Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraqua-bis(2-(((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)ammonio)acetato-κO)cobalt(II) hexahydrate, C36H48CoN2O28S2
Abstract
C36H48CoN2O28S2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 18.2239(13) Å, b = 7.1282(6) Å, c = 17.8550(13) Å, β = 97.883(2)°, V = 2297.5(3) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0906, wRref(F2) = 0.1998, T = 293(2) K.
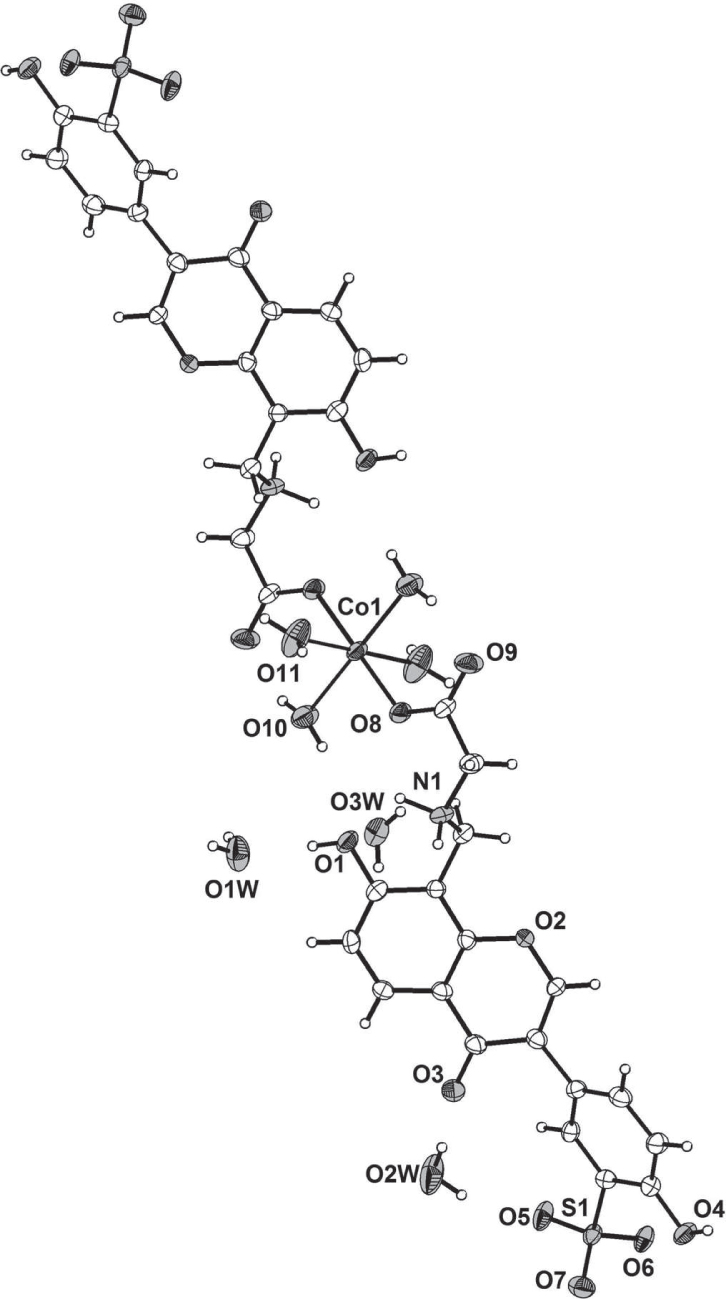
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Red block |
| Size: | 0.30 × 0.28 × 0.15 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.56 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker AXS, φ and ω-scans |
| 2θmax, completeness: | 27.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 35845, 5274, 0.163 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2811 |
| N(param)refined: | 313 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX [2, 3] , DIAMOND [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co1 | −0.5000 | −0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.0275(3) |
| S1 | 0.25874(7) | −0.39005(18) | −0.20198(7) | 0.0255(3) |
| O1 | −0.27920(17) | −0.2399(5) | 0.00580(18) | 0.0373(9) |
| H1B | −0.2718 | −0.2036 | 0.0516 | 0.056* |
| O2 | −0.15556(16) | −0.3760(5) | −0.20032(17) | 0.0263(8) |
| O3 | 0.04170(18) | −0.1889(6) | −0.0903(2) | 0.0456(11) |
| O4 | 0.21838(17) | −0.3221(5) | −0.36571(18) | 0.0355(9) |
| H4A | 0.2018 | −0.2920 | −0.4109 | 0.053* |
| O5 | 0.25134(19) | −0.4202(5) | −0.12272(18) | 0.0388(10) |
| O6 | 0.28921(18) | −0.5570(5) | −0.23371(18) | 0.0319(9) |
| O7 | 0.29976(18) | −0.2211(5) | −0.2152(2) | 0.0382(9) |
| O8 | −0.45071(18) | −0.3699(5) | −0.08387(18) | 0.0334(9) |
| O9 | −0.52745(19) | −0.4283(6) | −0.19075(19) | 0.0449(10) |
| O10 | −0.40980(19) | −0.4143(5) | 0.08001(19) | 0.0423(10) |
| H10A | −0.4168 | −0.4608 | 0.1223 | 0.064* |
| H10B | −0.3667 | −0.4332 | 0.0683 | 0.064* |
| O11 | −0.4435(2) | −0.7398(6) | −0.0231(2) | 0.0602(12) |
| H11W | −0.4185 | −0.7629 | −0.0589 | 0.090* |
| H11C | −0.4417 | −0.8310 | 0.0078 | 0.090* |
| N1 | −0.34356(19) | −0.2345(6) | −0.1521(2) | 0.0270(10) |
| H1A | −0.3676 | −0.1859 | −0.1066 | 0.040* |
| H1C | −0.3223 | −0.1360 | −0.1646 | 0.040* |
| C1 | −0.2140(3) | −0.2488(7) | −0.0217(3) | 0.0277(12) |
| C2 | −0.2169(2) | −0.3164(6) | −0.0953(3) | 0.0223(11) |
| C3 | −0.1516(3) | −0.3153(7) | −0.1266(3) | 0.0231(11) |
| C4 | −0.0844(2) | −0.2549(7) | −0.0876(3) | 0.0262(12) |
| C5 | −0.0848(3) | −0.1916(7) | −0.0140(3) | 0.0307(13) |
