Abstract
To evaluate the safety of stent malapposition of corrodible nitride iron stent as biodegradable cardiovascular implants, a total of 108 stents were implanted into the abdominal aortas, iliac arteries, and iliac artery bifurcations of 36 New Zealand white rabbits separately. Each rabbit was implanted with three stents. After a follow-up period of 3 months, no thrombus and embolism were found in local and downstream vessels. And no other adverse events occurred either. Stent strut covered by endothelial layer started to show signs of degradation, while struts exposed to bifurcated blood flow covered by a layer of tissue and no rust particle was found on the surface. Also, there were no traces of thrombosis and traces of excess inflammation. The authors conclude that the risk brought by stent malapposition in less than 9 months is acceptable.
1 Introduction
Coronary stent implantation is the most common and effective treatment means for coronary artery disease, which works by opening the narrowed arteries thus improving blood flow [1,2,3]. Coronary stents have undergone enormous development since their first introduction in 1987 [4]. Bio-absorbable coronary stents have been widely acknowledged to be the 4th revolution in vascular intervention, following Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angiography, Bare Metal Stent, and Drug-Eluting Stent (DES), getting over the adverse event of late stent thrombosis occurred in the third generation DES, providing mechanical support and anti-restenosis properties in short term and then metabolized physiologically, thus avoiding the permanent metallic enclosing of the treated coronary artery. Therefore, bio-absorbable coronary stents have extensive research significance.
Iron-based stents are a promising candidate for bio-absorbable stents, due to their good biocompatibility and outstanding mechanical performances like 316L stainless steel [5,6,7,8,9,10]. According to reported studies [8,9,10], it has been demonstrated that safety of iron stents implantation without the significant obstruction of the stented vessel as a result of inflammation, thrombotic events, or neointimal proliferation, but a faster degradation rate is demanded theoretically; an ideal bio-absorbable iron stent should provide enough support to ensure that preventing vascular retraction in the initial stage after implantation, after 3–6 months of action, most of the loss of support caused by the corrosion process is beneficial to tissue regeneration. However, some studies demonstrated that the corrosion rate of the pure iron stents was slower than required. For the past few years, further researches focused on modifying the composition, surface, and microstructure of pure iron stents to increase their corrosion rate [11,12,13,14]. Here vacuum plasma nitriding was employed to enhance its strength and corrosion rate by incorporating nitrogen into the iron matrix to form dispersive iron nitride precipitation phase [9,15]. But along with the increase of corrosion rate of the iron stent, the release of iron ions will also increase during the short term after implantation, especially the stage when the struts were not completely covered by endothelium cells. And too much iron in the body is at risk [16,17]. Some studies show that iron overload has a direct relationship with heart and liver disease, diabetes, and other relevant diseases [18,19]. Conversely, after the stent strut was completely covered by endothelium cells, the human body has a series of iron control mechanisms (an iron regulation mechanism) to control the systematic or local iron overload risk [20]. Hence, it is very necessary to evaluate the iron overload risk in the short term after the implantation of the nitrided iron stent.
Another safety concern about bio-corrodible stent is late thrombogenicity or embolism of corrosion products when exposed to blood flow for a long time, probably occurs in stent malapposition, which has not been reported yet. The stent malapposition is usually caused by inadequate expansion or plaque existed at the vascular wall [21]. And this phenomenon will eventually cause delayed endothelialization, stent thrombosis complications, and other diseases [22,23,24,25]. In vitro studies cannot fully simulate the real physical and chemical environment in vivo. Therefore, appropriate animal models are necessary to further study the implantation of bio-corrosive and degradable iron nitride stents.
Given these considerations, this study adopted implanting the bio-absorbable stent in the iliac artery bifurcation position of the New Zealand rabbit, to simulate the stent implantation state in a vessel. And through monitoring the thrombus and embolism of supported vessels and downstream vessels, the topography of nitrided iron stent after implantation for 1, 3, and 9 months separately, the corrosion rate and the late risk brought by the implanted stents were evaluated.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Stents
The degradable stents, with a pattern similar to a commercially available permanent coronary stent of a nominal inflated outer diameter of 3.0 mm and a nominal length of 18 mm, were laser cut from iron tubes (>99.8% iron, made by Biotyx Medical (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd). Vacuum plasma nitriding technique is added into the manufacturing process after laser cutting using a self-designed vacuum nitriding furnace. Vacuum plasma nitriding in an engineering field is originally a surface modification technology. However, when applied to small coronary stents, it becomes a bulk alloying method since the original strut thickness is 100 µm or less. As a result of dispersion strengthening and solution strengthening, the hardness, radial strength, and stiffness of the nitrided iron stent were significantly increased. After the treating process of vacuum nitriding, the nitrided iron stents were polished to achieve a strut thickness of 70 ± 5 µm. The stent weighs 10–15 mg. The stents were sterilized with ethylene oxide and stored in vacuumed packages before implantation operation.
2.2 Animals
The study was conducted with the approval of the local governmental authorities and adhered to the Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH publication 85–23, 1985). Thirty six adult New Zealand white rabbits (mean weight 2.2 kg, range 2.0–2.5 kg) were purchased from Guangdong province medical animal test center (China).
2.3 Procedure
Anesthesia was induced by pentobarbitone (30 mg/kg) intravenously. Antibiotic prophylaxis was administered intramuscularly. The right carotid artery was surgically exposed and a 5 French sheath was introduced over a 0.018-inch guidewire after being immersed in the heparinized saline for 0.5 h. Quantitative angiography of the descending aorta was performed to determine the luminal diameter of the descending aorta at the site of the implantation (5 French Berman angiography catheter, Arrow, Reading, Pennsylvania, USA). Balloon catheters with a diameter of 3 mm (Savy, Cordis, Miami, Florida, USA) were chosen to achieve a balloon to vessel ratio of about 1.2 ± 0.1. The degradable iron stent was manually crimped to the balloon catheter. Under fluoroscopic control, the stent was introduced and positioned at the predetermined implantation site. The stents were implanted with 8 atm for 10 s. After removal of the catheter and sheath, the carotid artery was ligated and the incision of the skin was closed with sutures. The animals were returned to the recovery area. Figure 1 shows the implantation position of a testing rabbit sacrificed after 3 months of implantation.
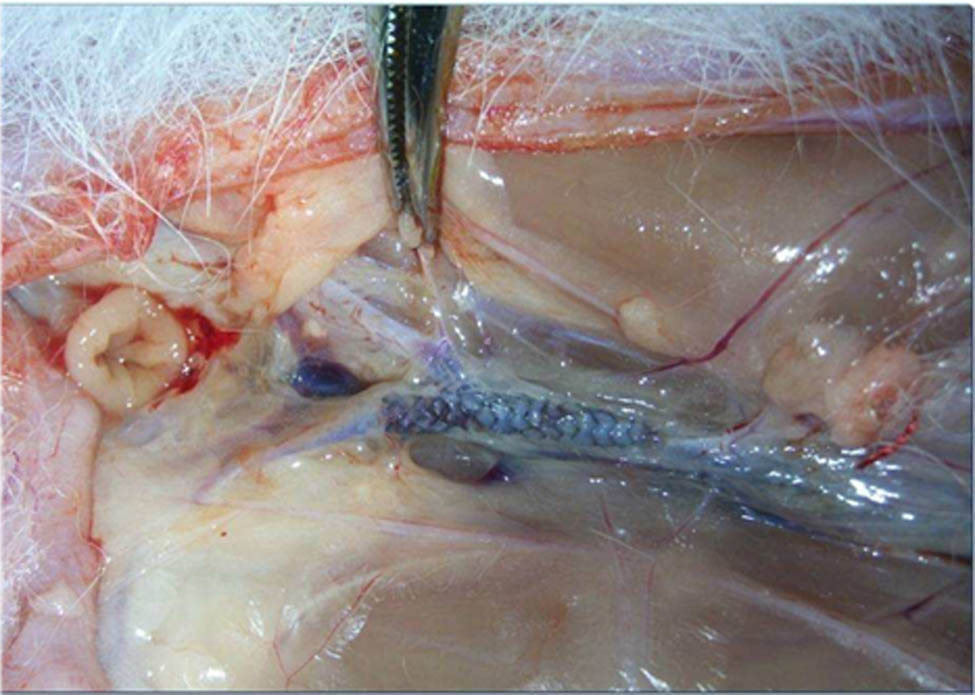
The implantation position of nitrided iron stent in a rabbit.
