Abstract
C24H18CuN12S2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 4), a = 11.038(2) Å, b = 8.9312(18) Å, c = 16.083(5) Å, β = 125.66(2)°, V = 1288.2(6) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0265, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0974, T = 293 K.
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
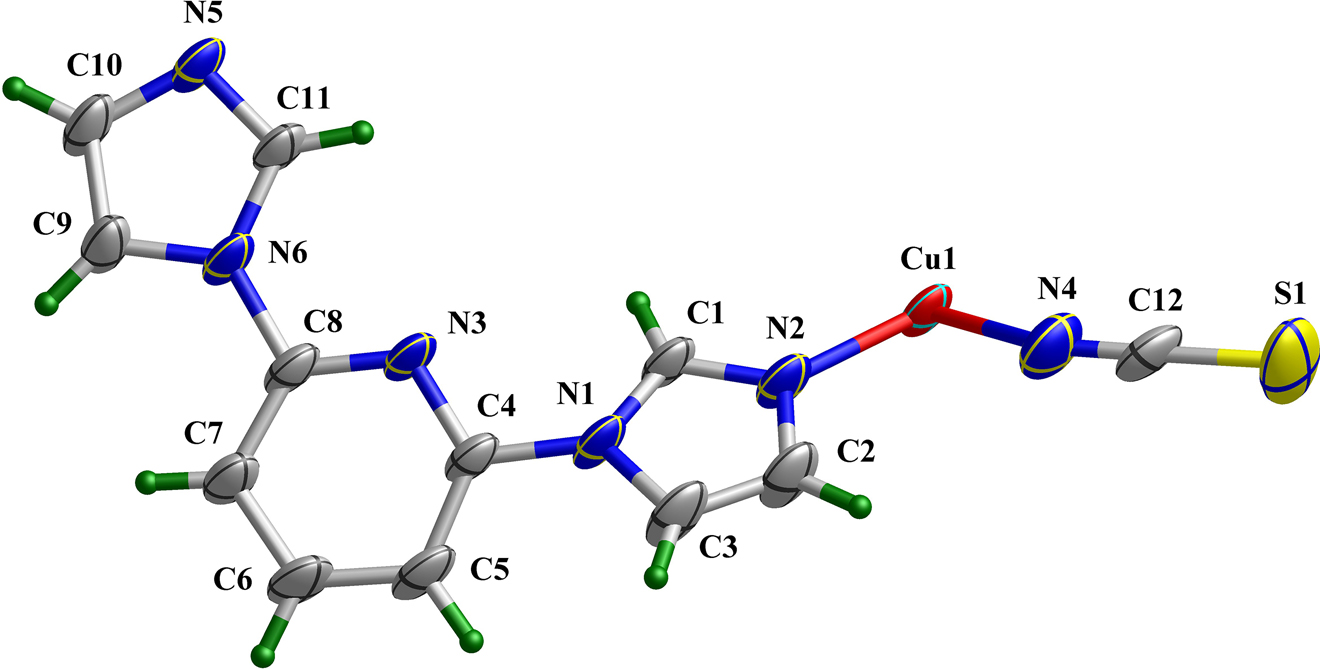
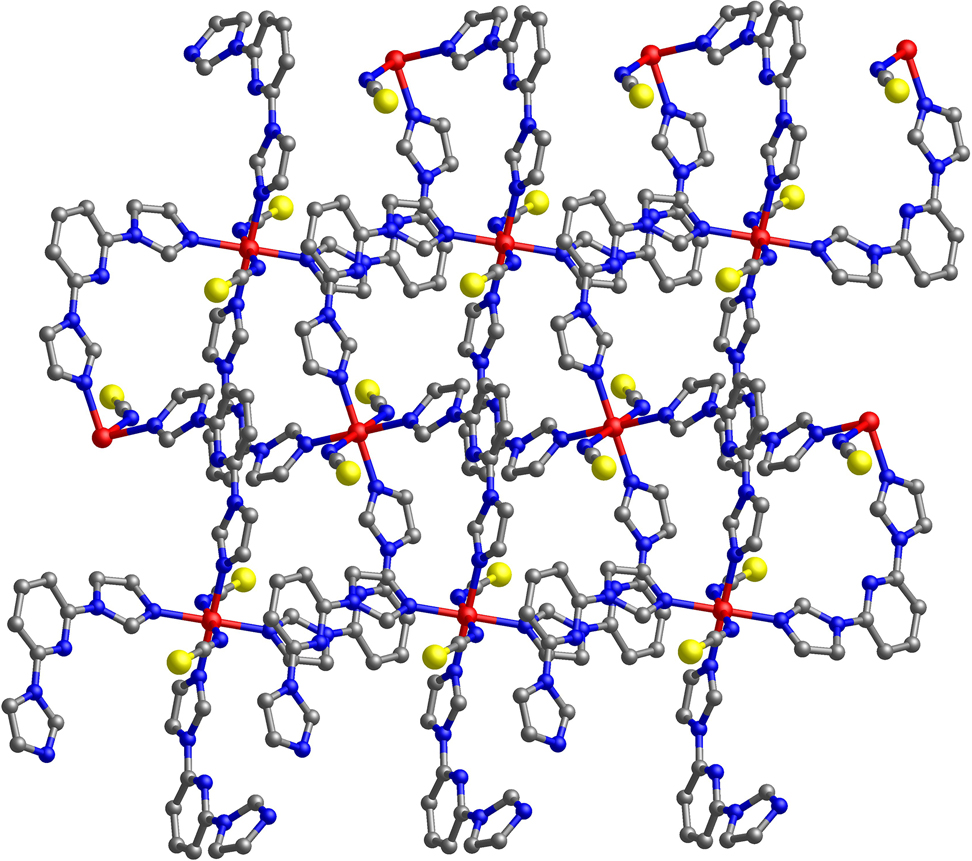
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, red |
| Size: | 0.18 × 0.15 × 0.12 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.05 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω-scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 26°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 6033, 2496, 0.027 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2082 |
| N(param)refined: | 179 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], OLEX2 [2], SHELX [3, 4], PLATON [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| x | y | z | U iso*/U eq | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.03267 (18) |
| S1 | −0.32137 (14) | −0.04437 (13) | −0.37442 (7) | 0.0776 (4) |
| N1 | 0.2056 (2) | 0.4126 (2) | 0.12582 (16) | 0.0324 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0776 (2) | 0.2157 (2) | 0.03442 (17) | 0.0361 (5) |
| N3 | 0.2557 (2) | 0.5153 (2) | 0.27563 (17) | 0.0311 (5) |
| N4 | −0.1542 (3) | 0.0728 (3) | −0.1783 (2) | 0.0544 (7) |
| N6 | 0.2931 (2) | 0.6057 (2) | 0.42386 (16) | 0.0335 (5) |
| C1 | 0.1392 (3) | 0.2831 (3) | 0.1231 (2) | 0.0329 (6) |
| H1 | 0.1375 | 0.2469 | 0.1766 | 0.039* |
| C2 | 0.1035 (3) | 0.3070 (3) | −0.0227 (2) | 0.0416 (7) |
| H2 | 0.0709 | 0.2881 | −0.0896 | 0.050* |
| C3 | 0.1829 (3) | 0.4270 (3) | 0.0325 (2) | 0.0414 (7) |
| H3 | 0.2160 | 0.5045 | 0.0118 | 0.050* |
| C4 | 0.2990 (3) | 0.5035 (3) | 0.2145 (2) | 0.0300 (6) |
| C5 | 0.4265 (3) | 0.5661 (3) | 0.2326 (2) | 0.0378 (6) |
