Abstract
C10H17F6N4OPS2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 13.0455(12) Å, b = 12.6114(12) Å, c = 10.7642(10) Å, β = 99.546(8)°, V = 1746.4(3) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0425, wRref(F2) = 0.1173, T = 150 K.
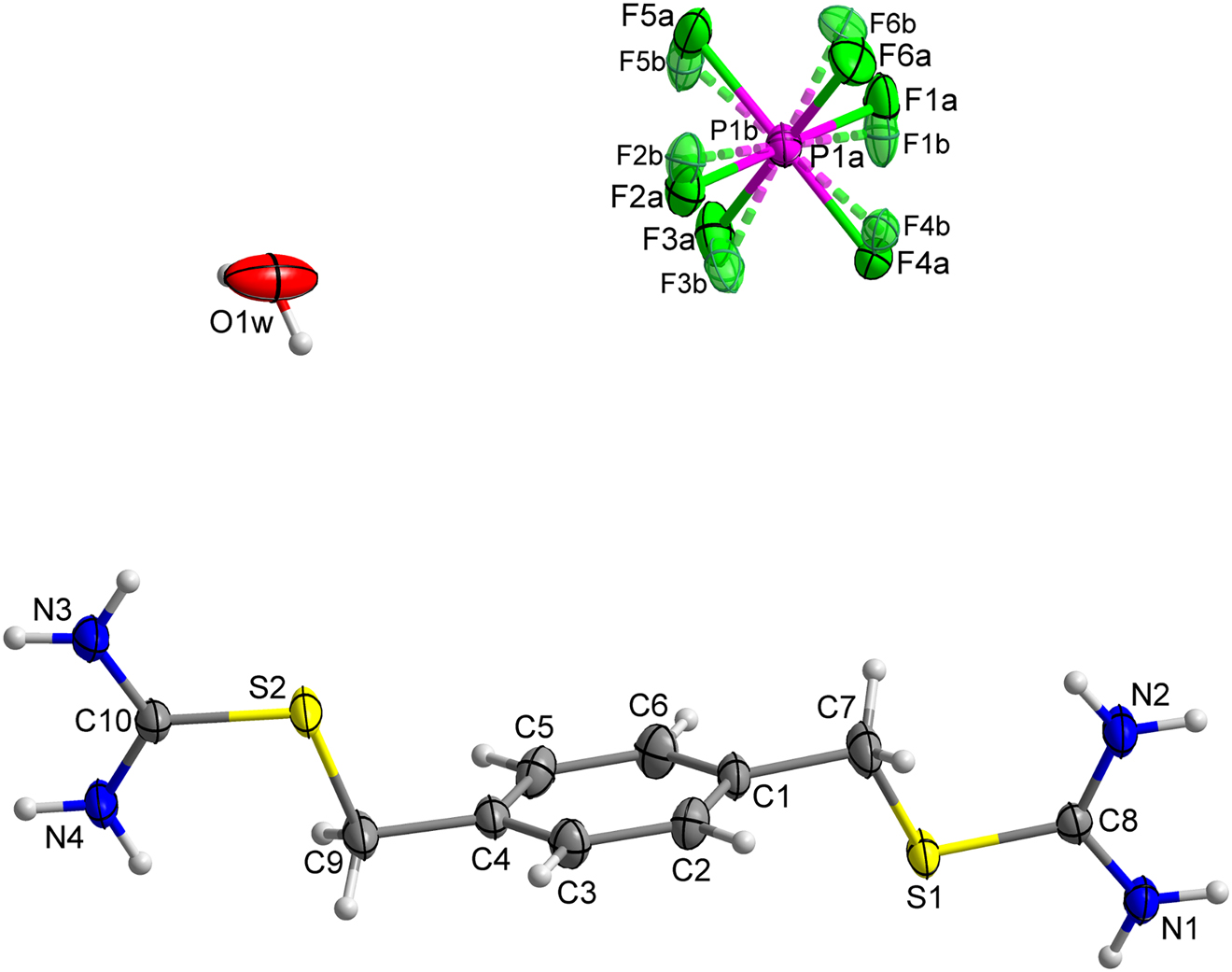
The asymmetric unit of the title structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless prism |
| Size 0.41 × 0.37 × 0.25 mm | |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.5418 Å) |
| μ: | 4.29 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Xcalibur, ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 77.8°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 15,711, 3652, 0.042 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3093 |
| N(param)refined: | 261 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SUPERFLIP [2], JANA2006 [3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.41813 (4) | 0.12832 (4) | 1.02025 (5) | 0.02515 (15) |
| S2 | 0.12109 (4) | 0.41067 (5) | 0.43485 (5) | 0.03245 (17) |
| O1w | 0.3599 (2) | 0.91493 (19) | 0.2163 (3) | 0.0612 (9) |
| N1 | 0.52470 (14) | 0.05921 (15) | 1.22986 (16) | 0.0252 (5) |
| N2 | 0.61464 (15) | 0.17645 (17) | 1.12547 (18) | 0.0308 (5) |
| N3 | 0.03372 (15) | 0.46666 (18) | 0.20929 (18) | 0.0318 (5) |
| N4 | −0.06054 (15) | 0.34561 (19) | 0.30126 (18) | 0.0322 (5) |
| C1 | 0.34751 (16) | 0.25763 (17) | 0.82646 (18) | 0.0241 (5) |
| C2 | 0.28882 (17) | 0.34897 (18) | 0.83177 (19) | 0.0270 (6) |
| C3 | 0.20163 (17) | 0.36718 (17) | 0.7409 (2) | 0.0272 (6) |
| C4 | 0.17224 (15) | 0.29423 (17) | 0.64494 (18) | 0.0243 (5) |
| C5 | 0.22993 (18) | 0.20180 (18) | 0.64130 (19) | 0.0280 (6) |
| C6 | 0.31726 (18) | 0.18424 (18) | 0.7315 (2) | 0.0294 (6) |
| C7 | 0.44451 (18) | 0.2392 (2) | 0.9218 (2) | 0.0338 (6) |
| C8 | 0.53010 (15) | 0.12252 (15) | 1.13325 (18) | 0.0209 (5) |
| C9 | 0.07977 (17) | 0.3147 (2) | 0.5435 (2) | 0.0328 (6) |
| C10 | 0.02186 (16) | 0.40545 (18) | 0.30522 (19) | 0.0256 (6) |
| H1c2 | 0.308437 | 0.399485 | 0.898172 | 0.0324* |
| H1c3 | 0.161524 | 0.4306 | 0.744467 | 0.0327* |
| H1c5 | 0.209275 | 0.150221 | 0.576376 | 0.0335* |
