Abstract
C9H14Cl3CuN, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 9.6625(6) Å, b = 9.3486(3) Å, c = 14.1168(8) Å, β = 102.288(5)°, V = 1245.97(11) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0182, wRref(F2) = 0.0499, T = 210(2) K.
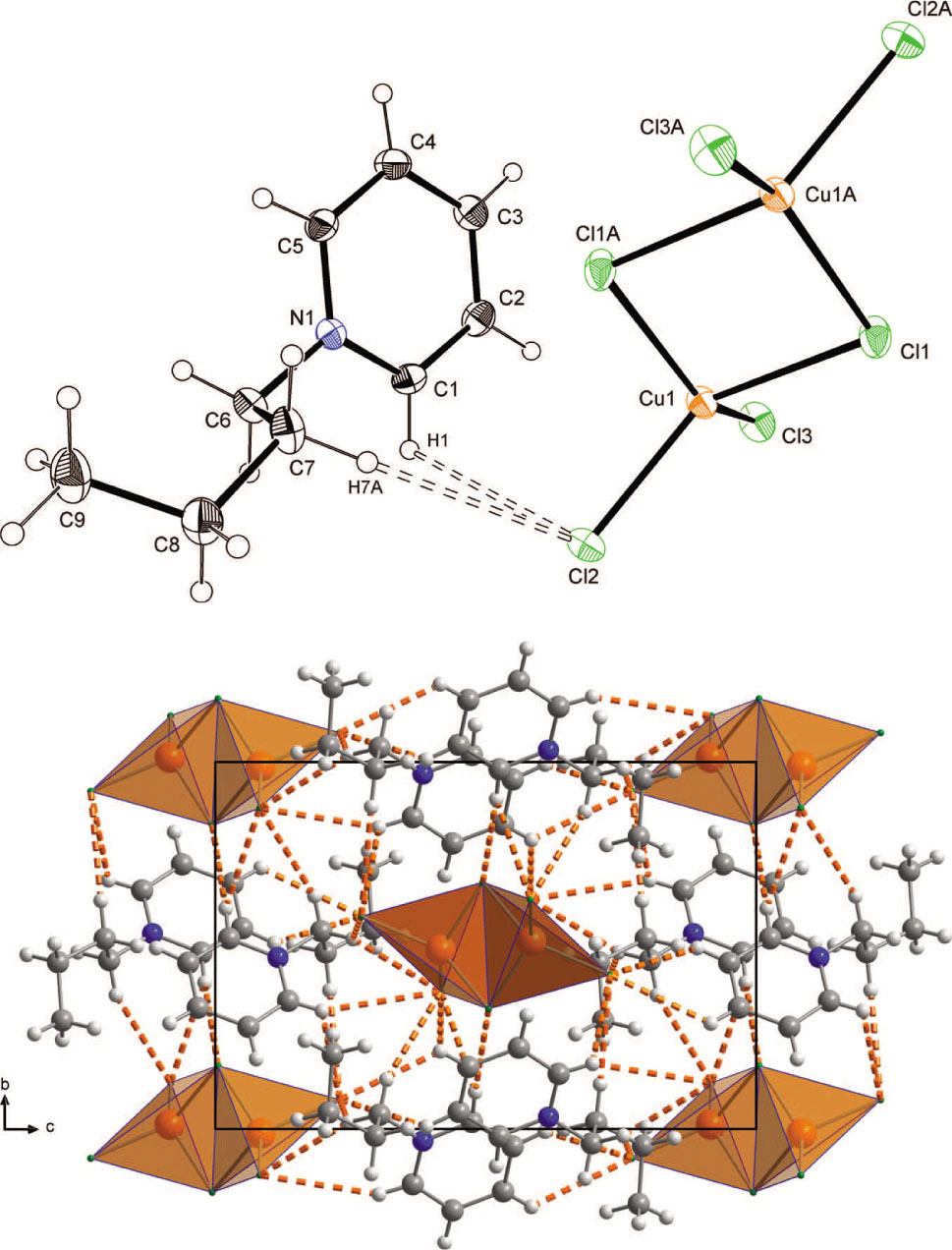
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 1.00 × 0.45 × 0.33 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.36 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | STOE IPDS 2, ω-scan, Δω = 1.0 deg |
| θmax, completeness: | 25°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 15411, 2186, 0.049 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2121 |
| N(param)refined: | 184 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], WinGX and ORTEP [2], DIAMOND [3], PLATON [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl1 | 0.50633(4) | 0.82761(4) | −0.00540(3) | 0.03410(12) |
| Cl2 | 0.44379(4) | 1.07973(4) | 0.22997(2) | 0.03259(12) |
| Cl3 | 0.20539(4) | 0.87418(4) | 0.08240(3) | 0.03547(12) |
| Cu1 | 0.40485(2) | 0.98814(2) | 0.08398(2) | 0.02442(10) |
| N1 | 0.28674(13) | 1.46735(14) | 0.11596(9) | 0.0242(3) |
| C1 | 0.21892(16) | 1.34958(18) | 0.13482(12) | 0.0297(3) |
| H1 | 0.2378(19) | 1.322(2) | 0.1974(15) | 0.039(5)* |
| C2 | 0.12862(17) | 1.27846(19) | 0.06119(12) | 0.0343(4) |
| H2 | 0.089(2) | 1.191(2) | 0.0757(15) | 0.051(6)* |
| C3 | 0.10826(16) | 1.33051(19) | −0.03214(12) | 0.0331(4) |
| H3 | 0.0436(19) | 1.288(2) | −0.0842(13) | 0.035(5)* |
| C4 | 0.17871(17) | 1.45291(19) | −0.04981(12) | 0.0329(4) |
| H4 | 0.163(2) | 1.4933(19) | −0.1093(16) | 0.038(6)* |
| C5 | 0.26794(18) | 1.51946(18) | 0.02547(12) | 0.0297(3) |
| H5 | 0.311(2) | 1.601(2) | 0.0194(14) | 0.037(5)* |
| C6 | 0.38816(16) | 1.53919(19) | 0.19600(11) | 0.0289(3) |
| H6A | 0.384(2) | 1.635(2) | 0.1834(14) | 0.038(5)* |
| H6B | 0.352(2) | 1.5181(19) | 0.2543(15) | 0.035(5)* |
| C7 | 0.53618(18) | 1.48169(19) | 0.20422(15) | 0.0350(4) |
| H7A | 0.533(2) | 1.378(2) | 0.2114(14) | 0.045(5)* |
| H7B | 0.562(2) | 1.501(2) | 0.1446(17) | 0.042(6)* |
| C8 | 0.64016(19) | 1.5454(2) | 0.29048(14) | 0.0395(4) |
| H8A | 0.725(3) | 1.495(2) | 0.2967(16) | 0.043(6)* |
| H8B | 0.607(2) | 1.525(2) | 0.3482(17) | 0.044(6)* |
| C9 | 0.6639(2) | 1.7040(2) | 0.28281(17) | 0.0471(5) |
| H9A | 0.584(2) | 1.757(2) | 0.2827(14) | 0.042(5)* |
| H9B | 0.739(2) | 1.741(2) | 0.3342(16) | 0.059(6)* |
| H9C | 0.695(3) | 1.726(3) | 0.2235(19) | 0.071(7)* |
Source of materials
The title compound has been prepared according to Refs. [5], [6], [7], [8]. To a solution of N-butylpyridinium chloride (0.342 g, 2 mmol) in dry acetonitrile (6 mL) copper(II) chloride (0.34 g, 2 mmol) was added. This mixture was stirred to reflux for 3 h. The solvent was evaporated with a rotary evaporator at 60 °C under reduced pressure and the product was dried in vacuo. Yield: 0.59 g (98.3%). MS positive mode: m/z = 136.1126 [C9H14N]+, and MS negative mode: m/z = 169.8 [CuCl3]−. Elemental analysis for C18H28Cl6Cu2N2 calculated (found) C, 35.31% (35.34%); H, 4.61% (4.43%); N, 4.58% (4.59%). Red crystals (Mp. 94–96 °C) suitable for single crystal X-ray diffraction were grown by diffusion of methyl tert-butyl ether vapor into ethanolic solution of the compound.
