromene-3-carboxylate, C23H21NO5
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-N′-(pyrimidin-2-yl)benzohydrazide, C11H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C23H29NO3
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(3-cyanophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C22H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 7β,9β-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of Ent-7β,20-epoxy-kaur-16-en-1β,6α,7α,14α,15α-pentaol-20-one, C20H30O8
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl)dihydro-1H,3H-furo[3,4-c]furan-3a(4H)-yl acetate, C22H20O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((4-((2-nitrophenoxy)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl) benzoate, C18H16N4O5
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5-carboxy-1-methyl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ2N,O)zinc(II), C12H14N4O10Zn
- Hydrothemal synthesis and crystal structure of triaqua-bis(5-carboxy-1-methyl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ2N,O;κ1O)manganese(II), C12H16N4O11Mn
- Redetermination of methyl 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22ClNO3
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-methyl-imdazol)-κN}-dithiocyano-κN-zinc(II) C24H22N12S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (5-fluoro-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)methyl furan-2-carboxylate, C10H7FN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(η6-cymene)-tri-μ2-chlorido-ruthenium(II) tetrafluoroborate, C20H28BCl3F4Ru2
- Crystal structure of 3,6-diphenyl-7H-[1,2,4]-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazine, C16H12N4S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1,3-bis[(3,4-dicyano)phenoxy]-4,6-dinitro-benzene, C22H8N6O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano [4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-hydroxy-(μ5-(5-(2-carboxylatophenoxy)isophthalato-κ6O1:O2:O3:O4:O5,O6)-(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)butane-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] hemihydrate, C25H22Co2N4O8.5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-bromophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22BrNO3
- Crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate trihydrate, C35H33NO12
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis(4-(10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C38H24N4OS2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(prop-1-en-1-yl)benzofuran-3-carbaldehyde, C18H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis{5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12(7H)-yl} carbonate, C29H24O5Bi2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-5-formyl-3,4-dimethylpyrrole-2-carboxylate — N-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethylpyrrole)-2-methylene-5-nitrobenzene-1,2-diamine (1:1), C26H31N5O7
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-6-bromo-4-chlorophenol, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(furan-2-yl(phenylamino)methylene)-5-methyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C21H16ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of N2,N4-dibutyl-6-chloro-N2,N4-bis(1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, C31H58ClN7 – Important intermediate of Chimassorb 119 synthesis
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-bromo-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl)ethanone oxime, C17H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of poly-{diaqua-bis[(μ2-3-nitrobenzenesulfonylglycine-κ3N:O:O′)(4,4′-bipyridine)manganese(II)]}-dimethylformamide (1/1), C39H35Mn2N9O15S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)-1-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C10H13ClN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-5-oxo-4-(4-chloro-phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-cyclopenta[b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C15H11ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of triaqua-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)cobalt(II) – 6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine (1/1), C16H18CoN6O7
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3-cyanophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C21H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-2,6-dinitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H5Cl2N5O7
- Crystal structure of 3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C8H8N2O5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-dimethyl-3,5-dinitrobenzene, C8H8N2O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C21H24ClNO3
- Crystal structure of N-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide, C14H10Cl3NO
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2c] chromene, C19H11FN2O3
- The crystal structure of (4-nitrophenyl) (5-ferrocenyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl) methanone, C21H12F3FeN3O3
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-((3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)methylene)bis(1,3-diethyl-6-hydroxy-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydropyrimidin-4(1H)-one), C24H30N4O6S2
- Crystal structure of (3aR,4R,5R,7R,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-7-ethyl-5-(1-hydroxy-2-((R)-3-hydroxypyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)-4,7,9,12-tetramethyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta[8]annulene-3,8-diol – a pleuromutilin derivative, C26H41NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-3-formyl-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-hexapyridine-dicadmium(II) – pyridine (1/1), C53H47Cd2N7O10
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carboxylate, C22H19NO6
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,5-ditrifluoromethylphenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate — water (2/1), C22H21F6NO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C17H13BrN2
