Abstract
C27H26P2S2, tetragonal, I4 (no. 79), a = 16.9196(12) Å, c = 9.4187(8) Å, V = 2696.3(4) Å3, Z = 4, R gt(F) = 0.0341, wR ref(F 2) = 0.0726, T = 173(2) K.
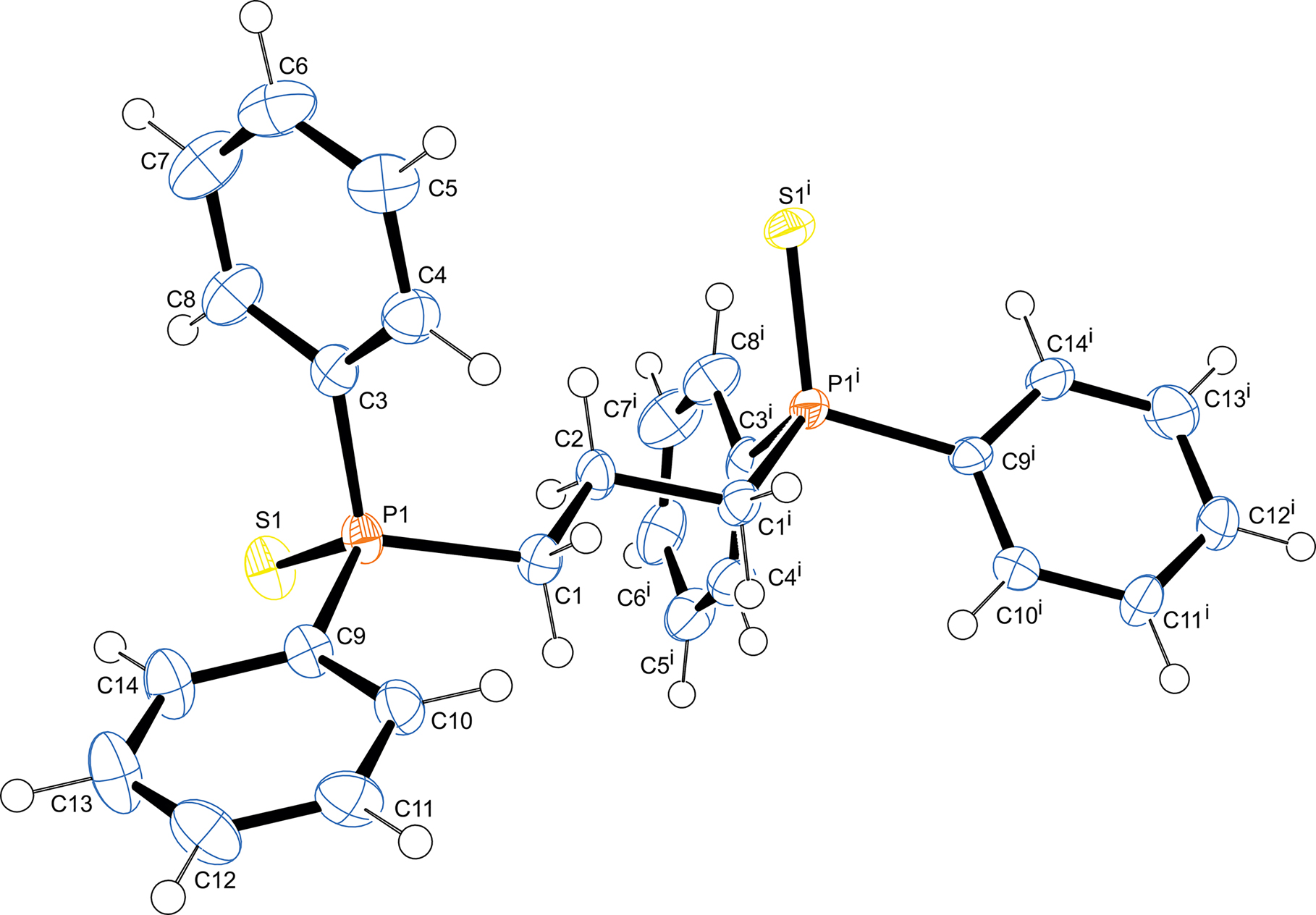
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless needle |
| Size: | 0.43 × 0.12 × 0.04 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.33 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 Venture Photon, ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl) measured, N(hkl) unique, R int: | 23,943, 2519, 0.100 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl) gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2150 |
| N(param) refined: | 141 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Shelx [2], WinGX [3], Platon [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.4835 (2) | 0.0725 (2) | 0.3939 (4) | 0.0230 (8) |
| H1A | 0.530652 | 0.082969 | 0.453356 | 0.028* |
| H1B | 0.438982 | 0.060132 | 0.458351 | 0.028* |
| C2 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.2994 (6) | 0.0249 (10) |
| H2Aa | 0.546234 | 0.010499 | 0.237823 | 0.03* |
| H2Ba | 0.453767 | −0.010499 | 0.23782 | 0.03* |
| C3 | 0.5493 (2) | 0.1916 (2) | 0.2026 (3) | 0.0241 (8) |
| C4 | 0.6214 (2) | 0.1926 (2) | 0.2714 (4) | 0.0317 (9) |
| H4 | 0.624941 | 0.174708 | 0.366807 | 0.038* |
| C5 | 0.6884 (3) | 0.2196 (2) | 0.2026 (4) | 0.0374 (10) |
| H5 | 0.737836 | 0.219749 | 0.250541 | 0.045* |
| C6 | 0.6837 (3) | 0.2461 (3) | 0.0646 (4) | 0.0424 (11) |
| H6 | 0.72944 | 0.265745 | 0.018098 | 0.051* |
| C7 | 0.6132 (3) | 0.2441 (3) | −0.0050 (4) | 0.0485 (12) |
| H7 | 0.610532 | 0.260883 | −0.101114 | 0.058* |
