Abstract
C20H17N4I, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 7.304(3) Å, b = 14.830(7) Å, c = 16.482(7) Å, β = 98.202(12)°, V = 1767.2(14) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0568, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1359, T = 150 K.
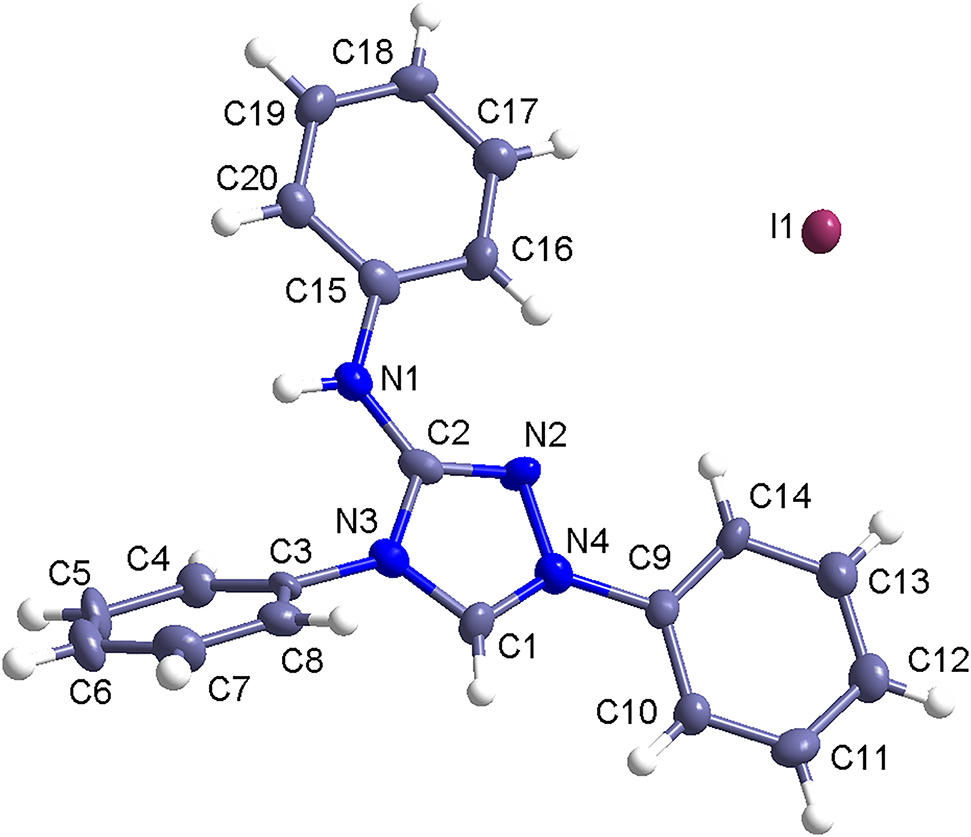
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Block, colourless |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.82 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Apex-II, φ and ω-scans |
| θ max, completeness: | 27°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 11,053, 3769, 0.113 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2σ(I obs), 2141 |
| N(param)refined: | 227 |
| Programs: | Bruker programs [1], SHELX [2], DIAMOND [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| x | y | z | U iso*/U eq | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 0.56872 (8) | 0.12954 (3) | 0.75290 (3) | 0.0299 (2) |
| N2 | 0.1730 (9) | 0.0904 (4) | 0.4935 (3) | 0.0250 (15) |
| C9 | 0.0807 (10) | 0.2444 (5) | 0.5183 (4) | 0.0232 (17) |
| C15 | 0.3227 (11) | −0.0959 (5) | 0.4937 (4) | 0.0293 (19) |
| C17 | 0.4414 (11) | −0.1190 (5) | 0.6349 (4) | 0.0312 (19) |
| H17 | 0.4647 | −0.0966 | 0.6894 | 0.037* |
| N1 | 0.2326 (8) | −0.0457 (4) | 0.4259 (3) | 0.0281 (16) |
| H1N | 0.2179 | −0.0724 | 0.3777 | 0.034* |
| C16 | 0.3557 (11) | −0.0633 (5) | 0.5737 (4) | 0.032 (2) |
| H16 | 0.3199 | −0.0038 | 0.5860 | 0.038* |
| N3 | 0.0885 (8) | 0.0840 (4) | 0.3591 (3) | 0.0241 (15) |
| N4 | 0.0970 (9) | 0.1712 (4) | 0.4628 (3) | 0.0273 (16) |
| C10 | −0.0140 (11) | 0.3222 (5) | 0.4889 (4) | 0.0280 (19) |
| H10 | −0.0659 | 0.3270 | 0.4329 | 0.034* |
| C7 | 0.0638 (12) | 0.0703 (6) | 0.1337 (5) | 0.040 (2) |
| H7 | 0.1034 | 0.1031 | 0.0898 | 0.048* |
| C4 | −0.0590 (11) | −0.0232 (5) | 0.2600 (4) | 0.0293 (19) |
| H4 | −0.1027 | −0.0546 | 0.3037 | 0.035* |
| C12 | 0.0420 (11) | 0.3832 (6) | 0.6263 (4) | 0.033 (2) |
| H12 | 0.0255 | 0.4300 | 0.6639 | 0.040* |
| C3 | 0.0477 (10) | 0.0514 (5) | 0.2759 (4) | 0.0216 (17) |
| C18 | 0.4942 (11) | −0.2060 (5) | 0.6197 (4) | 0.0298 (19) |
| H18 | 0.5487 | −0.2438 | 0.6631 | 0.036* |
| C5 | −0.1044 (12) | −0.0539 (6) | 0.1801 (4) | 0.037 (2) |
| H5 | −0.1791 | −0.1061 | 0.1690 | 0.045* |