Experimental details
Coordinates of hydrogen atoms were refined without any constraints or restraints.
Elemental analysis (CHN) was carried out on an Elementar vario EL III analyser with a limit of detection of 0.3%. Mass spectroscopy (MS) was performed on a Micromass QTOF (Quadrupol − Time of flight) with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source operating in positive and negative ionization modes, with a range of m/z 50-800. Samples were injected as dilute solutions in methanol. Melting points were measured with a Melting Point Meter KSP1N.
Comment
Copper (II) complexes exhibit very rich and diverse coordination geometries due to the presence of the Jahn-Teller distortions in the d9 electronic system [9]. Among those, chloridocuprate(II) salts have attracted considerable interest due to their magnetic [10, 11] , thermochromic [9], phase transition [12], and non-linear optical behavior [13]. For example, Willett and co-workers [14, 15] demonstrated that the hydrogen bonding plays an important role in the thermochromism that these compounds are known for; these authors also associated the color change with a change in ligand geometry.
Quite some of the tetrachloridocuprates are ionic liquids (ILs). ILs, low-temperature molten salts of a highly diverse chemical composition, have received tremendous attention for their (projected) high potential in many fields [16]. A number of these applications are driven by the specific physical and chemical properties of ILs, such as very low vapor pressure or low melting points but high ionicity [17], [18], [19], [20], [21]. As ILs are composed entirely of ions, their properties can be tuned by an judiciuous choice of the cation and the anion [22].
Of particular interest to the current study, metal-containing ILs (MILs) have been studied for a variety of properties such as their structural flexibility [23, 24] , electrochemical behavior [25], and the exploitation of their unique redox behavior, for example in applications for mercury removal from natural gas, etc. [26], [27], [28], [29]. Besides their intrinsic properties and application, MILs have also been used as ionic liquid precursors (ILPs) for inorganic nanomaterials, where the ILP acts as the solvent, the template, and the precursor for the inorganic material at the same time [19], [30], [31]. For example, ILPs have been used to synthesize CuCl, Au, Ag, metal oxide, Fe3C, and CuS nanomaterials [8], [30], [32], [33], [34], [35], [36], [37].
