Abstract
C6H2Br2N2Se, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 7.7277(4) Å, b = 19.6360(6) Å, c = 10.8656(5) Å, β = 102.124(4)°, V = 1611.98(12) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0482, wR ref (F2) = 0.1175, T = 290 K.
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the Figure 1. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
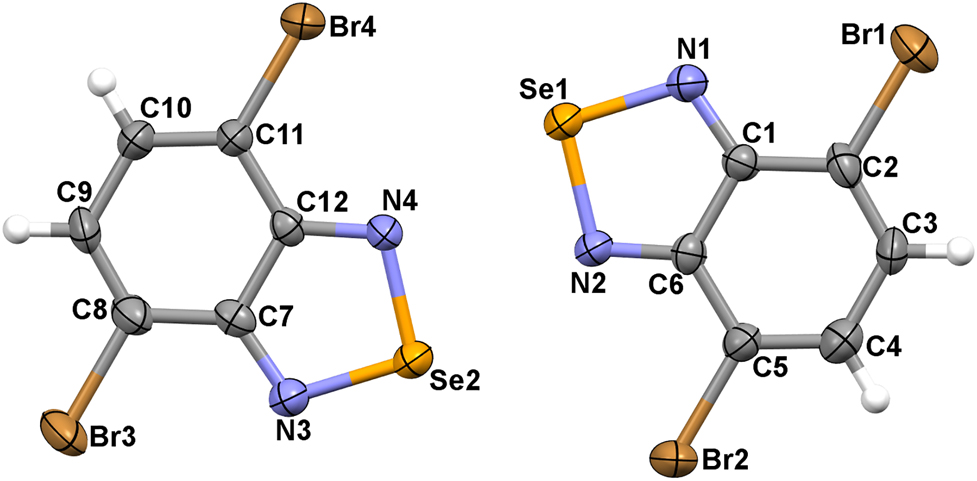
Molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids draw at the 50% probability level.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Brown block |
| Size: | 0.32 × 0.28 × 0.17 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 14.5 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 18,469, 3636, 0.075 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2375 |
| N(param)refined: | 199 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br1 | 0.51340 (11) | 0.82695 (4) | 0.67016 (8) | 0.0569 (2) |
| Br2 | 0.56356 (10) | 0.50297 (4) | 0.82913 (7) | 0.0510 (2) |
| Se1 | 0.25275 (9) | 0.61923 (3) | 0.44783 (6) | 0.0386 (2) |
| N1 | 0.3403 (7) | 0.6984 (3) | 0.5138 (5) | 0.0380 (13) |
| N2 | 0.3542 (6) | 0.5706 (3) | 0.5841 (5) | 0.0330 (12) |
| C1 | 0.4348 (8) | 0.6850 (3) | 0.6276 (6) | 0.0301 (14) |
| C2 | 0.5266 (8) | 0.7341 (3) | 0.7143 (6) | 0.0377 (16) |
| C3 | 0.6242 (8) | 0.7143 (3) | 0.8267 (6) | 0.0418 (17) |
| H3 | 0.6848 | 0.7469 | 0.8815 | 0.050* |
| C4 | 0.6360 (9) | 0.6440 (4) | 0.8628 (6) | 0.0437 (17) |
| H4 | 0.7041 | 0.6315 | 0.9406 | 0.052* |
| C5 | 0.5482 (8) | 0.5952 (3) | 0.7843 (6) | 0.0338 (15) |
| C6 | 0.4431 (8) | 0.6140 (3) | 0.6654 (5) | 0.0299 (14) |
| Br3 | −0.01261 (10) | 0.22100 (4) | 0.31893 (8) | 0.0592 (3) |
| Br4 | −0.06430 (10) | 0.54466 (4) | 0.15761 (7) | 0.0482 (2) |
| Se2 | 0.25383 (8) | 0.42750 (4) | 0.53765 (6) | 0.0379 (2) |
| N3 | 0.1699 (7) | 0.3480 (3) | 0.4694 (5) | 0.0367 (13) |
| N4 | 0.1468 (6) | 0.4774 (2) | 0.4045 (5) | 0.0340 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0702 (8) | 0.3615 (3) | 0.3575 (6) | 0.0306 (14) |
| C8 | −0.0253 (8) | 0.3134 (3) | 0.2715 (6) | 0.0399 (16) |
| C9 | −0.1235 (9) | 0.3331 (3) | 0.1608 (6) | 0.0410 (17) |
| H9 | −0.1855 | 0.3008 | 0.1063 | 0.049* |
| C10 | −0.1345 (8) | 0.4035 (3) | 0.1250 (6) | 0.0377 (16) |
| H10 | −0.2027 | 0.4159 | 0.0471 | 0.045* |
| C11 | −0.0476 (8) | 0.4523 (3) | 0.2019 (6) | 0.0322 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0582 (7) | 0.4333 (3) | 0.3212 (5) | 0.0269 (13) |
Source of material
The 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole was purchased from Alfa Chemical Co. Ltd. (Zhengzhou, China) and used without further purification. The 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole (3.41 mg, 0.01 mmol) was dissolved in approximately 10 mL of methanol with gentle stirring at room temperature. Then, the solution was set aside for crystallization by slow evaporation of the solvent at room temperature conditions. After about two days, brown block crystals of title compound suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction were obtained.
