Abstract
C20H13CdClN2O5, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 11.4994(9) Å, b = 13.1171(10) Å, c = 13.0233(10) Å, β = 109.126(8)°, V = 1856.0(3) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0341, wR ref(F 2) = 0.0779, T = 293 K.
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| Size: | 0.25 × 0.16 × 0.11 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.36 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 26.0°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 8934, 3648, 0.037 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 3019 |
| N(param)refined: | 265 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.6360 (3) | 0.4471 (3) | 0.7066 (3) | 0.0310 (8) |
| C2 | 0.7252 (3) | 0.4170 (3) | 0.8154 (2) | 0.0264 (7) |
| C3 | 0.7879 (3) | 0.3245 (2) | 0.8325 (3) | 0.0271 (7) |
| C4 | 0.8766 (3) | 0.3002 (3) | 0.9311 (3) | 0.0286 (8) |
| C5 | 0.9014 (3) | 0.3704 (3) | 1.0142 (3) | 0.0444 (10) |
| H5 | 0.961244 | 0.356168 | 1.080536 | 0.053* |
| C6 | 0.8383 (4) | 0.4618 (3) | 1.0000 (3) | 0.0501 (11) |
| H6 | 0.854872 | 0.508299 | 1.056891 | 0.060* |
| C7 | 0.7508 (4) | 0.4841 (3) | 0.9012 (3) | 0.0397 (9) |
| H7 | 0.708302 | 0.545582 | 0.892443 | 0.048* |
| C8 | 0.9412 (3) | 0.1985 (3) | 0.9473 (3) | 0.0350 (8) |
| C9 | 0.8172 (4) | 0.2793 (3) | 0.4820 (3) | 0.0515 (11) |
| H9 | 0.762374 | 0.247995 | 0.510980 | 0.062* |
| C10 | 0.9216 (5) | 0.2247 (4) | 0.4801 (4) | 0.0697 (14) |
| H10 | 0.936048 | 0.158934 | 0.508066 | 0.084* |
| C11 | 1.0008 (4) | 0.2699 (5) | 0.4365 (4) | 0.0727 (16) |
| H11 | 1.069858 | 0.234617 | 0.433903 | 0.087* |
| C12 | 0.9793 (3) | 0.3694 (4) | 0.3956 (3) | 0.0501 (11) |
| C13 | 1.0589 (4) | 0.4216 (5) | 0.3493 (4) | 0.0720 (16) |
| H13 | 1.129391 | 0.389251 | 0.345710 | 0.086* |
| C14 | 1.0331 (4) | 0.5172 (5) | 0.3108 (4) | 0.0737 (17) |
| H14 | 1.086825 | 0.549670 | 0.281352 | 0.088* |
| C15 | 0.9258 (4) | 0.5702 (4) | 0.3138 (3) | 0.0536 (12) |
| C16 | 0.8968 (5) | 0.6689 (4) | 0.2771 (3) | 0.0694 (15) |
| H16 | 0.946414 | 0.703985 | 0.245235 | 0.083* |
| C17 | 0.7956 (5) | 0.7142 (4) | 0.2878 (4) | 0.0704 (14) |
| H17 | 0.776304 | 0.781093 | 0.264727 | 0.085* |
| C18 | 0.7206 (4) | 0.6603 (3) | 0.3336 (3) | 0.0514 (11) |
| H18 | 0.650991 | 0.692135 | 0.339877 | 0.062* |
| C19 | 0.8469 (3) | 0.5206 (3) | 0.3599 (3) | 0.0349 (9) |
| C20 | 0.8726 (3) | 0.4183 (3) | 0.4007 (3) | 0.0363 (9) |
| Cd1 | 0.61898 (2) | 0.46910 (2) | 0.44675 (2) | 0.02491 (10) |
| Cl1 | 0.75343 (9) | 0.23209 (7) | 0.73064 (7) | 0.0468 (3) |
| N1 | 0.7938 (3) | 0.3728 (2) | 0.4446 (2) | 0.0356 (7) |
| N2 | 0.7446 (3) | 0.5658 (3) | 0.3685 (2) | 0.0376 (7) |
| O1 | 0.6733 (2) | 0.4381 (2) | 0.62756 (19) | 0.0425 (6) |
| O2 | 0.5343 (2) | 0.4825 (2) | 0.70580 (19) | 0.0419 (7) |
| O3 | 1.0328 (2) | 0.1897 (2) | 0.9177 (2) | 0.0507 (7) |
| O4 | 0.8970 (3) | 0.1315 (2) | 0.9909 (2) | 0.0545 (7) |
| O1W | 0.4311 (7) | 0.5239 (5) | 0.8766 (5) | 0.142 (2) |
| H1WA | 0.461801 | 0.508497 | 0.827478 | 0.213* |
| H1WB | 0.374252 | 0.480311 | 0.869334 | 0.213* |
Source of materials
A mixture of 0.0198 g Cd(NO3)2 ⋅ 4H2O (0.10 mmol), 0.0198 g 1,10-phenanthroline monohydrate (0.10 mmol), 0.0200 g 2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (0.10 mmol), 0.008 g NaOH (0.20 mmol) was added to 10 mL water and stirred to form a clear solution, then transferred to a 25 mL Teflon-lined autoclave and heated at 413 K in an oven for 72 h, cooled to room temperature. Colorless crystals were washed by deionized water and air-dried, yield 43% (based on 2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid).