One of the key challenges in the ILP approach is the fact that for successful and efficient inorganic nanomaterials synthesis the fraction of the metal (which will be transformed to e.g. a metal sulfide in the course of the reaction) needs to be fairly high. Strategies to increase the metal content in the ILPs are thus of a very direct interest for improved yields from the synthetic procedure. In the quest for higher metal contents in the ILPs, we have therefore expanded the ILP platform to multinuclear ILs that can also serve as ILPs. The title compound is the first example of such a binuclear ILP. The article current focuses on the structure of the title compound. The transformation of the ILP to a series of inorganic materials will be described elsewhere.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains one cation and a half anion upper part of the figure. The second half is generated by symmetry because the [Cu2Cl6]2− unit is centrosymmetric. The CuCl3 subunits are doubly-bridged over the inversion centre. The average Cu—Cl bond lengths are 2.1936(4) Å (terminal) and 2.3100(4) Å (bridging) with a bridging Cu—Cl—Cu angle of 91.27(2)°, giving a distance between both copper atoms of 3.3027(4) Å. The coordination environment of the Cu atoms can be better described by a flattened tetrahedron rather than square-planar arrangement. The corresponding angles are 88.73(2)° [Cl(bridging) − Cu − Cl(bridging)], 100.01(2)° [Cl(terminal) − Cu − Cl(terminal)] and 98.79(2)° to 140.43(2)° [Cl(terminal) − Cu − Cl(bridging)]. The plane formed by the Cu atom and both terminal Cl atoms is twisted by an angle of 55.12° with respect to the plane defined by both Cu atoms and the bridging Cl atoms. The Cambridge Database contains 64 structures with isolated bibridged [Cu2Cl6]2− dimers, for example in [P(C6H5)4]2[Cu2Cl6] [38]. In contrast to the synthesis described here, where a 1:1 ratio of copper(II) chloride and N-butylpyridinium chloride was used yielding the dinuclear species, mononuclear isolated tetrachloridocopper(II) [CuCl4]2− was formed when N-butylpyridinium and copper(II) chloride in a ratio of 2:1 are used. In contrast, infinite zig-zag chains where the [Cu2Cl6]2− moieties are linked by weak interactions are observed when piperazinium rather than N-butylpyridinium cation is employed [39].
The packing of the title compound is stabilized by non-classical C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds between the [Cu2Cl6]2− anions and the pyridinium cations lower part of the figure. There are no interactions between neighboring [Cu2Cl6]2− groups.
References
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar
Farrugia, L. J.: WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Cryst. 45 (2012) 849–854.10.1107/S0021889812029111Search in Google Scholar
Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.5.1. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany (2017).Search in Google Scholar
Spek, A. L.: PLATON − a multipurpose crystallographic tool. Acta Crystallogr. D65 (2011) 148–155.10.1107/S090744490804362XSearch in Google Scholar
Abouserie, A.; Zehbe, K.; Metzner, P.; Kelling, A.; Günter, C.; Schilde, U.; Strauch, P.; Körzdoerfer, T.; Taubert, A.: Alkylpyridinium Tetrahalidometallate Ionic Liquids and Ionic Liquid Crystals: Insights into the Origin of Their Phase Behavior. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. (2017) 5640–5649.10.1002/ejic.201700826Search in Google Scholar
Zhang, J.; Feng, H.; Yang, J.; Qin, Q.; Fan, H.; Wei, C.; Zheng, W.: Solvothermal synthesis of three-dimensional hierarchical CuS microspheres from a Cu-based ionic liquid precursor for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7 (2015) 21735–21744.10.1021/acsami.5b04452Search in Google Scholar
Neve, F.; Francescangeli, O.; Crispini, A.; Charmant, J.: A2 [MX4] copper (II) pyridinium salts. From ionic liquids to layered solids to liquid crystals. Chem. Mater. 13 (2001) 2032–2041.10.1021/cm000804dSearch in Google Scholar
Taubert, A.: CuCl Nanoplatelets from an ionic liquid-crystal precursor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 116 (2004) 5494–5496.10.1002/ange.200460846Search in Google Scholar
Bhattacharya, R.; Ray, M. S.; Dey, R.; Righi, L.; Bocelli, G.; Ghosh, A.: Synthesis, crystal structure and thermochromism of benzimidazolium tetrachlorocuprate: (C7H7N2)2[CuCl4]. Polyhedron. 21 (2002) 2561–2565.10.1016/S0277-5387(02)01237-8Search in Google Scholar
Losee, D. B.; Hatfield, W. E.: Megnetization measurements on diethylenetriammonium chlorocuprate (II): Anisotropy and exchange fields in a two-dimensional Heisenberg ferromagnet. Phys. Rev. B. 10 (1974) 1122.10.1103/PhysRevB.10.1122Search in Google Scholar
Rubtsova, T.; Kireeva, O.; Bulychev, B.; Streltsova, N.; Belsky, V.; Tarasov, B.: Complex formation of metal salts with macrocyclic polyethers in aprotic organic solvents: crystal structures of the molecular complex [MeCN.Mg.15C5(μ2-Cl)CuCl3] and the ionic complexes [(MeCN)2.Mg.15C5][Cu2Cl6], {[(MeCN)2.Mg.15C5][Cu3Cl8]}n, [(H2O)2.Mg.15C5][CuCl4].H2O and {[(H2O)2.Cu3Cl8][Mg.(H2O)6].[2(15C5)].H2On. Polyhedron. 11 (1992) 1929–1938.10.1016/S0277-5387(00)83742-0Search in Google Scholar
Natarajan, M.; Prakash, B.: Phase transitions in ABX3 type halides. Phys. Status Solidi A. 4 (1971) K167–K172.10.1002/pssa.2210040331Search in Google Scholar
Yu, J.-H.; Xu, J.-Q.; Song, Y.-J.; Bie, H.-Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, T.-G.: Syntheses and characterization of several copper-halo clusters. Chin. J. Chem. 23 (2005) 1030–1036.10.1002/cjoc.200591030Search in Google Scholar
