Abstract
C12H11ClN2O3S, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 4.7305(8) Å, b = 21.252(4) Å, c = 13.134(2) Å, β = 96.286(2)°, Z = 4, V = 1312.5(4) Å3, R gt (F) = 0.1002, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1118, T = 296 K.
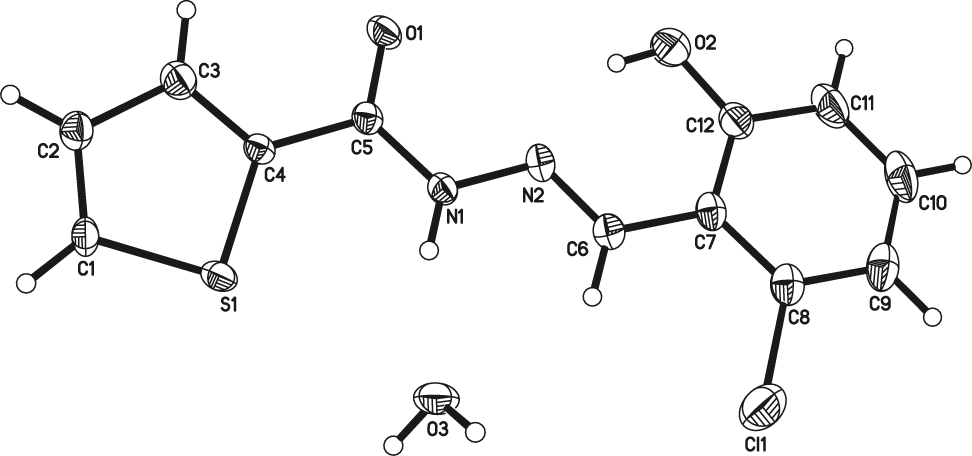
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, yellow |
| Size: | 0.23 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.46 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω-scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 26.4°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 7324, 2659, 0.041 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 1745 |
| N(param)refined: | 222 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], OLEX2 [2], SHELX [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| x | y | z | U iso*/U eq | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl1 | 0.4677 (2) | 0.41023 (5) | 0.07264 (7) | 0.0794 (3) |
| S1a | −0.5774 (5) | 0.18023 (13) | 0.17528 (12) | 0.0359 (5) |
| S1Ab | −0.5741 (13) | 0.1350 (2) | 0.3732 (5) | 0.0447 (10) |
| O1 | −0.1764 (4) | 0.23982 (9) | 0.43652 (13) | 0.0423 (5) |
| O2 | 0.3735 (5) | 0.38140 (11) | 0.45479 (15) | 0.0622 (6) |
| H2 | 0.257828 | 0.354991 | 0.431318 | 0.093* |
| N1 | −0.1034 (4) | 0.26832 (9) | 0.27581 (16) | 0.0313 (5) |
| H1 | −0.143715 | 0.262513 | 0.211040 | 0.038* |
| N2 | 0.0920 (4) | 0.31340 (9) | 0.31192 (16) | 0.0326 (5) |
| C1a | −0.8024 (13) | 0.1201 (3) | 0.2042 (5) | 0.0337 (13) |
| H1Aa | −0.930103 | 0.100100 | 0.155902 | 0.040* |
| C2a | −0.7712 (15) | 0.1056 (4) | 0.3049 (4) | 0.0366 (13) |
| H2Aa | −0.872661 | 0.074147 | 0.333992 | 0.044* |
| C3a | −0.560 (3) | 0.1452 (5) | 0.3620 (10) | 0.0389 (16) |
| H3a | −0.511765 | 0.142273 | 0.432393 | 0.047* |
| C4a | −0.442 (3) | 0.1868 (7) | 0.3015 (8) | 0.0268 (11) |
| C5 | −0.2301 (5) | 0.23355 (11) | 0.3434 (2) | 0.0284 (6) |
| C6 | 0.2079 (5) | 0.34486 (12) | 0.2449 (2) | 0.0336 (6) |
| H6 | 0.157538 | 0.336658 | 0.175699 | 0.040* |
| C7 | 0.4170 (5) | 0.39317 (11) | 0.2748 (2) | 0.0330 (6) |
| C8 | 0.5518 (6) | 0.42630 (12) | 0.2020 (2) | 0.0397 (7) |
| C9 | 0.7537 (6) | 0.47199 (13) | 0.2278 (3) | 0.0498 (8) |
| H9 | 0.842199 | 0.492646 | 0.177544 | 0.060* |
| C10 | 0.8213 (6) | 0.48633 (14) | 0.3294 (3) | 0.0602 (10) |
| H10 | 0.956530 | 0.517172 | 0.348116 | 0.072* |
| C11 | 0.6925 (7) | 0.45590 (15) | 0.4034 (3) | 0.0585 (9) |
| H11 | 0.739815 | 0.466481 | 0.471841 | 0.070* |
| C12 | 0.4919 (6) | 0.40935 (13) | 0.3775 (2) | 0.0425 (7) |
| O3 | −0.1429 (4) | 0.26026 (11) | 0.05977 (13) | 0.0520 (6) |
| H3B | −0.012476 | 0.256708 | 0.020446 | 0.078* |
| H3C | −0.296377 | 0.260587 | 0.019542 | 0.078* |
| C4Ab | −0.438 (6) | 0.1887 (12) | 0.2979 (14) | 0.031 (2) |
| C1Ab | −0.790 (3) | 0.1057 (6) | 0.2723 (8) | 0.037 (2) |
| H1AAb | −0.914296 | 0.072253 | 0.277537 | 0.044* |
| C2Ab | −0.761 (2) | 0.1356 (5) | 0.1846 (9) | 0.0316 (18) |
| H2AAb | −0.862352 | 0.126485 | 0.121661 | 0.038* |
| C3Ab | −0.559 (4) | 0.1821 (9) | 0.2017 (10) | 0.033 (2) |
| H3Ab | −0.508760 | 0.207596 | 0.149013 | 0.039* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.642 (3), bOccupancy: 0.358 (3).