2.4 Follow-up study
All animals were followed up and results were documented throughout the study. Vessel morphology was observed after 1 month (n = 15), 3 months (n = 15), and 9 months (n = 6).
2.5 Morphological investigation
After angiography for the downstream vessels (using an x-ray machine with the assistant of diatrizoate), 1,000 U of heparin were injected into the rabbits, and then the animals were sacrificed by an intravenous injection of a lethal dose of pentobarbital. Immediately after death, the infra diaphragmatic descending aorta was exposed and the stented segment with stents was identified and harvested. The segments were placed in 3.5% neutral buffered formalin and kept for histopathological investigation. The stents were cut longitudinally and the lumen of the stented vessel was evaluated for signs of adherent thrombi or overt neointimal obstruction of the vessel. One specimen of each study group was viewed under a scanning electron microscope after critical point drying and gold sputtering to assess the endothelialization of the stent struts.
3 Results
The SEM and EDS of the nitride iron material surface were shown in Figure S1 (Supporting Information). After nitride, the atom ratio of Nitrogen is about 5.27%, with a weight percent of 1.37%. The degradable iron stents were implanted in the predetermined segment of the iliac arteries in 36 rabbits without major complications. No abnormalities on macroscopic inspection of the implantation site were observed. During the 3 months of the follow-up period, no cases of animal death or other obvious symptoms of pathological changes occurred. After the animals were put to dissection, no thrombosis or angiemphraxis is observed in the downstream vessels. The segment of the iliac arteries was separated and cut down for the next study of degradation. There was also no blockage or thrombosis observed at the implant position. Figure 2 shows the rabbit iliac arteries with degradable iron stent after 1 month of implantation. As seen from Figure 2a, the strut in the orifice of vascular branch position was not covered by endothelial cells, and the other struts contacted with the vascular wall were covered by endothelial cells completely. In addition, the nitrided iron stent was corroded and there was no obvious corrosion product formed on the surface of the strut. Compared with the strut contacted with the vascular wall (position C in Figure 2b) and the transitional strut (incompletely covered by endothelial cells, position A in Figure 2b), the strut in the branch position is relatively smooth. In other words, the corrosion level in position B is relatively slight. SEM image gives information that the strut in the vascular branch position is covered by a layer of uniform complete fibrous tissue membrane, which effectively prevented the direct contact between the strut and the blood flow. In short, it increased safety when there was a stent malapposition state occurred.
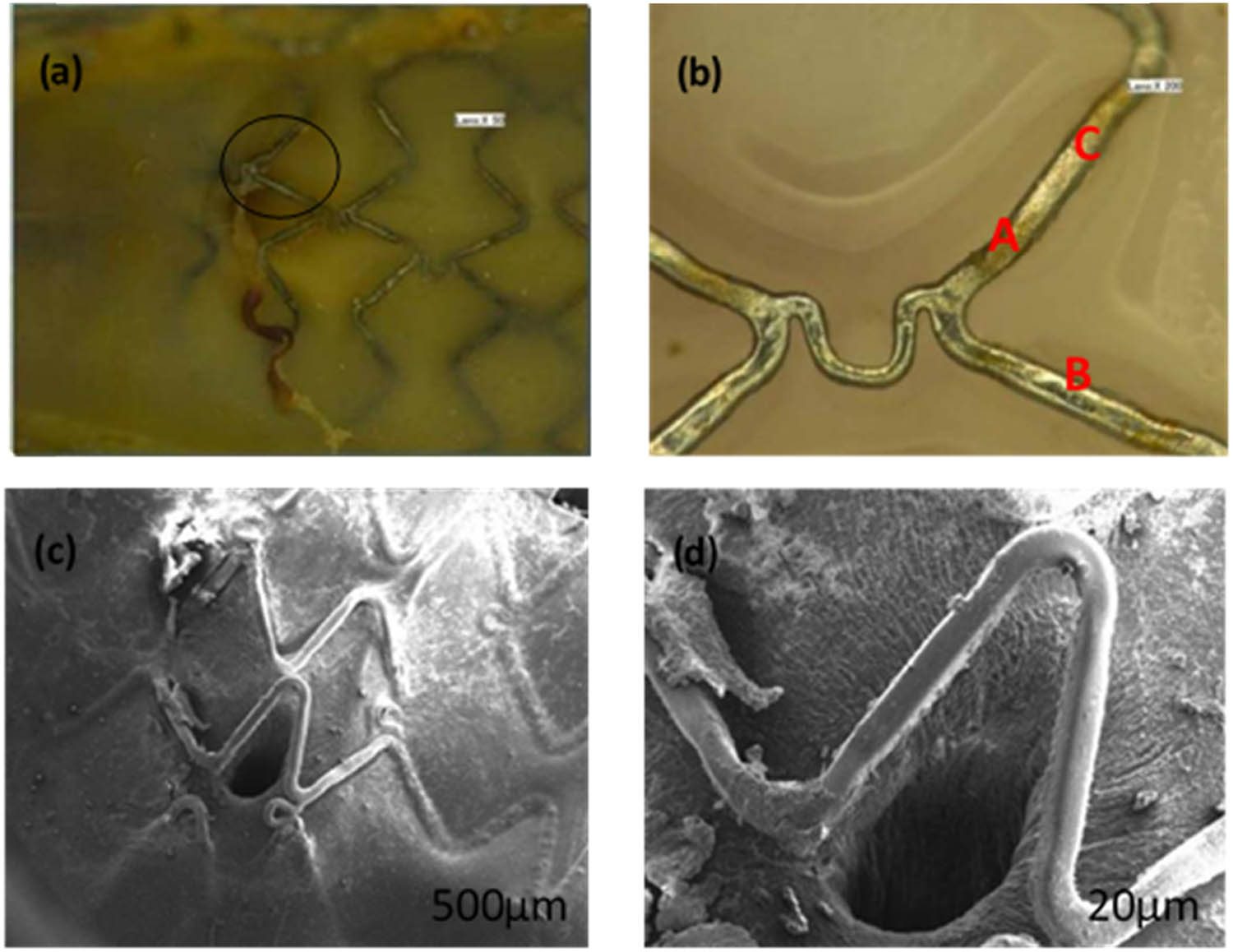
Rabbit iliac aorta with degradable iron stent after 1-month implantation. (b) is the scale-up diagram in (a); (d) is the scale-up diagram in (c).
Figure 3 shows rabbit iliac artery with degradable iron stent after 3 months implantation. As seen from Figure 3, the corrosion level increased compared with the case of 1 month. Iron transportation was observed from the implantation site towards the reticuloendothelial system after 1 month, and the level became more serious after 3 months. There are obvious black corrosion products stacked on the surface of the struts which are located at the transitional position. However, the strut which is located at the vascular branch position is still shining. No corrosion products could be detected on the strut surface. Figure 3c and d show the SEM images of rabbit iliac artery with degradable iron stent after 3 months of implantation. We can see that the fiber tissue membranes covered on the strut located at the branch position became thicker than the ones after 1 month of implantation. The thickness of the fiber tissue membrane is about several microns. The fiber tissue membrane shown in Figure 3d is deliberately broken for the aim of evaluating the thickness change.
