Abstract
C9H14F12N4P2, monoclinic, P21/m (no. 11), a = 5.8968(9) Å, b = 11.5554(18) Å, c = 12.994(2) Å, β = 94.577(2)°, V = 882.6(2) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0676, wR ref (F2) = 0.2020, T = 296(2) K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.17 × 0.15 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.37 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 6290, 1635, 0.028 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 1345 |
| N(param)refined: | 158 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.1006 (2) | 0.2500 | 0.61407 (10) | 0.0605 (5) |
| F1 | 0.3674 (7) | 0.2500 | 0.6214 (5) | 0.1334 (19) |
| F2 | 0.0933 (7) | 0.3455 (4) | 0.5280 (3) | 0.1516 (16) |
| F3 | −0.1652 (6) | 0.2500 | 0.5999 (4) | 0.1196 (17) |
| F4 | 0.1036 (6) | 0.1523 (4) | 0.6956 (3) | 0.1388 (14) |
| P2 | 0.1201 (2) | 0.2500 | 0.04918 (10) | 0.0589 (5) |
| F5a | −0.1333 (11) | 0.2204 (15) | 0.0491 (6) | 0.170 (7) |
| F6a | 0.050 (2) | 0.3636 (7) | 0.0950 (9) | 0.156 (4) |
| F7a | 0.3711 (10) | 0.2825 (19) | 0.0529 (6) | 0.179 (10) |
| F8a | 0.190 (3) | 0.1336 (8) | 0.0085 (11) | 0.190 (5) |
| F9a | 0.1523 (16) | 0.2038 (12) | 0.1611 (5) | 0.201 (9) |
| F10a | 0.0882 (13) | 0.2905 (13) | −0.0588 (5) | 0.179 (9) |
| N1 | 0.4653 (6) | 0.0018 (2) | 0.2353 (3) | 0.0657 (9) |
| N2 | 0.6369 (5) | 0.1470 (3) | 0.3087 (2) | 0.0572 (8) |
| C1 | 0.6139 (6) | 0.0828 (3) | 0.2237 (3) | 0.0586 (9) |
| H1 | 0.6921 | 0.0940 | 0.1651 | 0.070* |
| C2 | 0.3880 (9) | 0.0130 (4) | 0.3310 (4) | 0.0858 (14) |
| H2 | 0.2806 | −0.0340 | 0.3590 | 0.103* |
| C3 | 0.4935 (9) | 0.1032 (4) | 0.3773 (3) | 0.0825 (13) |
| H3 | 0.4739 | 0.1310 | 0.4431 | 0.099* |
| C4 | 0.7751 (9) | 0.2500 | 0.3232 (4) | 0.0679 (14) |
| H4A | 0.8911 | 0.2500 | 0.2743 | 0.081* |
| H4B | 0.8508 | 0.2500 | 0.3923 | 0.081* |
| C5 | 0.3919 (10) | −0.0859 (4) | 0.1587 (4) | 0.0988 (16) |
| H5A | 0.2809 | −0.1355 | 0.1862 | 0.148* |
| H5B | 0.3259 | −0.0487 | 0.0974 | 0.148* |
| H5C | 0.5206 | −0.1312 | 0.1421 | 0.148* |
-
aOccupancy: 0.5.
Source of material
Dibromomethane (1.74 g, 0.02 mol) and 1-methylimidazole (1.64 g, 0.02 mol) were added into a 10 mL reaction tubes of a microwave oven, and then the reaction proceeded under stirring at 70 °C for 8 min. A white solid was obtained after the reaction was completed and cooled down to room temperature; and the solid was washed with ethyl acetate and diethyl ether three times, respectively. The residual solvent was removed using a rotary evaporator and dried in vacuo at 50 °C for 30 min, and the white powder solid dimethylimidazole bromide was obtained with a yield of 76.62%. In the ion-exchanging reaction, the intermediate product (0.25 g, 0.0007 mol), potassium hexafluorophosphate (0.28 g, 0.0015 mol) and H2O (10 mL) were added to the reaction tube. Subsequently, the mixture was stirred at 85 °C for 8 min in a microwave oven; then, a colorless crystal was obtained with a yield of 43.40%.