| H5B | −0.0406 | −0.1512 | 0.0137 | 0.037* |
| C6 | −0.1473(3) | −0.1872(8) | 0.0184(3) | 0.0352(13) |
| H6B | −0.1460 | −0.1429 | 0.0675 | 0.042* |
| C7 | −0.0174(3) | −0.2490(7) | −0.1237(3) | 0.0283(12) |
| C8 | −0.0261(3) | −0.3161(7) | −0.2019(3) | 0.0263(11) |
| C9 | −0.0933(2) | −0.3743(7) | −0.2331(3) | 0.0253(11) |
| H9A | −0.0974 | −0.4180 | −0.2825 | 0.030* |
| C10 | 0.0374(2) | −0.3201(6) | −0.2455(3) | 0.0231(11) |
| C11 | 0.1084(3) | −0.3592(6) | −0.2112(3) | 0.0238(11) |
| H11A | 0.1160 | −0.3870 | −0.1598 | 0.029* |
| C12 | 0.1682(2) | −0.3582(6) | −0.2507(3) | 0.0229(11) |
| C13 | 0.1584(3) | −0.3220(7) | −0.3281(3) | 0.0272(12) |
| C14 | 0.0869(3) | −0.2850(7) | −0.3634(3) | 0.0301(12) |
| H14A | 0.0788 | −0.2619 | −0.4152 | 0.036* |
| C15 | 0.0285(3) | −0.2821(7) | −0.3224(3) | 0.0304(12) |
| H15A | −0.0186 | −0.2538 | −0.3470 | 0.037* |
| C16 | −0.2881(2) | −0.3888(7) | −0.1362(3) | 0.0267(11) |
| H16A | −0.3078 | −0.4846 | −0.1059 | 0.032* |
| H16B | −0.2792 | −0.4459 | −0.1835 | 0.032* |
| C17 | −0.4132(3) | −0.2899(8) | −0.2005(3) | 0.0333(13) |
| H17A | −0.4019 | −0.3822 | −0.2372 | 0.040* |
| H17B | −0.4344 | −0.1810 | −0.2279 | 0.040* |
| C18 | −0.4687(3) | −0.3708(7) | −0.1545(3) | 0.0271(12) |
| O1W | −0.2605(2) | −0.1193(6) | 0.1468(2) | 0.0550(12) |
| H1WA | −0.2859 | −0.0245 | 0.1563 | 0.082* |
| H1WB | −0.2626 | −0.2042 | 0.1799 | 0.082* |
| O2W | 0.1838(2) | −0.2563(7) | −0.0094(2) | 0.0707(14) |
| H2WB | 0.2140 | −0.2935 | −0.0386 | 0.106* |
| H2WA | 0.1413 | −0.2516 | −0.0359 | 0.106* |
| O3W | −0.3944(2) | 0.1807(6) | −0.1622(2) | 0.0569(12) |
| H3WA | −0.4259 | 0.1622 | −0.2012 | 0.085* |
| H3WB | −0.3588 | 0.2486 | −0.1724 | 0.085* |
Source of material
The educt sodium 5-(8-(((carboxymethyl)amino)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate was synthesized via a Mannich reaction. Formaldehyde solution (10 mL, 37%) and sodium 2-hydroxy-5-(7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)benzenesulfonate (3.56 g, 0.01 mol) were added to ethanol (200 mL, 95%) and stirred for 0.5 h at 338 K. Then, the saturated solution of glycine (1.12 g, 0.015 mol) was added to the reaction mixture. Then, water was added until a transparent solution was obtained. After 11 h reaction time, the mixture was filtered, and the residue was collected. Then the residue was dried at 383 K. Sodium 5-(8-(((carboxymethyl)amino)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate (2.262 g, 0.005 mol) was obtained. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AV400 NMR instrument. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 10.59 (s, 1H, H4A), 8.34 (s, 1H, H9A), 7.98 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H, H5B), 7.71 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H, H11A), 7.39 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.3 Hz, 1H, H15A), 7.08 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H, H6B), 6.85 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H, H14A), 4.30 (s, 2H, H16A, H16B), 3.39 (s, 2H, H17A, H17B); 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 174.62 (C7), 168.87 (C18), 163.16 (C1), 155.87 (C3), 153.25 (C13), 152.73 (C9), 131.48 (C15), 130.64 (C12), 127.74 (C5), 127.20 (C11), 123.02 (C10), 122.25 (C8), 116.29 (C4), 115.85 (C14), 115.12 (C6), 106.64 (C2), 48.87 (C17), 39.73 (C16). IR spectra (potassium bromide pellet) Nicolet 6700. IR (v/cm−1): 3493, 3041, 2876, 1633, 1505, 1448, 1396, 1360, 1323, 1277, 1207, 1178, 1065, 1052, 1205, 899, 844, 820, 797, 729, 678, 623, 543, 491. ESI-MS: m/z 420.17 [M–Na]−. The saturated solution of CoCl2⋅H2O (0.238 g, 0.001 mol) was added to the saturated solution of sodium salt described before (0.443 g, 0.001 mol). The mixture was stirred for 30 min at 343 K and a pink solution was obtained. After cooling to room temperature, red block-shaped crystals of the title compound were obtained. IR spectra (potassium bromide pellet) Nicolet 6700. IR (v/cm−1): 3448, 1629, 1529, 1458, 1432, 1414, 1334, 1285, 1210, 1175, 1100, 1028, 910, 826, 741, 629, 517, 487.
Experimental details
Carbon-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2 Ueq(C). The oxygen-bound and nitrogen-bound H atoms were located on a difference Fourier map and refined freely.
Discussion
In the last decade, much attention has been focused on flavonoids. The Mannich reaction has been considered as an effective method in introducing aminomethyl substituents into the desired flavonoid molecules to improve their biological activities [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11]. The goal of our work is to synthesize amino-acid derivatives of daidzein to obtain substances which have a good water solubility. Increasing the solubility of daidzein derivatives expands the capability for studying their biological activity and increases their bioavailability. To extend this research, we used sodium 5-(8-(((carboxymethyl)amino)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate to react with Co2+ ions and got a new complex. The studies on the bioactivity of the title compound are presently ongoing.
