Abstract
KNa3Te8O18·5H2O, triclinic,
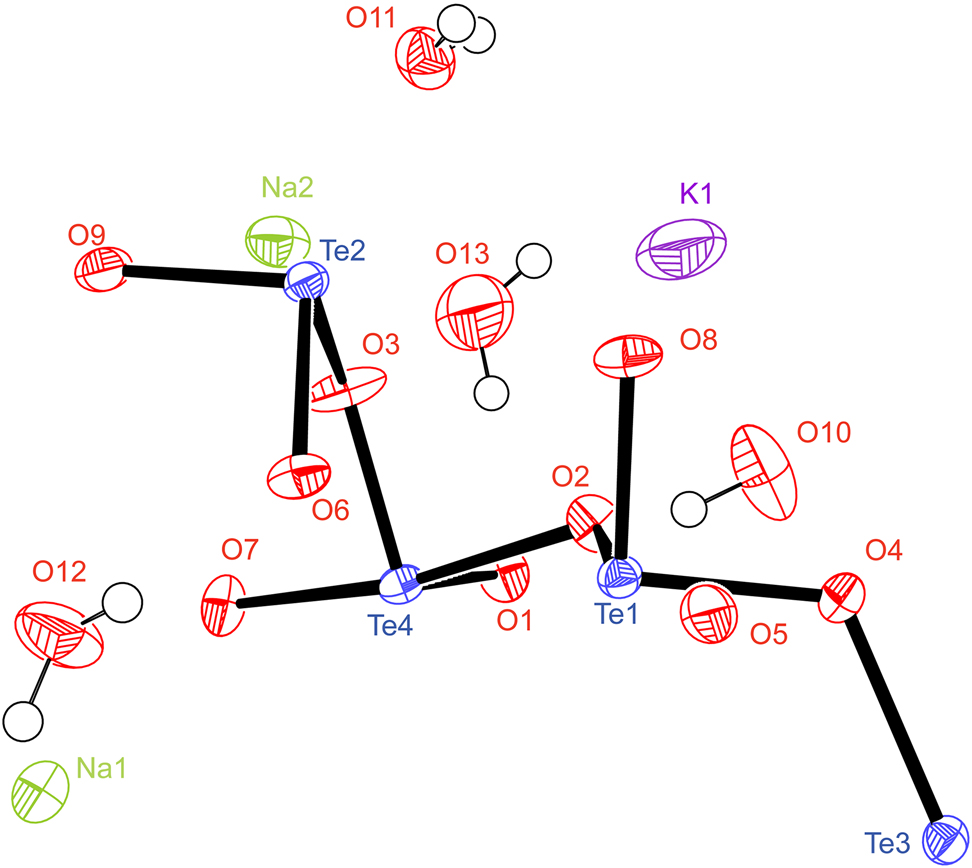
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless plate-like |
| Size: | 0.16 × 0.15 × 0.08 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 9.06 mm−1 |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 11,149, 3028, 0.021 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2970 |
| N(param)refined: | 204 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], WinGX/ORTEP [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.0718 (7) |
| Na1 | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0719 (12) |
| Na2 | 0.6282 (2) | 0.60310 (19) | 0.04273 (17) | 0.0271 (3) |
| Te1 | 0.14045 (3) | 0.15162 (2) | 0.66373 (2) | 0.01183 (6) |
| Te2 | 0.17769 (3) | 0.52011 (3) | 0.30803 (2) | 0.01277 (6) |
| Te3 | 0.17926 (3) | −0.17465 (3) | 0.97812 (2) | 0.01326 (6) |
| Te4 | 0.46186 (3) | 0.17301 (3) | 0.32481 (2) | 0.01295 (6) |
| O1 | 0.6810 (3) | 0.1596 (3) | 0.3230 (3) | 0.0196 (5) |
| O2 | 0.3696 (3) | 0.2070 (3) | 0.5341 (3) | 0.0189 (5) |
| O3 | 0.4302 (3) | 0.4056 (3) | 0.2427 (3) | 0.0255 (6) |
| O4 | 0.1931 (3) | 0.0903 (3) | 0.8377 (3) | 0.0164 (5) |
| O5 | −0.1541 (3) | 0.1123 (3) | 0.8632 (3) | 0.0194 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0960 (3) | 0.3129 (3) | 0.3831 (3) | 0.0195 (5) |
| O7 | 0.5801 (3) | 0.1798 (3) | 0.0978 (3) | 0.0196 (5) |
| O8 | 0.0787 (3) | 0.3772 (3) | 0.6528 (3) | 0.0186 (5) |
| O9 | 0.2022 (4) | 0.5754 (3) | 0.1066 (3) | 0.0247 (6) |
| O10 | 0.7538 (5) | 0.2273 (5) | 0.5285 (4) | 0.0471 (9) |
| H1 | 0.715 (6) | 0.199 (8) | 0.478 (6) | 0.071* |
| H2 | 0.859 (3) | 0.246 (8) | 0.480 (6) | 0.071* |
| O11 | 0.5128 (4) | 0.7766 (4) | 0.2051 (3) | 0.0278 (6) |
| H3 | 0.600 (3) | 0.803 (6) | 0.209 (5) | 0.042* |
| H4 | 0.423 (3) | 0.799 (6) | 0.271 (4) | 0.042* |
| O12 | 0.2025 (5) | 0.1862 (4) | 0.1443 (4) | 0.0415 (8) |
| H5 | 0.163 (7) | 0.101 (5) | 0.151 (6) | 0.062* |
| H6 | 0.149 (7) | 0.211 (7) | 0.224 (4) | 0.062* |
| O13 | 0.8193 (6) | 0.4849 (5) | 0.1685 (6) | 0.0664 (14) |
| H7 | 0.922 (4) | 0.505 (9) | 0.113 (7) | 0.100* |
| H8a | 0.786 (11) | 0.534 (16) | 0.233 (11) | 0.100* |