Bloomquist, D. R.; Willett, R. D.; Dodgen, H. W.: Thermochromism in copper (II) halide salts. 2. Bis (isopropylammonium) tetrachlorocuprate (II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103 (1981) 2610–2615.10.1021/ja00400a021Search in Google Scholar
Willett, R.; Haugen, J.; Lebsack, J.; Morrey, J.: Thermochromism in copper (II) chlorides. Coordination geometry changes in tetrachlorocuprate (2-) anions. Inorg. Chem. 13 (1974) 2510–2513.10.1021/ic50140a040Search in Google Scholar
Plechkova, N. V.; Seddon, K. R.: Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37 (2008) 123–150.10.1039/B006677JSearch in Google Scholar
Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T.: Ionic liquids in synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, Weinheim (2008).10.1002/9783527621194Search in Google Scholar
Castner, E. W. Jr.; Wishart, J. F.: Spotlight on ionic liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 132 (2010) 120901.10.1063/1.3373178Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Welton, T.: Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 99 (1999) 2071–2084.10.1021/cr980032tSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Wishart, J. F.; Castner, E. W. Jr.: The physical chemistry of ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B. 111 (2007) 4639–4640.10.1021/jp072262uSearch in Google Scholar
Freemantle, M.: An introduction to ionic liquids. Royal Society of Chemistry, Oxford (2010).10.1039/9781839168604Search in Google Scholar
Lei, Z.; Chen, B.; Koo, Y.-M.; MacFarlane, D. R.: Introduction: ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. (2017) 6633–6635.10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00246Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Farra, R.; Thiel, K.; Winter, A.; Klamroth, T.; Pöppl, A.; Kelling, A.; Schilde, U.; Taubert, A.; Strauch, P.: Tetrahalidocuprates (II) − structure and EPR spectroscopy. Part 1: Tetrabromidocuprates (II). New J. Chem. 35 (2011) 2793–2803.10.1039/c1nj20271eSearch in Google Scholar
Winter, A.; Thiel, K.; Zabel, A.; Klamroth, T.; Pöppl, A.; Kelling, A.; Schilde, U.; Taubert, A.; Strauch, P.: Tetrahalidocuprates (II) − structure and EPR spectroscopy. Part 2: Tetrachloridocuprates (II). New J. Chem. 38 (2014) 1019–1030.10.1039/c3nj01039bSearch in Google Scholar
Zazybin, A.; Rafikova, K.; Yu, V.; Zolotareva, D.; Dembitsky, V. M.; Sasaki, T.: Metal-containing ionic liquids: current paradigm and applications. Russ. Chem. Rev. 86 (2017) 1254.10.1070/RCR4743Search in Google Scholar
Pârvulescu, V. I.; Hardacre, C.: Catalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 107 (2007) 2615–2665.10.1021/cr050948hSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Binnemans, K.: Ionic liquid crystals. Chem. Rev. 105 (2005) 4148–4204.10.1021/cr0400919Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Holbrey, J. D.; Seddon, K. R.: Ionic liquids. Clean Products and Processes. 1 (1999) 223–236.10.1007/s100980050036Search in Google Scholar
Abai, M.; Atkins, M. P.; Hassan, A.; Holbrey, J. D.; Kuah, Y.; Nockemann, P.; Oliferenko, A. A.; Plechkova, N. V.; Rafeen, S.; Rahman, A. A.; Ramli, R.; Shariff, S. M.; Seddon, K. R.; Srinivasan, G.; Zou, Y.: An ionic liquid process for mercury removal from natural gas. Dalton Trans. 44 (2015) 8617–8624.10.1039/C4DT03273JSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Taubert, A.; Li, Z.: Inorganic materials from ionic liquids. Dalton Trans. (2007) 723–727.10.1039/B616593ASearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Duan, X.; Ma, J.; Lian, J.; Zheng, W.: The art of using ionic liquids in the synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials. CrystEngComm. 16 (2014) 2550–2559.10.1039/c3ce41203bSearch in Google Scholar
Taubert, A.; Steiner, P.; Mantion, A.: Ionic liquid crystal precursors for inorganic particles: Phase diagram and thermal properties of a CuCl nanoplatelet precursor. J. Phys. Chem. B. 109 (2005) 15542–15547.10.1021/jp051262wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
Taubert, A.; Arbell, I.; Mecke, A.; Graf, P.: Photoreduction of a crystalline Au (III) complex: A solidstate approach to metallic nanostructures. Gold Bulletin. 39 (2006) 205–211.10.1007/BF03215555Search in Google Scholar
Kim, Y.; Heyne, B.; Abouserie, A.; Pries, C.; Ippen, C.; Günter, C.; Taubert, A.; Wedel, A.: CuS nanoplates from ionic liquid precursors-Application in organic photovoltaic cells. J. Chem. Phys. 148 (2018) 193818.10.1063/1.4991622Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Antonietti, M.; Kuang, D.; Smarsly, B.; Zhou, Y.: Ionic liquids for the convenient synthesis of functional nanoparticles and other inorganic nanostructures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43 (2004) 4988–4992.10.1002/anie.200460091Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Dobbs, W.; Suisse, J. M.; Douce, L.; Welter, R.: Electrodeposition of Silver Particles and Gold Nanoparticles from Ionic Liquid-Crystal Precursors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 118 (2006) 4285–4288.10.1002/ange.200600929Search in Google Scholar
Li, R.; Du, J.; Luan, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhuang, G.; Li, Z.: Ionic liquid precursor-based synthesis of CuO nanoplates for gas sensing and amperometric sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 168 (2012) 156–164.10.1016/j.snb.2012.03.079Search in Google Scholar