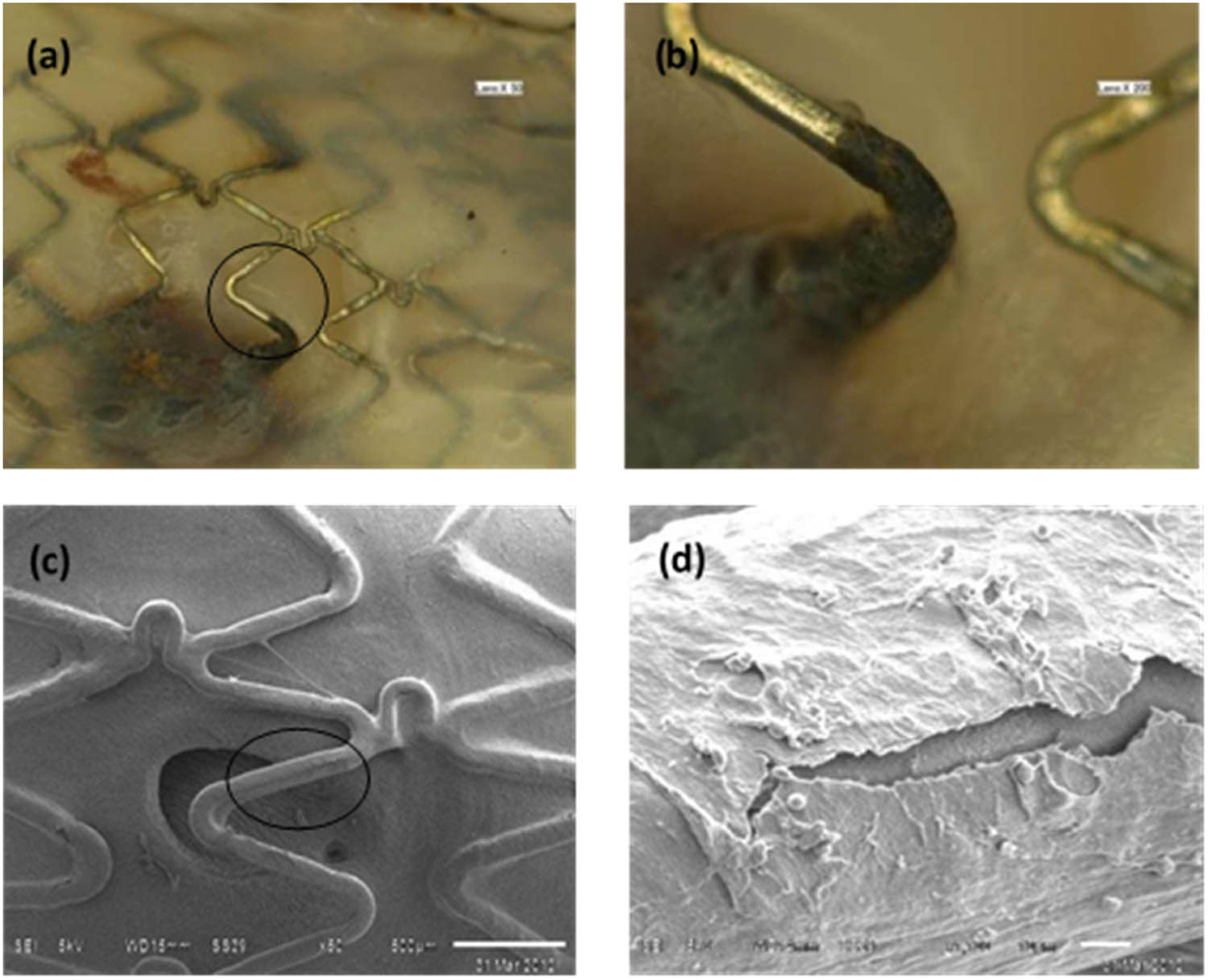
Rabbit iliac artery with degradable iron stent after 3 months implantation. (b) is the scale-up diagram in (a); (d) is the scale-up diagram in (c).
Figure 4 shows the strut located at the vascular branch position with a degradable iron stent after 9 months of implantation. As shown, the surface of the strut is relatively smooth, and also no obvious corrosion product was found. To evaluate the risk of thrombosis brought by the stent malposition, the rabbits’ lower limbs vessels’ X-ray morphology was performed before the rabbit was sacrificed at 3 and 9 months separately (Figure 5). As seen, there were no obstacles found and there was no abnormal blood flow of the downstream vessels.
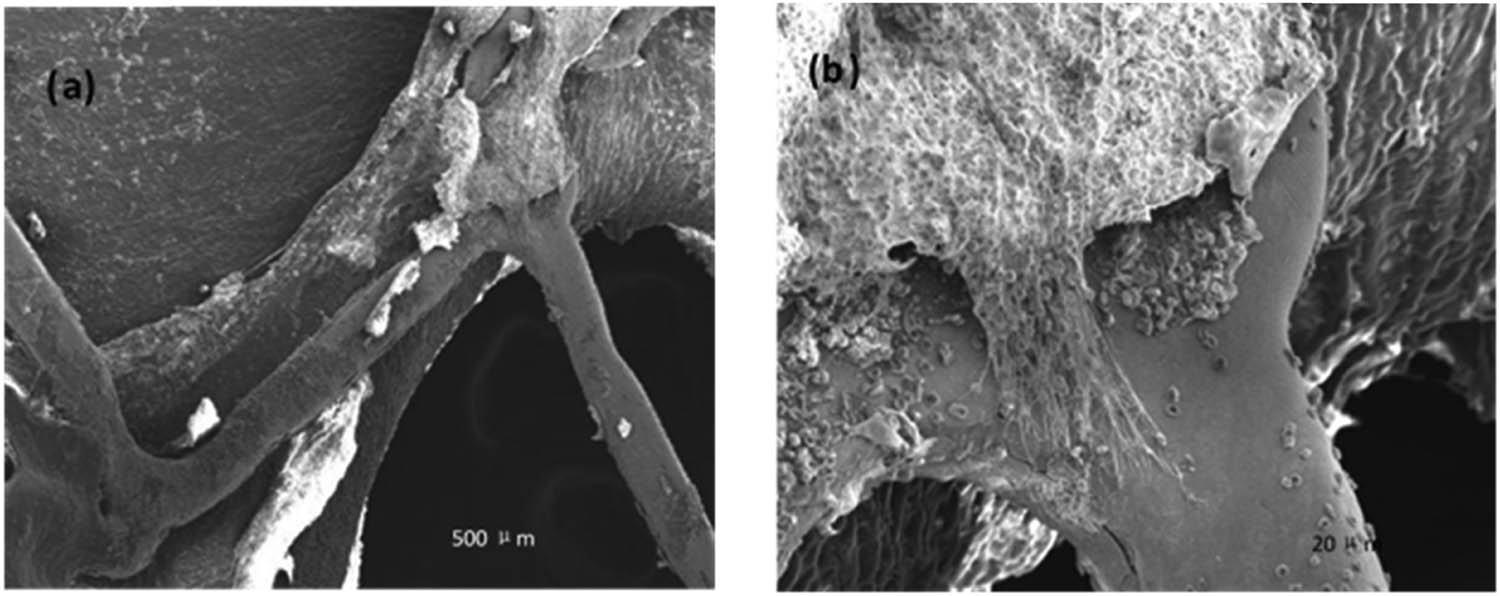
Rabbit iliac artery with degradable iron stent after 9 months implantation. (b) is the scale-up diagram in (a).
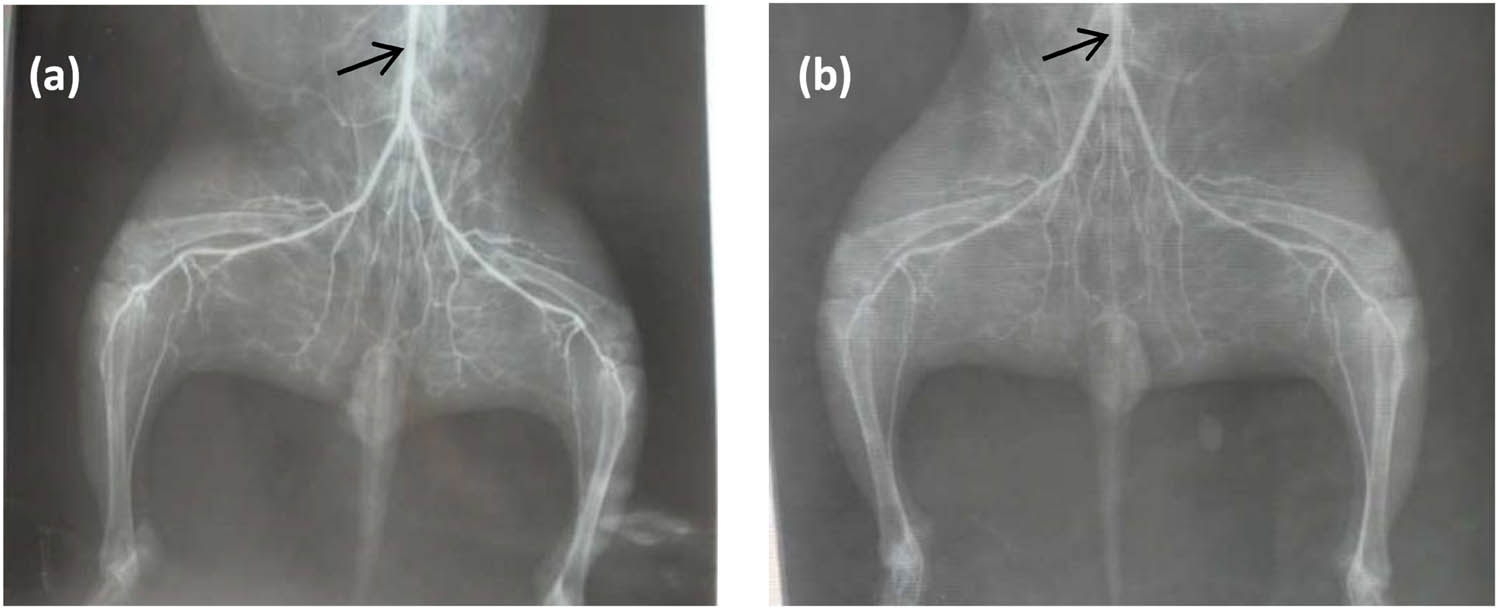
Rabbits’ downstream vessels’ X-ray morphology with a degradable iron stent at the iliac artery position: (a) 3 months after implantation; (b) 9 months after implantation, arrow position stand for the position of the implanted stent.