The asymmetric unit of the title structure consists of one half of a monomer complex (cf. the figure, the asymmetric unit is labeled) and three uncoordinated water molecules. The Co(II) atom lies on the inversion center and is six-coordinated by four O atoms from four coordinated water molecules and two O atoms from two monodentate coordinating ligands. The Co(II) atom adopts a slightly distorted octahedral geometry. The Co—O bond distances are in the range of 2.066(4) Å and 2.115(3) Å. The chromen moiety (C1/C6/C5/C4/C7/C8/C9/O2/C3/C2) is essentially planar, with a mean deviation of 0.0182 Å. The carboxylate groups adopt trans conformations, with the C18—C17—N1—C16 torsion angles to be −86.54°. The nitrogen atom N1 is protonated. There exist extensive H-bonding interactions between the ligands via the coordinated water molecules and uncoordinated water molecules to form a 3D supramolecular network. It is obvious that the hydrogen bonds play important roles in the self-assembly and enhance stability of the resultant structure.
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China (No. KY2015ZD104), the Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China (No. KY2016LX290) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2014GXNSFBA118062).
References
Bruker: APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Brucker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA (2009).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: SADABS 2.05. University Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany (2002).Search in Google Scholar
Sheldrick, G. M.: A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122.10.1107/S0108767307043930Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Brandenburg, K.: DIAMOND. Visual crystal structure information system. Version 3.2i. Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany (2012).Search in Google Scholar
Li, Y.; Qiang, X.; Luo, L.; Yang, X.; Xiao, G.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Sang, Z.; Su, F.; Deng, Y.: Multitarget drug design strategy against alzheimers disease: Homoisoflavonoid Mannich base derivatives serve as acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase B dual inhibitors with multifunctional properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 25 (2017) 714–726.10.1016/j.bmc.2016.11.048Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Frasinyuk, M. S.; Mrug, G. P.; Bondarenko, S. P.; Khilya, V. P.; Sviripa, V. M.; Syrotchuk, O. A.; Zhang, W.; Cai, X.; Fiandalo, M. V.; Mohler, J. L.: Antineoplastic isoflavonoids derived from intermediate ortho-quinone methides generated from mannich bases. ChemMedChem. 11 (2016) 600–611.10.1002/cmdc.201600008Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Frasinyuk, M. S.; Mrug, G. P.; Bondarenko, S. P.; Sviripa, V. M.; Zhang, W.; Cai, X.; Fiandalo, M. V.; Mohler, J. L.; Liu, C.; Watt, D. S.: Application of mannich bases to the synthesis of hydroxymethylated isoflavonoids as potential antineoplastic agents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 13 (2015) 11292–11301.10.1039/C5OB01828ESearch in Google Scholar
Frasinyuk, M. S.; Mrug, G. P.; Fedoryak, O. D.; Bondarenko, S. P.: Synthesis of amino-acid derivatives of formononetin and cladrin. Chem. Nat. Compd. 48 (2012) 570–573.10.1007/s10600-012-0313-2Search in Google Scholar
Frasinyuk, M. S.; Mrug, G. P.; Fedoryak, O. D.; Bondarenko, S. P.: Nitrogen-containing apigenin analogs: preparation and biological activity. Molecules 17 (2012) 14748–14764.10.3390/molecules171214748Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Frasinyuk, M. S.; Bondarenko, S. P.; Khilya, V. P.: Synthesis of analogs of natural 2′-methoxyisoflavones. Chem. Nat. Compd. 42 (2006) 142–147.10.1007/s10600-006-0063-0Search in Google Scholar
Aitmambetov, A.; Khilya, V. P.: Mannich bases and their salts in a series of synthetic isoflavone analogs. Chem. Nat. Compd. 30 (1994) 576–579.10.1007/BF00629866Search in Google Scholar
©2017 Hai-Lin Chen et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of potassium 1-methyl-1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole-5-thiolate, C2H3N4SK
- Crystal structure of bis(3-(3-ethylureido)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-aminium) bis (μ3-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(oxidomethyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato))-(μ6-oxo)-hexakis(μ2-oxo)-hexaoxo-hexavanadium(V) – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H60Cl2N6O23V6
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-methanolato-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-dimethanol-bis{6,6′-(1,3-dihydroxyl-2-acetylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(2-chloro-4-bromophenolato)}tetramanganese(III) C40H40Br4Cl4Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dibromo-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5)tetramanganese(III), C40H40Br8Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dichloro-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5), tetramanganese(III), C40H40Cl8Mn4O16