Experimental details
The structure was solved with the SHELXT [3] program using Intrinsic Phasing and refined with the SHELXL [4] refinement package. H atoms were placed in calculated positions and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2Ueq(C).
Comment
The term chalcogen bond was coined in 2009 [5]. Ten years later, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) issued a formal definition of the chalcogen bond [6]. In the crystals involving 2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole or its derivatives, the four-membered [Se–N]2 cyclic double chalcogen bonds were always formed [7]. Besides the cyclic double chalcogen bonds, the other types of chalcogen bonds can also be formed between the 2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole or its derivatives and their coformers [8]. In this work, we studied the non-covalent interactions in the crystal of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole. The focus of attention is: what kind of chalcogen bond can be formed in the title crystal.
All bond lengths and angles in the title crystal structure are in the normal ranges. The 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole molecules form 2D corrugated sheets which further self-assemble into a 3D layered structure. There are five types of non-covalent interactions in the crystal structure: the four-membered [Se–N]2 cyclic double chalcogen bonds, N–Se⃛Br chalcogen bonds, C–H⃛N hydrogen bonds, π⃛π stacking interactions and σ-hole(Br)⃛σ-hole(Br) stacking interactions [9, 10]; among them, the four-membered [Se–N]2 cyclic double chalcogen bonds and π⃛π stacking interactions are much stronger. According to the dispersion-corrected density functional theory calculations at the PBE0-D3/def2-TZVPP level of theory [11, 12], the binding energy of the four-membered [Se–N]2 cyclic double chalcogen bonds between two 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole molecules is 10.27 kcal/mol, and the binding energy of the π⃛π stacking interactions between two 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole molecules is 8.55 kcal/mol. The details and reliability of the PBE0-D3/def2-TZVPP calculations for the study of the non-covalent interactions can be found elsewhere [13], [14], [15]. Evidently, the larger binding energy of the four-membered [Se–N]2 cyclic double chalcogen bonds between two 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole molecules explains why the four-membered [Se–N]2 cyclic double chalcogen bonds were always found in the crystals involving 2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole or its derivatives.
In conclusion, there are two types of chalcogen bonds in the crystal of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole. One type is of the much stronger four-membered [Se–N]2 cyclic double chalcogen bonds, and the other is of the much weaker N–Se⃛Br chalcogen bonds.
Funding source: National Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21773104
Funding source: Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 13HASTIT015
Acknowledgment
Computer time was provided by the National Supercomputing Center in Shenzhen.
-
Author contributions: The author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21773104) and the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (Grant No. 13HASTIT015).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The author declares no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku. CrysAlisPro; Rigaku Inc: Tokyo, Japan, 2015.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Wang, W., Ji, B., Zhang, Y. Chalcogen bond: a sister noncovalent bond to halogen bond. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 8132–8135; https://doi.org/10.1021/jp904128b.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Aakeroy, C. B., Bryce, D. L., Desiraju, G. R., Frontera, A., Legon, A. C., Nicotra, F., Rissanen, K., Scheiner, S., Terraneo, G., Metrangolo, P., Resnati, G. Definition of the chalcogen bond. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 1889–1892; https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2018-0713.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Eichstaedt, K., Wasilewska, A., Wicher, B., Gdaniec, M., Połoński, T. Supramolecular synthesis based on a combination of Se…N secondary bonding interactions with hydrogen and halogen bonds. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1282–1293; https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01356.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Miao, S., Zhang, Y., Shan, L., Xu, M., Wang, J. G., Zhang, Y., Wang, W. A robust supramolecular heterosynthon assembled by a hydrogen bond and a chalcogen bond. Crystals 2021, 11, 1309; https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11111309.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Zhang, Y., Wang, W. The σ-hole…σ-hole stacking interaction: an unrecognized type of noncovalent interaction. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 214302; https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0033470.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Zhang, Y., Wang, W. The face-to-face σ-hole…σ-hole stacking interactions: structures, energies, and nature. Crystals 2021, 11, 877; https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080877.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Adamo, C., Barone, V. Toward reliable density functional methods without adjustable parameters: the PBE0 model. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 6158–6169; https://doi.org/10.1063/1.478522.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Grimme, S., Antony, J., Ehrlich, S., Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104; https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3382344.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Wang, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. B. Noncovalent π…π interaction between graphene and aromatic molecule: structure, energy, and nature. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 094302; https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4867071.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Wang, W., Sun, T., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. B. The benzene…naphthalene complex: a more challenging system than the benzene dimer for newly developed computational methods. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 114312; https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4931121.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Wang, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. B. Highly accurate benchmark calculations of the interaction energies in the complexes C6H6…C6X6 (X = F, Cl, Br, and I). Int. J. Quant. Chem. 2017, 117, e25345; https://doi.org/10.1002/qua.25345.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Weizhou Wang, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