Experimental details
The structure was solved by Direct Methods with the Shelxs-2018 program. All H-atoms from C atoms were positioned with idealized geometry and refined isotropically (U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C)) using a riding model with C—H = 0.930 Å. The H-atoms from O atoms positioned with Q peaks refined isotropically with the distance of O—H = 0.850 Å (U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O)). No suitable receptor was found for O1W—H1WB after careful refinement, resulting a B alert in the checkcif report.
Comment
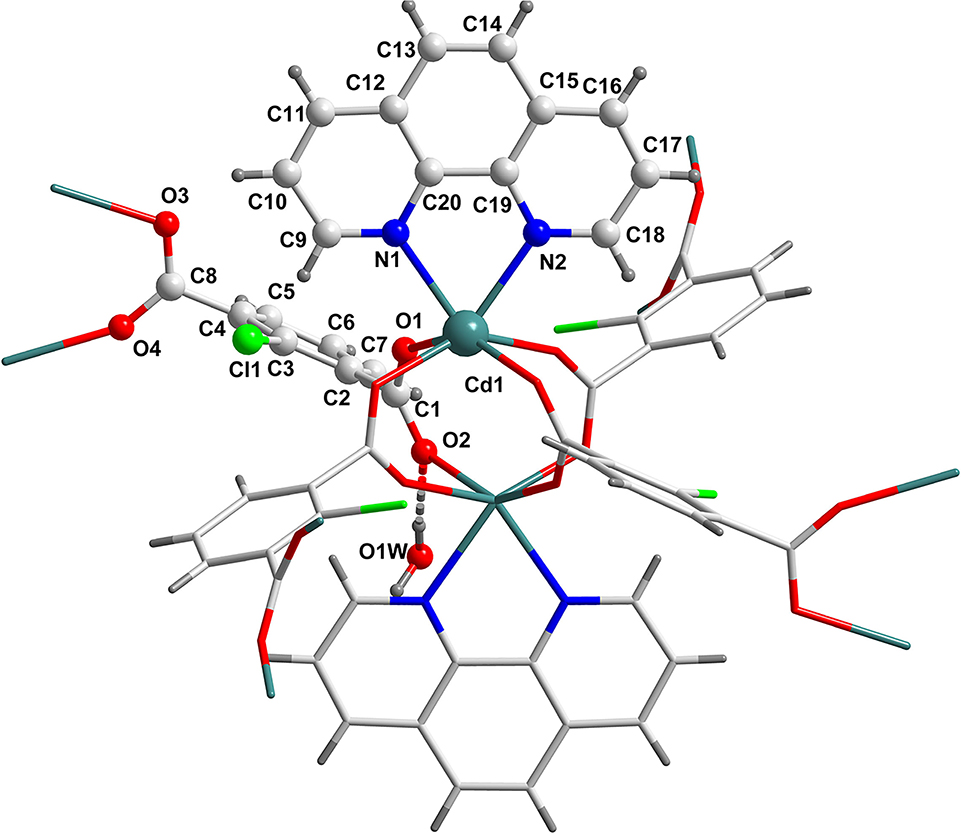
Substituents play a key role in the synthesis of metal-organic complexes. Many Cd(II) complexes based on isophthalic acid and its derivatives combining 1,10-phe-nanthroline have been published elsewhere, including isophthalate [5, 6], 5-substituted isophthalate (such as 5-methyl [7], 5-hydroxy [8], 5-iodo [9], 5-nitro [10], 5-ethoxyl [11], 5-phenyl [12], 5-(benzyloxy) [13], 5–ferrocene [14], 5-(((4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl)amino) [15], 5-((1H-benzimidazol-2-ylsulfanyl) [16] and 5-(1,3-benzo-thiazol-2-yl)) [17], 4-substituted isophthalic acid (4-(pyridin-4-yl)) [18], multi-substituted isophthalic acid (4,6-dimethyl-5-nitro [19] and 5-amino-2,4,6-triiodo [20]), and 2-substituted isophthalate (2-hydroxy [21]). Almost all the cadmium complexes mentioned above are 1D structures. It’s interesting that when the target ligand 2-substituted isophthalic acid, 2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid was used to synthesize Cd(II) complexes, a novel 2D structure was obtained.