Experimental details
All H atoms were included in calculated positions and refined as riding atoms, with C–H = 0.90–0.97 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2 Ueq(C) for all other H atoms.
Comment
Ionic liquids (ILs), as a class of organic ionic salt compounds with low melting point, are generally called room temperature ILs [5], and have the advantages of high selectivity and recyclability. After nearly 20 years of research and development, ILs have formed a wide variety and a large number of systems, which provides a good basis for the green catalytic reaction process [6], [7], [8], [9], and have been widely used Functional ILs containing hexfluorophosphate, have been widely studied due to their superior physical and chemical properties [10]. They are used in functional materials such as electric contact lubricants, gel electrolyte, and other functional materials [11, 12]. So far, most of the research work on hexafluorophosphate containing ILs has focused on monoimidazole based ILs [13]. Therefore, some diimidazole hexafluorophosphate ILs were synthesized by conventional oil bath heating in our group [14], [15], [16], [17], [18]. In order to explore a wider range of diimidazole ionic compounds and keep up with the pace of green chemistry, the synthesis of IL was carried out in microwave, and a crystalline compound was obtained in this experiment.
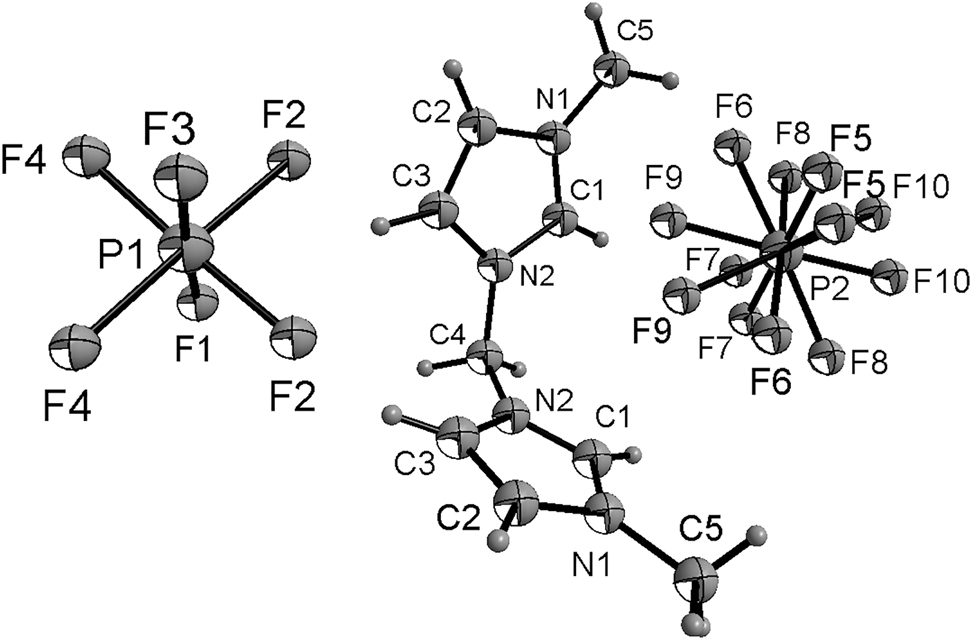
There is one half of a cation and two half anions in the asymmetric unit (shown in the figure). In the ions of the title compound bond lengths and angles are very similar to those given in the literature [18, 19]. The atoms of the imidazole ring are coplanar. The torsion angles of C3–C2–N1–C5, C2–C3–N2–C4, C3–N2–C4–N2′ are −179.5(4)°, 175.7(4)° and −75.4(4)°, respectively.