4 Discussions
Stent malapposition refers to improper contact between the struts and vascular walls [26]. And it includes two kinds: early acute and late chronic malapposition [27]. Early acute stent malapposition cases are mainly caused by the inexperienced operation, partially caused by some vascular diseases like calcified lesions [28]. Late stent malapposition is caused by the positive reconstruction of vessels or by the chronic rebound of the stent. Research has shown that late stent malapposition may lead to the formation of stent thrombosis [29,30]. Once the iron stent was implanted, it corrodes gradually; when there the stent malapposition happens, the struts’ endothelialization process would be delayed. At the same time, the corroded strut may produce degradation product particles. And the particles may flow away and even enter into the downstream small vessels. This hazard could cause complications like thrombosis and obstruction. However, the follow-up animal study of 1 and 3 months found that there are no attached degradation products found on the surface of the strut which is located at the vascular branch position. In addition, there was a layer of fiber tissue membranes covered on the strut. This kind of fiber layer tissue membrane isolated the stent strut and the flowing blood [31]. The strut at the branch position remained shining for 3 months. Corrosion mechanism is a major difference between the degradation iron metal stent and the permanent stent, thus the extensive research attention in the degradation vascular stent area [32,33,34,35]. The degradation process of the nitrided iron stent in vivo could be explained as follows: First, the iron was oxidized to metal ions following equation (1). The electrons from the anodic reaction were consumed by a corresponding cathodic reaction and the reduction of oxygen dissolved in water, following equation (2). These reactions occurred randomly over the entire surface where a difference existed, at grain boundaries or the interface between different phases [36].
Anodic reaction:
Cathodic reaction:
Then, the released metal ions reacted with the hydroxyl ion (OH−) released from the cathodic reaction to form insoluble hydroxides (hydrous metal oxides) according to equations (3) and (4).
However, the corrosion conditions are differences between the strut at the branch position and the position adjacent to the vascular wall. As for the strut at the branch position, the membrane covered on the strut is thinner; the iron ion released from the strut is easy to pass through the membrane and taken away by the blood flow. So, there was no corrosion product stacked on the surface of strut. Conversely, as for the strut at the position adjacent to vascular wall, 3 months after implantation it was revealed that it was covered by a relatively thicker and denser layer mainly composed of endothelium. Hence, the iron ion released from the strut is hard to pass through and chemical reactions (3) and (4) occurred. To some extent, this could explain the result we see from Figure 3. To further distinguish the difference of degradation conditions, SEM analysis was performed to the surface topography of strut at different implant positions after cleaning the corrosion product. As seen in Figure 6, the corrosion depth of the strut adjacent to the vascular wall is slightly deeper than the one at the branch position (6 months after implantation). The corrosion extent of the strut at the transitional position looks more serious (Figure 3b). This phenomenon may cause by the difference in oxygen diffusion rate. In another word, the oxygen concentration of the tissue fluid around the strut at the two positions is different. In addition, the difference in biochemical environment between the two positions also (galvanic corrosion) accelerated the corrosion rate at the transitional position [37].
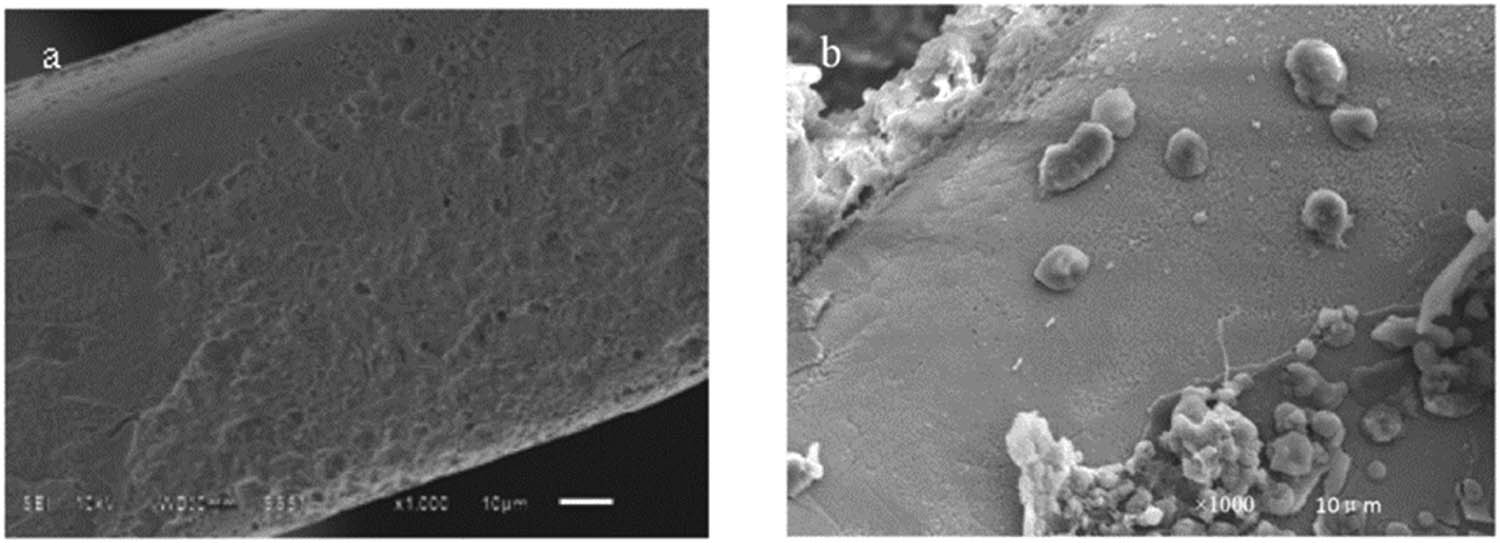
Surface topography of the strut after cleaning the corrosion products ((a) at the position adjacent to the vascular wall and (b) at the vascular branch position).
Figure 7 shows the corrosion speed between different existed states of an iron element. In a real degradation situation in vivo environment, corrosion products are always produced on the surface of an iron stent. The amount of rust is determined by the difference between V1 and V2, while V3 is not so important as V1 and V2 since rust will stay much longer than intact iron during the lifespan of the iron stent. And the final degradation time of the stent is mainly determined by V2 since V2 is much lower than V1. V2 becomes a bottleneck procedure in all degradation activities of the iron stent. The exception occurred before the iron stent is covered by tissue when the bloodstream flows on the surface of the iron stent, which will expedite the V2 extremely to the level faster than V1. So the struts of the stent at the branch position keep free rust on.
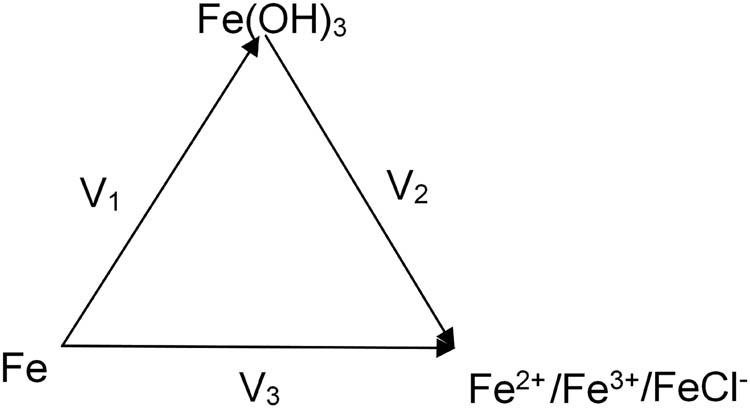
The sketch map of corrosion speed between the different states of an iron element.