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)}copper(II), C34H34CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-hydroxy-3-{[2-hydroxybenzylidene]amino}phenyl)ethan-1-one, C15H13NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′′:O′′}tricobalt(II), C44H49Cl2Co3N6O12
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-2,4-dichloro-6-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ5O:O,N,N′,O′}dicobalt(II) acetone solvate, C43H48Br4Co2N6O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′:O′}trizinc(II), C44H49Cl2N6O12Zn3
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(N,N′-diethylamine)-5′-methoxy -2,2′-[ethylenediyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenolato}-bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)trizinc(II), C46H56Zn3N6O14
- Crystal structure of tris(cyano-(hydrogen tris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate))-iron(III) 4-methoxypyridinium monohydrate, C24H32BN10O2Fe
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{1-(((4-(1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)naphthalen-2-olato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C38H30CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-{[(E)-2-Hydroxy-1-naphthalenylmethylene] amino}phenyl)ethanone oxime, C19H16N2O2
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 2-(2-naphthalenyl)-3-nitro-2H-1-benzopyran, C38H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C19H14N2O2
- N′-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethyl-pyrrol-2-yl-methylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide monohydrate, C17H21N3O5
- The crystal structure of carbonyl-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenylamino)pent-3-en-2-onato-κ2N,O]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), RhC30H25Cl2NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-5-(diethylamino)-2-(((1,1,2-trihydroxyethyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C15H24N2O4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,4-bis((2-ethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)(μ2-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C34H30N4O4Cd
- Crystal structure of 5,6-Dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-a]chinolizinium 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate - methanol - water (1/1/1), C36H33NO10
- A single crystal study on 2-(methylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid, C9H9NO3
- Crystal structure of the salt 1,1′-(ethane-1,2-diyl)bis(1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium) diperchlorate, C14H28N4(ClO4)2
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis((E)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)cyclopentan-1-one, C21H14F6O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-benzene-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)] 1.25 hydrate, C25H26.5N3O8.25FZn
- Crystal structure of 1-methyl-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium poly[aqua-bis(μ2-perchlorato-κ3O,O′:O′′)sodium], C7H17Cl2N2NaO9
- Crystal structure of trimethyammonium 2,6-dicarboxyisonicotinate monohydrate, C11H16N2O7
- Crystal structure of dodecaguanidinium bis(tetrapropylammonium) heptacarbonate, C43H128N38O21
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ6-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)nickel(II)diyttrium(III)]dihydrate, C20H16NiO22Y2
- Halogen bonds and π–π interactions in the crystal structure of 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene–N,N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C9H7F3I3NO
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetraethylammonium carbonate dihydrate, C10H30N4O5
- The crystal structure of oxonium chlorido-ethylenediaminetetraactetotin(IV) hydrate, C10H17ClN2O10Sn
- Crystal structure of 8-((E)-((4-((E)-1-((benzyloxy)imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C26H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(diethylamino)-2-(((2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C40H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(tri(p-tolyl)phosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C29H28O5PRe
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(benzyldiphenylphosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C27H24O5PRe
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium bis{3-(((3-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N,O′}manganese(III), C46H38MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-ethyldimethylethanaminium) bis(heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II), C12H32N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of bis(4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2-(2-((2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetate-κO)cadmium(II), C44H34N8CdCl4O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(pyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′] dihydrate, C48H42O22N2Ca
