Abstract
Based on the thermal theory of Newtonian mechanics, the pressure difference in the macro channels will drive the gas flow until the pressure difference inside is zero. However, the 12-year vacuum packaging experiments in our laboratory showed that when the macroscopic channel is reduced to a critical size and reaches the nanometer level, the gas flow inside the channel is hindered, that is, the differential pressure cannot become zero. To explain this paradoxical phenomenon, this study analyzes the flow of air molecules in the channel by using the De Broglie’s matter waves and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Based on the law of quantum mechanics, when the diameter of the nanochannel is reduced to a certain size, it has a localized high pressure in the channel, which impedes the gas flow. This article introduces quantum mechanics into nanochannel’s gas fluid dynamics for the first time, expanding the new direction of fluid mechanics.
Graphical abstract
1 Introduction
According to the thermal theory of Newtonian mechanics, when the gas components on both ends of a macroscopic channel are identical, the gas flow in the macro channel is driven by the differential pressure between the two sides of the channel. The pressure difference drives the gas flow until the pressure difference between the two sides of the channel is zero. However, our lab found that after 12 years, in the tube shell packaging experiments, the tube shell still maintains a high vacuum inside, which is inconsistent with the traditional theory, according to which the tube shell vacuum cannot be maintained for as long as 12 years. The prolonged holding of the vacuum indicates the hindrance of the gas flow in the channel.
As early as 1909, Knudsen experimentally studied the resistance properties of gas flow within the micron channel and pointed out the existence of a thin gas effect within it [1]. In 2018, Scorrano et al. proposed a widely applicable theoretical method for quantitatively predicting the closed gas flow in the Knudsen and transition zones. The channel sizes ranged from 2.5 to 250 nm. The validity of their established volumetric gas flow model was demonstrated by experimental measurements [2–7]. In 2019, Zhang et al. established a nanoscale pore model using molecular dynamics theory and simulated the transition flow and slip flow of methane molecules in carbon nanopores by molecular dynamics and found that the pore walls composed of carbon atoms have an adsorption [8–13]. In 2019, Baek and Akkutlu analyzed the average free path of gas molecules in organic nanotubes using molecular simulation, Monte Carlo simulation, and molecular dynamics and found that the nanoconfinement effect significantly changed the properties of the confined fluids and that the classical gas dynamics theory overestimated the average free path of oil and gas fluids under typical reservoir conditions [14–19]. In 2020, Hong et al. conducted experiments on laminar and turbulent (including blocked flow) gas flow in smooth microtubes under atmospheric backpressure and variable inlet pressure conditions and investigated their local friction factors [20–26]. The theoretical methods used in the above studies were based on Newtonian mechanics while the scales of the investigated nanochannels were all above 2 nm and did not consider the case of channels below 1 nm. When the channel size is reduced to a certain range, the laws of the gas flow in them may no longer follow the laws of Newtonian mechanics.
In 1999, Markus Arndt demonstrated the quantum effect of a fullerene molecule (C60) with 720 atomic masses [27–33]. In November 2019, the team further demonstrated the quantum effect of a short bacillus peptide molecule by double-slit interference experiments. This is a 15 amino acid length natural antibiotic with a mass of 1,882 atoms [34–40]. And the vacuum tube shells in this laboratory exhibit phenomenon that cannot yet be explained by Newtonian mechanics, namely, the maintenance of a higher vacuum for 12 years.
In this article, we consider to distinguish the gas flow in 1 nm scale nanochannels from that above 1 nm and introduce quantum mechanics to analyze the gas flow in microchannels below 1 nm scale. Whereas there are no studies to discuss the mechanism of the gas flow in the nanochannels on the scale below 1 nm, this article further introduces the De Broyne matter wave of quantum mechanics [41–46] and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle to analyze the gas flow in the nanochannels.
2 Experiment and analysis
In this study, the metal shell vacuum packaging is used as an example to analyze the nanochannels that exist inside it after vacuum packaging. As shown in Figure 1, the packaged tube shell is commonly used for hermetic packaging of electronic devices, where Figure 1(a) is the tube cap and Figure 1(b) is the tube seat. There is no getter in the tube shell, and the internal space after packaging is 2.1 cm3.
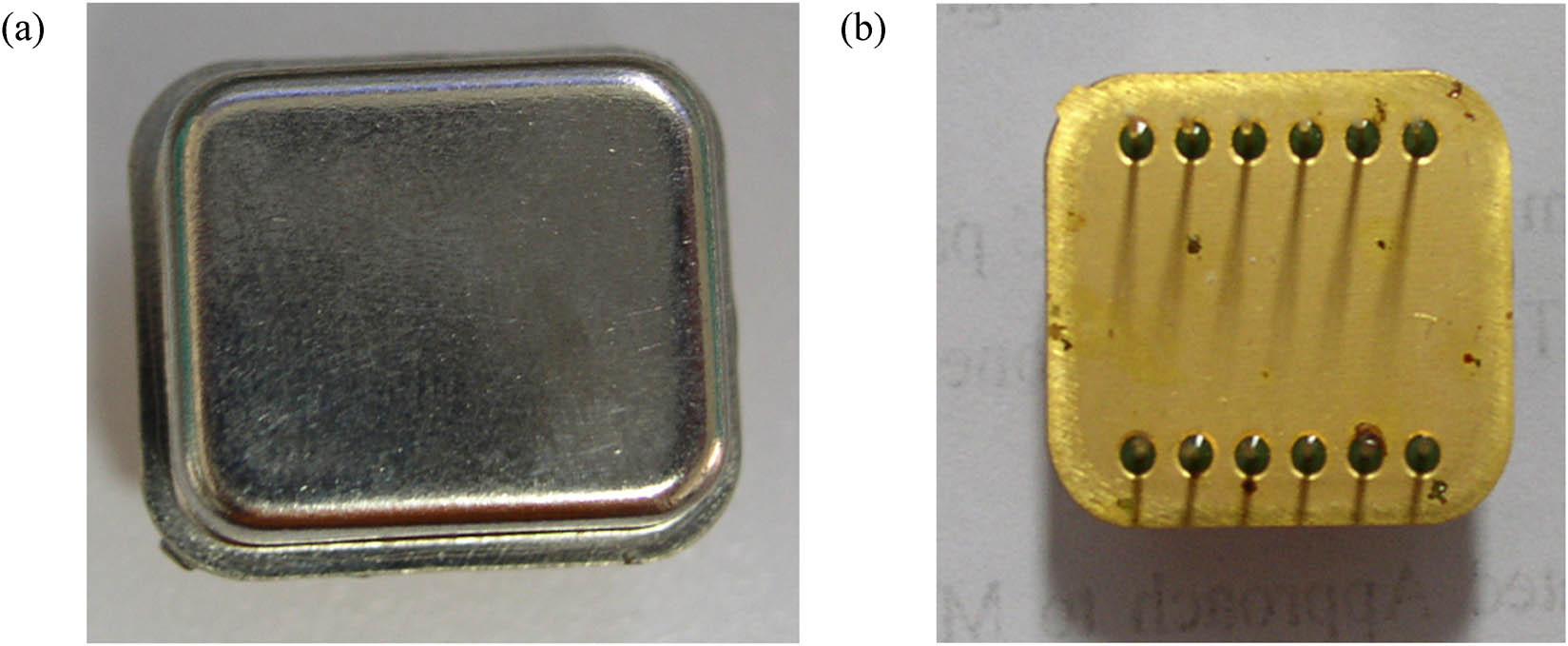
MD2A tube cap (a) and tube seat (b).