| C8 | 0.1115 (11) | 0.1017 (5) | 0.2139 (4) | 0.0301 (19) |
| H8 | 0.1838 | 0.1546 | 0.2256 | 0.036* |
| C13 | 0.1367 (12) | 0.3065 (6) | 0.6523 (5) | 0.040 (2) |
| H13 | 0.1880 | 0.3009 | 0.7084 | 0.048* |
| C2 | 0.1674 (11) | 0.0397 (5) | 0.4289 (4) | 0.0249 (18) |
| C1 | 0.0486 (11) | 0.1678 (5) | 0.3832 (4) | 0.0268 (19) |
| H1C | −0.0045 | 0.2153 | 0.3489 | 0.032* |
| C11 | −0.0307 (11) | 0.3916 (5) | 0.5427 (5) | 0.034 (2) |
| H11 | −0.0917 | 0.4457 | 0.5233 | 0.041* |
| C14 | 0.1597 (11) | 0.2362 (5) | 0.5983 (4) | 0.0275 (19) |
| H14 | 0.2286 | 0.1840 | 0.6168 | 0.033* |
| C19 | 0.4658 (11) | −0.2368 (5) | 0.5398 (4) | 0.032 (2) |
| H19 | 0.5086 | −0.2951 | 0.5278 | 0.038* |
| C6 | −0.0402 (12) | −0.0077 (6) | 0.1166 (4) | 0.036 (2) |
| H6 | −0.0671 | −0.0292 | 0.0619 | 0.043* |
| C20 | 0.3755 (11) | −0.1839 (5) | 0.4765 (4) | 0.0274 (19) |
| H20 | 0.3500 | −0.2072 | 0.4223 | 0.033* |
Source of materials
Nitron (0.5 g, 1.60 mmol) in THF (15 mL) was placed in a Schlenk flask, to which a solution of HI (57% w/w, 0.36 g, 1.60 mmol) in THF (5 mL) was added dropwise. The mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 10 min and the white solid formed was collected on a frit and dried under vacuum. Crystals suitable for the structural determination was obtained from slow evaporation of a methanol solution containing the compound.
Experimental details
All H atoms were fixed at calculated positions and then riding refinements were performed. Their U iso values were set to 1.2U eq of the parent atoms.
Comment
Nitron is a commercial name to 1,4-diphenyl-3-(phenylamino)-1H-1,2,4-triazolium inner salt, which has been extensively used in diverse fields for decades [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]. Recently, nitron has been shown to be a reliable N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) precursor for obtaining a wide range of transition-metal NHC complexes [9], [10], [11]. In the course of our investigation on metal NHC complexes, we had obtained its hydroiodide salt as a by-product. Crystal structures for nitron and its non-stoichiometric hydrochloride salt have been published [12]. But the structure of its stoichiometric hydroiodide salt has not yet been described.