- The crystal structure of (S)-2-benzylsuccinic acid, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-4-(pyridin-4-yl)isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′)yttrium(III)], C26H17N2O9Y
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C14H17N3O2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(methanol-κO)-bis{μ2-3-((4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olate-κ4O,N;O′:O′}dizinc(II), C38H38Zn2N2O14
- Crystal structure of bromido(4,4′-dimethoxy-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)(isopropyl(diphenyl)phosphane-κP)copper(I), C27H29BrCuN2O2P
- Crystal structure of bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane)-9,9-dioctylfluorene, C41H64B2O4
- Crystal structure of 11-oxo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H,5H,11H-pyrano[2,3-f]pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-10-carbaldehyde - a julolidine derivative, C16H15NO3
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-5,5-dibenzylbarbituric acid, C20H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium) poly[bis(μ2-heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II)], C10H28N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of 1-{4-[(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl} ethanone O-ethyl-oxime, C17H17ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of methyl N-(4-bromophenyl)carbamate, C8H8BrNO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-{4-[(2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone oxime, C15H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-butanebis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(hexafluorophosphate), C12H20F12N4P2
- (E)-N-benzylidene-3-(benzylthio)-5-p-tolyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-amine, C23H20N4S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-1-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C11H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,5-difluoro-10-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-4l4,5l4-dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine - a Z′ = 3 structure, C19H18B2F3N2
- The crystal structure of the Matrine derivative: 12-(1H-indol-1-yl)dodecahydro-1H,5H,10H-dipyrido[2,1-f:3′,2′,1′-ij][1,6]naphthyridin-10-one hydrate, C23H29N3O
- The crystal structure of tris(μ2-1,3-bis(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxido-1-(oxo)but-2-en-1-yl)phenyl-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(1,2-dimethoxyethane-κ2O,O′)dilutetium(III), C50H38F18Lu2O16
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(3-(2-(4-chlorobenzoyl)hydrazono)-2-oxoindolin-1-yl) acetic acid, C17H12ClN3O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraqua-bis(2-(((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)ammonio)acetato-κO)cobalt(II) hexahydrate, C36H48CoN2O28S2
- The crystal structure of N,N-dimethyl-2,6-di-p-tolylpyrimidin-4-amine, C20H21N3
- The crystal structure (E)-4-methyl-N′-(2-nitrobenzylidene)benzenesulfonohydrazide, C14H13N3O4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane κ2N:N′)-(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] hydrate, C26H24ZnN4O6
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(quinolin-2-ylmethylene)furan-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C15H13N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2,8-diphenyl-3,7,9-trioxa-1-azaspiro[4.5]dec-1-ene, C18H17N1O3
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxane-5,5-dicarboxylate, C16H19ClO6
- Crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole 3-oxide, C8H7N3O3
- Crystal structure of (acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(2-amino-6-chlorobenzoato-κO)-oxido(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)vanadium(IV) – trichloromethane (1/1)
- Crystal structure of (1E,4E)-1,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one, C17H12Cl2O
- The crystal structure of trans-dibromido-bis(pyridine-κN)platinum(II), C10H10Br2N2Pt
Articles in the same Issue
- Cover and Frontmatter
- Crystal structure of potassium 1-methyl-1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole-5-thiolate, C2H3N4SK
- Crystal structure of bis(3-(3-ethylureido)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-aminium) bis (μ3-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(oxidomethyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato))-(μ6-oxo)-hexakis(μ2-oxo)-hexaoxo-hexavanadium(V) – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H60Cl2N6O23V6