In this study, resistance welding is used to weld the abovementioned metal tube seat and tube cap in a vacuum environment. After welding, the internal nano capillary channels are shown in Figure 2.

Cross-sectional SEM image of a typical leakage hole in a vacuum packaging shell.
Based on the above experimental measurement, the vacuum packaging leakage model was established as shown in Figure 3. The external air can leak into the interior of the metal shell through the nano capillary tube. In this study, the specific leakage situation of the gas was first analyzed based on the characteristics of the airflow through the capillary pores [47,48]. The leakage rate of the gas (Q) is expressed as:
where d and L represent the diameter and length of the capillary tube, respectively,
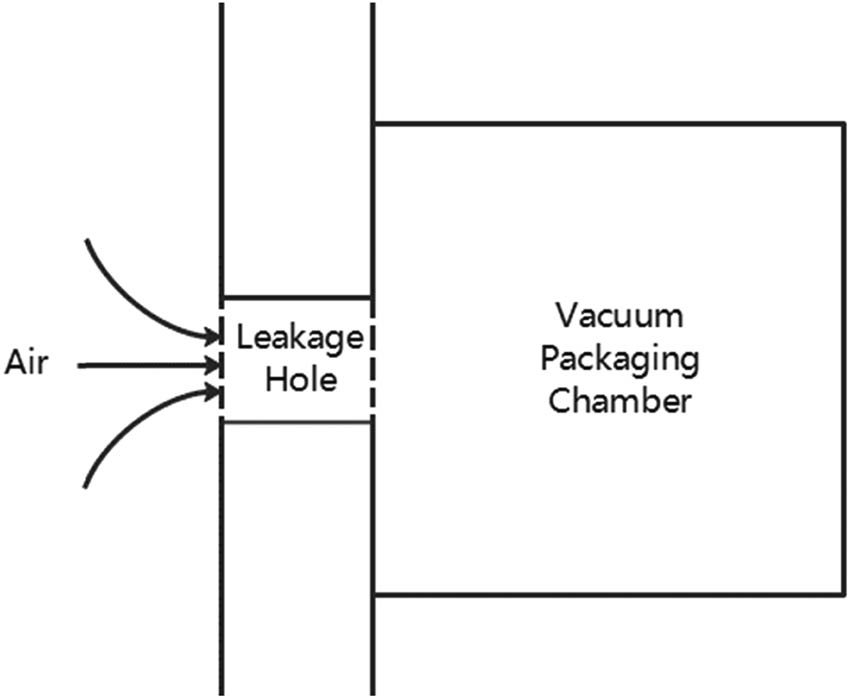
Schematic of vacuum packaging leakage model. This schematic is intended to illustrate the path of the gas into the vacuum packaging chamber, i.e., through the leakage hole into the packaging chamber.
The ideal gas law equation is shown below:
And the density per unit pressure
According to the equation above, formula (1) could be simplified as
As can be seen from (4) and (5), the gas leakage is related to the capillary structural parameters and the difference between internal and external pressures. The gas leakage rate is proportional to the third or fourth square of the capillary channel diameter, d, and inversely proportional to the capillary hole length L. Leakage rate can be reduced by decreasing the diameter or increasing the length of the capillary tube. The gas leakage rate is also proportional to the pressure difference at both sides of the channels. Gas leakage stops when the pressure difference between the two sides of the channel is zero.
The above gas leakage is derived according to Newton’s law. When the quality of vacuum welding is poor, it is obvious that the outside air will quickly leak into the metal shell. With the improvement in welding quality, the diameter of the leakage hole will be further reduced.
In this study, a tuning fork crystal oscillator is used to measure the change in air pressure inside the vacuum cavity of a metal channel shell as the welding quality improves. The MD2A shell was vacuum packaged in 2005 with a crystal oscillator inside the vacuum packaging to measure the vacuum. The resonant impedance of the crystal oscillator varies greatly with air pressure when the X- and Y-cut quartz oscillator is operating in bending oscillation mode. The direct digital frequency synthesizer (DDS) module is used to output a sinusoidal signal of analog scanning frequency, phase, and amplitude. The sinusoidal signal is filtered by a low-pass filter (LPF) unit and the final waveform is output to excite the crystal circuit at the end. As the crystal oscillator is connected to a resistor network, when the crystal reaches resonance, i.e., the crystal oscillator behaves as a pure impedance.
The resistance of the crystal oscillator at resonance is obtained by comparing the two voltage values at the front and end of the crystal oscillator. In this measurement system, the output is the voltage value.
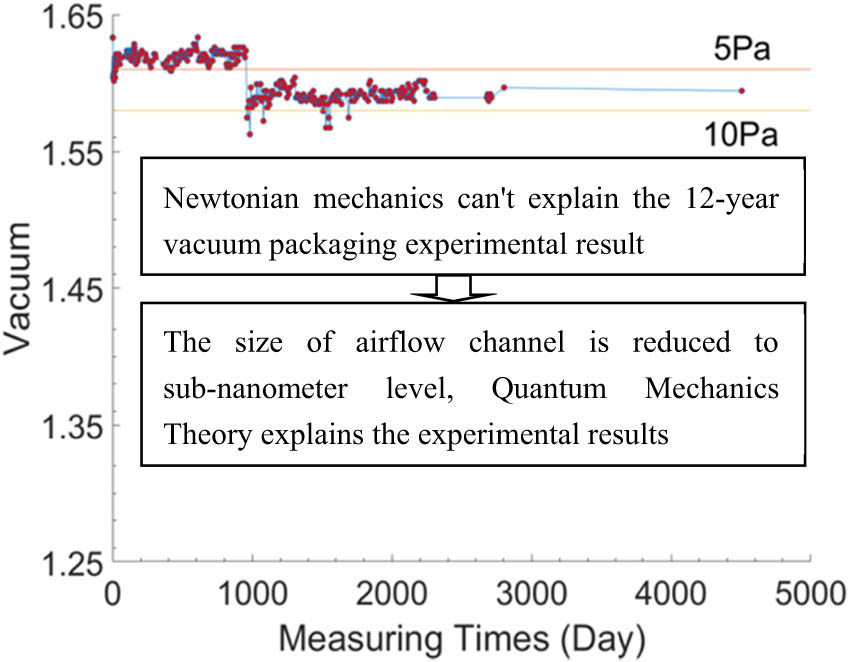
In this study, the metal tube shell with the crystal oscillator inside is vacuum welded using resistance welding equipment in a vacuum environment. The leakage rate of the vacuum packaged tube shell is about 10−8 to 10−9 Pa m3/s. This leakage rate indicates that there are nanotubes in the metal tube shell after packaging, if there are no nanotubes, the leakage rate should be about 10−11 to 10−12 Pa m3/s. According to the previous theoretical calculation, it is expected that the vacuum packaged tube shell will leak fast. However, after 12 years of test and observation, the vacuum inside the vacuum packaged channels shell is maintained as shown in Figure 4; it is found that the channels shell has been kept in vacuum for 12 years. Although there are fluctuations, no significant reduction in a vacuum was observed. The 12 years of vacuum packaging measurements show that when the diameter of the nanochannels is reduced to a certain degree, although there is a pressure difference of 1 atmosphere at both ends of the channels, there is a hindrance to the gas flow in the channels. Thus, the theoretical calculations are quite different from the experimental results, which further shows that the mechanism of airflow in the macroscopic channels will no longer apply to the nanochannels.

