Abstract
C19H20O8, triclinic,
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
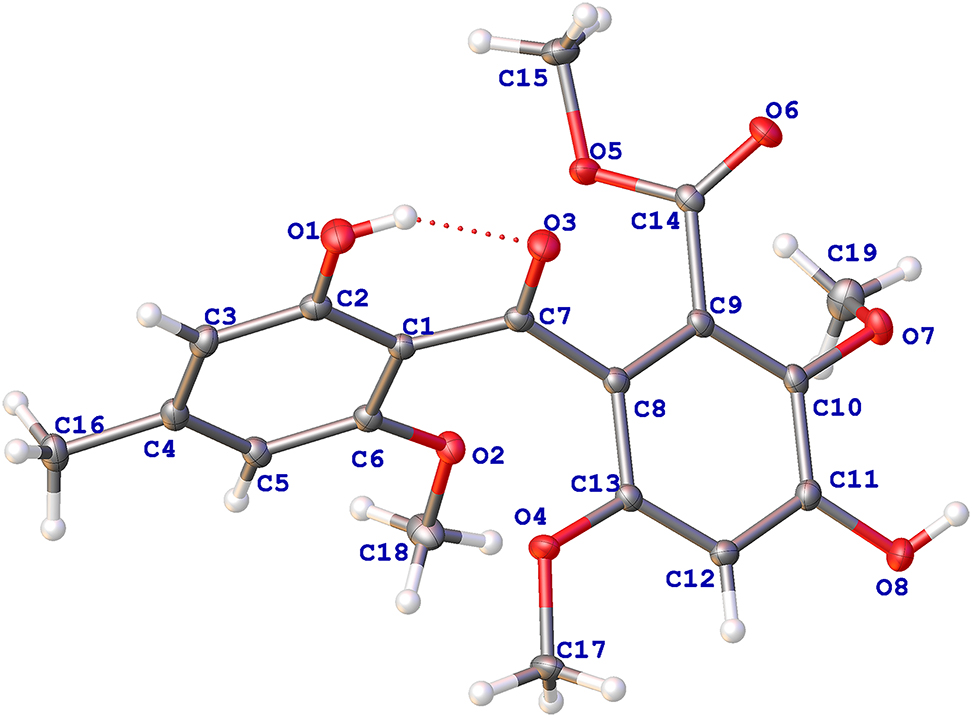
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, colourless |
| Size: | 0.14 × 0.12 × 0.1 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54184 Å) |
| μ: | 0.94 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, φ and ω-scans |
| θmax, completeness: | 74°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 5703, 3448, 0.01 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3217 |
| N(param)refined: | 252 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2, 3], OLEX2 [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.28517 (18) | 0.09974 (14) | 0.49229 (7) | 0.0306 (3) |
| H1 | 0.318511 | 0.036168 | 0.455598 | 0.046* |
| O2 | 0.38647 (16) | 0.51210 (13) | 0.25448 (6) | 0.0236 (3) |
| O3 | 0.36190 (17) | 0.02077 (13) | 0.34200 (7) | 0.0290 (3) |
| O4 | 0.02217 (15) | 0.37782 (14) | 0.25178 (6) | 0.0245 (3) |
| O5 | 0.72670 (15) | 0.10598 (13) | 0.24897 (7) | 0.0261 (3) |
| O6 | 0.74456 (17) | −0.09407 (14) | 0.16472 (7) | 0.0306 (3) |
| O7 | 0.61026 (16) | 0.11270 (14) | 0.01399 (7) | 0.0269 (3) |
| O8 | 0.25843 (18) | 0.29744 (15) | −0.03545 (7) | 0.0312 (3) |
| H8 | 0.314942 | 0.215291 | −0.059214 | 0.047* |
| C1 | 0.3272 (2) | 0.30330 (18) | 0.36853 (9) | 0.0200 (3) |
| C2 | 0.2894 (2) | 0.26020 (19) | 0.45730 (10) | 0.0227 (3) |
| C3 | 0.2498 (2) | 0.3838 (2) | 0.51176 (10) | 0.0256 (3) |
| H3 | 0.223409 | 0.353111 | 0.569684 | 0.031* |
| C4 | 0.2494 (2) | 0.5520 (2) | 0.48048 (10) | 0.0246 (3) |
| C5 | 0.2940 (2) | 0.59814 (19) | 0.39370 (10) | 0.0232 (3) |
| H5 | 0.296741 | 0.710901 | 0.372822 | 0.028* |
| C6 | 0.3340 (2) | 0.47659 (18) | 0.33881 (9) | 0.0206 (3) |
| C7 | 0.3449 (2) | 0.17365 (18) | 0.31313 (9) | 0.0202 (3) |