| C8 | 0.5450 (3) | 0.2178 (2) | 0.0628 (4) | 0.0368 (10) |
| H8 | 0.495885 | 0.217673 | 0.01396 | 0.044* |
| C9 | 0.4430 (2) | 0.2384 (2) | 0.4239 (4) | 0.0224 (8) |
| C10 | 0.4700 (2) | 0.2333 (2) | 0.5630 (3) | 0.0276 (8) |
| H10 | 0.497191 | 0.187345 | 0.594226 | 0.033* |
| C11 | 0.4570 (2) | 0.2956 (2) | 0.6564 (4) | 0.0328 (9) |
| H11 | 0.475015 | 0.291408 | 0.751618 | 0.039* |
| C12 | 0.4189 (2) | 0.3628 (2) | 0.6136 (4) | 0.0368 (10) |
| H12 | 0.411354 | 0.405279 | 0.678015 | 0.044* |
| C13 | 0.3914 (3) | 0.3683 (3) | 0.4749 (4) | 0.0434 (11) |
| H13 | 0.364186 | 0.414413 | 0.44459 | 0.052* |
| C14 | 0.4035 (2) | 0.3065 (2) | 0.3809 (4) | 0.0334 (9) |
| H14 | 0.384675 | 0.310668 | 0.286176 | 0.04* |
| P1 | 0.45974 (5) | 0.16121 (5) | 0.29354 (10) | 0.0218 (2) |
| S1 | 0.37049 (6) | 0.14747 (5) | 0.16383 (10) | 0.0319 (2) |
-
aOccupancy: 0.5.
Source of materials
All reagents are commercially available and were used without further purification. The title compound was prepared using mechanochemical methods under solvent-free conditions. Propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphane) [1.0435 g, 2.53 mmol] and elemental sulphur [0.1709 g, 5.33 mmol] were added to a reaction jar and ground for 90 min at a frequency of 25 Hz by rotary ball milling. Ethyl acetate (25 mL) was used to extract the product and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The title compound was obtained as a white residue. Yield 88% (1.0639 g, 2.23 mmol). Mp 104–109 °C. Crystals of the compound were obtained by slow evaporation, at ambient temperature, of a concentrated ethanolic solution over several days.