The title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/n (no. 14), with the formula C20H13CdClN2O5. The asymmetric unit is composed of one Cd(II) cation, one 1,10-phena-nthroline, one completely deprotonated 2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylate, and one crystal water molecule. The Cd1 center is coordinated by two nitrogen atoms (N1, N2) form a bidentate 1,10-phenanthroline and four carboxyl oxygen atoms (O1, O2 (code: 1 − x. 1 − y, 1 − z), O3 (code: −0.5 + x, 0.5 − y, −0.5 + z), O4 (code: 1.5 − x, 0.5 + y, 1.5 − z)) of four different 2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylate anions in a trigonal prismatic geometry. All of the carboxyl groups are bismonodentate, linking two crystallographic Cd(II) to form a dimer, which is decorated by two 1,10-phenanthroline to generate the second building units (SBUs). The SBUs are bridged together by the μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxy-late anions to generate a 2D structure. The distances of the Cd1—N, Cd—O, and the two Cd(II) cations in the same SBUs are comparable with the similar di–Cd(II) complex, respectively [22, 23].
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: None declared.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. CrysAlisPRO 1.171.38.43f; Rigaku OD: Oxfordshire, England, 2015.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. Using phases to determine the space group. Acta Crystallogr. 2018, A74, a353; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767318096472.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Zhang, L.-Y., Liu, G.-F., Zheng, S.-L., Ye, B.-H., Zhang, X.-M., Chen, X.-M. Helical ribbons of cadmium(II) and zinc(II) dicarboxylates with bipyridyl-like chelates-syntheses, crystal structures and photoluminescence. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 2965–2971; https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200300061.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Shi, X., Zhu, G., Wang, X., Li, G., Fang, Q., Zhao, X., Wu, G., Tian, G., Xue, M., Wang, R., Qiu, S. Polymeric frameworks constructed from a metal-organic coordination compound, in 1–D and 2–D systems: synthesis, crystal structures, and fluorescent properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 5, 341–346; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg049884e.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Wang, J., Lin, P., Du, S.-W. Temperature dependent assembly, structural diversity and luminescent property in two novel Cd coordination polymers. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2015, 34, 945–952.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Kariem, M., Yawer, M., Sheikh, H. N. Solvent induced synthesis, structure and properties of coordination polymers based on 5-hydroxyisophthalic acid as linker and 1,10-phenanthroline as auxiliary ligand. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 231, 239–247; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2015.08.036.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Zang, S.-Q., Fan, Y.-J., Li, J.-B., Hou, H.-W., Mak, T. C. W. Halogen bonding in the assembly of coordination polymers based on 5-iodo-isophthalic acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 3395–3405; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg200022j.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Ren, H., Yu, L.-X., Zhang, L.-R., Chen, Y.-L., Jiang, J.-H., Zhang, P., Song, T.-Y. Synthesis, structures and properties of two carboxylate-bridged coordination polymers with linear and ladder chain motifs. J. Coord. Chem. 2008, 61, 3960–3972; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970802187142.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Qin, W.-Q., Zhang, J.-R., Tian, X.-K., Yang, X.-G., Guo, Y.-M. Donor-acceptor structure of a coordination polymer with long-lived room temperature phosphorescence and angle-dependent polarized emission. CrystEngComm 2021, 23, 3094–3098; https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ce00303h.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Wu, D., Huang, W., Xu, J., Kirillov, A., Jiang, J. Tuning topological and dimensional versatility from 1D to 3D of Zn/Cd luminescent biphenyl-3,5-dicarboxylate coordination polymers by ancillary ligand. J. Coord. Chem. 2016, 69, 2200–2209.10.1080/00958972.2016.1196812Suche in Google Scholar