| C8 | 0.3325 (2) | 0.21632 (17) | 0.21981 (9) | 0.0199 (3) |
| C9 | 0.4823 (2) | 0.14568 (17) | 0.16078 (9) | 0.0206 (3) |
| C10 | 0.4630 (2) | 0.17475 (18) | 0.07444 (9) | 0.0220 (3) |
| C11 | 0.2890 (2) | 0.26826 (19) | 0.04760 (9) | 0.0231 (3) |
| C12 | 0.1398 (2) | 0.34005 (18) | 0.10547 (10) | 0.0224 (3) |
| H12 | 0.025385 | 0.404527 | 0.086877 | 0.027* |
| C13 | 0.1620 (2) | 0.31536 (18) | 0.19082 (9) | 0.0204 (3) |
| C14 | 0.6641 (2) | 0.03803 (18) | 0.19039 (9) | 0.0216 (3) |
| C15 | 0.8868 (3) | 0.0020 (2) | 0.29061 (12) | 0.0342 (4) |
| H15A | 1.004143 | −0.006154 | 0.251686 | 0.051* |
| H15B | 0.859065 | −0.109317 | 0.309234 | 0.051* |
| H15C | 0.903369 | 0.052617 | 0.338518 | 0.051* |
| C16 | 0.2051 (2) | 0.6858 (2) | 0.53927 (11) | 0.0307 (4) |
| H16A | 0.324327 | 0.701926 | 0.555742 | 0.046* |
| H16B | 0.122181 | 0.650514 | 0.588638 | 0.046* |
| H16C | 0.140345 | 0.790551 | 0.510958 | 0.046* |
| C17 | −0.1453 (2) | 0.4931 (2) | 0.22468 (11) | 0.0306 (4) |
| H17A | −0.105157 | 0.586860 | 0.187517 | 0.046* |
| H17B | −0.227882 | 0.534055 | 0.273037 | 0.046* |
| H17C | −0.215548 | 0.435839 | 0.195236 | 0.046* |
| C18 | 0.3681 (3) | 0.6854 (2) | 0.21888 (11) | 0.0337 (4) |
| H18A | 0.414300 | 0.691825 | 0.159579 | 0.051* |
| H18B | 0.443894 | 0.740677 | 0.246618 | 0.051* |
| H18C | 0.233743 | 0.740409 | 0.226462 | 0.051* |
| C19 | 0.7703 (3) | 0.2003 (2) | −0.00111 (11) | 0.0356 (4) |
| H19A | 0.861445 | 0.157026 | −0.046706 | 0.053* |
| H19B | 0.833769 | 0.183181 | 0.049097 | 0.053* |
| H19C | 0.723024 | 0.319289 | −0.015850 | 0.053* |
Source of materials
Light yellow crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation in the methanol and dichloromethane solution in a ratio of 1:2 at 4 °C.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined using a riding model with the relative isotropic parameters.
