Abstract
Ca11As10, tetragonal, I4/mmm (no. 139), a = 11.2532(1) Å, c = 16.2351(4) Å, and V = 2055.92(6) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0347, wR ref (F 2) = 0.0931, T = 150 K.
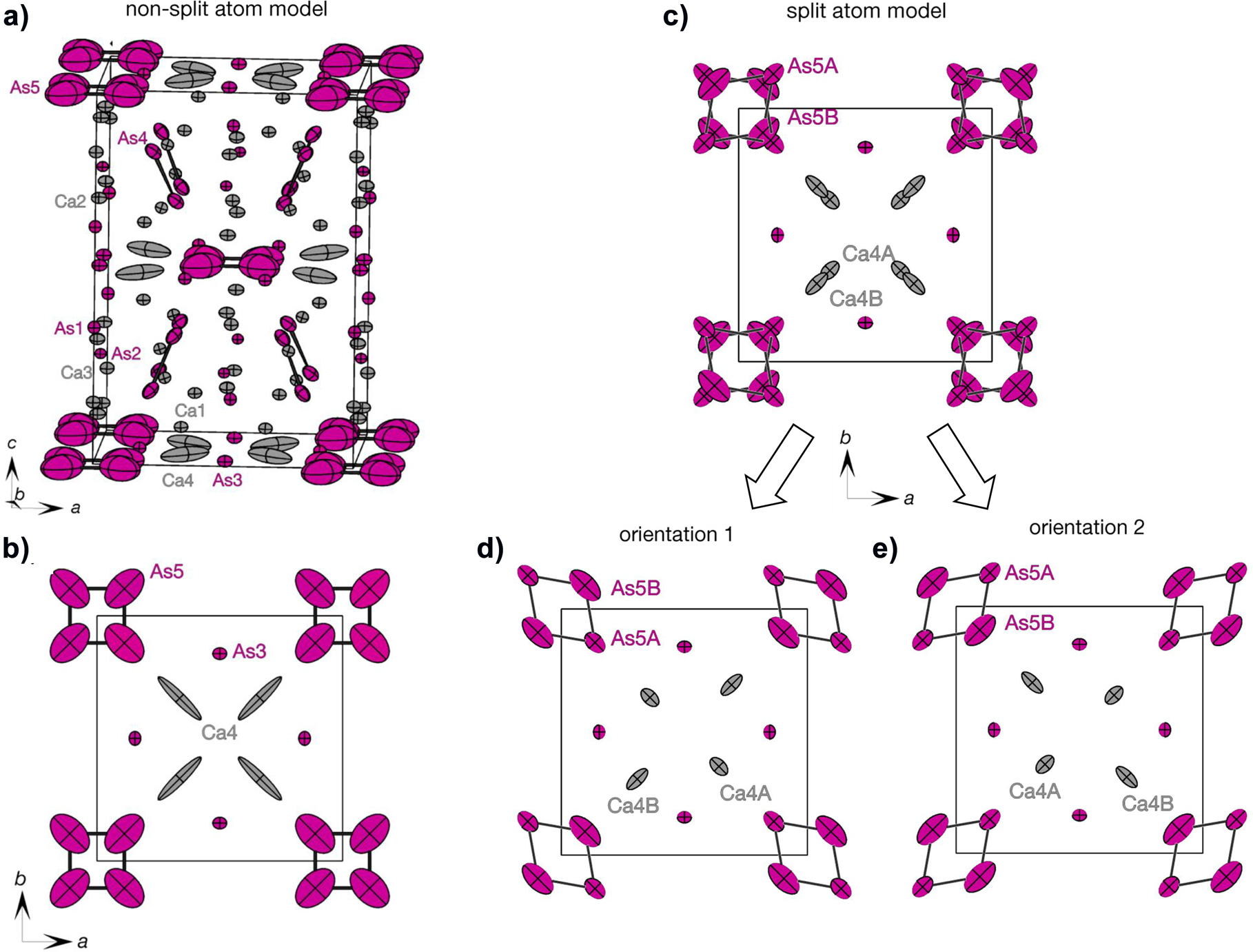
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Plate, dark grey |
| Size: | 0.2 × 0.12 × 0.03 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 18.75 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur, φ and ω-scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 27.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 15,111, 722, 0.064 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 596 |
| N(param)refined: | 49 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2, 3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.36542 (10) | 0.0110 (4) |
| As2 | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.2500 | 0.0083 (4) |
| As3 | 0.15420 (11) | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.0123 (3) |
| As4 | 0.20819 (6) | 0.20819 (6) | 0.18043 (6) | 0.0178 (3) |
| As5Aa | 0.1369 (7) | 0.1369 (7) | 0.0000 | 0.095 (3) |
| As5Bb | 0.0948 (5) | 0.0948 (5) | 0.0000 | 0.067 (2) |
| Ca1 | 0.33766 (15) | 0.0000 | 0.10361 (10) | 0.0132 (4) |
| Ca2 | 0.25281 (15) | 0.0000 | 0.31152 (10) | 0.0121 (4) |
| Ca3 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.1657 (2) | 0.0123 (7) |
| Ca4Aa | 0.3592 (7) | 0.3592 (7) | 0.0000 | 0.0218 (19) |
| Ca4Bb | 0.3077(9) | 0.3077 (9) | 0.0000 | 0.030 (2) |
-
Occupanies: a0.506(16), b0.494(16).