Currently adopted in vivo experiments are using bare nitride iron stents, without being coated with drug-eluting coatings. After being covered with coatings, the corrosion rate should be slower, especially at the initial contacting stage, which ultimately causes less corrosion products accumulation and thus lead to a safe performance at the implantable site. However, the endothelialization process might be affected by the released anti-hyperplasia drugs, as drug-releasing would possibly cause delayed healing of endothelium cell layer [38,39,40,41]. Future study will focus on this consideration. Overall, the data presented in this work properly supported the safety of the malapposition of the bio-corrodible nitrided iron stent.
5 Conclusion
After 3 months of implantation of the nitrided iron stents, no thromboembolic complications and no adverse events occurred; iron stent strut covered by endothelial layer started to show signs of degradation without evidence of stent particle embolization, thrombosis traces, and traces of excess inflammation. This animal study together with corrosion mechanism calculation concludes that the risk brought by stent malapposition within 9 months is acceptable.
-
Funding information: This program was financially supported by the National 863 Program (Grant No. 2011AA030103).
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to animals’ use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies for the care and use of animals.
References
[1] Suryawan D . Design and modeling balloon-expandable coronary stent for manufacturability. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. 2017;172:012014.10.1088/1757-899X/172/1/012014Search in Google Scholar
[2] Naghshtabrizi B , Monfared AM , Emami F , Poorolajal J . Impact of stent type on incidence of major adverse cardiac events in large coronary arteries with tubular and diffuse lesions. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2015;64(5):517–24.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Liu HF , Wang M , Xu YS , Kumar SM , Lu XR , Qiang LJ . Diagnostic accuracy of dual-source and 320-row computed tomography angiography in detecting coronary in-stent restenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Radiol. 2018;60(2):149–59.10.1177/0284185118774956Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] McKavanagh P , Zawadowski G , Ahmed N , Kutryk M . The evolution of coronary stents. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2018;16(3):219–28.10.1080/14779072.2018.1435274Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Zheng Q , Dong P , Li Z , Lv Y , An M , Gu L . Braided composite stent for peripheral vascular applications. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):1137–46.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0056Search in Google Scholar
[6] Shlofmitz E , Iantorno M , Waksman R . Restenosis of Drug-eluting stents: A new classification system based on disease mechanism to guide treatment and state-of-the-art review. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12(8):e007023.10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.007023Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Shi Y , Zhang L , Chen J , Zhang J , Yuan F , Shen L , et al. In vitro and in vivo degradation of rapamycin-eluting Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr alloy stents in porcine coronary arteries. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;80:1–6.10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.124Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Omar WA , Kumbhani DJ . The current literature on bioabsorbable stents: a review. Curr Atherosc Rep. 2019;21(12):54.10.1007/s11883-019-0816-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Nogic J , McCormick LM , Francis R , Nerlekar N , Jaworski C , West NEJ , et al. Novel bioabsorbable polymer and polymer-free metallic drug-eluting stents. J Cardiol. 2018;71(5):435–43.10.1016/j.jjcc.2017.12.007Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Li X , Zhang W , Lin W , Qiu H , Qi Y , Ma X , et al. Long-term efficacy of biodegradable metal-polymer composite stents after the first and the second implantations into porcine coronary arteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(13):15703–15.10.1021/acsami.0c00971Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Boland EL , Shine R , Kelly N , Sweeney CA , McHugh PE . A review of material degradation modelling for the analysis and design of bioabsorbable stents. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(2):341–56.10.1007/s10439-015-1413-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Lin W , Qin L , Qi H , Zhang D , Zhang G , Gao R , et al. Long-term in vivo corrosion behavior, biocompatibility and bioresorption mechanism of a bio-absorbable nitrided iron scaffold. Acta Biomater. 2017;54:454–68.10.1016/j.actbio.2017.03.020Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Fagali NS , Grillo CA , Puntarulo S , Fernandez Lorenzo de Mele MA . Is there any difference in the biological impact of soluble and insoluble degradation products of iron-containing biomaterials. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:238–46.10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.09.032Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Peuster M , Hesse C , Schloo T , Fink C , Beerbaum P , von Schnakenburg C . Long-term biocompatibility of a corrodible peripheral iron stent in the porcine descending aorta. Biomaterials. 2006;27(28):4955–62.10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.05.029Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Moravej M , Purnama A , Fiset M , Couet J , Mantovani D . Electroformed pure iron as a new biomaterial for degradable stents: in vitro degradation and preliminary cell viability studies. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(5):1843–51.10.1016/j.actbio.2010.01.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Mariot P , Leeflang MA , Schaeffer L , Zhou J . An investigation on the properties of injection-molded pure iron potentially for biodegradable stent application. Powder Technol. 2016;294:226–35.10.1016/j.powtec.2016.02.042Search in Google Scholar
[17] Gallart F , Prat N , Garcia-Roger EM , Latron J , Rieradevall M , Llorens P , et al. A novel approach to analysing the regimes of temporary streams in relation to their controls on the composition and structure of aquatic biota. Hydrol Earth Syst Sc. 2012;16(9):3165–82.10.5194/hess-16-3165-2012Search in Google Scholar
[18] Kong LB , Zhou YJ , Song KX , Hui D , Hu H , Guo BJ , et al. Effect of aging on properties and nanoscale precipitates of Cu–Ag–Cr alloy. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):70–8.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0007Search in Google Scholar
[19] Xie JL , Jiang HN , Li JY , Huang F , Zaman A , Chen XX , et al. Improved impedance matching by multi-componential metal-hybridized rGO toward high performance of microwave absorption. Nanotechnol Rev. 2021;10(1):1–9.10.1515/ntrev-2021-0001Search in Google Scholar
[20] Dejen KD , Zereffa EA , Murthy HCA , Merga A . Synthesis of ZnO and ZnO/PVA nanocomposite using aqueous Moringa Oleifeira leaf extract template: antibacterial and electrochemical activities. Rev Adv Mater Sci. 2020;59(1):464–76.10.1515/rams-2020-0021Search in Google Scholar
[21] Lin W , Zhang G , Cao P . Cytotoxicity and its test methodology for a bioabsorbable nitrided iron stent. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 2014;103(4):764–76.10.1002/jbm.b.33246Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Fagali NS , Madrid MA , Maceda B , Fernández M , Puerto R , Mele M . Effect of degradation products of iron-bio-absorbable implants on the physiological behavior of macrophages in vitro . Metallomics. 2020;12(11):1841–50.10.1039/d0mt00151aSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Lin W , Zhang H , Zhang W , Qi H , Ding J . In vivo degradation and endothelialization of an iron bio-absorbable scaffold. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(4):1028–39.10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.09.020Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Cocato ML , Lobo AR , Azevedo-Martins AK , Filho JM , Rose M , Colli C . Effects of a moderate iron overload and its interaction with yacon flour, and/or phytate, in the diet on liver antioxidant enzymes and hepatocyte apoptosis in rats. Food Chem. 2019;285(Jul 1):171–9.10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.142Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Zhang P , Chen L , Zhao Q , Du X , Jiang H . Ferroptosis was more initial in cell death caused by iron overload and its underlying mechanism in Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152(5):227–34.10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.03.015Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Gkouvatsos K , Papanikolaou G , Pantopoulos K . Regulation of iron transport and the role of transferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2012;1820(3):188–202.10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.10.013Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Im E , Lee SY , Hong SJ , Ahn CM , Kim JS , Kim BK , et al. Impact of late stent malapposition after drug-eluting stent implantation on long-term clinical outcomes. Atherosclerosis. 2019;288:118–23.10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.07.014Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] O’Brien CC , Lopes AC , Kolandaivelu K , Kunio M , Brown J , Kolachalama VB , et al. Vascular response to experimental stent malapposition and under-expansion. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(7):2251–60.10.1007/s10439-015-1518-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Poon EKW , Thondapu V , Hayat U , Barlis P , Yap CY , Kuo PH , et al. Elevated blood viscosity and microrecirculation resulting from coronary stent malapposition. J Biomech Eng. 2018;140(5):051006.10.1115/1.4039306Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Im E , Hong S , Ahn C , Kim J , Kim B , Ko Y , et al. Long‐term clinical outcomes of late stent malapposition detected by optical coherence tomography after drug‐eluting stent implantation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(7):e011817.10.1161/JAHA.118.011817Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Guo N , Mintz GS . Drug-eluting stent malapposition and its relationship to drug-eluting stent thrombosis. Interv Cardiol. 2012;4(5):521–5.10.2217/ica.12.53Search in Google Scholar