Tran Qui, D.; Daoud, A.; Mhiri, T.: Structure of Tetraphenylphosphonium Trichlorocuprate. Acta Crystallogr. C45 (1989) 33–35.10.1107/S0108270188009904Search in Google Scholar
Daoud, A.; Salah, A. B.; Chappert, C.; Renard, J. P.; Cheikhrouhou, A.; Duc, T.; Verdaguer, M.: Crystal structure and magnetic properties of piperazinium hexadichlorocuprate: A new S = 1/2 antiferromagnetic chain with alternating exchange. Phys. Rev. B. 33 (1986) 6253–6260.10.1103/PhysRevB.33.6253Search in Google Scholar
©2018 A. Abouserie et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C17H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraazaadamantane-1,3-diium 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C16H18N4O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrabutyl-ammonium 5-hydroxyisophthalate dihydrate, C25H50N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalate-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)nickel(II), NiC21H20N6O6
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzoato-κ1O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II), C28H26CuN2O9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-pyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ2O:O′)] cadmium(II), C20H17CdN5O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiolato-κ2S:N)mercury(II)], C3H3ClHgN2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C14H10Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of a new polymorph of bis[μ-1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P:P′-disilver(I)] bis(tetrafluoroborate), [Ag(dppp)]2(BF4)2, C54H52Ag2B2F8P4
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(R-tert-butylsulfonamido)-1,3,5-triazine – ethyl acetate (2/1), C38H58N10O6S4
- Crystal structure of 6-amino-8-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-2-methyl-2,3,8,8a-tetrahydro-1H-iso-quinoline-5,7,7-tricarbonitrile monohydrate, C20H21N5O2
- Crystal structure of methyl (1-phenylethyl)carbamate, C10H13NO2
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-(μ2-squarato-κ2O:O′)-tetrakis(tri-p-tolylphosphane-κP)disilver(I) – methanol (1/2), C92H98Ag2O8P4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bis(triazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(5-tert-butyl-isophthalate-κO)copper(II)]tetrahydrate, C36H46CuN6O12
- Crystal structure of 4-aminopyridinium 4-acetyl-(pyridin-4-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-5-olate monohydrate, C14H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(8-bromo-2-phenylimidazo[1,2-α]pyridin-3-yl)-6,7-dimethyl-3-phenylquinoxaline, C29H21BrN4
- Crystal structure of aqua(1-(2-pyridyl)ethanone oxime-κ2N,N′)(1-(2-pyridyl)ethanone oximato-κ2N,N′) nitrate monohydrate, C14H19N5O7Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-(μ4-oxalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ8-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ8O1:O2:O3:O4:O5:O6:O7:O8)yttrium(III)], C6H5O8Y
- Crystal structure of bis{catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)silver(I)]} diaqua-bis(5-(4-carboxyphenyl)pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) octahydrate, C31H35Ag2N4O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(2-(benzylamino)-2-oxo-1-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-bromophenyl)-3-chloroacrylamide hydrate, C27H22BrClN2O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[octaaqua-bis(μ2-4,6-dicarboxyisophthalate-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)disodium(I)] dihydrate, C20H28CdNa2O26
- Crystal structure of acetonitrile{bis(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N′′}-{maleato-κO}zinc(II) perchlorate - acetonitrile (1/1), C24H24ClN7O8Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-2H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C16H10Br2N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-3,5-bis(pyridin-4-ylmethoxy)benzoate-κ2N:O) manganese(II)] tetrahydrate [(3,5-bis-(pyridin-4-ylmethoxy)-benzoic-κ1Oκ1N) manganese(II)] trihydrate, C38H42MnN4O14
- The crystal structure of 2-carboxybenzaldehyde-2-phenylacetohydrazone, C16H14N2O3
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-aqua-(μ2-2-naphthylamine-1-sulfonato-κ3O,O′:O′′)sodium(I)], C10H10N1O4S1Na
- The crystal structure of phthalazin-1(2H)-one, C8H6N2O1
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl(Z)-N-(adamantan-1-yl)morpholine-4-carbothioimidate, C24H28F6N2OS
- Crystal structure of diazido-bis(μ2-pyridin-2-ylmethanolato-κ2N:O)-bis(pyridin-2-ylmethanolato-κ2N,O)dicobalt(III) – methanol (1/3), C27H35Co2N10O7
- Crystal structure of N-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinesulfonamide, C14H14F3N5O6S
- Crystal structure of 1-phenyl-N′-(1-phenyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonyl)-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C28H20N6O2S2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(4-hydroxybenzoato-κO)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)] hydrate, C24H20N2O7Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-5-(4-(2,6-di(pyridine-2-yl)pyridine-4-yl)phenoxy)isophthalato-κ5O:O′,O′′:N,N′,N′′cobalt(II)], C29H17CoN3O5
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-5-(4-(2,6-di(pyridine-2-yl)pyridine-4-yl)phenoxy)isophthalato-κ6O:O′,O′′:N,N′,N′′)cobalt(II)] C29H17CoN3O5