- Crystal structure of (5-ethyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C14H20O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(4-bromo-2-(1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)benzamide, C15H13BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of caffeinium triiodide – caffeine (1/1), C16H21I3N8O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-methyl-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H28O2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(2-azidoethyl)piperazine-1,4-diium dichloride, C8H18N8Cl2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(1,3-bis(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene)-(morpholine-κ1N)palladium(II), C23H29Cl2N3OPd(II)
- The crystal structure of 1-((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-yl)methyl)-1,3-diphenylurea, C24H21ClN4O
- Crystal structure of 6-(2-bromoacetamido)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2,3,4,5-Tetrayl tetraacetate, C16H22BrNO10
- Crystal structure of 5-methylpyrazine-2-carbohydrazide, C6H8N4O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-5-(tert-butyl)isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)(-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N′′)manganese(II)], C32H28N4O5Mn
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)-3-cyano-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-4H-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobenzo-pyran, C18H16N4O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ5O,O′:O′′,O′′′:O′′′)(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], C100H60N12O16Cd4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C19H18N2O6
- Crystal structure of 1-{4-[(2-hydroxy-5-methyl benzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone O-ethyl-oxime, C18H20N2O2
- Crystal structure of bis{4-methyl-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(ethoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)}copper(II), C36H38CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}nickel(II), C34H34N4NiO6
- Crystal structure of poly[μ8-3-carboxyphthalat-κ8-O:O1,O1,O1:O2:O3,O3:O4)silver(I)], C9H4Ag2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)iminio)methyl)-5-methoxyphenolate, C16H16N2O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one oxime, C16H16N2O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(tert-butyl)-4-chloro-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine, C13H14Cl1N3
- Crystal structure of (6,6′-(((((2-aminoethyl)azanediyl)bis(ethane-2,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dichlorophenolato)-κ6N,N′,N′′,N′′′,O,O′)cadmium(II) – ethanol – water (1/1/1), C22H28CdCl4N4O4
- Crystal structure of 6-chloro-N-methylpyrimidin-4-amine, C5H6ClN3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-2-naphtholato-κ2N,O}nickel(II), C40H34N4NiO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-bromophenyl)ethenesulfonyl fluoride (C8H6BrFO2S)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2,2′-ethylenedioxybis(benzimide)-2,2′-bis[O-(1-propyloxyamide)]oxime-4,4′,6,6′-tetrachlorodiphenol, C36H34Cl4N4O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)cadmium(II) – methanol (1/1), C26H28N10O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)-bis(nitrato-κ2O,O′)samarium(III), C12H14N7O9Sm
- Crystal structure of hexaaqua-{(E)-N′-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)isonicotinohydrazide-κ3N,N′,O}praseodym(III) trichloride monohydrate, C12H25Cl3N5O8Pr
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(3-cyanophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C21H22N2O3
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carboxylate, C22H19NO6
- Crystal structure of 2,12-dibromo-5,15-dihexyl-5,15-dihydrobenzo [1,2-b:5,6-c′]dicarbazole, C38H38Br2N2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carboxylate, C22H19NO7
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c] chromene-3-carboxylate, C23H21NO5
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-N′-(pyrimidin-2-yl)benzohydrazide, C11H10N4O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C23H29NO3
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(3-cyanophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C22H24N2O3
- Crystal structure of 7β,9β-dihydroxy-15-oxo-ent-kauran-16-en-19,6β-olide, C20H26O5
- Crystal structure of Ent-7β,20-epoxy-kaur-16-en-1β,6α,7α,14α,15α-pentaol-20-one, C20H30O8
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ylmethyl)dihydro-1H,3H-furo[3,4-c]furan-3a(4H)-yl acetate, C22H20O8
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-((4-((2-nitrophenoxy)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl) benzoate, C18H16N4O5
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(5-carboxy-1-methyl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ2N,O)zinc(II), C12H14N4O10Zn
- Hydrothemal synthesis and crystal structure of triaqua-bis(5-carboxy-1-methyl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylato-κ2N,O;κ1O)manganese(II), C12H16N4O11Mn
- Redetermination of methyl 4-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-quinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22ClNO3
- Crystal structure of bis{1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1-H-1,3-(2-methyl-imdazol)-κN}-dithiocyano-κN-zinc(II) C24H22N12S2Zn
- Crystal structure of (5-fluoro-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)methyl furan-2-carboxylate, C10H7FN2O5
- Crystal structure of bis(η6-cymene)-tri-μ2-chlorido-ruthenium(II) tetrafluoroborate, C20H28BCl3F4Ru2
- Crystal structure of 3,6-diphenyl-7H-[1,2,4]-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazine, C16H12N4S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1,3-bis[(3,4-dicyano)phenoxy]-4,6-dinitro-benzene, C22H8N6O6