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 31760193
Funding source: Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 20202BABL205003
Award Identifier / Grant number: GJJ190181
Award Identifier / Grant number: GJJ200404
Award Identifier / Grant number: GJJ200462
Award Identifier / Grant number: S202110410095
Acknowledgments
X-ray data were collected at Instrumental Analysis Center Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang, 330063, People’s Republic of China.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31760193), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province of China (No. 20202BABL205003), the Key Research Foundation of Education Department of Jiangxi Province of China (Nos. GJJ190181, GJJ200404, GJJ200462), and National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (No. S202110410095).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Apex2, Saint and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. Diamond. Visual Crystal Structure Information System (ver. 4.0); Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Abdullayev, Y. Unveiling the catalytic effects of Brønsted acidic ionic liquid on quantitative α-glucose conversion to 5-HMF: experimental and computational studies. Renew. Energy. 2021, 171, 383–390; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.02.119.Search in Google Scholar
6. Sun, J., Wang, J. Q., Wang, L., Zhang, S. J. Green catalytic process based on ionic liquid. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 44, 100–113.10.1360/032013-275Search in Google Scholar
7. Hosseini, M. Simultaneous concentration and determination of cadmium and lead ions using in situ solvent formation microextraction method based on functionalized ionic liquid. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 76, 1189–1197; https://doi.org/10.1134/s1061934821100075.Search in Google Scholar
8. Abdelhamid, A. A., Salah, H. A., Marzouk, A. A. Synthesis of imidazole derivatives: ester and hydrazide compounds with antioxidant activity using ionic liquid as an efficient catalyst. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2020, 57, 676–685; https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.3808.Search in Google Scholar
9. Kong, J. H., Lan, Y. D., Chen, J., Huang, C. G., Xiong, W. M. Preparation and component analysis of biodiesel catalyzed by functionalized dication ionic liquid. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis. 2016, 38, 386–390.Search in Google Scholar
10. Cheng, D. H., Chen, X. W., Shu, Y., Wang, J. H. Extraction of cytochrome C with ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-trimethylsilimidazole hexafluorophosphate. Anal. Chem. 2008, 36, 1187–1190, https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-2040(08)60066-3.Search in Google Scholar
11. Li, X. X., Han, D., Lin, T. R., Cui, Y., Peng, J., Li, J. Q., Zhai, M. L. Radiation synthesis and properties of imidazolium six fluorophosphate polyionic liquid gel electrolyte. Acta Macromol. Sin. 2018, 3, 349–355.Search in Google Scholar
12. Talukdar, S., Ghosh, P. An ionic liquid as a potential multifunctional lubricating oil additive. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 36, 1920–1927.10.1080/10916466.2018.1519574Search in Google Scholar
13. Huang, T., Zhao, W., Zhang, X. H., Nie, X. L., Xiong, W. M. Synthesis and characterization of diimidazole-based hexafluorophosphate ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114465; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114465.Search in Google Scholar
14. Zhou, Y. H., Huang, T., Nie, X. L., Chen, J., Xiong, W. M. Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C16H20F12N4P2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 1217–1219.10.1515/ncrs-2020-0268Search in Google Scholar
15. Zhao, W., Liu, X. T., Wu, S. Q., Xiong, W. M., Nie, X. L. Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate), C18H24F12N4P2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 545–547; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0639.Search in Google Scholar
16. Huang, T., Chen, J. Z., Nie, X. L., Chen, J., Xiong, W. M. Crystal structure of 3,3′-(1,2-phenylene-bis(methylene))bis(1-vinyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorophosphate)(V), C18H20F12N4P2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2021, 236, 369–371.10.1515/ncrs-2020-0555Search in Google Scholar
17. Xiong, W. M., Huang, T., Liao, S., Chen, J., Nie, X. L. Crystal structure of 3-(2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)-1-vinyl-1H-imidazol-3-iumhexafluoridophosphate(V), C9H13F6N2O2P. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 1029–1031; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0147.Search in Google Scholar
18. Zhao, W., Chen, J., Xiong, W. M., Lan, Y. D., Nie, X. L. Crystal structure of 1,1′-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(3-ethyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluorido phosphate), C16H28F12N4P2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2019, 234, 609–611.10.1515/ncrs-2018-0527Search in Google Scholar
19. Peppel, T., Hinz, A., Thiele, P., Geppert-Rybczyńska, M., Lehmann, J. K., Köckerling, M. Synthesis, properties, and structures of low-melting tetraisocyanatocobaltate(II)-based ionic liquids. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 885–893; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201601250.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Zhang Huang-Xian et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