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(acetato-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ3-4,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)isophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′,O′′′)lanthanum(III), C16H15LaN4O8
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-carboxy-1-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5-carboxylate dihydrate, C18H12N2O8
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-(((E)-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl)oxime, C18H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C32H30N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(9-aminoacridin-10-ium) tetrachloridocuprate(II) monohydrate, C26H24Cl4CuN4O
- The crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-N′-[(E)-(4-fluoro-3-methoxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide, C19H21F1N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-4-tolyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C31H26N8O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-5-methyl-1-(4-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbohydrazide, C19H19N5O2
- Crystal structure and molecular packing of O-ethyl (2-chlorophenyl)carbamothioate, C9H10ClNOS
- Crystal structure of pyrene-2-carbaldehyde, C17H10O
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-diiodo-6-(4-methyl-2-nitrostyryl)phenol, C14H10I2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C14H10Cl2N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-bromo-4-chloro-6-(4-methoxy-2-nitrostyryl)phenol, C14H10BrClN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,6-diiodo-2-(((4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)-3-methylphenol, C14H10I2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 7-bromo-1-cyclopropyl-8-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid an intermediate of the ozenoxacin synthesis, C14H12BrNO3
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)copper(II) C24H20N10O2Cu
- Crystal structure of diaqua-dinitrato-k2O,O′((Z)-N-((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)europium(II), C12H14N7O9Eu
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-amino-5-(5-methyl-1-(4-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbonyl)-2-(phenylamino)thiophene-3-carboxylate, C24H23N5O3S
- The crystal structure of acridin-10-ium2-carboxybenzoate, C21H15NO4
- The crystal structure of 3-((phenylamino)methylene)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H17N1O4
- Crystal structure of 12-chloro-5,6,7,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxastibocine, C14H12ClOSb
- Crystal structure of 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)phenethyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C24H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C9H8N2OS
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (2-(4-oxo-2-thioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)ethyl)carbamate, C15H19N3O3S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-formyl-3,4-dimethylpyrrole-2-carboxylate–1-(propan-2-ylidene)thiosemicarbazide (1/1), C14H22N4O3S
- Crystal structure of bis-(N′-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethyl-pyrrol-2-yl-methylidene)-3-hydroxybenzohydrazide-κ2O,N)copper(II) – dimethylformamide (1/2), C40H50N8O10Cu
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κO)bis{2-((1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN}zinc(II), C22H22N12O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 4-phenyl-3-((4-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C17H14N6S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-nitrophenyl)-3-phenyl-3-(phenylamino)acrylamide, C21H17N3O3
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(pentane-1,5-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(hexafluorophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(furan-2-ylmethanaminium)-catena-[bis(μ2-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C26H24CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of methyl (R)-4-(o-chlorobenzoyl)-1-thia-4-azaspiro[4.5]decane-3-carboxylate, C17H20ClNO3S
- Crystal structure of 2-[[4-[2-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]phenyl] methyl]-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C28H29N3O3
- The crystal structure of benzenaminium 5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromene-8-sulfonate hydrate, C21H19NO8S
- Crystal structure of semiconducting potassium poly[(μ2-tetraselenido-κ2Se1:Se4)(μ2-pentaselenido-κ1Se1:Se1)argentate(I)], K3AgSe9
- Crystal structure of 2-isopropyl-8-methyl-phenanthrene-3,4-dione, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of 2-isopropyl-8,8-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrophenanthrene-3,4-dione, C19H22O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-4-bromophenol, C14H13BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,1-di(4-cyanophenyl)-2,2-diphenylethene, C28H18N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxylamido-κ2O,N)-oxido(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2O,N)vanadium(V), C4H7N4O5V
- The crystal structure of In1.2B3O5.6(OH)1.4
- The crystal structure of chlorido(2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenolato-κ2N,O)(2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol-κN)copper(II), C18H15ClCuN4O2
- Crystal structure of 1-heptylpyridazin-1-ium iodide, C11H19N2I
- The crystal structure of N-butylpyridinium bis(μ2-dichlorido)-tetrachloridodicopper(II), C18H28N2Cu2Cl6