| H1c6 | 0.357174 | 0.120661 | 0.728167 | 0.0353* |
| H1c7 | 0.459561 | 0.301362 | 0.973066 | 0.0406* |
| H2c7 | 0.501045 | 0.22124 | 0.878919 | 0.0406* |
| H1c9 | 0.024192 | 0.344322 | 0.580718 | 0.0393* |
| H2c9 | 0.059543 | 0.249931 | 0.499397 | 0.0393* |
| H1n1a | 0.5762 (17) | 0.057 (3) | 1.291 (2) | 0.0303* |
| H2n1b | 0.471 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 1.231 (4) | 0.0303* |
| H1n2c | 0.6680 (16) | 0.170 (3) | 1.184 (2) | 0.0369* |
| H2n2d | 0.617 (3) | 0.218 (2) | 1.063 (2) | 0.0369* |
| H1n3a | −0.012 (2) | 0.462 (3) | 0.1418 (19) | 0.0381* |
| H2n3e | 0.0919 (17) | 0.499 (3) | 0.212 (4) | 0.0381* |
| H1n4 | −0.1101 (18) | 0.346 (3) | 0.238 (2) | 0.0386* |
| H2n4f | −0.073 (3) | 0.314 (3) | 0.367 (2) | 0.0386* |
| H1o1w | 0.337 (4) | 0.865 (3) | 0.170 (4) | 0.0734* |
| H2o1w | 0.337 (4) | 0.909 (4) | 0.282 (2) | 0.0734* |
| P1ag | 0.77735 (9) | 0.12491 (10) | 0.46082 (11) | 0.02217 (15) |
| F1ag | 0.8655 (2) | 0.0294 (2) | 0.5059 (2) | 0.0357 (5) |
| F2ag | 0.6866 (2) | 0.21992 (19) | 0.4160 (2) | 0.0285 (5) |
| F3ag | 0.6816 (2) | 0.0345 (3) | 0.4402 (3) | 0.0358 (6) |
| F4ag | 0.7611 (2) | 0.1415 (3) | 0.61192 (17) | 0.0281 (5) |
| F5ag | 0.7919 (2) | 0.1098 (3) | 0.30920 (17) | 0.0403 (7) |
| F6ag | 0.8708 (2) | 0.2162 (2) | 0.4827 (3) | 0.0410 (6) |
| P1bh | 0.7778 (6) | 0.1269 (7) | 0.4604 (8) | 0.02217 (15) |
| F1bh | 0.8479 (12) | 0.0218 (13) | 0.5213 (15) | 0.0357 (5) |
| F2bh | 0.7052 (12) | 0.2323 (13) | 0.4001 (16) | 0.0285 (5) |
| F3bh | 0.6671 (12) | 0.0628 (13) | 0.4723 (16) | 0.0358 (6) |
| F4bh | 0.7817 (11) | 0.1768 (15) | 0.6066 (9) | 0.0281 (5) |
| F5bh | 0.7724 (11) | 0.0789 (15) | 0.3135 (9) | 0.0403 (7) |
| F6bh | 0.8866 (12) | 0.1927 (13) | 0.4498 (15) | 0.0410 (7) |
-
aOccupancy: 0.90(6), bOccupancy: 0.73(6), cOccupancy: 0.96(6), dOccupancy: 0.87(6), eOccupancy: 0.81(6), fOccupancy: 0.82(15), gOccupancy: 0.883(10), hOccupancy: 0.117(10).
Source of material