[32] Naganuma T . Acute stent malapposition: harmful or harmless? Int J Cardiol. 2020;299:106–7.10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.08.057Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Lee SY , Ahn JM , Mintz GS , Hong SJ , Ahn CM , Park DW , et al. Ten-year clinical outcomes of late-acquired stent malapposition after coronary stent implantation. Arterioscl Throm Vas. 2020;40(1):288–95.10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313602Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Takano T , Ozaki K , Hoyano M , Yanagawa T , Minamino T . Stent malapposition occurred 17 days following percutaneous coronary intervention for a severe calcified lesion in acute myocardial infarction. J Cardiol Cases. 2019;20(1):4–7.10.1016/j.jccase.2019.02.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Jiao ZY , Zhang DP , Xia K , Wang LF , Yang XC . Clinical analysis of acute myocardial infarction caused by coronary embolism. J Thorac Dis. 2017;9(9):2898–903.10.21037/jtd.2017.07.92Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Roth C , Gangl C , Dalos D , Delle‐Karth G , Neunteufl T , Berger R . Incidence of late-acquired stent malapposition of drug eluting stents with second generation permanent and biodegradable polymer coatings – a prospective, randomized comparison using optical coherence tomography. J Interv Cardiol. 2018;31(6):780–91.10.1111/joic.12572Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Guan GP , Yu CL , Xing MY , Wu YF , Hu XY , Wang HJ , et al. Hydrogel small-diameter vascular graft reinforced with a braided fiber strut with improved mechanical properties. Polymers (Basel). 2019;11(5):810.10.3390/polym11050810Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Zhu WQ , Shao SY , Xu LN , Chen WQ , Yu XY , Tang KM , et al. Enhanced corrosion resistance of zinc-containing nanowires-modified titanium surface under exposure to oxidizing microenvironment. J Nanobiotechnol. 2019;17:55.10.1186/s12951-019-0488-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Zhang B , Yao R , Li L , Wang Y , Luo R , Yang L , et al. Green tea polyphenol induced Mg2+ -rich multilayer conversion coating: toward enhanced corrosion resistance and promoted in situ endothelialization of AZ31 for potential cardiovascular applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(44):41165–77.10.1021/acsami.9b17221Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Zhang H , Xie L , Shen X , Shang T , Luo R , Li X , et al. Catechol/polyethyleneimine conversion coating with enhanced corrosion protection of magnesium alloys: potential applications for vascular implants. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(43):6936–49.10.1039/C8TB01574KSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Zhang F , Hu C , Yang L , Liu K , Ge Y , Wei Y , et al. A conformally adapted all-in-one hydrogel coating: towards robust hemocompatibility and bactericidal activity. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(11):2697–708.10.1039/D1TB00021GSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2021 Xiaoli Shi et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Improved impedance matching by multi-componential metal-hybridized rGO toward high performance of microwave absorption
- Pure-silk fibroin hydrogel with stable aligned micropattern toward peripheral nerve regeneration
- Effective ion pathways and 3D conductive carbon networks in bentonite host enable stable and high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
- Fabrication and characterization of 3D-printed gellan gum/starch composite scaffold for Schwann cells growth
- Synergistic strengthening mechanism of copper matrix composite reinforced with nano-Al2O3 particles and micro-SiC whiskers
- Deformation mechanisms and plasticity of ultrafine-grained Al under complex stress state revealed by digital image correlation technique
- On the deformation-induced grain rotations in gradient nano-grained copper based on molecular dynamics simulations
- Removal of sulfate from aqueous solution using Mg–Al nano-layered double hydroxides synthesized under different dual solvent systems
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel synthesis of TiO2-mixed metal oxide nanocatalyst for degradation of organic pollutant
- Electrophoretic deposition of graphene on basalt fiber for composite applications
- Polyphenylene sulfide-coated wrench composites by nanopinning effect
- Thermal conductivity and thermoelectric properties in 3D macroscopic pure carbon nanotube materials
- An effective thermal conductivity and thermomechanical homogenization scheme for a multiscale Nb3Sn filaments
- Friction stir spot welding of AA5052 with additional carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composite interlayer
- Improvement of long-term cycling performance of high-nickel cathode materials by ZnO coating
- Quantum effects of gas flow in nanochannels
- An approach to effectively improve the interfacial bonding of nano-perfused composites by in situ growth of CNTs
- Effects of nano-modified polymer cement-based materials on the bending behavior of repaired concrete beams
- Effects of the combined usage of nanomaterials and steel fibres on the workability, compressive strength, and microstructure of ultra-high performance concrete
- One-pot solvothermal synthesis and characterization of highly stable nickel nanoparticles
- Comparative study on mechanisms for improving mechanical properties and microstructure of cement paste modified by different types of nanomaterials
- Effect of in situ graphene-doped nano-CeO2 on microstructure and electrical contact properties of Cu30Cr10W contacts
- The experimental study of CFRP interlayer of dissimilar joint AA7075-T651/Ti-6Al-4V alloys by friction stir spot welding on mechanical and microstructural properties
- Vibration analysis of a sandwich cylindrical shell in hygrothermal environment
- Water barrier and mechanical properties of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch (TPS)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) blend bionanocomposites
- Strong quadratic acousto-optic coupling in 1D multilayer phoxonic crystal cavity
- Three-dimensional shape analysis of peripapillary retinal pigment epithelium-basement membrane layer based on OCT radial images
- Solvent regulation synthesis of single-component white emission carbon quantum dots for white light-emitting diodes
- Xanthate-modified nanoTiO2 as a novel vulcanization accelerator enhancing mechanical and antibacterial properties of natural rubber
- Effect of steel fiber on impact resistance and durability of concrete containing nano-SiO2
- Ultrasound-enhanced biosynthesis of uniform ZnO nanorice using Swietenia macrophylla seed extract and its in vitro anticancer activity
- Temperature dependence of hardness prediction for high-temperature structural ceramics and their composites
- Study on the frequency of acoustic emission signal during crystal growth of salicylic acid
- Controllable modification of helical carbon nanotubes for high-performance microwave absorption
- Role of dry ozonization of basalt fibers on interfacial properties and fracture toughness of epoxy matrix composites
- Nanosystem’s density functional theory study of the chlorine adsorption on the Fe(100) surface
- A rapid nanobiosensing platform based on herceptin-conjugated graphene for ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor cells in early breast cancer
- Improving flexural strength of UHPC with sustainably synthesized graphene oxide
- The role of graphene/graphene oxide in cement hydration
- Structural characterization of microcrystalline and nanocrystalline cellulose from Ananas comosus L. leaves: Cytocompatibility and molecular docking studies
- Evaluation of the nanostructure of calcium silicate hydrate based on atomic force microscopy-infrared spectroscopy experiments
- Combined effects of nano-silica and silica fume on the mechanical behavior of recycled aggregate concrete
- Safety study of malapposition of the bio-corrodible nitrided iron stent in vivo
- Triethanolamine interface modification of crystallized ZnO nanospheres enabling fast photocatalytic hazard-free treatment of Cr(vi) ions
- Novel electrodes for precise and accurate droplet dispensing and splitting in digital microfluidics
- Construction of Chi(Zn/BMP2)/HA composite coating on AZ31B magnesium alloy surface to improve the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility
- Experimental and multiscale numerical investigations on low-velocity impact responses of syntactic foam composites reinforced with modified MWCNTs
- Comprehensive performance analysis and optimal design of smart light pole for cooperative vehicle infrastructure system
- Room temperature growth of ZnO with highly active exposed facets for photocatalytic application
- Influences of poling temperature and elongation ratio on PVDF-HFP piezoelectric films
- Large strain hardening of magnesium containing in situ nanoparticles
- Super stable water-based magnetic fluid as a dual-mode contrast agent
- Photocatalytic activity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles: In vitro antimicrobial, biocompatibility, and molecular docking studies
- Hygrothermal environment effect on the critical buckling load of FGP microbeams with initial curvature integrated by CNT-reinforced skins considering the influence of thickness stretching
- Thermal aging behavior characteristics of asphalt binder modified by nano-stabilizer based on DSR and AFM
- Building effective core/shell polymer nanoparticles for epoxy composite toughening based on Hansen solubility parameters
- Structural characterization and nanoscale strain field analysis of α/β interface layer of a near α titanium alloy
- Optimization of thermal and hydrophobic properties of GO-doped epoxy nanocomposite coatings
- The properties of nano-CaCO3/nano-ZnO/SBR composite-modified asphalt
- Three-dimensional metallic carbon allotropes with superhardness
- Physical stability and rheological behavior of Pickering emulsions stabilized by protein–polysaccharide hybrid nanoconjugates
- Optimization of volume fraction and microstructure evolution during thermal deformation of nano-SiCp/Al–7Si composites