Crystal structure of Ca11As10 (Ca – light gray and As – magenta): a) and b) non-split atom model; c)–e) split atom model. Atoms are represented as atomic displacement ellipsoids with 90% probability level. The covalent As–As bonds are shown in black.
Source of material
The title compound Ca11As10 has been synthesized via high-temperature solid-state reaction. Sample preparation and manipulations were done under protective atmosphere in an argon-filled glove box (MBraun 20G, argon purity 99.998%). Starting materials were elements of high purity: ingots of calcium (Alfa Aesar, 99.5%) and arsenic pieces (ChemPur, 99.999%). The compound Ca11As10 was prepared by placing Ca and As (11:10) in a graphitized silica ampoule and heat-treated in a Muffel furnace. The sealed ampoule was heated to 1173 K in 6 h, held at this temperature for 48 h and then cooled to 973 K in 42 h. After 24 h at 973 K the ampoule was cooled to room-temperature with a rate of 4.5 K/min.
Experimental details
The ampoule was opened in the glove box and capillaries (XRD capillaries, Hilgenberg, 0.3 mm inner diameter) were prepared for powder X-ray diffraction analysis. The product was investigated by means of powder X-ray diffraction (Stoe StadiP with Ge (111) monochromized Cu-K
α
1 radiation (1.54056 Å)). An external Si standard was used for data correction. Single crystal X-ray diffraction was performed with an Oxford Diffractions Xcalibur 3 with graphite monochromatized Mo-K
α
radiation (0.71071 Å) at 150 K. The sample is air and moisture sensitive. The powder X-ray diffraction pattern for the sample Ca–As (11:10) shows the binary phases Ca11As10 and CaAs. The tetragonal lattice parameters were obtained from least-square fits of the powder data using Rietveld refinement. Single crystal data for Ca11As10 were collected at 150 K under constant N2-flow. An empirical absorption correction was applied [1]. The starting atomic parameters for Ca11As10 were deduced from an automatic interpretation of Direct Methods with SHELXS-97 [2]. The structures were then refined using SHELXL-97 (full-matrix least-square on
Discussion
So far, seven binary Ca–As compounds have been investigated: CaAs3, Ca2As3, CaAs, Ca16As11, Ca4As3, Ca5As3 and Ca2As [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10]. All binary phases except Ca5As3 and Ca2As, which are intermetallic compounds, belong to the Zintl phases with polyanionic substructures. The dimensionality of the polyanionic substructure decreases with increasing Ca-content. In CaAs3 the As-substructure is made up by [As3]2− networks, in Ca2As3 the As forms [As6]8− chairs and in CaAs and Ca16As11 compounds the [As–As]4− dumbbells are present. In the structure of Zintl phase Ca4As3 both [As–As]4− dumbbells and isolated As3− are found as polyanions.