The solution of thiourea (0.63 g, 8.33 mmol) in ethanol (50 mL) was heated to reflux. To this solution 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)benzene (1.00 g, 3.78 mmol) was added. The heating continued for 50 min, then the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature. The resulting crystals were filtered off, washed with hexane and dried under reduced pressure resulting in yield of 1.34 g (85%) of 2,2′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))diisothiouronium bromide. The reaction product was dissolved in water and mixed with water solution containing an equimolar amount of silver hexafluorophosphate; the resulting AgBr was filtered off. The filtrate was allowed to slowly evaporate, forming crystals of the title compound.
Experimental details
H atoms bonded to C were placed in calculated positions. H bonded to N and O were refined with restrained bond lengths (N—H = 0.86 Å, O—H = 0.82 Å). Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N,O). The H bonded to N of S-alkylthiourea and isothiouronium groups are disordered with only H1n4 fully localized occupancies of remaining hydrogen atoms were refined with a sum constrained to 6 to keep the electroneutrality of crystal structure. The hexafluorophosphate anion was found to be disordered over two positions. Molecular refinement without any restraints was used to model the disorder (see Table 2).
Comment
Thiourea derivatives are used in anion complexation for their ability to form hydrogen bonds in a specific prearranged manner [5]. Recently their cytostatic potential was studied with promising results [6].
The crystal structure of the title compound is depicted in the figure. The asymmetric unit consists of one 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium cation, one hexafluorophosphate anion and one molecule of water. Significant differences were observed between the C—S bond lengths with C(meth)—S bond at 1.821(3) and 1.825(3) Å and C(iso)—S bond at 1.7405(19) and 1.740(2) Å. This difference is caused by electron delocalization within the isothiouronium groups. However, the delocalization is not complete, since very small differences between C—N bond lengths remain with the C—N(s-cis) bonds at 1.310(3) and 1.308(3) Å and C—N(s-trans) at 1.322(3) and 1.319(3) Å.