Relationship between vacuum holding voltage and time in vacuum packaging shell. According to the experimental data, the vacuum level kept fluctuating in a stable range until day 954 while there was a significant decrease from the 954th day to the 961st day, and continued to fluctuate in a stable range after the 961st day, until the 5,355th day, when the vacuum level remained at 1.5512. Data on the vacuum holding time of other packing shells are shown in the Appendix.
3 Discussion
When the leakage holes of metal tube shells are small and reach the nanometer level, this study introduces the De Broglie’s Matter Waves and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics to analyze the air molecular flow.
Similar to the diffraction that occurs when a particle passes through a single slit, as shown in Figure 5, this study assumes that air molecules will also diffract when passing through nanochannels. The phenomenon exhibits that they are a form of waves, as shown in Figure 6, based on De Broglie’s Matter Waves. These molecules will have momentum perpendicular to their original direction of motion when diffraction occurs, and the momentum in this perpendicular direction has uncertainty.

Single-slit diffraction pattern of particles. In the process of light propagation, when it encounters an obstacle or a small hole, the light will deviate from the straight path of propagation and travel around behind the obstacle. This study assumes that air molecules will also diffract when passing through nanochannels.

Section of nanochannels. This diagram demonstrates that air molecules also pass through tiny tubes as they move from area 2 to area 1.
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, the more accurately we know the position of an air molecule, the less accurately we know its momentum. Then the less accurately we know the momentum in the vertical direction and the greater the resistance to the original direction of motion of molecules after collision with the wall of the channel. While it is not possible to exactly know the motion of individual molecules, it is possible to know the statistical pattern of the motion of many molecules. Since the mean free path of air molecules (

Schematic diagram of air molecular collision in the channels. This diagram demonstrates the possible movements of air molecules from area 2 to area 1, one is to stop at area 2, the other is to pass through a small pipe to area 1, and some will collide with the sidewalls of area 2.
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
where
The nanochannels model of the metal shell can be simplified as shown in Figure 5, in which area 1 of the channels is connected to area 2, and both are simplified to cube structures. Air is filled inside the channels, and air molecules can be set as microscopic particles in quantum mechanics. The above nanochannels model is packaged in a vacuum environment of 10 Pa.
In area 1, we have the equation (8):
where
It can be deduced from equation (8) that
In area 2, we have equation (10):
where
It can be deduced from equation (10) that
Since the volume of area 2 is larger than that of area 1, we can get the expression:
The gap between the molecules of gas under vacuum at room temperature is very large, and the molecular spacing reaches more than 10 times the order of magnitude of the molecular diameter, and the interaction force between the molecules is very weak and can be ignored. In addition to the collision of gas molecules with each other and the collision with the wall of the leaky hole, it is regarded as a completely elastic collision. The pressure on the wall at the collision can be calculated by using the momentum theorem, then we can obtain:
where n is the total number of leakage gas molecules, v is the rate, and V is the volume of the leakage hole.
Consider the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules,
Since the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules is proportional to the thermodynamic temperature,
It can be seen from equation (14) that the energy is discontinuous and the temperature is also discontinuous.
By combining equations (12–14), pressure can be described as follows
where K is Boltzmann’s constant and T is the thermodynamic temperature. From formula (15), it can be seen that the pressure is also discontinuous when n and V are constant.
Think about the 1-D case:
Since the ratio of n to V is constant when packaged in a vacuum chamber, then we can obtain
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, when the uncertainty of position becomes smaller, the uncertainty of momentum will increase, and the uncertainty of
4 Conclusion
This article introduces quantum mechanics into nanochannels gas fluid dynamics for the first time, expanding the new direction of fluid mechanics.
Twelve years of vacuum packaging experiments show that when the diameter of the nanochannels are reduced to a certain level, there is a hindrance to the gas flow in the channels even though there is a pressure difference of 1 atmosphere between the two ends of the channels.
When the diameter of the nanochannels is reduced to a certain degree, the gas flow in the channels is fluctuating.
When the diameter of the nanochannels is reduced to a certain degree, the gas is locally at high pressure at the minimum diameter.
Leakage rate detection values indicate the presence of nanochannels after the packaging of the metal shell.
Appendix

Relationship between vacuum holding voltage and time in No. 72406 vacuum packaging shell.

Relationship between vacuum holding voltage and time in No. 72411 vacuum packaging shell.

Relationship between vacuum holding voltage and time in No. 72416 vacuum packaging shell.
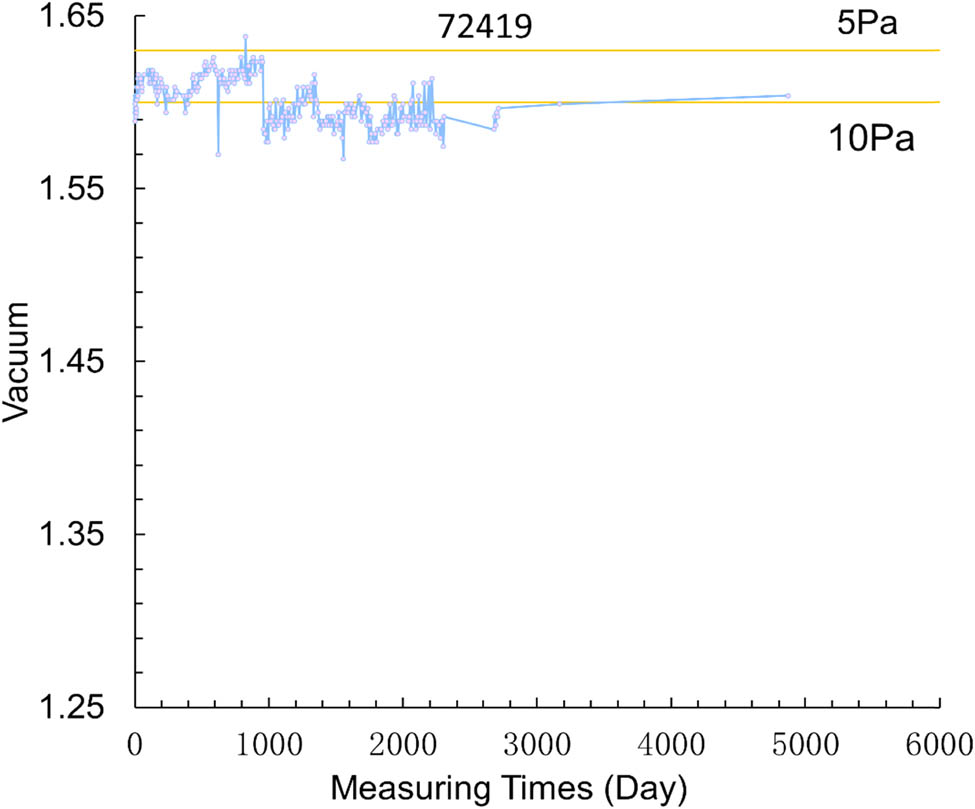
Relationship between vacuum holding voltage and time in No. 72419 vacuum packaging shell.