- Phase analysis and corrosion behavior of brazing Cu/Al dissimilar metal joint with BAl88Si filler metal
- High-efficiency nano polishing of steel materials
- On the rheological properties of multi-walled carbon nano-polyvinylpyrrolidone/silicon-based shear thickening fluid
- Fabrication of Ag/ZnO hollow nanospheres and cubic TiO2/ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts for RhB degradation
- Fabrication and properties of PLA/nano-HA composite scaffolds with balanced mechanical properties and biological functions for bone tissue engineering application
- Investigation of the early-age performance and microstructure of nano-C–S–H blended cement-based materials
- Reduced graphene oxide coating on basalt fabric using electrophoretic deposition and its role in the mechanical and tribological performance of epoxy/basalt fiber composites
- Effect of nano-silica as cementitious materials-reducing admixtures on the workability, mechanical properties and durability of concrete
- Machine-learning-assisted microstructure–property linkages of carbon nanotube-reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites produced by laser powder bed fusion
- Physical, thermal, and mechanical properties of highly porous polylactic acid/cellulose nanofibre scaffolds prepared by salt leaching technique
- A comparative study on characterizations and synthesis of pure lead sulfide (PbS) and Ag-doped PbS for photovoltaic applications
- Clean preparation of washable antibacterial polyester fibers by high temperature and high pressure hydrothermal self-assembly
- Al 5251-based hybrid nanocomposite by FSP reinforced with graphene nanoplates and boron nitride nanoparticles: Microstructure, wear, and mechanical characterization
- Interlaminar fracture toughness properties of hybrid glass fiber-reinforced composite interlayered with carbon nanotube using electrospray deposition
- Microstructure and life prediction model of steel slag concrete under freezing-thawing environment
- Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles from the seed coat waste of pistachio (Pistacia vera) and their effect on the growth of eggplant
- Study on adaptability of rheological index of nano-PUA-modified asphalt based on geometric parameters of parallel plate
- Preparation and adsorption properties of nano-graphene oxide/tourmaline composites
- A study on interfacial behaviors of epoxy/graphene oxide derived from pitch-based graphite fibers
- Multiresponsive carboxylated graphene oxide-grafted aptamer as a multifunctional nanocarrier for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics and bioactive compounds in cancer therapy
- Piezoresistive/piezoelectric intrinsic sensing properties of carbon nanotube cement-based smart composite and its electromechanical sensing mechanisms: A review
- Smart stimuli-responsive biofunctionalized niosomal nanocarriers for programmed release of bioactive compounds into cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- Photoremediation of methylene blue by biosynthesized ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposites using Callistemon viminalis leaves aqueous extract: A comparative study
- Study of gold nanoparticles’ preparation through ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and lyophilisation for possible use as markers in LFIA tests
- Review Articles
- Advance on the dispersion treatment of graphene oxide and the graphene oxide modified cement-based materials
- Development of ionic liquid-based electroactive polymer composites using nanotechnology
- Nanostructured multifunctional electrocatalysts for efficient energy conversion systems: Recent perspectives
- Recent advances on the fabrication methods of nanocomposite yarn-based strain sensor
- Review on nanocomposites based on aerospace applications
- Overview of nanocellulose as additives in paper processing and paper products
- The frontiers of functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites as chemical sensors
- Material advancement in tissue-engineered nerve conduit
- Carbon nanostructure-based superhydrophobic surfaces and coatings
- Functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites for smart optoelectronic applications
- Interfacial technology for enhancement in steel fiber reinforced cementitious composite from nano to macroscale
- Metal nanoparticles and biomaterials: The multipronged approach for potential diabetic wound therapy
- Review on resistive switching mechanisms of bio-organic thin film for non-volatile memory application
- Nanotechnology-enabled biomedical engineering: Current trends, future scopes, and perspectives
- Research progress on key problems of nanomaterials-modified geopolymer concrete
- Smart stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for the cancer therapy – nanomedicine
- An overview of methods for production and detection of silver nanoparticles, with emphasis on their fate and toxicological effects on human, soil, and aquatic environment
- Effects of chemical modification and nanotechnology on wood properties
- Mechanisms, influencing factors, and applications of electrohydrodynamic jet printing
- Application of antiviral materials in textiles: A review
- Phase transformation and strengthening mechanisms of nanostructured high-entropy alloys
- Research progress on individual effect of graphene oxide in cement-based materials and its synergistic effect with other nanomaterials
- Catalytic defense against fungal pathogens using nanozymes
- A mini-review of three-dimensional network topological structure nanocomposites: Preparation and mechanical properties
- Mechanical properties and structural health monitoring performance of carbon nanotube-modified FRP composites: A review
- Nano-scale delivery: A comprehensive review of nano-structured devices, preparative techniques, site-specificity designs, biomedical applications, commercial products, and references to safety, cellular uptake, and organ toxicity
- Effects of alloying, heat treatment and nanoreinforcement on mechanical properties and damping performances of Cu–Al-based alloys: A review
- Recent progress in the synthesis and applications of vertically aligned carbon nanotube materials
- Thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of mono and hybrid organic- and synthetic-based nanofluids: A critical review
- Recent advances in waste-recycled nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Waste-to-wealth
- Layup sequence and interfacial bonding of additively manufactured polymeric composite: A brief review
- Quantum dots synthetization and future prospect applications
- Approved and marketed nanoparticles for disease targeting and applications in COVID-19
- Strategies for improving rechargeable lithium-ion batteries: From active materials to CO2 emissions
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Improved impedance matching by multi-componential metal-hybridized rGO toward high performance of microwave absorption
- Pure-silk fibroin hydrogel with stable aligned micropattern toward peripheral nerve regeneration
- Effective ion pathways and 3D conductive carbon networks in bentonite host enable stable and high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
- Fabrication and characterization of 3D-printed gellan gum/starch composite scaffold for Schwann cells growth
- Synergistic strengthening mechanism of copper matrix composite reinforced with nano-Al2O3 particles and micro-SiC whiskers
- Deformation mechanisms and plasticity of ultrafine-grained Al under complex stress state revealed by digital image correlation technique
- On the deformation-induced grain rotations in gradient nano-grained copper based on molecular dynamics simulations
- Removal of sulfate from aqueous solution using Mg–Al nano-layered double hydroxides synthesized under different dual solvent systems
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel synthesis of TiO2-mixed metal oxide nanocatalyst for degradation of organic pollutant
- Electrophoretic deposition of graphene on basalt fiber for composite applications
- Polyphenylene sulfide-coated wrench composites by nanopinning effect
- Thermal conductivity and thermoelectric properties in 3D macroscopic pure carbon nanotube materials
- An effective thermal conductivity and thermomechanical homogenization scheme for a multiscale Nb3Sn filaments
- Friction stir spot welding of AA5052 with additional carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composite interlayer
- Improvement of long-term cycling performance of high-nickel cathode materials by ZnO coating
- Quantum effects of gas flow in nanochannels
- An approach to effectively improve the interfacial bonding of nano-perfused composites by in situ growth of CNTs
- Effects of nano-modified polymer cement-based materials on the bending behavior of repaired concrete beams
- Effects of the combined usage of nanomaterials and steel fibres on the workability, compressive strength, and microstructure of ultra-high performance concrete
- One-pot solvothermal synthesis and characterization of highly stable nickel nanoparticles
- Comparative study on mechanisms for improving mechanical properties and microstructure of cement paste modified by different types of nanomaterials
- Effect of in situ graphene-doped nano-CeO2 on microstructure and electrical contact properties of Cu30Cr10W contacts
- The experimental study of CFRP interlayer of dissimilar joint AA7075-T651/Ti-6Al-4V alloys by friction stir spot welding on mechanical and microstructural properties
- Vibration analysis of a sandwich cylindrical shell in hygrothermal environment
- Water barrier and mechanical properties of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch (TPS)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) blend bionanocomposites
- Strong quadratic acousto-optic coupling in 1D multilayer phoxonic crystal cavity
- Three-dimensional shape analysis of peripapillary retinal pigment epithelium-basement membrane layer based on OCT radial images
- Solvent regulation synthesis of single-component white emission carbon quantum dots for white light-emitting diodes
- Xanthate-modified nanoTiO2 as a novel vulcanization accelerator enhancing mechanical and antibacterial properties of natural rubber
- Effect of steel fiber on impact resistance and durability of concrete containing nano-SiO2