The crystal structure packing is controlled by hydrogen bonds, with isothiouronium groups forming seven N—H
Funding source: Czech Science Foundation
Award Identifier / Grant number: 20–14770Y
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This research was supported by the project 20–14770Y of the Czech Science Foundation and The University of Chemistry and Technology, Prague.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku, O. D. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2020.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Palatinus, L., Chapuis, G. SUPERFLIP – a computer program for the solution of crystal structures by charge flipping in arbitrary dimensions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 786–790; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807029238.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Petricek, V., Dusek, M., Palatinus, L. Crystallographic computing system JANA2006: general features. Z. Kristallogr. – Cryst. Mater. 2014, 229, 345–352.10.1515/zkri-2014-1737Suche in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. Diamond; Crystal Impact GbR: Bonn, Germany, 1999.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Leung, A. N., Degenhardt, D. A., Bühlmann, P. Effect of spacer geometry on oxoanion binding by bis- and tetrakis-thiourea hosts. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 2530–2536; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2008.01.026.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Desai, D., Madhunapantula, S. V., Gowdahalli, K., Sharma, A., Chandagaludoreswamy, R., El–Bayoumy, K., Robertson, G. P., Amin, S. Synthesis and characterization of a novel iNOS/Akt inhibitor Se,Se′-1,4-phenylenebis(1,2-ethanediyl)bisisoselenourea (PBISe)—against colon cancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2038–2043; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.09.071.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Václav Eigner and Roman Holakovský, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3, 4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO3
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-methoxy-2-((2-methoxypyridin-3-yl)methylene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1 (2H)-one, C18H17NO3
- The crystal structure of N 6,N 6′-di(pyridin-2-yl)-[2,2′-bipyridine]-6,6′-diamine, C20H16N6
- The crystal structure of {N 1,N 2-bis[2,4-dimethyl-6-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)(phenyl)methyl]acenaphthylene-1,2-diimino-κ2 N, N′}-dibromido-nickel(II) – dichloromethane(1/2), C64H64Br2Cl4N2Ni
- Synthesis and crystal structure of nonacarbonyltris[(2-thia-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricylco[3.3.1.1]decane-κ1 P)-2,2-dioxide]triruthenium(0) – acetonitrile (7/6), C25.71H32.57N9.86O15P3S3Ru3
- A new polymorph of 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-benzimidazole (C13H9N3O2)
- The crystal structure of 2,2′-((1E,1′E)-(naphthalene-2,3 diylbis(azanylylidene)) bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methylphenol), C26H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-iodido)-bis(η6-benzene)-bis(iodido)-diosmium(II), C12H12I4Os2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN 3)borato}copper(II), C30H44B2CuN12
- Crystal structure of (E)-3-((4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)thio)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one, C15H20O2S
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(p-tolylazanediyl)bis(1-phenylethan-1-one), C23H21NO2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of the crystal sponge the poly[tetrakis(μ3-2,4,6-tris(pyridin-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine)-dodecaiodidohexazinc(II) nitrobenzene solvate], C72H48I12N24Zn6⋅10(C6H5NO2)
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C44H45N5O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-7-fluoro-2-(3-fluorobenzylidene)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C17H12F2O1
- Crystal structure of tetrabutylammonium sulfanilate – 1-(diaminomethylene)thiourea (1/2)
- Crystal structure of [2,2′-{azanediyl)bis[(propane-3,1-diyl)(azanylylidene)methylylidene]} bis(3,5-dichlorophenolato)-κ2O,O′]-isothiocyanato-κN-iron(III), C21H19Cl4FeN4O2S
- Crystal structure of (4-chlorophenyl)(4-hydroxyphenyl)methanone, C13H9ClO2
- Crystal structure of 6,6′-((pentane-1,3-diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromolphenolato-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)copper(II),) C19H16Br4CuN2O2