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-methanolato-κ3O:O:O)-bis(μ2-methanolato-κ2O:O)-dimethanol-bis{6,6′-(1,3-dihydroxyl-2-acetylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(2-chloro-4-bromophenolato)}tetramanganese(III) C40H40Br4Cl4Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dibromo-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5)tetramanganese(III), C40H40Br8Mn4O16
- Synthesis and crystal structure tetrakis(μ2-methanolato)-dimethanol-bis(μ2-2-acetyl-1,3-bis(3,5-dichloro-2-oxidophenyl)propane-1,3-bis(olato)-κ5O1,O2,O3:O3,O4,O5), tetramanganese(III), C40H40Cl8Mn4O16
- Crystal structure of bis{5-methoxy-2-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)}copper(II), C34H34CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(2-hydroxy-3-{[2-hydroxybenzylidene]amino}phenyl)ethan-1-one, C15H13NO3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′′:O′′}tricobalt(II), C44H49Cl2Co3N6O12
- Crystal structure of bis{μ2-2,4-dichloro-6-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ5O:O,N,N′,O′}dicobalt(II) acetone solvate, C43H48Br4Co2N6O9
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)-bis{μ2-4-chloro-2-(8-(4-(diethylamino)-2-oxidophenyl)-3,6-dioxa-2,7-diazaocta-1,7-dien-1-yl)phenolato-κ6O:O,N,N′,O′:O′}trizinc(II), C44H49Cl2N6O12Zn3
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(N,N′-diethylamine)-5′-methoxy -2,2′-[ethylenediyldioxybis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenolato}-bis(μ2-acetato-κ2O:O′)trizinc(II), C46H56Zn3N6O14
- Crystal structure of tris(cyano-(hydrogen tris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate))-iron(III) 4-methoxypyridinium monohydrate, C24H32BN10O2Fe
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{1-(((4-(1-(hydroxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)naphthalen-2-olato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C38H30CuN4O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-{[(E)-2-Hydroxy-1-naphthalenylmethylene] amino}phenyl)ethanone oxime, C19H16N2O2
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 2-(2-naphthalenyl)-3-nitro-2H-1-benzopyran, C38H26N2O6
- Crystal structure of 2-benzoyl-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarbonitrile, C19H14N2O2
- N′-(5-ethoxycarbonyl-3,4-dimethyl-pyrrol-2-yl-methylidene)-4-hydroxybenzohydrazide monohydrate, C17H21N3O5
- The crystal structure of carbonyl-[4-(2,4-dichlorophenylamino)pent-3-en-2-onato-κ2N,O]-(triphenylphosphine-κP)rhodium(I), RhC30H25Cl2NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-5-(diethylamino)-2-(((1,1,2-trihydroxyethyl)iminio)methyl)phenolate, C15H24N2O4
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1,4-bis((2-ethyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)(μ2-isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)cadmium(II)], C34H30N4O4Cd
- Crystal structure of 5,6-Dihydro-9,10-dimethoxybenzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-a]chinolizinium 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-7-olate - methanol - water (1/1/1), C36H33NO10
- A single crystal study on 2-(methylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid, C9H9NO3
- Crystal structure of the salt 1,1′-(ethane-1,2-diyl)bis(1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium) diperchlorate, C14H28N4(ClO4)2
- Crystal structure of 2,5-bis((E)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)cyclopentan-1-one, C21H14F6O
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-benzene-1,4-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)-(1-ethyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methylpiperazin-1-ium-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)zinc(II)] 1.25 hydrate, C25H26.5N3O8.25FZn
- Crystal structure of 1-methyl-1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-ium poly[aqua-bis(μ2-perchlorato-κ3O,O′:O′′)sodium], C7H17Cl2N2NaO9
- Crystal structure of trimethyammonium 2,6-dicarboxyisonicotinate monohydrate, C11H16N2O7
- Crystal structure of dodecaguanidinium bis(tetrapropylammonium) heptacarbonate, C43H128N38O21
- Crystal structure of poly[tetraaqua-bis(μ6-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)nickel(II)diyttrium(III)]dihydrate, C20H16NiO22Y2
- Halogen bonds and π–π interactions in the crystal structure of 1,3,5-trifluoro-2,4,6-triiodobenzene–N,N-dimethylformamide (1/1), C9H7F3I3NO
- Crystal structure of guanidinium tetraethylammonium carbonate dihydrate, C10H30N4O5
- The crystal structure of oxonium chlorido-ethylenediaminetetraactetotin(IV) hydrate, C10H17ClN2O10Sn
- Crystal structure of 8-((E)-((4-((E)-1-((benzyloxy)imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one, C26H22N2O4
- Crystal structure of bis{5-(diethylamino)-2-(((2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2O,N}copper(II), C40H38CuN4O6
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(tri(p-tolyl)phosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C29H28O5PRe