Relationship between vacuum holding voltage and time in No. 72420 vacuum packaging shell.
-
Funding information: The authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Knudsen M. Die Gesetze der Molekularstromung und der inneren riebungsstromung der gase durch rohnen. Ann Phys. 1909;333(5):999–16.10.1002/andp.19093330505Search in Google Scholar
[2] Scorrano G, Bruno G, Trani DN, Ferrari M, Pimpinelli A, Grattoni A. Gas flow at the ultra-nanoscale: universal predictive model and validation in nanochannels of Ångstrom-level resolution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(38):32233–8.10.1021/acsami.8b11455Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Sartipzadeh O, Naghib SM, Shokati F, Rahmanian M, Majidzadeh-A K, Zare Y, et al. Microfluidic-assisted synthesis and modelling of monodispersed magnetic nanocomposites for biomedical applications. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):1397–1407.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0097Search in Google Scholar
[4] Wu T, Zhang D. Impact of adsorption on gas transport in nanopores. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23629.10.1038/srep23629Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Ding L, Wei Y, Li L, Zhang T, Wang H, Xue J, et al. MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):155.10.1038/s41467-017-02529-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Park HB, Kamcev J, Robeson LM, Elimelech M, Freeman BD. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science. 2017;356(6343):eaab0530.10.1126/science.aab0530Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Chang N, Gu ZY, Wang HF, Yan XP. Metal−organic-framework-based tandem molecular sieves as a dual platform for selective microextraction and high-resolution gas chromatographic separation of N-alkanes in complex matrixes. Anal Chem. 2011;83:7094–101.10.1021/ac2014004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Zhang J, Pei G, Zhang L. Molecular dynamics simulation of methane gas flow in nanopores. Petroleum. 2019;5(3):252–9.10.1016/j.petlm.2018.12.008Search in Google Scholar
[9] Wang Z, Cai K, Lu Y, Wu H, Li Y, Zhou Q. Insight into the working wavelength of hotspot effects generated by popular nanostructures. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):24–34.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0003Search in Google Scholar
[10] Wang R, Peng F, Song K, Feng G, Guo Z. Molecular dynamics study of interfacial properties in CO2, enhanced oil recovery. Fluid Phase Equil. 2018;467(15):25–32.10.1016/j.fluid.2018.03.022Search in Google Scholar
[11] Jin Z, Firoozabadi A. Flow of methane in shale nanopores at low and high pressure by molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Phys. 2015;143(10):104315.10.1063/1.4930006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Song X, Chen JK. A comparative study on poiseuille flow of simple fluids through cylindrical and slit-like nanochannels. Int J Heat Mass Tran. 2018;51(7):1770–9.10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.07.019Search in Google Scholar
[13] Liu Y, Wilcox J. Molecular simulation of CO2 adsorption in micro- and meso-porous carbons with surface heterogeneity. Int J Coal Geol. 2012;104(1):83–95.10.1016/j.coal.2012.04.007Search in Google Scholar
[14] Baek S, Akkutlu IY. Mean free path of gas molecules in organic nanochannels using molecular simulations. SPE J. 2019;24(6):2555–73.10.2118/198889-PASearch in Google Scholar
[15] Ma W, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Zhang L, Hu J, Jiang L. Miniature on-fiber extrinsic fabry-perot interferometric vibration sensors based on micro-cantilever beam. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):293–8.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0028Search in Google Scholar
[16] Arlemark EJ, Reese JM. Investigating the effect of solid boundaries on the gas molecular mean-free-path. Proceedings of the ASME 2009 7th international conference on nanochannels, microchannels, and minichannels, Pohang, South Korea; 2009 June 22–24. p. 397–405.10.1115/ICNMM2009-82080Search in Google Scholar
[17] Arlemark EJ, Dadzie SK, Reese JM. An extension to the Navier-Stokes equations to incorporate gas molecular collisions with boundaries. J Heat Transfer. 2010;132(4):041006.10.1115/1.4000877Search in Google Scholar
[18] Fichman M, Hetsroni G. Viscosity and slip velocity in gas flow in microchannels. Phys Fluids. 2005;17(12):123102.10.1063/1.2141960Search in Google Scholar
[19] Javadpour F, Fisher D, Unsworth M. Nanoscale gas flow in shale gas sediments. J Can Pet Technol. 2007;46(10):55–61.10.2118/07-10-06Search in Google Scholar
[20] Hong C, Shigeishi T, Asako Y, Faghri M. Experimental investigations of local friction factors of laminar and turbulent gas flows in smooth micro-tubes. Int J Heat Mass Transfer. 2020;158:120035.10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120035Search in Google Scholar
[21] Ma W, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Zhang L, Hu J, Jiang L. Miniature on-fiber extrinsic fabry-perot interferometric vibration sensors based on micro-cantilever beam. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):293–8.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0028Search in Google Scholar
[22] Choi SB, Barron RF, Warrington RO. Fluid flow and heat transfer in microtubes. Micromech Sens Actuat Syst. 1991;32:123–34.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Celata GP, Lorenzini M, Morini GL, Zummo G. Friction factor in micropipe gas flow under laminar, transition and turbulent flow regime. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2009;30(5):814–22.10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2009.02.015Search in Google Scholar
[24] Lorenzini M, Morini GL, Salvigni S. Laminar, transitional and turbulent fric- tion factors for gas flows in smooth and rough microtubes. Int J Therm Sci. 2010;49(2):248–55.10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2009.07.025Search in Google Scholar
[25] Roohi E, Darbandi M, Mirjalili V. DSMC solution of supersonic to choked sub- sonic flow in micro to nano channels. Proceedings of the ASME 6th international conference on nanochannels, microchannels and minichannels, Darmstadt, Germany; 2008 June 23–25. p. 985–93.10.1115/ICNMM2008-62282Search in Google Scholar
[26] Kermani EL, Roohi E, Porté-Agel F. Evaluating the modulated gradient model in large eddy simulation of channel flow with OpenFOAM. J Turbul. 2018;19(7):600–20.10.1080/14685248.2018.1483078Search in Google Scholar
[27] Arndt M, Nairz O, Vos-Andreae J, Keller C, van der Zouw G, Zeilinger A. Wave–particle duality of C60 molecules. Nature. 1999;401:680–2.10.1038/44348Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Wang X, Xu P, Han R, Ren J, Li L, Han N, et al. A review on the mechanical properties for thin film and block structure characterised by using nanoscratch test. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):628–44.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0055Search in Google Scholar
[29] Zurek WH. Decoherence and the transition from quantum to classical. Phys Today. 1991;1:36–44.10.1063/1.881293Search in Google Scholar
[30] Joos E, Zeh HD, Kiefer C, Giulini DJ, Kupsch J. Decoherence and the appearance of the classical world in quantum theory. Berlin: Springer; 1996.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Grisenti RE, Schöllkopf W, Toennies JP, Manson JR, Savas TA, Smith HI. He atom diffraction from nanostructure transmission gratings: the role of imperfections. Phys Rev A. 2000;61(3):033608.10.1103/PhysRevA.61.033608Search in Google Scholar