Source of materials
A mixture of thiophene-2-carbohydrazide (142.2 mg, 1 mmol) and 2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzaldehyde (156.6 mg, 1 mmol) was dissolved in 20 mL ethanol. A catalytic amount of glacial acetic acid was added and used as catalyst. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 5 h, then cooled to room temperature and filtered, and then left at room temperature quietly. After a few days, light yellow block crystals were obtained.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were positioned geometrically, with C–H = 0.93 Å, N–H = 0.86 Å and O–H = 0.82–0.85 Å. The thiophene ring is disordered over two positions. The two parts were disordered over opposite direction and overlapped each other with site occupation factors of 0.642 and 0.358. The disorder is omitted in the figure for clarity.
Comment
Some thiophene-based Schiff bases have attracted attention due to their biological activities such as antioxidant, antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial activities and structural chemistry [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12]. In order to synthesize new thiophene-based Schiff bases, the title compound was synthesized and its crystal structure determined and reported here.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound consists of one formula unit (cf. the figure). The bond length between C6 and N2 is 1.277(3) Å, indicating that the reaction of Schiff base has taken place, and the C=N bond was also formed. The dihedral angle between the thiophene and benzene rings is 12.154(1)° in the major component. Due to the consequence of repulsion between the nitrogen lone pairs and the adjacent N bonds, the angle of C6=N2–N1 is 116.7(2)°. Geometric parameters are in the expected ranges [6], [7], [8], [9], [10, 13]. In the crystal packing, the molecules are linked into one-dimensional chains along the b-axis by O–H⃛O hydrogen bonds. In addition, intramolecular O–H⃛N and N–H⃛O hydrogen bonds further consolidate the crystal structure.
Funding source: Nanyang Institute of Technology
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by Nanyang Institute of Technology for financial assistances.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2008.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O.-V., Bourhis, L.-J., Gildea, R.-J., Howard, J.-A.-K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
4. Mossine, V.-V., Kelley, S.-P., Mawhinney, T.-P. Intra-molecular 1,5-S⃛N σ-hole interaction in (E)-(N)′-(pyridin-4-ylmethylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide. Acta Crystallogr. 2020, E76, 557–561; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989020003011.Search in Google Scholar
5. Cardoso, L.-N.-F., Noguiera, T.-C.-M., Kaiser, C.-R., Wardell, J.-L., Wardell, S.-M.-S.-V., de Souza, M.-V.-N. Crystal structures of 2-[5-nitrothien-2-yl)–CH=N–NR–CO(CH2)n]thiophene compounds (R = H or Me; n = 0 or 1). Z. für Kristallogr. - Cryst. Mater. 2016, 231, 167–178; https://doi.org/10.1515/zkri-2015-1902.Search in Google Scholar
6. Cardoso, L.-N.-F., Noguiera, T.-C.-M., Wardell, J.-L., Wardell, S.-M.-S.-V., de Souza, M.-V.-N., Jotanid, M.-M., Tiekinke, E.-R.-T. (N)′-[(1E)-(5–Nitrofuran-2-yl)methylidene] thiophene-2-carbohydrazide: crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis. Acta Crystallogr. 2016, E72, 1025–1031; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989016009968.Search in Google Scholar
7. Warad, I., Haddad, S.-F., Al-Noaimi, M., Hammouti, B., Hadda, T.-B. (N)′-[(E)-2-Chlorobenzylidene] thiophene-2-carbohydrazide. Acta Crystallogr. 2013, E69, o1442; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536813020850.Search in Google Scholar
8. Zhang, S.-L., Zhang, L., Wen, Q.-M., Geng, R.-X., Zhou, C.-H. N′2,N′5-Bis[(E)-2-hydroxybenzylidene]-3,4-dimethylthiophene-2,5-dicarbohydrazide. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o1752; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536812020260.Search in Google Scholar
9. Alanazi, A.-M., Lahsasni, S., El-Emam, A.-A., Ng, S.-W. N′-[(1E)-(4-Fluorophenyl)methylidene]thiophene-2-carbohydrazide. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o315; https://doi.org/10.1107/s160053681105611x.Search in Google Scholar
10. Alanazi, A.-M., Kadi, A.-A., El-Emam, A.-A., Ng, S.-W. N′-[(1E)-(4-Fluorophenyl)methylidene]thiophene-2-carbohydrazide. Acta Crystallogr. 2012, E68, o314.10.1107/S1600536811056121Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Mohan, M., Pangannaya, S., Satyanarayan, M.-N., Trivedi, D.-R. Multicoloured thiophene based AIEgens: single crystal structure elucidation, spectral behaviour and DFT studies. Chem. Sel. 2018, 3, 3803–3813; https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201800252.Search in Google Scholar
12. Boulguemh, I.-E., Beghidja, A., Khattabi, L., Long, J., Beghidja, C. Monomeric and dimeric copper (II) complexes based on bidentate N′-(propan-2-ylidene) thiophene carbohydrazide Schiff base ligand: synthesis, structure, magnetic properties, antioxidant and anti-Alzheimer activities. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2020, 507, 119519; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2020.119519.Search in Google Scholar
13. Liu, J., Hao, H., Du, C. Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-hydroxybenzohydrazide, C14H11ClN2O3. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 929.10.1515/ncrs-2021-0154Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Haiyan Yu and Meng Wang, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