- Chlorido-(2,2′-(ethane-bis(5-methoxyphenolato))-κ4 N,N′,O,O′)manganese(III) monohydrate, C19H18Cl2CuN2O2
- Crystal structure of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(4-methoxybenzylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one, C22H28O2
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-(((2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diyl)bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2-chlorophenolato)-κ4N,N′,O,O′]copper(II)
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-((thiophen-2-ylmethyl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C30H20O4N2Cl2S2
- Crystal structure of bis{hydridotris(3-trifluoromethyl-5-methylpyrazolyl-1-yl)borato-κN 3}manganese(II), C30H26B2F18MnN12
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-(2-methylbenzo[b]thienyl)-3,3,4,4,5,5-hexafluorocyclopent-ene, C21H14F6S
- Crystal structure of 2-(3-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 4,5-diiodo-1,3-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-3-ium chloride – chloroform (1/1), C21H23Cl4I2N3
- Crystal structure of azido-k1 N-{6,6′-((((methylazanediyl)bis(propane-3,1-diyl))bis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(2,4-dibromophenolato)k5 N,N′,N″,O,O′}cobalt(III)-methanol (1/1)), C21H23Br4CoN6O3
- The crystal structure of 2-(4-((carbamimidoylthio)methyl)benzyl)isothiouronium hexafluorophosphate monohydrate, C10H17F6N4OPS2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C9H14F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of (4′E)-6′-(diethylamino)-2-[(E)-[(pyren-1-yl)methylidene]amino]-4′-{2-[(2E)-1,3,3-trimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ylidene]ethylidene}-1′,2,2′,3,3′,4′-hexahydrospiro[isoindole-1,9′-xanthene]-3-one, C54H48N4O2
- Crystal structure of poly[bis(μ2-2,6-bis(1-imidazoly)pyridine-κ2 N,N′)-bis(thiocyanato-κ1 N)copper(II)] dithiocyanate, C24H18CuN12S2
- Cones with a three-fold symmetry constructed from three hydrogen bonded theophyllinium cations that coat [FeCl4]− anions in the crystal structure of tris(theophyllinium) bis(tetrachloridoferrate(III)) chloride trihydrate, C21H33Cl9Fe2N12O9
- Crystal structure of 14-O-[(4-(4-hydroxypiperidine-1-yl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2-yl)thioacetyl]-mutilin monohydrate, C32H49N3O6S
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-chloro-2-(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazinyl)pyridine, C13H12ClN3
- The crystal structure of 4-phenyl-4-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinylidene]butanoic acid, C16H15N3O3
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium pentaiodide monohydrate C6H9I5N2O3
- Crystal structure of bis(μ3-oxido)-bis(μ2-2-formylbenzoato-k2O:O′)-bis(2-(dimethoxymethyl)-benzoato-κO)-oktakismethyl-tetratin(IV)
- Crystal structure of 2-((E)-(((E)-2-hydroxy-4-methylbenzylidene) hydrazineylidene)methyl)-4-methylphenol, C16H16N2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-((5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylene)hydrazinyl) methaniminium nitrate monohydrate, C14H26N10O10
- The crystal structure of N′-(2-chloro-6-hydroxybenzylidene)thiophene-2-carbohydrazide monohydrate, C12H11ClN2O3S
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1,1′-(biphenyl-4,4′-diyl)bis(1H-imidazol)-κ2N:N′)-bis(4-bromobenzoate-κ1O)zinc(II)], C64H44Br4N8O8Zn2
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1-(4-carboxybenzyl)pyridin-1-ium-4-carboxylato-κ1O)-(μ2-oxalato-κ4 O:O′:O″:O‴)dioxidouranium(VI)], C16H11NO10U
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-phenylfuran, C22H21BrO2
- Halogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,3′:5′,4″-terpyridine — 1,3-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1/1), C21H11F4I2N3
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethan-1-aminium 2-(4-acetylphenoxy)acetate, C20H22N2O4
- Chalcogen bonds in the crystal structure of 4,7-dibromo-2,1,3-benzoselenadiazole, C6H2Br2N2Se
- The crystal structure of 1,4-bis((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl)-piperazine-2,5-dione dihydrate, C20H22N6O4
- The crystal structure of C19H20O8
- The crystal structure of KNa3Te8O18·5H2O exhibiting a ∞2[Te4O9]2− layer
- Erratum
- Erratum to: Crystal structure of (Z)-3-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-1,3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one, C23H16BrNO