The title compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/n. Among the four C–N bond distances in the triazolium ring, the C2–N2 distance of 1.300(9) Å is the shortest, whereas the longest one is the C2–N3 distance of 1.377(9) Å. The two C–N distances flanking the C1 carbon are 1.349(9) and 1.311(8) Å, respectively. The N–N distance is 1.386(8) Å. The least squares plane of the phenyl ring at the four-position was twisted from that of the triazolium ring with an inter-planar angle of 42.9(3)°. The other two phenyl rings are, however, almost co-planar with the heterocyclic ring. The planarity of these rings allows intermolecular π–π stacking interactions to occur. The iodide ions are involved in short contacts of the types N–H⋯I and C–H⋯I with the organic cations, linking them into one-dimensional zigzag chains along the b-axis. The structure is further stabilized by π–π stacking interactions between these chains.
Funding source: National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan
Award Identifier / Grant number: 111-2113-M-018-002
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: The authors thank the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan for the financial support of this work (111-2113-M-018-002).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SMART APEX-II CCD; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, WI, USA, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.0; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Azeredo, J., Oliveira, R. A new method for precipitating bacterial exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol. Tech. 1996, 10, 341–344; https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00173251.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Yang, H.-H., Cheng, S.-K., Hsieh, L.-T. Characterization of nitrate particulate dry deposition by vacuum-deposited thin film reaction method. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1785–1793; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.12.031.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Yang, H.-H., Hsieh, L.-T., Cheng, S.-K. Determination of atmospheric nitrate particulate size distribution and dry deposition velocity for three distinct areas. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1447–1453; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.067.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Hassan, S. S. M., Eldin, A. G., Amr, A. E. E., Al-Omar, M. A., Kamel, A. H., Khalifa, N. M. Improved solid-contact nitrate ion selective electrodes based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) as an ion-to-electron transducer. Sensors 2019, 19, 3891; https://doi.org/10.3390/s19183891.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
8. Amit, E., Berg, I., Gross, E. Self-assembled monolayers of nitron: self-activated and chemically addressable N-heterocyclic carbene monolayers with triazolone structural motif. Chem. Eur J. 2020, 26, 13046–13052; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202001595.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Färber, C., Leibold, M., Bruhn, C., Maurer, M., Siemeling, U. Nitron: a stable N-heterocyclic carbene that has been commercially available for more than a century. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 227–229; https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc16460k.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
10. Quinlivan, P. J., Loo, A., Shlian, D. G., Martinez, J., Parkin, G. N-Heterocyclic carbene complexes of nickel, palladium, and iridium derived from nitron: synthesis, structures, and catalytic properties. Organometallics 2021, 40, 166–183; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00679.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Sevim, M., Kavukcu, S. B., Kinal, A., Şahin, O., Türkmen, H. C–C coupling formation using nitron complexes. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 16903–16915; https://doi.org/10.1039/d0dt02937h.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Cannon, J. R., Raston, C. L., White, A. H. Crystal structures of nitron and its non-stoichiometric hydrochloride. Aust. J. Chem. 1980, 33, 2237–2247; https://doi.org/10.1071/ch9802237.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of undecacalcium decaarsenide, Ca11As10
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diiodido-(μ2-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-((pyridin-4- ylmethylene)amino)-1,2-dihydro-3H -pyrazol-3-one-κ2 N: O)zinc(II)], C17H16I2N4OZn
- The crystal structure of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)porphyrin-21,23-diido-κ4 N 4-naphthalocyanido-κ4 N 4-neodymium(IV) - chloroform (1/6) C114H90N12Cl18Nd
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2-chlorobenzyl)urea, C14H12BrClN2O
- Crystal structure of bis[benzyl(methyl)carbamodithioato-κ 2 S,S′]-di-n-butyltin(IV), C26H38N2S4Sn
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate – methanol (1/2), C25H32N2O4S⋅2CH3OH