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5-((2-hydroxy-6-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile)-diaqua-dichloridoiron(II), C4H10Cl2N2O2Fe
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-methyl oxime, C17H18N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,3,5,7-tetraazaadamantane-1,3-diium 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C16H18N4O8
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetrabutyl-ammonium 5-hydroxyisophthalate dihydrate, C25H50N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalate-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ2-1,4-bis((1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)nickel(II), NiC21H20N6O6
- Crystal structure of aqua-bis(3,4-dimethoxybenzoato-κ1O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)copper(II), C28H26CuN2O9
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-(μ2-(3,5-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-pyridine-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-2-(carboxylatomethyl)benzoato-κ2O:O′)] cadmium(II), C20H17CdN5O5
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[chlorido-(μ2-5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiolato-κ2S:N)mercury(II)], C3H3ClHgN2S2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C14H10Cl2N2O3
- Crystal structure of a new polymorph of bis[μ-1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane-κ2P:P′-disilver(I)] bis(tetrafluoroborate), [Ag(dppp)]2(BF4)2, C54H52Ag2B2F8P4
- The crystal structure of 2-phenyl-4,6-bis(R-tert-butylsulfonamido)-1,3,5-triazine – ethyl acetate (2/1), C38H58N10O6S4
- Crystal structure of 6-amino-8-(2-methoxy-phenyl)-2-methyl-2,3,8,8a-tetrahydro-1H-iso-quinoline-5,7,7-tricarbonitrile monohydrate, C20H21N5O2
- Crystal structure of methyl (1-phenylethyl)carbamate, C10H13NO2
- Crystal structure of dimethanol-(μ2-squarato-κ2O:O′)-tetrakis(tri-p-tolylphosphane-κP)disilver(I) – methanol (1/2), C92H98Ag2O8P4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[bis(μ2-1,4-bis(triazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-bis(5-tert-butyl-isophthalate-κO)copper(II)]tetrahydrate, C36H46CuN6O12
- Crystal structure of 4-aminopyridinium 4-acetyl-(pyridin-4-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-5-olate monohydrate, C14H16N6O3
- Crystal structure of 2-(8-bromo-2-phenylimidazo[1,2-α]pyridin-3-yl)-6,7-dimethyl-3-phenylquinoxaline, C29H21BrN4
- Crystal structure of aqua(1-(2-pyridyl)ethanone oxime-κ2N,N′)(1-(2-pyridyl)ethanone oximato-κ2N,N′) nitrate monohydrate, C14H19N5O7Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-(μ4-oxalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-(μ8-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-κ8O1:O2:O3:O4:O5:O6:O7:O8)yttrium(III)], C6H5O8Y
- Crystal structure of bis{catena-poly[(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)silver(I)]} diaqua-bis(5-(4-carboxyphenyl)pyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′)disilver(I) octahydrate, C31H35Ag2N4O9
- Crystal structure of (E)-N-(2-(benzylamino)-2-oxo-1-(4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)ethyl)-N-(4-bromophenyl)-3-chloroacrylamide hydrate, C27H22BrClN2O5
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[octaaqua-bis(μ2-4,6-dicarboxyisophthalate-κ2O:O′)cadmium(II)disodium(I)] dihydrate, C20H28CdNa2O26
- Crystal structure of acetonitrile{bis(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-κ3N,N′,N′′}-{maleato-κO}zinc(II) perchlorate - acetonitrile (1/1), C24H24ClN7O8Zn
- Crystal structure of 2-amino-4-(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methyl-5-oxo-2H,5H-pyrano[4,3-b]pyran-3-carbonitrile, C16H10Br2N2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-(μ2-3,5-bis(pyridin-4-ylmethoxy)benzoate-κ2N:O) manganese(II)] tetrahydrate [(3,5-bis-(pyridin-4-ylmethoxy)-benzoic-κ1Oκ1N) manganese(II)] trihydrate, C38H42MnN4O14
- The crystal structure of 2-carboxybenzaldehyde-2-phenylacetohydrazone, C16H14N2O3
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-aqua-(μ2-2-naphthylamine-1-sulfonato-κ3O,O′:O′′)sodium(I)], C10H10N1O4S1Na
- The crystal structure of phthalazin-1(2H)-one, C8H6N2O1
- Crystal structure of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzyl(Z)-N-(adamantan-1-yl)morpholine-4-carbothioimidate, C24H28F6N2OS
- Crystal structure of diazido-bis(μ2-pyridin-2-ylmethanolato-κ2N:O)-bis(pyridin-2-ylmethanolato-κ2N,O)dicobalt(III) – methanol (1/3), C27H35Co2N10O7
- Crystal structure of N-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinesulfonamide, C14H14F3N5O6S
- Crystal structure of 1-phenyl-N′-(1-phenyl-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbonyl)-5-(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carbohydrazide, C28H20N6O2S2
- The crystal structure of poly[bis(4-hydroxybenzoato-κO)-(μ2-4,4′-bipyridine-κ2N:N′)copper(II)] hydrate, C24H20N2O7Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-5-(4-(2,6-di(pyridine-2-yl)pyridine-4-yl)phenoxy)isophthalato-κ5O:O′,O′′:N,N′,N′′cobalt(II)], C29H17CoN3O5
- Crystal structure of poly[μ3-5-(4-(2,6-di(pyridine-2-yl)pyridine-4-yl)phenoxy)isophthalato-κ6O:O′,O′′:N,N′,N′′)cobalt(II)] C29H17CoN3O5
- Crystal structure of diaqua-(acetato-κ3O,O′:O′′)-(μ3-4,6-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)isophthalato-κ4O:O′:O′′,O′′′)lanthanum(III), C16H15LaN4O8
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 6-carboxy-1-(3,5-dicarboxyphenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-3-ium-5-carboxylate dihydrate, C18H12N2O8