- Crystal structure of fac-(acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)tricarbonyl(benzyldiphenylphosphine-κP)rhenium(I), C27H24O5PRe
- Crystal structure of triethylammonium bis{3-(((3-oxidonaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olato-κ3O,N,O′}manganese(III), C46H38MnN3O8
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-ethyldimethylethanaminium) bis(heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II), C12H32N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of bis(4-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridine-κ2N:N′)-bis(2-(2-((2,6-difluorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetate-κO)cadmium(II), C44H34N8CdCl4O4
- Crystal structure of 4,4′-(1,4-phenylene)bis(pyridin-1-ium) catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,5-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′] dihydrate, C48H42O22N2Ca
- The crystal structure of (S)-2-benzylsuccinic acid, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ3-4-(pyridin-4-yl)isophthalato-κ4O,O′:O′′:O′′′)-(μ2-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato-κ2O:O′)yttrium(III)], C26H17N2O9Y
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C14H17N3O2
- Crystal structure of tetrakis(methanol-κO)-bis{μ2-3-((4-methoxy-2-oxidobenzylidene)amino)-2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-olate-κ4O,N;O′:O′}dizinc(II), C38H38Zn2N2O14
- Crystal structure of bromido(4,4′-dimethoxy-2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)(isopropyl(diphenyl)phosphane-κP)copper(I), C27H29BrCuN2O2P
- Crystal structure of bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane)-9,9-dioctylfluorene, C41H64B2O4
- Crystal structure of 11-oxo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H,5H,11H-pyrano[2,3-f]pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-10-carbaldehyde - a julolidine derivative, C16H15NO3
- Crystal structure of 1,3-dimethyl-5,5-dibenzylbarbituric acid, C20H20N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium) poly[bis(μ2-heptaselenido-κ2Se1,Se7)palladate(II)], C10H28N2PdSe14
- Crystal structure of 1-{4-[(5-Chloro-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl} ethanone O-ethyl-oxime, C17H17ClN2O2
- The crystal structure of methyl N-(4-bromophenyl)carbamate, C8H8BrNO2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-{4-[(2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino]phenyl}ethanone oxime, C15H14N2O2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-butanebis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium)bis(hexafluorophosphate), C12H20F12N4P2
- (E)-N-benzylidene-3-(benzylthio)-5-p-tolyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-amine, C23H20N4S
- Crystal structure of ethyl 5-methyl-1-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxylate, C11H12N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5,5-difluoro-10-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,3,7,9-tetramethyl-5H-4l4,5l4-dipyrrolo[1,2-c:2′,1′-f][1,3,2]diazaborinine - a Z′ = 3 structure, C19H18B2F3N2
- The crystal structure of the Matrine derivative: 12-(1H-indol-1-yl)dodecahydro-1H,5H,10H-dipyrido[2,1-f:3′,2′,1′-ij][1,6]naphthyridin-10-one hydrate, C23H29N3O
- The crystal structure of tris(μ2-1,3-bis(4,4,4-trifluoro-3-oxido-1-(oxo)but-2-en-1-yl)phenyl-κ4O,O′:O′′,O′′′)-bis(1,2-dimethoxyethane-κ2O,O′)dilutetium(III), C50H38F18Lu2O16
- The crystal structure of (Z)-2-(3-(2-(4-chlorobenzoyl)hydrazono)-2-oxoindolin-1-yl) acetic acid, C17H12ClN3O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of trans-tetraqua-bis(2-(((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)ammonio)acetato-κO)cobalt(II) hexahydrate, C36H48CoN2O28S2
- The crystal structure of N,N-dimethyl-2,6-di-p-tolylpyrimidin-4-amine, C20H21N3
- The crystal structure (E)-4-methyl-N′-(2-nitrobenzylidene)benzenesulfonohydrazide, C14H13N3O4S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,3-bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)propane κ2N:N′)-(μ2-5-methoxyisophthalato-κ2O:O′)zinc(II)] hydrate, C26H24ZnN4O6
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(quinolin-2-ylmethylene)furan-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C15H13N3O3
- Crystal structure of 2,8-diphenyl-3,7,9-trioxa-1-azaspiro[4.5]dec-1-ene, C18H17N1O3
- Crystal structure of diethyl 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dioxane-5,5-dicarboxylate, C16H19ClO6
- Crystal structure of 1-(carboxymethyl)-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole 3-oxide, C8H7N3O3
- Crystal structure of (acetylacetonato-κ2O,O′)-(2-amino-6-chlorobenzoato-κO)-oxido(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)vanadium(IV) – trichloromethane (1/1)
- Crystal structure of (1E,4E)-1,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one, C17H12Cl2O
- The crystal structure of trans-dibromido-bis(pyridine-κN)platinum(II), C10H10Br2N2Pt