| H9b | 0.810 (11) | 0.381 (2) | 0.210 (16) | 0.100* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.53(3), bOccupancy: 0.47(3).
Source of material
All starting materials were from commercial sources and used without further purification. The reagents of 2 mmol NaOH, 4 mmol TeO2, 1 mmol KF, and 2 mL H2O were thoroughly mixed and sealed in a stainless autoclave with a 23 mL Teflon liner. The mixture was heated at 463 K in an oven for three days, and then cooled to room temperature at a rate of 6 K/h. Colorless plate-like crystals of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O were collected and washed with purified water.
Experimental details
The structure was solved by direct method with SHELXS and further refined with the SHELXL program. The oxygen-bound H atoms were located on a difference Fourier map and refined with distances O–H = 0.85 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O).
Comment
Metal tellurites with lone-pair electrons have received great attention owing to their structural diversity and potential applications such as in the field of piezoelectricity, pyroelectricity, and second-order nonlinear optics [4], [5], [6], [7]. Usually, the Te(IV)–O units can adopt three geometry patterns in various crystal structures: TeO3 trigonal pyramid, TeO4 sphenoid, and TeO5 distorted square pyramid. The three types of Te–O units can further build up a large number of structural motifs when connected with each other or with other atomic groups. Such examples include the recently synthesized hexamolybdotellurates A4Mo6TeO22·2H2O (A = NH4, Rb) and (NH4)2K2TeMo6O22·2H2O, which are built by the [Mo6O22]8− group with TeO4 units as connectors [8, 9]. Further rich examples are the alkali-metal tellurites, including Na2TeO3 [10], Na2Te2O5·2H2O [11], Na4Te4O10 [12], K2Te4O9·3.2H2O [13], K2Te4O9 [14]. Chen et al. discussed that the size of alkali-metal cations, H2O molecules, and the interaction between framework oxygen atoms and alkali cations can play great roles in the formation of centric-acentric structure for the alkali-metal tellurites [15]. Here we synthesized the title new double alkali-metal tellurite to provide further insight on the intrinsic mechanism of centric-acentric formation of alkali-metal tellurites.