[32] Chapman MS, Hammond TD, Lenef A, Schmiedmayer J, Rubenstein RA, Smith E, et al. Photon scattering from atoms in an atom interferometer: coherence lost and regained. Phys Rev Lett. 1995;75(21):3783–7.10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.3783Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Werner SA, Colella R, Overhauser AW, Eagen CF. Observation of the phase shift of a neutron due to precession in a magnetic field. Phys Rev Lett. 1975;35:1053–5.10.1103/PhysRevLett.35.1053Search in Google Scholar
[34] Shayeghi A, Rieser P, Richter G, Sezer U, Rodewald JH, Geyer P, et al. Matter-wave interference of a native polypeptide. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1447.10.1038/s41467-020-15280-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Simionescu OG, Pachiu C, Ionescu O, Dumbrăvescu N, Buiu O, Popa RC, et al. Nanocrystalline graphite thin layers for low-strain, high-sensitivity piezoresistive sensing. Rev Adv Mater Sci. 2020;59(1):306–13.10.1515/rams-2020-0031Search in Google Scholar
[36] Kovachy T, Asenbaum P, Overstreet C, Donnelly CA, Dickerson SM, Sugarbaker A, et al. Quantum superposition at the half-metre scale. Nature. 2015;528:530–3.10.1038/nature16155Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Schätti J, Rieser P, Sezer U, Richter G, Geyer P, Rondina GG, et al. Pushing the mass limit for intact launch and photoionization of large neutral biopolymers. Commun Chem. 2018;1:93.10.1038/s42004-018-0095-ySearch in Google Scholar
[38] Parker RH, Yu C, Zhong W, Estey B, Müller H. Measurement of the fine-structure constant as a test of the standard model. Science. 2018;360(6385):191–5.10.1126/science.aap7706Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Rodewald J, Dörre N, Grimaldi A, Geyer P, Felix L, Mayor M, et al. Isotope-selective high-order interferometry with large organic molecules in free fall. New J Phys. 2018;20:033016.10.1088/1367-2630/aaade2Search in Google Scholar
[40] Nimmrichter S, Hornberger K, Haslinger P, Arndt M. Testing spontaneous localization theories with matter-wave interferometry. Phys Rev A. 2011;83(4):043621.10.1103/PhysRevA.83.043621Search in Google Scholar
[41] Zeng J. Quantum mechanics. 5th ed. Beijing: Science Press; 2019.Search in Google Scholar
[42] Jahangir A, Malik F, Muhammad N, Fayyaz R, Abbasi JN, Nazir A. Reflection phenomena of waves through rotating elastic medium with micro-temperature effect. Rev Adv Mater Sci. 2020;59(1):455–63.10.1515/rams-2020-0036Search in Google Scholar
[43] Basdevant JL, Dalibaed J. The quantum mechanics solver: how to apply quantum theory to modern physics. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2005.Search in Google Scholar
[44] Landau LD, Lifshiz EM. Quantum mechanics, non-relativistic theory. 3rd ed. Oxford: Pergamon Press; 1977.Search in Google Scholar
[45] Merzbacher E. Quantum mechanics. 3rd ed. New York: Wiley; 1970.Search in Google Scholar
[46] Robinett RW. Quantum mechanic: classical results, modern systems, and visualized examples. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006.10.1093/oso/9780198530978.001.0001Search in Google Scholar
[47] Da D. Vacuum design manual. 3rd ed. Beijing: National Defense Industrial Press; 2004.Search in Google Scholar
[48] Dash CS, Prabaharan SRS. Nano resistive memory (Re-RAM) devices and their applications. Rev Adv Mater Sci. 2019;58(1):248–70.10.1515/rams-2019-0014Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Xuefang Wang et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Improved impedance matching by multi-componential metal-hybridized rGO toward high performance of microwave absorption
- Pure-silk fibroin hydrogel with stable aligned micropattern toward peripheral nerve regeneration
- Effective ion pathways and 3D conductive carbon networks in bentonite host enable stable and high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
- Fabrication and characterization of 3D-printed gellan gum/starch composite scaffold for Schwann cells growth
- Synergistic strengthening mechanism of copper matrix composite reinforced with nano-Al2O3 particles and micro-SiC whiskers
- Deformation mechanisms and plasticity of ultrafine-grained Al under complex stress state revealed by digital image correlation technique
- On the deformation-induced grain rotations in gradient nano-grained copper based on molecular dynamics simulations
- Removal of sulfate from aqueous solution using Mg–Al nano-layered double hydroxides synthesized under different dual solvent systems
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel synthesis of TiO2-mixed metal oxide nanocatalyst for degradation of organic pollutant
- Electrophoretic deposition of graphene on basalt fiber for composite applications
- Polyphenylene sulfide-coated wrench composites by nanopinning effect
- Thermal conductivity and thermoelectric properties in 3D macroscopic pure carbon nanotube materials
- An effective thermal conductivity and thermomechanical homogenization scheme for a multiscale Nb3Sn filaments
- Friction stir spot welding of AA5052 with additional carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composite interlayer
- Improvement of long-term cycling performance of high-nickel cathode materials by ZnO coating
- Quantum effects of gas flow in nanochannels
- An approach to effectively improve the interfacial bonding of nano-perfused composites by in situ growth of CNTs
- Effects of nano-modified polymer cement-based materials on the bending behavior of repaired concrete beams
- Effects of the combined usage of nanomaterials and steel fibres on the workability, compressive strength, and microstructure of ultra-high performance concrete
- One-pot solvothermal synthesis and characterization of highly stable nickel nanoparticles
- Comparative study on mechanisms for improving mechanical properties and microstructure of cement paste modified by different types of nanomaterials
- Effect of in situ graphene-doped nano-CeO2 on microstructure and electrical contact properties of Cu30Cr10W contacts
- The experimental study of CFRP interlayer of dissimilar joint AA7075-T651/Ti-6Al-4V alloys by friction stir spot welding on mechanical and microstructural properties
- Vibration analysis of a sandwich cylindrical shell in hygrothermal environment
- Water barrier and mechanical properties of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch (TPS)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) blend bionanocomposites
- Strong quadratic acousto-optic coupling in 1D multilayer phoxonic crystal cavity
- Three-dimensional shape analysis of peripapillary retinal pigment epithelium-basement membrane layer based on OCT radial images
- Solvent regulation synthesis of single-component white emission carbon quantum dots for white light-emitting diodes
- Xanthate-modified nanoTiO2 as a novel vulcanization accelerator enhancing mechanical and antibacterial properties of natural rubber
- Effect of steel fiber on impact resistance and durability of concrete containing nano-SiO2
- Ultrasound-enhanced biosynthesis of uniform ZnO nanorice using Swietenia macrophylla seed extract and its in vitro anticancer activity
- Temperature dependence of hardness prediction for high-temperature structural ceramics and their composites
- Study on the frequency of acoustic emission signal during crystal growth of salicylic acid
- Controllable modification of helical carbon nanotubes for high-performance microwave absorption
- Role of dry ozonization of basalt fibers on interfacial properties and fracture toughness of epoxy matrix composites
- Nanosystem’s density functional theory study of the chlorine adsorption on the Fe(100) surface
- A rapid nanobiosensing platform based on herceptin-conjugated graphene for ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor cells in early breast cancer
- Improving flexural strength of UHPC with sustainably synthesized graphene oxide
- The role of graphene/graphene oxide in cement hydration