| H5 | 0.4539 | 0.5513 | 0.1884 | 0.045* |
| N5 | 0.1602 (2) | 0.5600 (2) | 0.48272 (17) | 0.0341 (5) |
| C6 | 0.5110 (3) | 0.6518 (3) | 0.3199 (2) | 0.0436 (7) |
| H6 | 0.5972 | 0.6978 | 0.3348 | 0.052* |
| C7 | 0.4700 (3) | 0.6703 (3) | 0.3851 (2) | 0.0403 (7) |
| H7 | 0.5256 | 0.7288 | 0.4438 | 0.048* |
| C8 | 0.3416 (3) | 0.5973 (3) | 0.3591 (2) | 0.0322 (6) |
| C12 | −0.2225 (3) | 0.0252 (3) | −0.2593 (2) | 0.0395 (7) |
| C11 | 0.1728 (3) | 0.5339 (3) | 0.4079 (2) | 0.0363 (6) |
| H11 | 0.1080 | 0.4741 | 0.3514 | 0.044* |
| C9 | 0.3593 (3) | 0.6829 (3) | 0.5149 (2) | 0.0432 (7) |
| H9 | 0.4438 | 0.7430 | 0.5459 | 0.052* |
| C10 | 0.2767 (3) | 0.6533 (3) | 0.5499 (2) | 0.0416 (7) |
| H10 | 0.2956 | 0.6905 | 0.6104 | 0.050* |
Source of materials
All the reagents were commercially available and used as received without further purification. About 13.5 mg CuSCN (0.1 mmol) and 10.3 mg NH4SCN (0.1 mmol) were dissolved in DMF (3 mL) with strong stirring to obtain a colorless solution. Then, 42.2 mg 2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine (2,6-BIP) (0.2 mmol) was added to the mixture, which turns into the blue-green solution immediately. After filtration, 1 mL DMF and 5 mL acetonitrile were added to the upper layer of the filtrate as buffer solution and diffusion solution, sequentially. Green crystals were obtained after a week at room temperature in the dark with a yield of 38 mg (64% based Cu). Anal. Calcd. for C24H18CuN12S2: C, 47.87%; H, 3.01%; N, 27.91%. Found C, 48.02%; H, 3.03%; N, 27.76%. IR (KBr, ν/cm−1): 2083(s), 2054(s), 1654(m), 1605(s), 1585(m), 1491(s), 1458(s), 1319(w), 1286(w), 1233(m), 1176(w), 1061(m), 1004(w) (pyridine: C=N), 849(w), 792(m), 743(w), 653(m).
Experimentaldetails
The structure was solved by direct methods and refined using the SHELX software [3]. All of the hydrogen atoms were added using a riding model [4].