The title compound contains the [Te4O9]2− anion layered structure that has been found in the double alkali-metal tellurite RbK3Te8O18·5H2O. However, different to the noncentrosymmetric structure of RbK3Te8O18·5H2O, substitution of Rb and K with the corresponding smaller K and Na leads to a centrosymmetric structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O [15]. There are two kinds of Te–O connection fashions, i.e., Te(1)O3 in trigonal pyramid, and Te(2)–Te(4) are in TeO4 sphenoid structures. Te(2)O4, Te(3)O4, and Te(4)O4 sphenoids are connected to each other through corner-sharing to form a [Te6O12O12/2] pentagonal ring. The Te(1)O3 trigonal pyramid connects three neighboring [Te6O12O12/2] pentagonal ring up to the [Te4O9]2− anion layer. The bond valence sums (BVS) are calculated to be 3.66, 4.02, 3.95, and 4.02 for central cations Te(1), Te(2), Te(3), and Te(4), respectively [16]. K+ and Na+ cations lie between the layers for charge balance, and the water molecules are arranged around the K+ cations to separate them with Na+ cations. The K–O distances are distributed in the range of 2.847–3.074 Å when the nearest six oxygen atoms are considered, and the BVS of the K+ cation is calculated to be 0.71, indicating that some more oxygen neighbors still contribute. Na(1) cation is coordinated by eight oxygen atoms with Na–O distances of 2.301–2.919 Å with BVS = 1.03, and Na(2) is coordinated by six oxygen atoms with Na–O distances of 2.321–2.737 Å with BVS = 1.09.
Funding source: Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation
Award Identifier / Grant number: ZR2020ME021
-
Author contributions: The author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This research was supported by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (ZR2020ME021).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The author declares no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Saint (v8.34A); Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2013.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Bergman, J. G., Boyd, G. D., Ashkin, A. New nonlinear optical materials - metal oxides with nonbonded electrons. J. Appl. Phys. 1969, 40, 2860–2863; https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1658089.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Mercurio, D., El Farissi, M., Frit, B., Goursat, P. Etude structurale et densification d’un nouveau materiau piezoelectrique: Bi2TeO5. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1983, 9, 467–476; https://doi.org/10.1016/0254-0584(83)90073-1.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Goodey, J., Broussard, J., Halasyamani, P. S. Synthesis, structure, and characterization of a new second-harmonic-generating tellurite: Na2TeW2O9. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3174–3180; https://doi.org/10.1021/cm020087i.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Ra, H. S., Ok, K. M., Halasyamani, P. S. Combining second-order Jahn–Teller distorted cations to create highly efficient SHG materials: synthesis, characterization, and NLO properties of BaTeM2O9 (M = Mo6+ or W6+). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7764–7765; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja035314b.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Vidyavathy, Vidyasagar, K. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of novel one-dimensional tellurites of molybdenum(VI), A4Mo6TeO22·2H2O (A = NH4, Rb). Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 1394–1400; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic980957r.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Geng, L., Wang, Y. Synthesis and characterization of ammonium potassium tellurium polyoxomolybdate: (NH4)2K2TeMo6O22·2H2O with one-dimensional anionic polymeric chain [TeMo6O22]4−. Crystals 2021, 11, 375; https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040375.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Masse, R., Guitel, J. C., Tordjman, I. Preparation chimioue et structure cristalline des tellurites de sodium et d’argent: Na2TeO3, Ag2TeO3. Mater. Res. Bull. 1980, 15, 431–436; https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(80)90048-3.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Daniel, F., Moret, J., Maurin, M., Philippot, E. Etude cristallographique du tellurite de sodium a deux molecules d’eau, Na2TeIV2O5·2H2O. Acta Crystallogr. 1981, B37, 1278–1281; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0567740881005657.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Tagg, S. L., Huffman, J. C., Zwanziger, J. W., Occhailini, D., Pedersen, S. U., Niinisto, L., Styring, S., Tommos, C., Warncke, K., Wood, B. R. Crystal structure of sodium ditellurite, Na4Te4O10. Acta Chem. Scand. 1997, 51, 118–121; https://doi.org/10.3891/acta.chem.scand.51-0118.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Ok, K. M., Halasyamani, P. S. New tellurites: syntheses, structures, and characterization of K2Te4O9·3.2H2O, KGaTe6O14, and KGaTe2O6·1.8H2O. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4278–4284; https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0103489.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Becker, C. R., Tagg, S. L., Huffman, J. C., Zwanziger, J. W. Crystal structures of potassium tetratellurite, K2Te4O9, and potassium ditellurite, K2Te2O5, and structural trends in solid alkali tellurites. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 5559–5564; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic970497m.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Chen, Y.-G., Yang, N., Yao, X.-N., Li, C.-B., Guo, Y., Zhang, X.-M. Synergetic influence of alkali-metal and lone-pair cations on frameworks of tellurites. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 5406–5412; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b00266.Suche in Google Scholar
16. Brese, N. E., O’Keeffe, M. Bond-valence parameters for solids. Acta Crystallogr. 1991, B47, 192–197; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768190011041.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Lei Geng, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