Comment
Strain Aspergillus fumigatus was collected from Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan province, China, and identified by 18S RNA gene sequence. The specimen was stored at Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, P. R. China. The stored strain was cultured and fermented on rice medium (sea salt 2 g/L, rice 350 g/L) at 28 °C for 30 days [5]. The fermentation was soaked in an equal volume of methanol. After being concentrated with a rotary evaporator, it was extracted with ethyl acetate. The ethyl acetate extract was repeatedly washed with methanol after drying. Methanol insoluble and methanol soluble portions were obtained afterwards. The methanol-insoluble substance was then identified as trypacidin. Trypacidin was added with 2 mL sodium hydroxide methanol solution (1 mol/L), stirred and reacted for 12 h at room temperature. The reaction was ended by adding formic acid to adjust pH value to neutrality, and then the products were further isolated and purified by silica gel chromatography using a solvent system of 2:1 CH2Cl2/MeOH to afford the title compound. Its crystals were obtained by being dissolved in mixed solvent of CH2Cl2/MeOH(2/1, v/v) and slowly evaporated at 4 °C.
The structure was clarified by comprehensive analysis of spectral data and confirmed by X-ray crystallography. Geometric parameters are all in the expected ranges. The title compound was named as asperfumin. Liu et al. [6] first purified, identified, and enumerated the 1H NMR and 13C NMR data of asperfumin with a benzophenone structure. Asperfumin is NRPS gene clusters dependent [7] and could inhibit the secretion of IL-6 and decrease collagen IV and fibronectin production at 10 μM in mesangial cells treated with high glucose. Moreover, it didn't exhibit cytotoxicity against mesangial cells at 10 μM using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazoliumbromide (MTT) assay [8].
Funding source: Guangzhou Education Bureau Yangcheng Scholars Project
Award Identifier / Grant number: 202032774
Funding source: Scientific Research Foundation of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Health and Family Planning Bureau
Award Identifier / Grant number: GM2019020026
Funding source: National Students Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Award Identifier / Grant number: 202010570028
Funding source: Special Funds for Undergraduates’ Scientific and Technological Innovation Training Programs in Guangdong
Award Identifier / Grant number: pdjh2021b0417
Award Identifier / Grant number: pdjh2020b0487
Award Identifier / Grant number: S201910570075
Award Identifier / Grant number: S201910570069
Funding source: Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship in GZHMU
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2020A068
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019A076
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2018A107
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2018A103
Funding source: High-level University Construction Fund of Guangdong Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 06-410-2107242
Award Identifier / Grant number: 06-410-2107249
Award Identifier / Grant number: 06-410-2107273
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by Guangzhou Education Bureau Yangcheng Scholars Project (202032774), Scientific Research Foundation of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Health and Family Planning Bureau from Guangming District (GM2019020026), National Students Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (202010570028), Special Funds for Undergraduates’ Scientific and Technological Innovation Training Programs in Guangdong (pdjh2021b0417, pdjh2020b0487, S201910570075, S201910570069), Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship in GZHMU (2020A068, 2019A076, 2018A107, 2018A103), and High-level University Construction Fund of Guangdong Province (06-410-2107242, 06-410-2107249, 06-410-2107273).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Oxford Diffraction Ltd. CrysAlisPRO: Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England, 2006.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT - integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Zhang, J. Y., Lai, Z. Z., Huang, W. J., Ling, H. P., Lin, M. T., Tang, S. L., Liu, Y., Tao, Y. W. Apicidin inhibited proliferation and invasion and induced apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway in non-small cell lung cancer GLC-82 cells. Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1374–1382; https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520617666170419120044.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Liu, J. Y., Song, Y. C., Zhang, Z., Wang, L., Guo, Z. J., Zou, W. X., Tan, R. X. Aspergillus fumigatus CY018, an endophytic fungus in Cynodon dactylon as a versatile producer of new and bioactive metabolites. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 114, 279–287; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.07.008.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Frisvad, J. C., Rank, C., Nielsen, K. F., Larsen, T. O. Metabolomics of Aspergillus fumigatus. Med. Mycol. J. 2009, 47, S53–S71; https://doi.org/10.1080/13693780802307720.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Yang, Y., Yan, Y. M., Wei, W., Luo, J., Zhang, L. S., Zhou, X. J., Wang, P. C., Yang, Y. X., Cheng, Y. X. Anthraquinone derivatives from Rumex plants and endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus and their effects on diabetic nephropathy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3905–3909; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.04.059.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Bao-Long Lai et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