The title compound Ca11As10 is the second (besides Eu11As10 [11]) As-representative of the Ho11Ge10 structure type [12]. The structure contains 8 [As2]4− dumbbells, 2 tetrameric [As4]4− units, 16 isolated As3− anions and 44 Ca2+ cations and thus corresponds to an electron-precise Zintl phase. The disorder on the 8h position of As5 with rather large anisotropic displacement parameters is similarly present in other Ho11Ge10 – type representatives [13], [14], [15], [16], and a reduction in symmetry to the orthorhombic Immm space group (as was applied for Ba11Sb10 [17]) does not solve the disorder problem. The crystal structure was therefore refined in the tetragonal I4/mmm space group but the 8h Wyckoff position of As5 and Ca4 were each split into two positions: As5A and As5B, Ca4A and Ca4B, respectively. The occupancy for Ca4A and Ca4B as well as for As5A and As5B was refined to 0.5 each. The distances between the As atoms in the dumbbell of 2.622(1) Å and in the [As4]4− unit of 2.650(10) Å are slightly longer as in other binary Ca–As compounds. The distances between As atoms and Ca atoms range from 2.718(13) Å to 3.538(11) Å within the first coordination sphere.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: VH thanks the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation, Grant HL 62/3-1) for funding.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. CrysAlis RED Scale3/ABSPACK, Version 1.171.33.34d; Oxford Diffraction: Poland Sp. z o.o., 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXS-2014, Program for the Determination of Crystal Structure; University of Goettingen: Goettingen, Germany, 2014.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXL-2014, Program for Crystal Structure Refinement; University of Goettingen: Goettingen, Germany, 2014.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brice, J. F., Courtois, A., Protas, J., Aubry, J. Preparation et etude structurale d’un triarseniure de calcium: CaAs3. J. Solid State Chem. 1976, 17, 393–397; https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-4596(76)80009-6.Search in Google Scholar
5. Deller, K., Eisenmann, B. Die Kristallstruktur des Ca2As3. Z. Naturforsch. 1976, 31b, 1023–1027; https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-1976-0804.Search in Google Scholar
6. Iandelli, A., Franceschi, E. On the crystal structure of the compounds CaP, SrP, CaAs, SrAs and EuAs. J. Less Common. Met. 1973, 30, 211–216; https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5088(73)90107-0.Search in Google Scholar
7. Leon-Escamilla, E. A., Hurng, W. M., Peterson, E. S., Corbett, J. D. Synthesis, structure, and properties of Ca16Sb11, a complex Zintl phase. Twelve other isotypic compounds formed by divalent metals and pnictogens. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 36, 703–710; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic961035w.Search in Google Scholar
8. Hoffmann, A. V., Hlukhyy, V., Fassler, T. F. Ca4As3 – a new binary calcium arsenide. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, E71, 1548–1550; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989015022367.Search in Google Scholar
9. Hütz, A., Nagorsen, G. Die Kristallstruktur der intermetallischen phase Ca5As3. Z. Metallkd. 1975, 66, 314; https://doi.org/10.1515/ijmr-1975-660515.Search in Google Scholar
10. Hütz, A., Nagorsen, G. Die Kristallstruktur der intermetallischen Phase Ca2As. Z. Metallkd. 1974, 65, 618; https://doi.org/10.1515/ijmr-1974-650910.Search in Google Scholar
11. Taylor, J. B., Calvert, L. D., Utsunomiya, Z., Wang, Y., Despault, J. G. Rare earth arsenides: the metal-rich Europium arsenides. J. Less Common Met. 1978, 57, 39–51; https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5088(78)90161-3.Search in Google Scholar
12. Smith, G. S., Johnson, Q., Tharp, A. G. The crystal structure of Ho11Ge10. Acta Crystallogr. 1967, 23, 640–644; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0365110x67003329.Search in Google Scholar
13. Deller, K., Eisenmann, B. Zur Kenntnis von Ca11Sb10 und Ca11Bi10. Z. Naturforsch. 1976, 31b, 29–34; https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-1976-0105.Search in Google Scholar
14. Schmelczer, R., Schwarzenbach, D., Hulliger, F. The crystal structure of Eu11Sb10. Z. Naturforsch. 1979, 34b, 1213–1217; https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-1979-0909.Search in Google Scholar
15. Derrien, G., Tillard-Charbonnel, M., Manteghetti, A., Monconduit, L., Belin, C. Synthesis and crystal structure of M11X10 compounds (M–Sr, Ba; X–Bi, Sb). Electronic requirements and chemical bonding. J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 164, 169–175.10.1006/jssc.2001.9470Search in Google Scholar
16. Clark, H. L., Simpson, H. D., Steinfink, H. Crystal structure of Yb11Sb10. Inorg. Chem. 1970, 9, 1962–1964; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic50090a049.Search in Google Scholar
17. Emmerling, F., Längin, N., Pickhard, F., Wendorff, M., Röhr, C. Verbindungen mit Pentelid–Hanteln M2: A11M6 und A11M10. Z. Naturforsch. 2004, 59b, 7–16; https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-2004-0102..Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7