- Structural characterization of microcrystalline and nanocrystalline cellulose from Ananas comosus L. leaves: Cytocompatibility and molecular docking studies
- Evaluation of the nanostructure of calcium silicate hydrate based on atomic force microscopy-infrared spectroscopy experiments
- Combined effects of nano-silica and silica fume on the mechanical behavior of recycled aggregate concrete
- Safety study of malapposition of the bio-corrodible nitrided iron stent in vivo
- Triethanolamine interface modification of crystallized ZnO nanospheres enabling fast photocatalytic hazard-free treatment of Cr(vi) ions
- Novel electrodes for precise and accurate droplet dispensing and splitting in digital microfluidics
- Construction of Chi(Zn/BMP2)/HA composite coating on AZ31B magnesium alloy surface to improve the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility
- Experimental and multiscale numerical investigations on low-velocity impact responses of syntactic foam composites reinforced with modified MWCNTs
- Comprehensive performance analysis and optimal design of smart light pole for cooperative vehicle infrastructure system
- Room temperature growth of ZnO with highly active exposed facets for photocatalytic application
- Influences of poling temperature and elongation ratio on PVDF-HFP piezoelectric films
- Large strain hardening of magnesium containing in situ nanoparticles
- Super stable water-based magnetic fluid as a dual-mode contrast agent
- Photocatalytic activity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles: In vitro antimicrobial, biocompatibility, and molecular docking studies
- Hygrothermal environment effect on the critical buckling load of FGP microbeams with initial curvature integrated by CNT-reinforced skins considering the influence of thickness stretching
- Thermal aging behavior characteristics of asphalt binder modified by nano-stabilizer based on DSR and AFM
- Building effective core/shell polymer nanoparticles for epoxy composite toughening based on Hansen solubility parameters
- Structural characterization and nanoscale strain field analysis of α/β interface layer of a near α titanium alloy
- Optimization of thermal and hydrophobic properties of GO-doped epoxy nanocomposite coatings
- The properties of nano-CaCO3/nano-ZnO/SBR composite-modified asphalt
- Three-dimensional metallic carbon allotropes with superhardness
- Physical stability and rheological behavior of Pickering emulsions stabilized by protein–polysaccharide hybrid nanoconjugates
- Optimization of volume fraction and microstructure evolution during thermal deformation of nano-SiCp/Al–7Si composites
- Phase analysis and corrosion behavior of brazing Cu/Al dissimilar metal joint with BAl88Si filler metal
- High-efficiency nano polishing of steel materials
- On the rheological properties of multi-walled carbon nano-polyvinylpyrrolidone/silicon-based shear thickening fluid
- Fabrication of Ag/ZnO hollow nanospheres and cubic TiO2/ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts for RhB degradation
- Fabrication and properties of PLA/nano-HA composite scaffolds with balanced mechanical properties and biological functions for bone tissue engineering application
- Investigation of the early-age performance and microstructure of nano-C–S–H blended cement-based materials
- Reduced graphene oxide coating on basalt fabric using electrophoretic deposition and its role in the mechanical and tribological performance of epoxy/basalt fiber composites
- Effect of nano-silica as cementitious materials-reducing admixtures on the workability, mechanical properties and durability of concrete
- Machine-learning-assisted microstructure–property linkages of carbon nanotube-reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites produced by laser powder bed fusion
- Physical, thermal, and mechanical properties of highly porous polylactic acid/cellulose nanofibre scaffolds prepared by salt leaching technique
- A comparative study on characterizations and synthesis of pure lead sulfide (PbS) and Ag-doped PbS for photovoltaic applications
- Clean preparation of washable antibacterial polyester fibers by high temperature and high pressure hydrothermal self-assembly
- Al 5251-based hybrid nanocomposite by FSP reinforced with graphene nanoplates and boron nitride nanoparticles: Microstructure, wear, and mechanical characterization
- Interlaminar fracture toughness properties of hybrid glass fiber-reinforced composite interlayered with carbon nanotube using electrospray deposition
- Microstructure and life prediction model of steel slag concrete under freezing-thawing environment
- Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles from the seed coat waste of pistachio (Pistacia vera) and their effect on the growth of eggplant
- Study on adaptability of rheological index of nano-PUA-modified asphalt based on geometric parameters of parallel plate
- Preparation and adsorption properties of nano-graphene oxide/tourmaline composites
- A study on interfacial behaviors of epoxy/graphene oxide derived from pitch-based graphite fibers
- Multiresponsive carboxylated graphene oxide-grafted aptamer as a multifunctional nanocarrier for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics and bioactive compounds in cancer therapy
- Piezoresistive/piezoelectric intrinsic sensing properties of carbon nanotube cement-based smart composite and its electromechanical sensing mechanisms: A review
- Smart stimuli-responsive biofunctionalized niosomal nanocarriers for programmed release of bioactive compounds into cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- Photoremediation of methylene blue by biosynthesized ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposites using Callistemon viminalis leaves aqueous extract: A comparative study
- Study of gold nanoparticles’ preparation through ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and lyophilisation for possible use as markers in LFIA tests
- Review Articles
- Advance on the dispersion treatment of graphene oxide and the graphene oxide modified cement-based materials
- Development of ionic liquid-based electroactive polymer composites using nanotechnology
- Nanostructured multifunctional electrocatalysts for efficient energy conversion systems: Recent perspectives
- Recent advances on the fabrication methods of nanocomposite yarn-based strain sensor
- Review on nanocomposites based on aerospace applications
- Overview of nanocellulose as additives in paper processing and paper products
- The frontiers of functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites as chemical sensors
- Material advancement in tissue-engineered nerve conduit
- Carbon nanostructure-based superhydrophobic surfaces and coatings
- Functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites for smart optoelectronic applications
- Interfacial technology for enhancement in steel fiber reinforced cementitious composite from nano to macroscale
- Metal nanoparticles and biomaterials: The multipronged approach for potential diabetic wound therapy
- Review on resistive switching mechanisms of bio-organic thin film for non-volatile memory application
- Nanotechnology-enabled biomedical engineering: Current trends, future scopes, and perspectives
- Research progress on key problems of nanomaterials-modified geopolymer concrete
- Smart stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for the cancer therapy – nanomedicine
- An overview of methods for production and detection of silver nanoparticles, with emphasis on their fate and toxicological effects on human, soil, and aquatic environment
- Effects of chemical modification and nanotechnology on wood properties
- Mechanisms, influencing factors, and applications of electrohydrodynamic jet printing