Comment
Coordination polymers (CPs) have received enormous interests because of their intriguing skeletal structures, as well as the potential applications in gas absorption [6], catalysis [7], magnetism [8, 9], photoluminescence [10], [11], [12] and so on. Consequently, considerable efforts in this field have been devoted to the design and syntheses of various kinds of CPs to obtain desirable properties [13]. To extend the types of CPs, different rigid or flexible ligands have been extensively used in the preparation of CPs [14, 15]. In recent years, many CPs based on semi-rigid ligands such as bis(imidazole) derivatives have been reported [16, 17]. From the view of structural chemistry, the hinged 2,6-BIP molecule is a typical semi-rigid ligand, in which the C–N bonds between three rings can rotate to some extent. Therefore, the introduction of 2,6-BIP ligand can affect the spatial configuration of CPs and then modify the corresponding properties.
As shown in the upper part of the figure, the asymmetric unit of the title structure consists of a half Cu(II) cation (located on a center of symmetry), one 2,6-BIP molecule and one SCN− ion. The Cu(II) center is six-coordinated by six N atoms, in which two N atoms from SCN− ions and four from 2,6-BIP ligands, forming an octahedral configuration. The Cu–N bond lengths are in the range of 2.016(2)–2.419(3) Å, while the bond angles of N–Cu–N range from 87.80(9) to 180.0°. The connection between Cu(II) ions and 2,6-BIP ligands leads to a four-membered metal ring, and these rings are further extend to a two-dimensional network, exhibiting a four-connected sql topological structure (lower part of the figure). Due to the rotability of C–N bond in 2,6-BIP ligand, the dihedral angles between the pyridine ring and two imidazole rings are 3.4° and 35.6°, respectively, which resulting in the 2D structure of title CP to be helical.