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde O-(2-(((E)-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene)amino)oxy)ethyl)oxime, C18H21N3O3
- Crystal structure of bis{2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C32H30N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of bis(9-aminoacridin-10-ium) tetrachloridocuprate(II) monohydrate, C26H24Cl4CuN4O
- The crystal structure of 4-tert-butyl-N′-[(E)-(4-fluoro-3-methoxyphenyl)methylidene]benzohydrazide, C19H21F1N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(3-(5-methyl-1-4-tolyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-(5-methyl-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, C31H26N8O
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-5-methyl-1-(4-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbohydrazide, C19H19N5O2
- Crystal structure and molecular packing of O-ethyl (2-chlorophenyl)carbamothioate, C9H10ClNOS
- Crystal structure of pyrene-2-carbaldehyde, C17H10O
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-diiodo-6-(4-methyl-2-nitrostyryl)phenol, C14H10I2N2O3
- Crystal structure of (E)-2,4-dichloro-6-(((4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)phenol, C14H10Cl2N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-bromo-4-chloro-6-(4-methoxy-2-nitrostyryl)phenol, C14H10BrClN2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-4,6-diiodo-2-(((4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)imino)methyl)-3-methylphenol, C14H10I2N2O4
- The crystal structure of 7-bromo-1-cyclopropyl-8-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid an intermediate of the ozenoxacin synthesis, C14H12BrNO3
- Crystal structure of bis(N-(1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-κ3N,N′,O)copper(II) C24H20N10O2Cu
- Crystal structure of diaqua-dinitrato-k2O,O′((Z)-N-((E)-1-(pyrazin-2-yl)ethylidene)nicotinohydrazonato-k3N,N′,O)europium(II), C12H14N7O9Eu
- Crystal structure of ethyl 4-amino-5-(5-methyl-1-(4-tolyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbonyl)-2-(phenylamino)thiophene-3-carboxylate, C24H23N5O3S
- The crystal structure of acridin-10-ium2-carboxybenzoate, C21H15NO4
- The crystal structure of 3-((phenylamino)methylene)-1,5-dioxaspiro[5.5]undecane-2,4-dione, C16H17N1O4
- Crystal structure of 12-chloro-5,6,7,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[c,f][1,5]oxastibocine, C14H12ClOSb
- Crystal structure of 4-((1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)methyl)phenethyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate, C24H21NO5S
- Crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,3-dihydro-2-thioxoquinazolin-4(1H)-one, C9H8N2OS
- Crystal structure of tert-butyl (2-(4-oxo-2-thioxo-1,4-dihydroquinazolin-3(2H)-yl)ethyl)carbamate, C15H19N3O3S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-formyl-3,4-dimethylpyrrole-2-carboxylate–1-(propan-2-ylidene)thiosemicarbazide (1/1), C14H22N4O3S
- Crystal structure of bis-(N′-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethyl-pyrrol-2-yl-methylidene)-3-hydroxybenzohydrazide-κ2O,N)copper(II) – dimethylformamide (1/2), C40H50N8O10Cu
- Crystal structure of bis(acetato-κO)bis{2-((1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-κN}zinc(II), C22H22N12O4Zn
- Crystal structure of 4-phenyl-3-((4-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thione, C17H14N6S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-N-(4-nitrophenyl)-3-phenyl-3-(phenylamino)acrylamide, C21H17N3O3
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(pentane-1,5-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(hexafluorophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(furan-2-ylmethanaminium)-catena-[bis(μ2-phthalato-κ2O:O′)cobalt(II)], C26H24CoN2O10
- Crystal structure of methyl (R)-4-(o-chlorobenzoyl)-1-thia-4-azaspiro[4.5]decane-3-carboxylate, C17H20ClNO3S
- Crystal structure of 2-[[4-[2-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]phenyl] methyl]-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, C28H29N3O3
- The crystal structure of benzenaminium 5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromene-8-sulfonate hydrate, C21H19NO8S
- Crystal structure of semiconducting potassium poly[(μ2-tetraselenido-κ2Se1:Se4)(μ2-pentaselenido-κ1Se1:Se1)argentate(I)], K3AgSe9
- Crystal structure of 2-isopropyl-8-methyl-phenanthrene-3,4-dione, C18H16O2
- Crystal structure of 2-isopropyl-8,8-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrophenanthrene-3,4-dione, C19H22O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(1-((2-aminophenyl)imino)ethyl)-4-bromophenol, C14H13BrN2O
- Crystal structure of 1,1-di(4-cyanophenyl)-2,2-diphenylethene, C28H18N2
- Crystal structure of bis(hydroxylamido-κ2O,N)-oxido(1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylato-κ2O,N)vanadium(V), C4H7N4O5V
- The crystal structure of In1.2B3O5.6(OH)1.4
- The crystal structure of chlorido(2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenolato-κ2N,O)(2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl)phenol-κN)copper(II), C18H15ClCuN4O2
- Crystal structure of 1-heptylpyridazin-1-ium iodide, C11H19N2I
- The crystal structure of N-butylpyridinium bis(μ2-dichlorido)-tetrachloridodicopper(II), C18H28N2Cu2Cl6
- Crystal structure of 6-hydroxy-5-((2-hydroxy-6-oxocyclohex-1-en-1-yl)(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl)-1,3-dimethylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, C20H22N2O6
- Crystal structure of bis(acetonitrile)-diaqua-dichloridoiron(II), C4H10Cl2N2O2Fe