- Application of antiviral materials in textiles: A review
- Phase transformation and strengthening mechanisms of nanostructured high-entropy alloys
- Research progress on individual effect of graphene oxide in cement-based materials and its synergistic effect with other nanomaterials
- Catalytic defense against fungal pathogens using nanozymes
- A mini-review of three-dimensional network topological structure nanocomposites: Preparation and mechanical properties
- Mechanical properties and structural health monitoring performance of carbon nanotube-modified FRP composites: A review
- Nano-scale delivery: A comprehensive review of nano-structured devices, preparative techniques, site-specificity designs, biomedical applications, commercial products, and references to safety, cellular uptake, and organ toxicity
- Effects of alloying, heat treatment and nanoreinforcement on mechanical properties and damping performances of Cu–Al-based alloys: A review
- Recent progress in the synthesis and applications of vertically aligned carbon nanotube materials
- Thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of mono and hybrid organic- and synthetic-based nanofluids: A critical review
- Recent advances in waste-recycled nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Waste-to-wealth
- Layup sequence and interfacial bonding of additively manufactured polymeric composite: A brief review
- Quantum dots synthetization and future prospect applications
- Approved and marketed nanoparticles for disease targeting and applications in COVID-19
- Strategies for improving rechargeable lithium-ion batteries: From active materials to CO2 emissions
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Improved impedance matching by multi-componential metal-hybridized rGO toward high performance of microwave absorption
- Pure-silk fibroin hydrogel with stable aligned micropattern toward peripheral nerve regeneration
- Effective ion pathways and 3D conductive carbon networks in bentonite host enable stable and high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
- Fabrication and characterization of 3D-printed gellan gum/starch composite scaffold for Schwann cells growth
- Synergistic strengthening mechanism of copper matrix composite reinforced with nano-Al2O3 particles and micro-SiC whiskers
- Deformation mechanisms and plasticity of ultrafine-grained Al under complex stress state revealed by digital image correlation technique
- On the deformation-induced grain rotations in gradient nano-grained copper based on molecular dynamics simulations
- Removal of sulfate from aqueous solution using Mg–Al nano-layered double hydroxides synthesized under different dual solvent systems
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel synthesis of TiO2-mixed metal oxide nanocatalyst for degradation of organic pollutant
- Electrophoretic deposition of graphene on basalt fiber for composite applications
- Polyphenylene sulfide-coated wrench composites by nanopinning effect
- Thermal conductivity and thermoelectric properties in 3D macroscopic pure carbon nanotube materials
- An effective thermal conductivity and thermomechanical homogenization scheme for a multiscale Nb3Sn filaments
- Friction stir spot welding of AA5052 with additional carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composite interlayer
- Improvement of long-term cycling performance of high-nickel cathode materials by ZnO coating
- Quantum effects of gas flow in nanochannels
- An approach to effectively improve the interfacial bonding of nano-perfused composites by in situ growth of CNTs
- Effects of nano-modified polymer cement-based materials on the bending behavior of repaired concrete beams
- Effects of the combined usage of nanomaterials and steel fibres on the workability, compressive strength, and microstructure of ultra-high performance concrete
- One-pot solvothermal synthesis and characterization of highly stable nickel nanoparticles
- Comparative study on mechanisms for improving mechanical properties and microstructure of cement paste modified by different types of nanomaterials
- Effect of in situ graphene-doped nano-CeO2 on microstructure and electrical contact properties of Cu30Cr10W contacts
- The experimental study of CFRP interlayer of dissimilar joint AA7075-T651/Ti-6Al-4V alloys by friction stir spot welding on mechanical and microstructural properties
- Vibration analysis of a sandwich cylindrical shell in hygrothermal environment
- Water barrier and mechanical properties of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch (TPS)/poly(lactic acid) (PLA) blend bionanocomposites
- Strong quadratic acousto-optic coupling in 1D multilayer phoxonic crystal cavity
- Three-dimensional shape analysis of peripapillary retinal pigment epithelium-basement membrane layer based on OCT radial images
- Solvent regulation synthesis of single-component white emission carbon quantum dots for white light-emitting diodes
- Xanthate-modified nanoTiO2 as a novel vulcanization accelerator enhancing mechanical and antibacterial properties of natural rubber
- Effect of steel fiber on impact resistance and durability of concrete containing nano-SiO2
- Ultrasound-enhanced biosynthesis of uniform ZnO nanorice using Swietenia macrophylla seed extract and its in vitro anticancer activity
- Temperature dependence of hardness prediction for high-temperature structural ceramics and their composites
- Study on the frequency of acoustic emission signal during crystal growth of salicylic acid
- Controllable modification of helical carbon nanotubes for high-performance microwave absorption
- Role of dry ozonization of basalt fibers on interfacial properties and fracture toughness of epoxy matrix composites
- Nanosystem’s density functional theory study of the chlorine adsorption on the Fe(100) surface
- A rapid nanobiosensing platform based on herceptin-conjugated graphene for ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor cells in early breast cancer
- Improving flexural strength of UHPC with sustainably synthesized graphene oxide
- The role of graphene/graphene oxide in cement hydration
- Structural characterization of microcrystalline and nanocrystalline cellulose from Ananas comosus L. leaves: Cytocompatibility and molecular docking studies
- Evaluation of the nanostructure of calcium silicate hydrate based on atomic force microscopy-infrared spectroscopy experiments
- Combined effects of nano-silica and silica fume on the mechanical behavior of recycled aggregate concrete
- Safety study of malapposition of the bio-corrodible nitrided iron stent in vivo
- Triethanolamine interface modification of crystallized ZnO nanospheres enabling fast photocatalytic hazard-free treatment of Cr(vi) ions
- Novel electrodes for precise and accurate droplet dispensing and splitting in digital microfluidics
- Construction of Chi(Zn/BMP2)/HA composite coating on AZ31B magnesium alloy surface to improve the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility
- Experimental and multiscale numerical investigations on low-velocity impact responses of syntactic foam composites reinforced with modified MWCNTs
- Comprehensive performance analysis and optimal design of smart light pole for cooperative vehicle infrastructure system
- Room temperature growth of ZnO with highly active exposed facets for photocatalytic application
- Influences of poling temperature and elongation ratio on PVDF-HFP piezoelectric films
- Large strain hardening of magnesium containing in situ nanoparticles
- Super stable water-based magnetic fluid as a dual-mode contrast agent
- Photocatalytic activity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles: In vitro antimicrobial, biocompatibility, and molecular docking studies