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 51602130
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 51602130).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
5. Spek, A. L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889802022112.Search in Google Scholar
6. Jiang, X., Li, Z., Zhai, Y., Yan, G., Xia, H., Li, Z. Porous coordination polymers based on azamacrocyclic complex: syntheses, solvent induced reversible crystal-to-crystal transformation and gas sorption properties. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 805–813; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ce42021c.Search in Google Scholar
7. Paul, A., Karmakar, A., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C., Pombeiro, A. J. L. 1D Zn(II) coordination polymers as effective heterogeneous catalysts in microwave-assisted single-pot deacetalization-knoevenagel tandem reactions in solvent-free conditions. Catalysts 2021, 11, 90; https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11010090.Search in Google Scholar
8. Wang, Y. F., Li, S. H., Ma, L. F., Geng, J. L., Wang, L. Y. Syntheses, crystal structures, and magnetic studies of two cobalt(II) coordination polymers based on concurrent ligand extension. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2015, 62, 42–46; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2015.10.023.Search in Google Scholar
9. Qian, J., Yoshikawa, H., Humphrey, M. G., Zhang, J. F., Awaga, K., Zhang, C. In situ formed [M(CN)9] (M = W, Mo) as a building block for the construction of two nona-cyanometalate-bridged heterometallic coordination polymers. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 4363–4372; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ce00579j.Search in Google Scholar
10. Zhang, J. F., Jia, D., Humphrey, M. G., Meng, S. C., Zaworotko, M. J., Cifuentes, M. P., Zhang, C. Ammonium-crown ether supramolecular cation-templated assembly of an unprecedented heterobicluster-metal coordination polymer with enhanced NLO properties. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3797–3800; https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc10076c.Search in Google Scholar
11. Yang, J. X., Qin, Y. Y., Ye, R. P., Zhang, X., Yao, Y. G. Employing mixed-ligand strategy to construct a series of luminescent Cd(II) compounds with structural diversities. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 8309–8320; https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ce01607c.Search in Google Scholar
12. Heine, J., Müller-Buschbaum, K. Engineering metal-based luminescence in coordination polymers and metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9232–9242; https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60232j.Search in Google Scholar
13. Leong, W. L., Vittal, J. J. One-dimensional coordination polymers: complexity and diversity in structures, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 688–764; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr100160e.Search in Google Scholar
14. Adeline, Y. R., Katharina, M. F. Coordination polymer networks with O- and N-donors: what they are, why and how they are made. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 2127–2157.10.1016/j.ccr.2006.02.013Search in Google Scholar
15. Xin, L. Y., Liu, G. Z., Li, X. L., Wang, L. Y. Structural diversity for a series of metal(II) complexes based on flexible 1,2-phenylenediacetate and dipyridyl-type coligand. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 147–157; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg200903k.Search in Google Scholar
16. Han, M. L. Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis (3-carboxy-5-methoxybenzoato-κO)-(1,2-bis(imidazol-1-yl)ethane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)], C26H28CoN4O12, [Co(C9H6O5)2(H2O)2(C8H10N4)]. Z. Kristallogr. NCS. 2019, 234, 617–618; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2018-0555.Search in Google Scholar
17. Son, S. U., Park, K. H., Kim, B. Y., Chung, Y. K. Construction of cylindrical nanotubular materials by self-assembly of Co(NCS)2 with bent-building blocks having diimidazole rings. Cryst. Growth Des. 2003, 3, 507–512; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg034010y.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Lu Li et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