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano [4,3-b]pyran-3-carboxylate, C18H15Cl2NO5
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-hydroxy-(μ5-(5-(2-carboxylatophenoxy)isophthalato-κ6O1:O2:O3:O4:O5,O6)-(μ2-1,4-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)butane-κ2N:N′)dicobalt(II)] hemihydrate, C25H22Co2N4O8.5
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(4-bromophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C20H22BrNO3
- Crystal structure of 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate trihydrate, C35H33NO12
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis(4-(10H-phenothiazin-10-yl)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole, C38H24N4OS2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-(prop-1-en-1-yl)benzofuran-3-carbaldehyde, C18H14O3
- Crystal structure of bis{5H-dibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxabismocin-12(7H)-yl} carbonate, C29H24O5Bi2
- Crystal structure of ethyl-5-formyl-3,4-dimethylpyrrole-2-carboxylate — N-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethylpyrrole)-2-methylene-5-nitrobenzene-1,2-diamine (1:1), C26H31N5O7
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-6-bromo-4-chlorophenol, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(furan-2-yl(phenylamino)methylene)-5-methyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C21H16ClN3O2
- Crystal structure of N2,N4-dibutyl-6-chloro-N2,N4-bis(1,2,2,6,6-pentamethylpiperidin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, C31H58ClN7 – Important intermediate of Chimassorb 119 synthesis
- Crystal structure of 1-(5-bromo-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-indol-7-yl)ethanone oxime, C17H15BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of poly-{diaqua-bis[(μ2-3-nitrobenzenesulfonylglycine-κ3N:O:O′)(4,4′-bipyridine)manganese(II)]}-dimethylformamide (1/1), C39H35Mn2N9O15S2
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)-1-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)pyridin-1-ium perchlorate, C10H13ClN2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-5-oxo-4-(4-chloro-phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-cyclopenta[b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C15H11ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of triaqua-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-κ3O,N,O′)cobalt(II) – 6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine (1/1), C16H18CoN6O7
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3-cyanophenyl)-7,7-dimethyl-5-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate, C21H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-chloro-2,6-dinitrophenyl)-1-(4-chloro-3-nitrophenyl)diazene 1-oxide, C12H5Cl2N5O7
- Crystal structure of 3,4-dimethyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C8H8N2O5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-dimethyl-3,5-dinitrobenzene, C8H8N2O4
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-(3-chlorophenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C21H24ClNO3
- Crystal structure of N-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide, C14H10Cl3NO
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-cyano-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2c] chromene, C19H11FN2O3
- The crystal structure of (4-nitrophenyl) (5-ferrocenyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl) methanone, C21H12F3FeN3O3
- Crystal structure of 5,5′-((3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)methylene)bis(1,3-diethyl-6-hydroxy-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydropyrimidin-4(1H)-one), C24H30N4O6S2
- Crystal structure of (3aR,4R,5R,7R,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-7-ethyl-5-(1-hydroxy-2-((R)-3-hydroxypyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy)-4,7,9,12-tetramethyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta[8]annulene-3,8-diol – a pleuromutilin derivative, C26H41NO5
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-3-formyl-5-methoxy-2-oxidobenzoato-κ3O,O′:O′)-hexapyridine-dicadmium(II) – pyridine (1/1), C53H47Cd2N7O10
- Crystal structure of ethyl 2-amino-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-4H,5H-pyrano[3,2-c]chromene-3-carboxylate, C22H19NO6
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-(3,5-ditrifluoromethylphenyl)-2,7,7-trimethyl-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate — water (2/1), C22H21F6NO3
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-perimidine, C17H13BrN2
- Crystal structure of (5-ethyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-dioxan-5-yl)methanol, C14H20O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(4-bromo-2-(1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)benzamide, C15H13BrN2O2
- Crystal structure of caffeinium triiodide – caffeine (1/1), C16H21I3N8O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-methyl-4-(3-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate, C19H21NO4
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H28O2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(2-azidoethyl)piperazine-1,4-diium dichloride, C8H18N8Cl2
- The crystal structure of dichlorido-(1,3-bis(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-1H-imidazol-2(3H)-ylidene)-(morpholine-κ1N)palladium(II), C23H29Cl2N3OPd(II)
- The crystal structure of 1-((5-chloro-3-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-yl)methyl)-1,3-diphenylurea, C24H21ClN4O
- Crystal structure of 6-(2-bromoacetamido)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2,3,4,5-Tetrayl tetraacetate, C16H22BrNO10
- Crystal structure of 5-methylpyrazine-2-carbohydrazide, C6H8N4O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-5-(tert-butyl)isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)(-4′-(pyridin-4-yl)-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine-κ3N,N′,N′′)manganese(II)], C32H28N4O5Mn