- Hygrothermal environment effect on the critical buckling load of FGP microbeams with initial curvature integrated by CNT-reinforced skins considering the influence of thickness stretching
- Thermal aging behavior characteristics of asphalt binder modified by nano-stabilizer based on DSR and AFM
- Building effective core/shell polymer nanoparticles for epoxy composite toughening based on Hansen solubility parameters
- Structural characterization and nanoscale strain field analysis of α/β interface layer of a near α titanium alloy
- Optimization of thermal and hydrophobic properties of GO-doped epoxy nanocomposite coatings
- The properties of nano-CaCO3/nano-ZnO/SBR composite-modified asphalt
- Three-dimensional metallic carbon allotropes with superhardness
- Physical stability and rheological behavior of Pickering emulsions stabilized by protein–polysaccharide hybrid nanoconjugates
- Optimization of volume fraction and microstructure evolution during thermal deformation of nano-SiCp/Al–7Si composites
- Phase analysis and corrosion behavior of brazing Cu/Al dissimilar metal joint with BAl88Si filler metal
- High-efficiency nano polishing of steel materials
- On the rheological properties of multi-walled carbon nano-polyvinylpyrrolidone/silicon-based shear thickening fluid
- Fabrication of Ag/ZnO hollow nanospheres and cubic TiO2/ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts for RhB degradation
- Fabrication and properties of PLA/nano-HA composite scaffolds with balanced mechanical properties and biological functions for bone tissue engineering application
- Investigation of the early-age performance and microstructure of nano-C–S–H blended cement-based materials
- Reduced graphene oxide coating on basalt fabric using electrophoretic deposition and its role in the mechanical and tribological performance of epoxy/basalt fiber composites
- Effect of nano-silica as cementitious materials-reducing admixtures on the workability, mechanical properties and durability of concrete
- Machine-learning-assisted microstructure–property linkages of carbon nanotube-reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites produced by laser powder bed fusion
- Physical, thermal, and mechanical properties of highly porous polylactic acid/cellulose nanofibre scaffolds prepared by salt leaching technique
- A comparative study on characterizations and synthesis of pure lead sulfide (PbS) and Ag-doped PbS for photovoltaic applications
- Clean preparation of washable antibacterial polyester fibers by high temperature and high pressure hydrothermal self-assembly
- Al 5251-based hybrid nanocomposite by FSP reinforced with graphene nanoplates and boron nitride nanoparticles: Microstructure, wear, and mechanical characterization
- Interlaminar fracture toughness properties of hybrid glass fiber-reinforced composite interlayered with carbon nanotube using electrospray deposition
- Microstructure and life prediction model of steel slag concrete under freezing-thawing environment
- Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles from the seed coat waste of pistachio (Pistacia vera) and their effect on the growth of eggplant
- Study on adaptability of rheological index of nano-PUA-modified asphalt based on geometric parameters of parallel plate
- Preparation and adsorption properties of nano-graphene oxide/tourmaline composites
- A study on interfacial behaviors of epoxy/graphene oxide derived from pitch-based graphite fibers
- Multiresponsive carboxylated graphene oxide-grafted aptamer as a multifunctional nanocarrier for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics and bioactive compounds in cancer therapy
- Piezoresistive/piezoelectric intrinsic sensing properties of carbon nanotube cement-based smart composite and its electromechanical sensing mechanisms: A review
- Smart stimuli-responsive biofunctionalized niosomal nanocarriers for programmed release of bioactive compounds into cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- Photoremediation of methylene blue by biosynthesized ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposites using Callistemon viminalis leaves aqueous extract: A comparative study
- Study of gold nanoparticles’ preparation through ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and lyophilisation for possible use as markers in LFIA tests
- Review Articles
- Advance on the dispersion treatment of graphene oxide and the graphene oxide modified cement-based materials
- Development of ionic liquid-based electroactive polymer composites using nanotechnology
- Nanostructured multifunctional electrocatalysts for efficient energy conversion systems: Recent perspectives
- Recent advances on the fabrication methods of nanocomposite yarn-based strain sensor
- Review on nanocomposites based on aerospace applications
- Overview of nanocellulose as additives in paper processing and paper products
- The frontiers of functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites as chemical sensors
- Material advancement in tissue-engineered nerve conduit
- Carbon nanostructure-based superhydrophobic surfaces and coatings
- Functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites for smart optoelectronic applications
- Interfacial technology for enhancement in steel fiber reinforced cementitious composite from nano to macroscale
- Metal nanoparticles and biomaterials: The multipronged approach for potential diabetic wound therapy
- Review on resistive switching mechanisms of bio-organic thin film for non-volatile memory application
- Nanotechnology-enabled biomedical engineering: Current trends, future scopes, and perspectives
- Research progress on key problems of nanomaterials-modified geopolymer concrete
- Smart stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for the cancer therapy – nanomedicine
- An overview of methods for production and detection of silver nanoparticles, with emphasis on their fate and toxicological effects on human, soil, and aquatic environment
- Effects of chemical modification and nanotechnology on wood properties
- Mechanisms, influencing factors, and applications of electrohydrodynamic jet printing
- Application of antiviral materials in textiles: A review
- Phase transformation and strengthening mechanisms of nanostructured high-entropy alloys
- Research progress on individual effect of graphene oxide in cement-based materials and its synergistic effect with other nanomaterials
- Catalytic defense against fungal pathogens using nanozymes
- A mini-review of three-dimensional network topological structure nanocomposites: Preparation and mechanical properties
- Mechanical properties and structural health monitoring performance of carbon nanotube-modified FRP composites: A review
- Nano-scale delivery: A comprehensive review of nano-structured devices, preparative techniques, site-specificity designs, biomedical applications, commercial products, and references to safety, cellular uptake, and organ toxicity
- Effects of alloying, heat treatment and nanoreinforcement on mechanical properties and damping performances of Cu–Al-based alloys: A review
- Recent progress in the synthesis and applications of vertically aligned carbon nanotube materials
- Thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of mono and hybrid organic- and synthetic-based nanofluids: A critical review
- Recent advances in waste-recycled nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Waste-to-wealth
- Layup sequence and interfacial bonding of additively manufactured polymeric composite: A brief review
- Quantum dots synthetization and future prospect applications
- Approved and marketed nanoparticles for disease targeting and applications in COVID-19
- Strategies for improving rechargeable lithium-ion batteries: From active materials to CO2 emissions