- Synthesis and crystal structure of {(N′,N″-(((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2,1-phenylene))-bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2-hydroxybenzohydrazonato)-κ6 N 2 O 4}copper(II), C30H24CuN4O6
- The crystal structure of ((E)-2,4-dibromo-6-(((5-(nitro)-2-oxidophenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ 3 N,O,O′)tris(pyridine-κN)manganese(II), C28H21Br2MnN5O4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-((3R,10S,13R,17S)-10,13-dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta-[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethan-1-one, C28H41NO
- The crystal structure of 3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide(1/1), C13H10N4O7
- Crystal structure of poly[tetrakis(μ3-2-aminonicotinato-κ3N,O,O′)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O,O′:O″,O′″)-(μ4-oxalato-κ6 N:N′:O,O′:O″,O′″)dicopper(I)-disamarium(III)], [SmCu(C6N2H5O2)2(C2O4)] n
- The crystal structure of 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzoic- acid—pyrazine-2-carboxamide—water (1/1/1), C12H13N3O7
- Crystal structure of N-ethyl-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]piperazine-1-carbothioamide, C14H18F3N3S
- The crystal structure of 3-anilino-1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ium iodide, C20H17N4I
- The crystal structure of (tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine)-benzoato-copper(II) perchlorate monohydrate, CuC31H28N7O7Cl
- Crystal structure of [2-hydroxy-3-methyl-benzoato-k1 O-triphenyltin(IV)], C26H22O3Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(4-(hydroxymethyl)-benzoato-k1 O)zinc(II), C16H18O8Zn
- The crystal structure of dicarbonyl-(N-nitroso-N-oxido-phenylamine-κ 2 O,O)-rhodium(I), C8H5N2O4Rh
- The crystal structure of oxalic acid – 2-ethoxybenzamide (2/1), C20H24N2O8
- The crystal structure of ethyl 7-ethyl-5-methyl-4,7-dihydrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxylate, C10H15N5O2
- Crystal structure of poly[(N,N-dimethylacetamide-κO) (μ4-2-nitroisophthalato-κ 4 O:O′:O″:O′″)manganese(II)], C11H10N2O7Mn
- Crystal structure of 14-O-acetyldelcosine, C26H41NO8
- The crystal structure of poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-(μ 4-2-chlorobenzene-1,3-dicarboxylato-κ5 O:O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H13CdClN2O5
- Crystal structure of propane-1,3-diylbis(diphenylphosphine sulfide) ethanol solvate, C27H26P2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{[(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazinocarbonylmethyl]-trimethylammonium} tetrabromozincate, C32H54N8O4ZnBr4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of dimethyl 2,2′-(2,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-3,4-diyl)dibenzoate, C34H30O7
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-oxo-2-phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H12O3
- The crystal structure of tetra(imidazole-κ1 N)zinc(II) μ2-oxido-hexaoxido-divanadium(VI) C12H16N8O6V2Zn
- Crystal structure of S-2-(1-(5-methylpyridin-2-ylamino)octyl)-3-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, C24H28N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxido-2-oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-oktakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) – methanol – pyridine (1/1/1) C76H65N13Cl2Ni3O9
- The crystal structure of methyl 3,5-diaminobenzoate, C8H10N2O2
- Crystal structure of 10-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-5H-dibenzo[a,d][7]annelen-5-one, C27H17NO
- Crystal structure of ethyl 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylate, C16H20N2O5
- The crystal structure of 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-cycloheptylurea, C14H19BrN2O
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis(1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-yl)-3,6-bis ((4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)methylene)-1,4-dialuminacyclohexane – benzene (1/2), C50H72Al2B2O4
- Crystal structure of bis(μ 3-diphenylphosphinato)-tetrakis(μ 2-diphenylphosphinato)-bis(diphenylphosphinato)-bis(μ 2-hydroxo)dicopper(II)-ditin(IV), C104H100O18P8Cu2Sn2
- Crystal structure of 3-((3,4-dichloroisothiazol-5-yl)methoxy)benzo[d] isothiazole 1,1-dioxide, C11H6Cl2N2O3S2
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-(2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, C17H11FO3
- The crystal structure of tris(carbonyl)-bis(carbonyl)-[μ-propane-1,2- dithiolato]-(benzyldiphenylphosphine)diiron (Fe—Fe), C27H23Fe2O5PS2
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-chlorophenethyl)-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium nitrate, C16H23N4O4Cl
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-disulfanediyldi(1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-amine) monohydrate, C4H8N8OS2
- The crystal structure of trans-[bis(4-methylpyridine-κN)bis(quinoline-2-carboxylato- κ 2 N,O)cadmium(II)], C32H26CdN4O4
- The crystal structure of ethyl 2′-hydroxy-4′,6′-dimethoxy-3-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboxylate, C28H28O7