13. Zhang, D.-W., Zhao, G.-Y. Synthesis, crystal structure, and photoluminescent property of a new 1D→2D interdigitated framework. Synth. React. Inorg., Met.-Org., Nano-Met. Chem. 2015, 45, 524–526; https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2013.841212.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Li, X., Wu, B.-L., Liu, W., Niu, C.-Y., Niu, Y.-Y., Zhang, H.-Y. Syntheses, crystal structures, and magnetic properties of five new coordination compounds bearing ferrocenedicarboxylate ligands. J. Coord. Chem. 2009, 62, 3142–3156; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958970903045280.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Huang, M.-L., Wu, W.-S., Chen, W.-Z. Syntheses, crystal structures and fluorescent properties of one-dimensional coordination polymers with N-p-tolylsulfonyl-5-aminoisophthalic acid. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 33, 66–72.Suche in Google Scholar
16. Yin, W.-Y., Zhuang, G.-Y., Huang, Z.-L., Cheng, H.-J., Zhou, L., Ma, H., Wang, H., Tang, X.-Y., Ma, Y.-S., Yuan, R.-X. Structural diversification and photocatalytic properties of three Cd(II) coordination polymers decorated with different auxiliary ligands. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 235, 93–99; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2015.12.020.Suche in Google Scholar
17. Liu, L., Ran, Y., DuWang, J. Z., Liu, M., Mu, Y. A luminescent Cd(ii) coordination polymer as a multi-responsive fluorescent sensor for Zn2+, Fe3+ and Cr2O72− in water with fluorescence enhancement or quenching. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11266–11272; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra10203b.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
18. Song, W., Xu, X.-L., Yang, Y.-J., Li, S. H. Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ3-5-carboxy-2-(pyridin-4-yl)benzoato- κ5O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴)(1,10- phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)cadmium(II)], C100H60N12O16Cd4. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2018, 233, 755–756; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2017-0299.Suche in Google Scholar
19. Xu, Y.-M., Zhao, X.-L., Hu, T.-P. Synthesis, structure and thermal stability of a cadmium coordination polymer: [Cd(phen)(4,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-isophthalic acid)]n. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2011, 30, 1442–1446.Suche in Google Scholar
20. Zhang, K.-L., Chang, Y., Zhang, J.-B., Yuan, L.-M., Deng, Y., Diao, G.-W., Ng, S. W. Synthesis, crystal structures and characterization of four coordination polymers based on 5-amino-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalic acid. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 1263–1272; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2011.03.050.Suche in Google Scholar
21. Zhao, Q., Chen, X., Huang, G. The crystal structure of catena- poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-(μ3-2-hydroxybenzene- 1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5O,O′:O″,O‴:O‴)- cadmium(II)], C20H12CdN2O5. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2022, 237, 1139–1141 https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022–0389.10.1515/ncrs-2022-0389Suche in Google Scholar
22. Li, J.-X., Du, Z.-X. A binuclear cadmium(II) cluster based on π ⃛ π stacking and halogen ⃛ halogen interactions: synthesis, crystal analysis and fluorescent properties. J. Cluster Sci. 2020, 31, 507–511; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01666-w.Suche in Google Scholar
23. Yang, Y.-Q., Li, C.-H., Li, W., Kuang, Y.-F. Synthesis, crystal structure, luminescent and electrochemical properties of a new binuclear Cd(II) complex with 2,4–DAA as ligand. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 26, 1890–1894.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7