- Ultrasound-enhanced biosynthesis of uniform ZnO nanorice using Swietenia macrophylla seed extract and its in vitro anticancer activity
- Temperature dependence of hardness prediction for high-temperature structural ceramics and their composites
- Study on the frequency of acoustic emission signal during crystal growth of salicylic acid
- Controllable modification of helical carbon nanotubes for high-performance microwave absorption
- Role of dry ozonization of basalt fibers on interfacial properties and fracture toughness of epoxy matrix composites
- Nanosystem’s density functional theory study of the chlorine adsorption on the Fe(100) surface
- A rapid nanobiosensing platform based on herceptin-conjugated graphene for ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor cells in early breast cancer
- Improving flexural strength of UHPC with sustainably synthesized graphene oxide
- The role of graphene/graphene oxide in cement hydration
- Structural characterization of microcrystalline and nanocrystalline cellulose from Ananas comosus L. leaves: Cytocompatibility and molecular docking studies
- Evaluation of the nanostructure of calcium silicate hydrate based on atomic force microscopy-infrared spectroscopy experiments
- Combined effects of nano-silica and silica fume on the mechanical behavior of recycled aggregate concrete
- Safety study of malapposition of the bio-corrodible nitrided iron stent in vivo
- Triethanolamine interface modification of crystallized ZnO nanospheres enabling fast photocatalytic hazard-free treatment of Cr(vi) ions
- Novel electrodes for precise and accurate droplet dispensing and splitting in digital microfluidics
- Construction of Chi(Zn/BMP2)/HA composite coating on AZ31B magnesium alloy surface to improve the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility
- Experimental and multiscale numerical investigations on low-velocity impact responses of syntactic foam composites reinforced with modified MWCNTs
- Comprehensive performance analysis and optimal design of smart light pole for cooperative vehicle infrastructure system
- Room temperature growth of ZnO with highly active exposed facets for photocatalytic application
- Influences of poling temperature and elongation ratio on PVDF-HFP piezoelectric films
- Large strain hardening of magnesium containing in situ nanoparticles
- Super stable water-based magnetic fluid as a dual-mode contrast agent
- Photocatalytic activity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles: In vitro antimicrobial, biocompatibility, and molecular docking studies
- Hygrothermal environment effect on the critical buckling load of FGP microbeams with initial curvature integrated by CNT-reinforced skins considering the influence of thickness stretching
- Thermal aging behavior characteristics of asphalt binder modified by nano-stabilizer based on DSR and AFM
- Building effective core/shell polymer nanoparticles for epoxy composite toughening based on Hansen solubility parameters
- Structural characterization and nanoscale strain field analysis of α/β interface layer of a near α titanium alloy
- Optimization of thermal and hydrophobic properties of GO-doped epoxy nanocomposite coatings
- The properties of nano-CaCO3/nano-ZnO/SBR composite-modified asphalt
- Three-dimensional metallic carbon allotropes with superhardness
- Physical stability and rheological behavior of Pickering emulsions stabilized by protein–polysaccharide hybrid nanoconjugates
- Optimization of volume fraction and microstructure evolution during thermal deformation of nano-SiCp/Al–7Si composites
- Phase analysis and corrosion behavior of brazing Cu/Al dissimilar metal joint with BAl88Si filler metal
- High-efficiency nano polishing of steel materials
- On the rheological properties of multi-walled carbon nano-polyvinylpyrrolidone/silicon-based shear thickening fluid
- Fabrication of Ag/ZnO hollow nanospheres and cubic TiO2/ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts for RhB degradation
- Fabrication and properties of PLA/nano-HA composite scaffolds with balanced mechanical properties and biological functions for bone tissue engineering application
- Investigation of the early-age performance and microstructure of nano-C–S–H blended cement-based materials
- Reduced graphene oxide coating on basalt fabric using electrophoretic deposition and its role in the mechanical and tribological performance of epoxy/basalt fiber composites
- Effect of nano-silica as cementitious materials-reducing admixtures on the workability, mechanical properties and durability of concrete
- Machine-learning-assisted microstructure–property linkages of carbon nanotube-reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites produced by laser powder bed fusion
- Physical, thermal, and mechanical properties of highly porous polylactic acid/cellulose nanofibre scaffolds prepared by salt leaching technique
- A comparative study on characterizations and synthesis of pure lead sulfide (PbS) and Ag-doped PbS for photovoltaic applications
- Clean preparation of washable antibacterial polyester fibers by high temperature and high pressure hydrothermal self-assembly
- Al 5251-based hybrid nanocomposite by FSP reinforced with graphene nanoplates and boron nitride nanoparticles: Microstructure, wear, and mechanical characterization
- Interlaminar fracture toughness properties of hybrid glass fiber-reinforced composite interlayered with carbon nanotube using electrospray deposition
- Microstructure and life prediction model of steel slag concrete under freezing-thawing environment
- Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles from the seed coat waste of pistachio (Pistacia vera) and their effect on the growth of eggplant
- Study on adaptability of rheological index of nano-PUA-modified asphalt based on geometric parameters of parallel plate
- Preparation and adsorption properties of nano-graphene oxide/tourmaline composites
- A study on interfacial behaviors of epoxy/graphene oxide derived from pitch-based graphite fibers
- Multiresponsive carboxylated graphene oxide-grafted aptamer as a multifunctional nanocarrier for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics and bioactive compounds in cancer therapy
- Piezoresistive/piezoelectric intrinsic sensing properties of carbon nanotube cement-based smart composite and its electromechanical sensing mechanisms: A review
- Smart stimuli-responsive biofunctionalized niosomal nanocarriers for programmed release of bioactive compounds into cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- Photoremediation of methylene blue by biosynthesized ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposites using Callistemon viminalis leaves aqueous extract: A comparative study
- Study of gold nanoparticles’ preparation through ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and lyophilisation for possible use as markers in LFIA tests
- Review Articles
- Advance on the dispersion treatment of graphene oxide and the graphene oxide modified cement-based materials
- Development of ionic liquid-based electroactive polymer composites using nanotechnology
- Nanostructured multifunctional electrocatalysts for efficient energy conversion systems: Recent perspectives
- Recent advances on the fabrication methods of nanocomposite yarn-based strain sensor
- Review on nanocomposites based on aerospace applications
- Overview of nanocellulose as additives in paper processing and paper products
- The frontiers of functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites as chemical sensors
- Material advancement in tissue-engineered nerve conduit
- Carbon nanostructure-based superhydrophobic surfaces and coatings
- Functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites for smart optoelectronic applications
- Interfacial technology for enhancement in steel fiber reinforced cementitious composite from nano to macroscale
- Metal nanoparticles and biomaterials: The multipronged approach for potential diabetic wound therapy
- Review on resistive switching mechanisms of bio-organic thin film for non-volatile memory application
- Nanotechnology-enabled biomedical engineering: Current trends, future scopes, and perspectives
- Research progress on key problems of nanomaterials-modified geopolymer concrete
- Smart stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for the cancer therapy – nanomedicine
- An overview of methods for production and detection of silver nanoparticles, with emphasis on their fate and toxicological effects on human, soil, and aquatic environment
- Effects of chemical modification and nanotechnology on wood properties
- Mechanisms, influencing factors, and applications of electrohydrodynamic jet printing
- Application of antiviral materials in textiles: A review
- Phase transformation and strengthening mechanisms of nanostructured high-entropy alloys
- Research progress on individual effect of graphene oxide in cement-based materials and its synergistic effect with other nanomaterials
- Catalytic defense against fungal pathogens using nanozymes
- A mini-review of three-dimensional network topological structure nanocomposites: Preparation and mechanical properties
- Mechanical properties and structural health monitoring performance of carbon nanotube-modified FRP composites: A review
- Nano-scale delivery: A comprehensive review of nano-structured devices, preparative techniques, site-specificity designs, biomedical applications, commercial products, and references to safety, cellular uptake, and organ toxicity
- Effects of alloying, heat treatment and nanoreinforcement on mechanical properties and damping performances of Cu–Al-based alloys: A review
- Recent progress in the synthesis and applications of vertically aligned carbon nanotube materials
- Thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of mono and hybrid organic- and synthetic-based nanofluids: A critical review
- Recent advances in waste-recycled nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Waste-to-wealth
- Layup sequence and interfacial bonding of additively manufactured polymeric composite: A brief review
- Quantum dots synthetization and future prospect applications
- Approved and marketed nanoparticles for disease targeting and applications in COVID-19
- Strategies for improving rechargeable lithium-ion batteries: From active materials to CO2 emissions