Experimental details
Intensity data were determined on a Bruker Venture D8 Photon CMOS diffractometer at 173 K using an Oxford Cryostream 600 cooler. Data reduction was carried out using the program Saint+, version 6.02 [1] and empirical absorption corrections were made using Sadabs [1]. The structure was solved in the WinGX [2] suite of programs, using intrinsic phasing through Shelxt [3] and refined using using Shelxl-2017 [3]. All hydrogen atoms were placed at idealized positions and refined as riding atoms with isotropic parameters 1.2 times those of their parent atoms. The SQUEEZE algorithm was used to circumvent the disordered solvent. The residual electron density calculations revealed 74e per unit cell which was assigned to two molecules of ethanol (74e per asymmetric unit; one ethanol molecule gives 26e). Diagrams and publication material were generated using Ortep-3 [2], and Platon [4].
Comment
Diphosphane chalcogenides have broad application as reagents in chalcone atom transfer reactions and nanocrystal synthesis [5], as ligands in transition metal catalysts [6] and also in organometallic and polymer chemistry [7]. The compound reported here is isostructural with the previously published selenide analogue but with an altered crystal system [8].
The title compound crystallizes in a tetragonal crystal system with space group I4 (no. 79). The molecule is symmetric (symmetry code: (i) −x + 1, −y, z) with the asymmetric unit comprising one-half of the molecule. The unit cell contains eight molecules of the title compound. The P–S bond distance was measured as 1.956 Å which is within the range of a P=S double bond as expected [8], [9], [10].
In this molecule the S–P–Calkyl angle was found to be 113.40° and the two S–P–Caryl bond angles as 112.55° and 112.80°. These bond angles are larger than the ideal angles for an sp3 hybridized phosphorus atom. The variation in bond angles is attributed to electronic factors effected by the P=S double bond. The bond angle defined by the aryl carbons in Caryl–P–Caryl was measured at 104.22° which is a slight contraction from the ideal angle of 109.5° for a regular tetrahedron, despite the two bulky aromatic rings. Similarly reduced bond angles were also found for the reported selenide analogue [8]. The aromatic C=C bond lengths in the phenyl rings range from 1.362 to 1.392 Å. The variation in π-bond lengths is attributed to the electronic effect of the phosphorus atom as has been found in the related P(C6H5)3 compound [11].
In the crystal, there is evidence of three intermolecular hydrogen bond interactions between C–H…S with distances of 2.802 Å, 2.908 Å and 2.925 Å. In addition, the structure also contains intermolecular T-shaped π interactions. These noncovalent interactions contribute to the formation of the molecular architecture.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: None declared.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Saint–Plus and Sadabs; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2004.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX suite for small-molecule single-crystal crystallography. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 837–838; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889899006020.Search in Google Scholar
4. Spek, A. L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
5. Bazargan, M., Mirzaei, M., Franconetti, A., Frontera, A. On the preferences of five-membered chelate rings in coordination chemistry: insights from the Cambridge Structural Database and theoretical calculations. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 5476–5490; https://doi.org/10.1039/c9dt00542k.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Chan, L., Hutchison, G. R., Morris, G. M. Understanding ring puckering in small molecules and cyclic peptides. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 743–755; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.0c01144.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
7. Al–Noaimi, M., Nafady, A., Warad, I., Alshwafy, R., Husein, A., Talib, W. H., Hadda, T. B. Heterotrimetallic Ru(II)/Pd(II)/Ru(II) complexes: synthesis, crystal structure, spectral characterization, DFT calculation and antimicrobial study. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2014, 122, 273–282; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.11.052.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Bratsos, I., Jedner, S., Gianferrara, T., Alessio, E. Ruthenium anticancer compounds: challenges and expectations. CHIMIA 2007, 61, 692–697; https://doi.org/10.2533/chimia.2007.692.Search in Google Scholar
9. Zhou, H., Huang, H. A Ruthenium catalyst with simple triphenylphosphane for the enantioselective hydrogenation of aromatic ketones. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2253–2257; https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201300080.Search in Google Scholar
10. Ghosh, A., Kumar, R. Efficient heterogeneous catalytic systems for enantioselective hydrogenation of prochiral carbonyl compounds. J. Catal. 2004, 228, 386–396; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2004.08.040.Search in Google Scholar
11. Dharmaraj, N., Viswanathamurthi, P., Natarajan, K. Ruthenium(II) complexes containing bidentate Schiff bases and their antifungal activity. Transition Met. Chem. 2001, 26, 105–109; https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007132408648.10.1023/A:1007132408648Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7

